Ilmu Tehnik Kelistrikan
Tempat belajar ilmu tekhnik listrik mulai dari dasar hingga listrik mahir
- INSTALASI LISTRIK
- PENGUKURAN LISTRIK
- SUMBER LISTRIK

Cara membaca TRIP UNIT CIRCUIT BREAKER
ELECTRICAL CLASSROOM
A complete Electrical Engineering portal
MCB Trip Curves – B, C, D, K, and Z trip curves
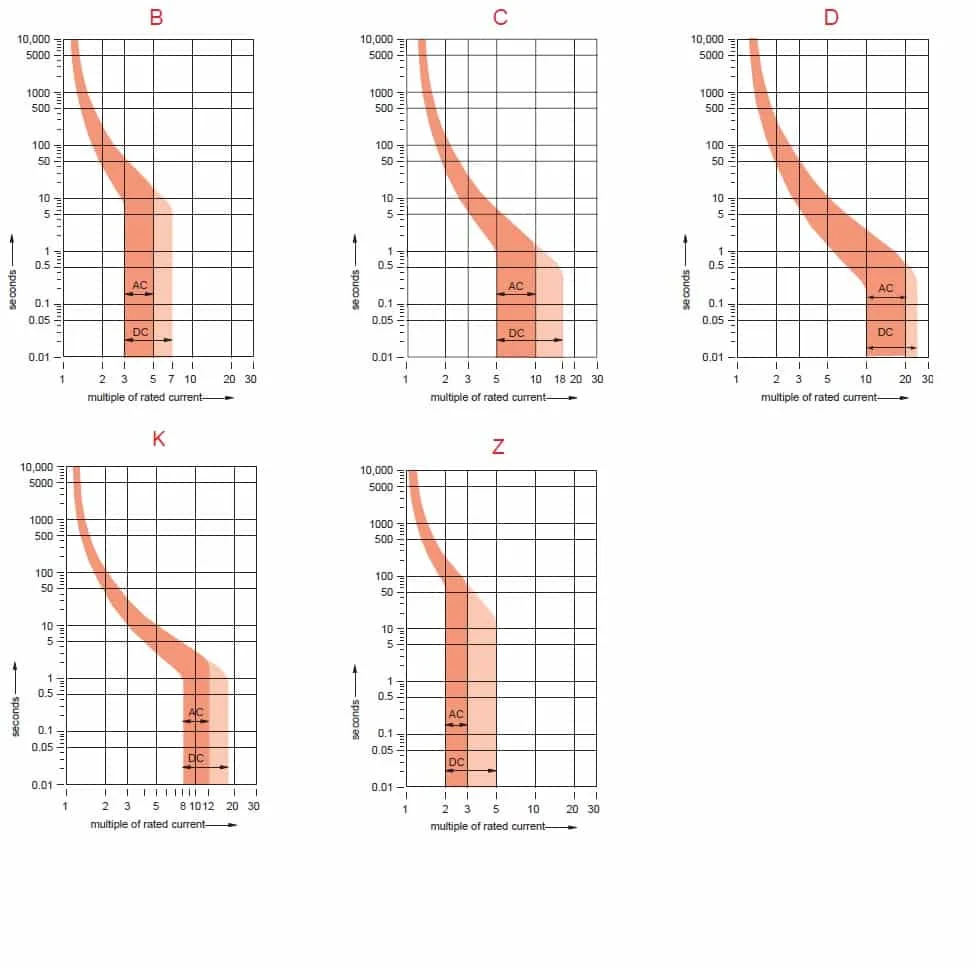
MCB (Miniature circuit breaker) is a re-settable device designed to protect a circuit from short circuits and overcurrents. The trip curve of an MCB (B, C, D, K, and Z curves) tells us about the trip current rating of Miniature Circuit breakers. The trip current rating is the minimum current at which the MCB will trip instantaneously. It is required that the trip current must persist for 0.1s.
Class B trip curve
Class c trip curve, class d trip curve, class k trip curve, class z trip curve, class a trip curve, importance of mcb trip curve types, trip curves for other circuit breakers.
The MCB trip curves, also known as I-t tripping characteristic consist of two sections viz, overload section and short circuit section. Overload section describes the trip time required for various levels of overload currents and the short circuit section describes the instantaneous trip current level of MCB.
Read More: Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) – Principle of operation
The MCB with class B trip characteristics trips instantaneously when the current flowing through it reaches between 3 to 5 times the rated current. These MCBs are suitable for cable protection.
MCB with class C trip characteristics trips instantaneously when the current flowing through it reaches between 5 to 10 times the rated current. Suitable Domestic and residential applications and electromagnetic starting loads with medium starting currents.
MCB with class D trip characteristics trips instantaneously when the current flowing through it reaches between Above 10(excluding 10) to 20 times the rated current. Suitable for inductive and motor loads with high starting currents.
MCB with class K trip characteristics trips instantaneously when the current flowing through it reaches between 8 to 12 times the rated current. Suitable for inductive and motor loads with high inrush currents.
MCB with class Z trip characteristics trips instantaneously when the current flowing through it reaches between 2 to 3 times the rated current. These types of MCBs are highly sensitive to short circuits and are used for the protection of highly sensitive devices such as semiconductor devices.
MCB with class A trip characteristics trips instantaneously when the current flowing through it reaches between 2 to 3 times the rated current. Like Class Z MCBs, these are also highly sensitive to short circuits and are used for the protection of semiconductor devices.
MCBs with trip curve class B and trip curve class C is the most commonly used ones. MCBs with Class C trip curves can be found in the lighting power distribution boards in residential and commercial buildings. It trips as soon as the current rises between 5 to 10 times its rated current. Class B MCBs are used in the protection of electronic devices such as PLC, DC power supplies, etc. in control panels. It trips as soon as the current rises between 3 to 5 times its rated current.
In some applications, frequent current peaks occur for a very short period (100ms to 2s). For such applications, class Z-type MCBs shall be used. Class Z-type MCBs are used in circuits with semiconductor devices.
It is important to choose an appropriate MCB current rating and trip curve in order to safeguard the circuit from damage during faults. Hence it is necessary to calculate the short circuit current and inrush current before choosing an appropriate MCB rating. If the chosen MCB rating is much higher than required, then it may not trip in the event of a fault. Similarly, if the MCB is underrated, then it may cause nuisance trips, for example even the starting currents or inrush currents may trip the MCB.
External selection tool: https://new.abb.com/low-voltage/solutions/selectivity/tools-support/curves
All circuit breakers, such as MCCB, ACB, VCB, etc have their own trip characteristics. The only thing is that may not follow the categorization as that of MCB. Also, the circuit breaker curve types are not the same for all types of circuit breakers. It varies from one circuit breaker type to the other and depends on many design factors.
Learn more about MCB:
- What is an MCB?
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) – Principle of operation
- What is kA rating of MCB and MCCB?
Related Articles: 1. Difference between MCB and MCCB 2. Difference between contactors and relays 3. Difference between Soft Starters and VFDs 4. Difference between MCCB and RCCB 5. Difference between MCB and RCBO 6. Difference between RCCB and RCBO 7. Difference between MPCB and MCCB
27 thoughts on “MCB Trip Curves – B, C, D, K, and Z trip curves”
Very good explanation. I understood the concept. Thank you.
Thank you, Mr. Sanket. Kindly browse through our articles. Please subscribe or follow us on twitter/facebook for instant updates.
Thankhs google team good explace thanks again
Very good mcb make , what Amps load trip make
Very good. Nice explain.. Good job
Explanation is good but your second paragraph doesn’t match the charts. It looks like it is the B-curve that trips between 3-5 times its rated current, and C-curve that trips between 5-10 times its rated current.
Very good, thanks
very good …..thanks
Thanks very much
Very good explanation
Is this curves is applicable to Rccb ?
No. These curves are applicable for mcbs only.
Thanks for your information
The information about mcb is very useful and helpful for a technician, many many thanks for sharing your information.
Great information, I got to know a few more details out of what I wanted to know.
Which type is better choice for UPS protection?
The explanations are very good but in the video is a mistake at minute 0.38. The short circuit sections with the overload section are reversed.
Good for selection of MCB’s
On the c type Mcb on the time curves at a short circuit fault current at 220amp it shows dis connection at 6/7seconds are you saying that disconnection will be instant at this current or 6/7 seconds.
I use B-curve in my home when short circuit occured in the appliace MCB tripped but my appliance burned. My appliance lead wires were shorted by a metal piece was lying on it.I thought MCB could have protected but not. And I also headed big noise of it.
Sorry to hear that. This could be because the MCB was oversized: Much higher than the rated current of the appliance or the MCB could be faulty. We suggest you replace it with a new one. Make sure that you are choosing the right one.
Thanks for sharing such an informative article about MCB.
sir Type C is used for average current load. Type B and C are the most commonly used in DBs. Tripping of MCB Type C is 5-10 times higher than normal. eg: if a 6A mcb put in acircuit , the rated current is 6 A , then how ever the type c mcb with stand 5 to 10 times higherr than normal .
hello, what about the CL curve mcb, because in my home installation I used the cl4 code on the mcb
Perhaps you are referring to product name of the MCB and not its trip curve.
The information is quite educative. Thank you so much
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Understanding Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) Types and Tripping Curves
- by Bhekusizi Dhlodhlo
- Categories: Blog

Table of Contents
Introduction.
Miniature circuit breakers (MCB) provide protection against short circuits and are rated normally up to 125A. They can be combined with a residual current device, to provide protection against short circuits, overloaded circuits and ground faults.
MCB’s tripping characteristics are represented graphically in a trip curve. The curve shows the response of the thermal and magnetic trip element to various overload and short circuit situations.
Those curves are designated letters according to the circuit breaker type. The circuit breaker Types are B, C, D, K and Z corresponding to similar lettered circuit breaker curves.
Why so many different circuit breaker types?

Circuit breaker curves determine the breaker's reaction time to faults. They're the first line of defence against electrical faults. Learn how to select the correct one! 🛡️ #SafetyFirst #ElectricalEngineering #SparkyCalc Tweet
There so many reasons why we need different circuit breaker types with different trip curves and some of the main reasons are:
Selective Coordination
Different electrical components within a system might have varying levels of fault currents they can handle before tripping.
By using different tripping curves, we can ensure that only the faulty component is disconnected during a fault, allowing the rest of the system to remain operational.
This selective coordination can be achieved by use of circuit breakers with different tripping curves in a system. We discuss this in more detail in our blog on understanding circuit breaker co-ordination
Equipment Protection
Different types of equipment have different thermal and electromagnetic characteristics. A more sensitive trip curve might be suitable for protecting sensitive electronic equipment, while a less sensitive one may be appropriate for heavy-duty machinery. This ensures that the protection device responds appropriately to the specific needs of the equipment.
Start-Up and Inrush Currents
Some devices such as large motors experience higher currents during startup or inrush periods. A circuit breaker that allows the flow of high inrush current without tripping can be used in this instance
Fault Types
Different fault types, such as short circuits and overloads, require distinct response times and current thresholds. Circuit breakers with different tripping curves can be used to address these specific fault conditions appropriately.
Safety and Personnel Protection
Human safety is a critical concern. Tripping curves can be designed to quickly disconnect power in situations where personnel might be at risk, while also preventing unnecessary tripping due to minor fluctuations.
Reading Trip Curves

Reading a Trip curve is not that difficult, give me a sec and I’II explain it to you.

A typical tripping curve is shown above. The horizontal X-axis represents the multiples of the current flowing through the circuit breaker. While the Y-axis represents the tripping time of the circuit breaker on a logarithmic scale. A log scale is used so as to fit a wider range of values on the axis.
The top part of the curve is the thermal section of the trip curve’s responds to overloads which are sustained or long-lasting overcurrent conditions.
Therefore, a circuit breaker with a thermal trip curve is better suited for high-inrush current applications. The thermal trip curve is typically curved, reflecting the fact that the response time of the circuit breaker increases as the level of overcurrent increases. The thermal trip unit responds relatively slowly yet consistently.
The second part of the curve is the magnetic current section of the trip curve responds to short circuits. It relies on a magnetic coil or solenoid opening when the overcurrent’s design limit is reached.
The magnetic trip curve is typically a straight line, reflecting the fact that the response time of the circuit breaker is nearly instantaneous for high levels of current.
The bottom part of the time-current curve shows the performance of the instantaneous trip component (short circuit) of the circuit breaker.
The maximum clearing time (time it takes for breakers to completely open) decreases as current increases. This is because of the blow-apart contact design which utilizes the magnetic field built-up around the contacts.
Breaker types and their trip curves
Now that we’ve learned how to read a trip curve, let’s explore how the type of breaker is linked to these curves and what these curves actually mean.
The first type of circuit breaker that we will look at is the Type B.

Type B circuit breakers have relatively fast tripping characteristics. They are designed to protect sensitive and low-power circuits, such as lighting circuits and some electronic devices.
The standards state that these breakers trip at 4 times the rated current but MCB’s being mechanical devices are not that exact and will trip anywhere between 3 to 5 times the rated current. The tripping characteristics of this circuit breaker is called a B Curve.

The next one on our list is the Type C circuit breaker.

Type C circuit breakers have medium tripping characteristics. They are commonly used in applications like small motors, small transformers, and general domestic applications where a moderate level of inrush current is expected during normal operation.
These breakers provide a balance between protecting against overcurrents and allowing for some temporary overloads. The standards state that they should trip at 7.5 times the rated current but will trip anywhere between 5 to 10 times the rated current. The tripping characteristics of this circuit breaker is called a C Curve.

Next we will discuss the Type D circuit breaker.

Curve D circuit breakers have a delayed tripping characteristic. They are often used in applications with high inrush currents, such as large motors, industrial equipment, and power distribution systems.
These breakers can handle significant overcurrents for a longer time before tripping, which is suitable for equipment that experiences frequent startup surges.
The standards state that they should trip at 12.5 times the rated current but will trip anywhere between 10 to 20 times the rated current. The tripping characteristics of this circuit breaker is called a D Curve.

Lets move on to Type K. This circuit breaker is specifically designed for air conditioning and heat pump systems, which often experience high inrush currents during compressor startup.
Type K provides a delayed response to accommodate these inrush currents while still providing protection against sustained overcurrents. These trip at 8 to 12 times the rated current. The tripping characteristics of this circuit breaker is called a K Curve.

Finally we have Type Z. This circuit breaker is used for specialized applications where the tripping time is extremely fast, even faster than Type A.
It’s often used in situations where human safety is the primary concern, such as in some elevator systems or medical equipment. This circuit breaker trips at 2 to 3 times the rated current. The tripping characteristics of this circuit breaker is called a Z Curve.

Rounding Up
I encourage you to reflect on your current or upcoming projects. Are you using the most appropriate type of MCB? Could a different tripping curve offer better protection or efficiency? If you’re unsure, review the technical aspects we’ve discussed, or consult with a professional.
Your thoughts and experiences are invaluable to this discussion. Please contact me for further discussions. Let’s continue to learn and grow together in our understanding of electrical systems. For more insights, check out similar topics on our blog page and home page . And for updates, don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter.
Recent Posts
Understanding voltage drop, as/nzs3008, understanding power cable insulation, understanding ingress protection (ip) ratings, understanding earth fault loop impedance, az/nzs3000, understanding ac induction motor starting, subscribe to our newsletter, get updates and learn from the best, browse some of our featured calculators, want to know when we have new content, i’m here to assist you.
Something in this article isn’t Clear? Feel free to contact me, and I will be more than happy to answer all of your questions.
Share this post

My name is Bheki and I’m an Electrical Engineer. I have a passion for engineering and teaching/mentoring. Qualifications: BEng (Electronic) Hons, MIEAust, CPEng, NER, APEC Engineer IntPE(Aus), RPEQ.
Keep Reading
Copyright © 2024 Powered by SparkyCalc . All rights reserved.
Lets share the love
- Updates & Blogs – Distributor Schneider Electric Indonesia
Standar Terkait Data Listrik (Kurva Tripping)
Berikut adalah kurva tripping dimana kurva-kurva ini terdiri beberapa daerah yang dibatasi oleh arus :
1. In (Arus nominal / Arus operasional)
In (dalam A – Ampere) merupakan arus nominal Circuit Breaker (CB) untuk dapat beroperasi dengan baik dalam range arus tsb (sesuai spesifikasi CB).
2. Ir (Arus thermal / Arus pengaturan lebih)
Ir (dalam A) adalah fungsi dari In, yang menyatakan proteksi tripping dikarenakan pengaruh thermal. Ir dikenal sebagai proteksi waktu panjang (Long Time Protection LTP).
3. Isd atau Im (short time delay current / Arus magnetic)
Isd (dalam kA) adalah fungsi dari Ir, menyatakan proteksi hubung pendek. Isd dikenal sebagai proteksi waktu pendek (Short Time Protection STM).
4. Ii atau Iinst (Arus Instantaneous / Arus setelan tripping seketika)
Ii atau Iinst (dalam kA) adalah fungsi dari In, yang menyatakan proteksi hubung pendek seketika. Untuk arus lebih tinggi (hubung pendek) lebih besar dari pada ambang Ii, pemutus sirkit harus secepat mungkin memutuskan arus gangguan.
5. Icu (rated breaking capacity / Kapasitas pemutusan tertinggi)
(dalam kA) adalah nilai maksimum arus hubung pendek yang dapat diterima pemutus sirkit, tanpa mengalami kerusakan . Nilainya diuji dengan standard urutan uji coba. Karakteristik ini ditetapkan pada tegangan khusus Ue.
6. Ics (Rated service short-circuit breaking capacity / kapasitas pemutusan layanan pengenal)
(kA rms) , diberikan pabrik pembuat dan dinyatakan dalam % terhadap Icu. Kinerja Ics penting dalam menggambarkan kemampuan pemutus sirkit dalam operasi normal secara total dalam membuka arus hubung pendek sebanyak 3x (O – CO – CO pada Ics). Semakin tinggi Ics, semakin efektif dan bagus kinerja pemutus sirkit. Untuk CB domestik, Ics = k Icn. k nilai faktor sesuai dengan IEC 60898 tabel XIV. Di indsutri Eropa, Ics = Icu.
7. Icm (making current / Kapasitas kemampuan hubung pendek pengenal )
(puncak kA) adalah nilai maksimum arus hubung pendek asimetris untuk dialirkan pada pemutus sirkit. CB Masterpact NW08H2 dengan Icu(rated breaking capacity) 100 kA, maka nilai Icm sebesar 100 x 2.2 = 220 kA.
8. Icw (rated short-time withstand current / ketahanan arus waktu pendek pengenal)
Terdapat 2 kategori (A dan B), berdasarkan IEC 60947-2,dimana: Kategori A, tidak ada waktu tunda dalam operasi seketika (instantaneous) hubung singkat Kategori B, untuk membedakan dengan pemutus sirkit lain berdasar waktu, ada waktu tunda dalam memutuskan arus. Icw adalah arus maksimum dimana pemutus sirkit kategori B dapat menahan, secara thermal dan electrodynamic, tanpa menanggung kerusakan, untuk periode waktu yang diberikan.

LV switchgear: functions and selection
- LV switchgear functions - Electrical protection
- LV switchgear functions - Isolation
- LV switchgear functions - Switchgear control
- Elementary switching devices
- Combined switchgear elements
- Switchgear selection
- Tabulated functional capabilities of LV switchgear
- Standards and description of circuit-breakers
Fundamental characteristics of a circuit-breaker
- Other characteristics of a circuit-breaker
- Selection of a circuit-breaker
- Coordination between circuit-breakers
- Selectivity MV/LV in a consumer’s substation
- Selectivity of Residual Current Devices (RCDs)
- Maintenance of low voltage switchgear
- 1 Rated operational voltage (Ue)
- 2 Rated current (In)
- 3 Frame-size rating
- 4 Overload relay trip-current setting (Irth or Ir)
- 5 Short-circuit relay trip-current setting (Im)
- 6 Circuit breaker suitable for isolation
- 7 Rated short-circuit breaking capacity (Icu or Icn)
- 9 Related technical guides
The fundamental characteristics of a circuit-breaker are:
- Its rated voltage Ue
- Its rated current In
- Its tripping-current-level adjustment ranges for overload protection (Ir [1] or Irth [1] ) and for short-circuit protection (Im) [1]
- Its short-circuit current breaking rating (Icu for industrial CBs; Icn for domestic-type CBs).
Rated operational voltage (Ue)
This is the voltage at which the circuit-breaker has been designed to operate, in normal (undisturbed) conditions.
Other values of voltage are also assigned to the circuit-breaker, corresponding to disturbed conditions as noted in Other characteristics of a circuit-breaker .
Rated current (In)
This is the maximum value of current that a circuit-breaker, fitted with a specified overcurrent tripping relay, can carry indefinitely at an ambient temperature stated by the manufacturer, without exceeding the specified temperature limits of the current carrying parts.
A circuit-breaker rated at In = 125 A for an ambient temperature of 40°C will be equipped with a suitably calibrated overcurrent tripping relay (set at 125 A). The same circuit-breaker can be used at higher values of ambient temperature however, if suitably “derated”. Thus, the circuit-breaker in an ambient temperature of 50°C could carry only 117 A indefinitely, or again, only 109 A at 60°C, while complying with the specified temperature limit.
Derating a circuit-breaker is achieved therefore, by reducing the trip-current setting of its overload relay, and marking the CB accordingly. The use of an electronic-type of tripping unit, designed to withstand high temperatures, allows circuit-breakers (derated as described) to operate at 60°C (or even at 70°C) ambient.
Note: In for circuit-breakers (in IEC 60947-2) is equal to Iu for switchgear generally, Iu being the rated uninterrupted current.
Frame-size rating
A circuit breaker which can be fitted with overcurrent tripping units of different current level-setting ranges, is assigned a rating which corresponds to the highest current-level-setting tripping unit that can be fitted.
A Compact NSX630N circuit-breaker can be equipped with 11 electronic trip units from 150 A to 630 A. The size of the circuit-breaker is 630A.
Overload relay trip-current setting (Irth or Ir)
Apart from small circuit-breakers which are very easily replaced, industrial circuit-breakers are equipped with removable, i.e. exchangeable, overcurrent-trip relays. Moreover, in order to adapt a circuit-breaker to the requirements of the circuit it controls, and to avoid the need to install over-sized cables, the trip relays are generally adjustable. The trip-current setting Ir or Irth (both designations are in common use) is the current above which the circuit-breaker will trip. It also represents the maximum current that the circuit-breaker can carry without tripping. That value must be greater than the maximum load current IB, but less than the maximum current permitted in the circuit Iz (see chapter Sizing and protection of conductors ).
The thermal-trip relays are generally adjustable from 0.7 to 1.0 times In, but when electronic devices are used for this duty, the adjustment range is greater; typically 0.4 to 1 times In.
(see Fig. H27 )
A NSX630N circuit-breaker equipped with a 400 A Micrologic 6.3E overcurrent trip relay, set at 0.9, will have a trip-current setting:
Ir = 400 x 0.9 = 360 A
Note: For circuit-breakers equipped with non-adjustable overcurrent-trip relays, Ir = In. Example: for iC60N 20 A circuit-breaker,
Ir = In = 20 A.
Short-circuit relay trip-current setting (Im)
Short-circuit tripping relays (instantaneous or slightly time-delayed) are intended to trip the circuit-breaker rapidly on the occurrence of high values of fault current. Their tripping threshold Im is:
- Either fixed by standards for domestic type CBs, e.g. IEC 60898, or,
- Indicated by the manufacturer for industrial type CBs according to related standards, notably IEC 60947-2.
For the latter circuit-breakers there exists a wide variety of tripping devices which allow a user to adapt the protective performance of the circuit-breaker to the particular requirements of a load (see Fig. H28 , Fig. H29 and Fig. H30 ).
- ^ 50 In in IEC 60898, which is considered to be unrealistically high by most European manufacturers (Schneider Electric = 10 to 14 In).
- ^ 1 2 For industrial use, IEC standards do not specify values. The above values are given only as being those in common use.
Circuit breaker suitable for isolation
A circuit-breaker is suitable for isolating a circuit if it fulfills all the conditions prescribed for a disconnector (at its rated voltage) in the relevant standard. In such a case it is referred to as a circuit-breaker-disconnector and marked on its front face with the symbol
All Acti 9, Compact NSX and Masterpact LV switchgear of Schneider Electric ranges are in this category.
Rated short-circuit breaking capacity (Icu or Icn)
The short-circuit current-breaking performance of a LV circuit-breaker is related (approximately) to the cos φ of the fault-current loop. Standard values for this relationship have been established in some standards
The short-circuit current-breaking rating of a CB is the highest (prospective) value of current that the CB is capable of breaking without being damaged. The value of current quoted in the standards is the rms value of the AC component of the fault current, i.e. the DC transient component (which is always present in the worst possible case of short-circuit) is assumed to be zero for calculating the standardized value. This rated value (Icu) for industrial CBs and (Icn) for domestic-type CBs is normally given in kA rms.
Icu (rated ultimate s.c. breaking capacity) and Ics (rated service s.c. breaking capacity) are defined in IEC 60947-2 together with a table relating Ics with Icu for different categories of utilization A (instantaneous tripping) and B (time-delayed tripping) as discussed in Other characteristics of a circuit-breaker .
Tests for proving the rated s.c. breaking capacities of CBs are governed by standards, and include:
- Operating sequences, comprising a succession of operations, i.e. closing and opening on short-circuit
- Current and voltage phase displacement. When the current is in phase with the supply voltage (cosφ for the circuit = 1), interruption of the current is easier than that at any other power factor. Breaking a current at low lagging values of cosφ is considerably more difficult to achieve; a zero power-factor circuit being (theoretically) the most onerous case.
In practice, all power-system short-circuit fault currents are (more or less) at lagging power factors, and standards are based on values commonly considered to be representative of the majority of power systems. In general, the greater the level of fault current (at a given voltage), the lower the power factor of the fault-current loop, for example, close to generators or large transformers.
Figure H31 below extracted from IEC 60947-2 relates standardized values of cos φ to industrial circuit-breakers according to their rated Icu.
- The dielectric withstand capability
- The disconnection (isolation) performance and
- The correct operation of the overload protection have not been impaired by the test.
- ^ 1 2 3 Current-level setting values which refer to the current-operated thermal and “instantaneous” magnetic tripping devices for over-load and short-circuit protection.
Related technical guides

Combine the benefits of selectivity and cascading to maximize power availability of your LV design at optimized cost.
- Chapter - LV switchgear: functions and selection
- Eig-content-pages
- previous page
About this wiki
The Electrical Installation Guide is now available here as a wiki (Electrical Installation Wiki). This wiki is a collaborative platform, brought to you by Schneider Electric: our experts are continuously improving its content, as they were doing for the guide. Collaboration to this wiki is also open to all.
- How to browse and search
- How to contribute
- Recent changes
- Special pages
- Random page
Jenis MCB – Kurva Trip dan Kelas Miniature Circuit Breaker
Mengetahui tiap jenis MCB akan membantu kalian memaksimalkan efisiensi dan meminimalkan biaya.
Karakteristik trip, atau jangkauan arus trip pada perangkat yang beroperasi jika ada short circuit atau overload (beban berlebih), digunakan untuk membedakan MCB dalam beberapa kategori.
MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) adalah saklar yang aktif otomatis untuk melindungi perangkat dari overload atau short circuit.
Berdasarkan keadaan trip arus berlebih, MCB dibagi menjadi beberapa kategori berbeda.
Apa itu MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)?
Untuk permulaan, apa itu miniature circuit breaker? MCB adalah jenis saklar listrik yang beroperasi secara otomatis. Miniature circuit breaker didesain untuk melindungi rangkaian listrik dari kecelakaan karena arus berlebih.
Untuk melindungi kegagalan listrik dan perangkat, mereka didesain untuk menyebabkan trip ketika overload atau short circuit terjadi.
Pada lingkungan perumahan, komersial, dan industri, MCB umum digunakan sebagai komponen isolasi. Mereka adalah bagian dari keluarga besar komponen circuit breaker dengan tambahan daya.
Bagaimana Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) Bekerja?
Arus berlebih – arus listrik yang melebihi nilai aman yang ditetapkan – memicu circuit breaker, yang mana menggunakan mekanisme mekanik yang kokoh untuk mengurangi kegagalan dan alarm yang salah.
Arus berlebih memanaskan, membengkokkan, dan menyebabkan trip dalam MCB. Hal ini mengaktifkan saklar yang memisahkan kontak listrik, yang memiliki arc (pengosongan listrik).
Arc chute adalah strip logam terisolasi yang membagi dan mendinginkan arc. Ketika kegagalan sudah diperbaiki dan MCB direset, koneksi kembali tertutup.
MCB adalah jenis circuit breaker yang melindungi perangkat dari beban berlebih dan short circuit. Prosedur berbeda digunakan untuk mendeteksi keduanya.
Strip bimetal memberikan proteksi overload lewat operasi termal, sedangkan coil trip memberikan proteksi short circuit lewat operasi elektromagnetik.
MCB akan trip (aktif) dengan sangat cepat jika pengosongan cukup tinggi – dalam rentang satu per sepuluh detik. Komponen akan lebih lambat dalam merespon ketika arus berlebih mencapai batasan aman.
Arus yang membuat MCB mengalami trip secara langsung menentukan perbedaan antara jenis MCB. Kurva trip MCB dapat dihitung dari waktu untuk trip (waktu interrupt) dengan arus yang diberikan.
Jenis MCB ini juga disebut kurva atau kelas. Di bawah ini adalah tabel trip untuk tiap jenis MCB.
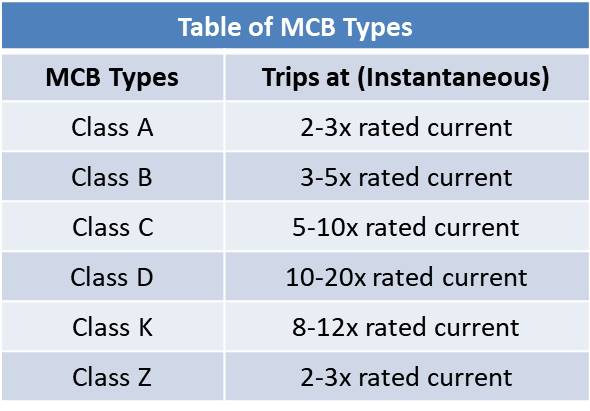
Tipe A, B, C, D, K, dan Z adalah jenis MCB yang dapat diperoleh di pasaran. Jenis B, C, dan D adalah tiga jenis paling umum yang digunakan. Tiap jenis dibuat sesuai dengan kekuatan lonjakan listrik dalam berbagai kesempatan.
Variasi ini umum dianggap sebagai “kurva trip”, meskipun mereka juga dapat dianggap sebagai “karakteristik trip” atau “karakteristik overcurrent”.
Di bawah adalah kurva trip tiap jenis MCB.
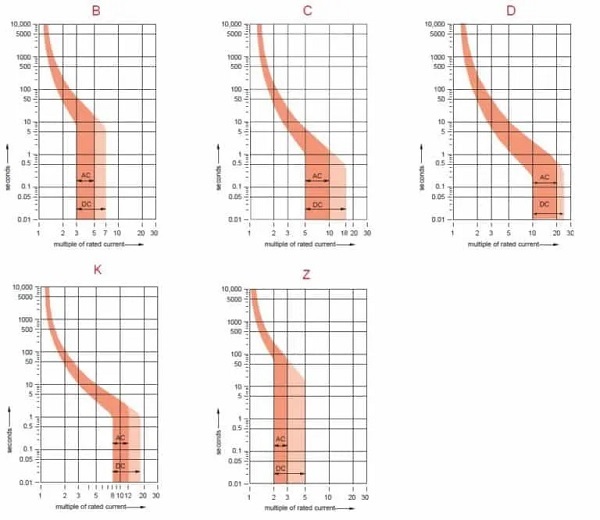
Mari kita lihat perbedaan tiap jenis:
Miniature Circuit Breaker : Jenis A
MCB yang sangat sensitif adalah MCB jenis A, yang mana cukup jarang dimanfaatkan. Mereka dibuat untuk trip secara instan ketika arus melebihi 2-3 kali arus yang ditetapkan.
Hasilnya, mereka terbatas untuk perangkat yang sensitif.
Miniature Circuit Breaker : Jenis B
Dengan waktu operasi 0.04 hingga 13 detik, ketika arus 3 hingga 5 kali nilai arus yang ditetapkan. Ini digunakan dengan beban resistif total tanpa induktif atau dengan beban induktif rendah dengan induktansi yang tidak signifikan.

MCB ini umumnya digunakan untuk aplikasi rumahan daya rendah seperti rangkaian pencahayaan dan perkabelan rumahan. Mereka tidak umum digunakan untuk aplikasi induktif seperti motor.
Miniature Circuit Breaker : Jenis C
Jenis C memiliki waktu operasi 0.04 hingga 5 detik ketika arus bernilai 5 hingga 10 kali arus yang ditetapkan. Jenis ini digunakan pada beban induktif seperti motor, kipas angin, trafo, dan perangkat lain dimana ada resiko lonjakan arus yang cepat.

Pada nilai arus 5 hingga 10 kali dari arus yang ditetapkan, MCB jenis C didesain untuk trip secara langsung.
MCB jenis C umum digunakan pada aplikasi industri dan komersial untuk motor kecil, kipas, trafo, dan pencahayaan neon.
Miniature Circuit Breaker : Jenis D
MCB jenis D adalah MCB yang paling tidak sensitif, didesain untuk trip secara langsung ketika arus 10 hingga 20 kali nilai arus yang ditetapkan.

Hasilnya, jenis ini ideal untuk beban induktif dan aplikasi lain dengan lonjakan daya yang besar. Uninterruptible power supply (UPS), motor berat, trafo, mesin X-ray, dan mesin welding semuanya menggunakan MCB jenis D.
Miniature Circuit Breaker : Jenis K
Ketika arus mencapai 8 hingga 12 kali nilai arus yang ditetapkan dan waktu operasi kurang dari 0.1 detik, jenis K akan trip. Jenis ini digunakan untuk melindungi beban induktif dari arus lonjakan yang tinggi.
Miniature Circuit Breaker : Jenis Z
MCB jenis Z memiliki waktu operasi kurang dari 0.1 detik dan dapat mengatasi arus 2 hingga 3 kali nilai arus yang ditetapkan.
Jika dibandingkan jenis B, C, dan D; jenis A, K, dan Z memiliki waktu operasional yang sangat pendek. Kelas A, K, dan Z adalah breaker yang sangat sensitif yang bekerja dengan cepat dan melindungi perangkat sensitif.

MCB jenis Z didesain untuk aplikasi yang rentan, sama seperti jenis A. ketika arus mencapai 2-3 kali dari arus yang ditetapkan, mereka didesain untuk trip secara langsung. Rangkaian semikonduktor sering dilindungi tipe Z.
Apa yang Harus Diperhatikan Ketika Memilih Jenis MCB
Jenis MCB yang harus dibeli ditentukan oleh karakteristik perangkat atau instalasi. Bandingkan beberapa hal di bawah ketika mencari sebuah MCB:
- Nilai arus. Ini adalah nilai arus yang akan digunakan untuk menentukan karakteristik trip.
- Nilai arus trip. Nilai arus yang dikalikan beberapa kali sesuai keinginan kalian untuk mengalami trip. Jenis MCB akan ditentukan oleh hal ini.
- Kapasitas sebelum rusak. Kapasitas sebuah MCB bergantung pada nilai arus tertinggi dan tegangan yang dapat diputus dengan aman. Nilai arus maksimum pada tegangan tertentu dapat untuk menghitung kapasitas kerusakan.
- Jumlah pole. Jumlah pole menandakan jumlah fasa (atau rangkaian) maksimum yang dapat dilindungi oleh satu MCB. MCB satu pole hanya melindungi satu rangkaian, tetapi tiga pole MCB dapat melindungi hingga tiga. MCB akan trip jika salah satu pole overload.
- Karakteristik trip.
- Kapasitas breaker pada MCB adalah arus tertinggi yang dapat diputus tanpa merusak atau menghasilkan percikan api. Ini harus sesuai dengan kekuatan lonjakan yang diperhitungkan pada sebuah area instalasi. Kiloampere (kA) adalah satuan standar untuk pengukuran arus listrik, dan tiap satu setara dengan 1,000 ampere.
- Dalam wadah MCB, jumlah pole atau saklar trip. Konfigurasi satu, dua, tiga, netral, dan empat dapat dipilih. Model tiga pole banyak digunakan dan dapat memutus arus pada tiga rangkaian dalam satu waktu jika salah satu pole mengalami kegagalan.
Keputusan lain adalah durabilitas atau ketahanan sebuah MCB, yang menandakan jumlah siklus yang diperhitungkan untuk sebuah MCB dapat tetap berfungsi normal. MCB sering dibuat dengan dapat beroperasi dua kali secara manual.
Selalu konsultasikan dengan konsultan atau datasheet sebuah MCB.
Ringkasan Jenis MCB
Untuk melindungi rangkaian dari kerusakan saat ada kegagalan, hal yang penting adalah memilih rating dan kurva trip MCB yang sesuai. Hasilnya, sebelum menentukan rating MCB yang dapat diterima, kita perlu memperhitungkan arus short circuit dan arus yang masuk.
Jika rating MCB dipilih dengan nilai yang terlalu tinggi dari yang diperlukan, ada kemungkinan tidak terjadi trip saat ada kegagalan atau malfungsi.
Sebaliknya, jika rating MCB dipilih dengan nilai yang terlalu rendah, hal ini dapat menyebabkan trip yang tidak diperlukan seperti saat arus awal motor menyala atau saat arus masuk pertama kali.
Jenis MCB juga berhubungan dengan tingkat tegangan serta kategori pengukuran .
Tinggalkan komentar Batalkan balasan
Simpan nama, email, dan situs web saya pada peramban ini untuk komentar saya berikutnya.
EDUKASIKINI.COM
Membahas Tuntas Pengetahuan Listrik, Teknologi, Pengetahuan Sosial Secara Gratis
Memahami Kurva Tripping Pada Circuit Breaker
Kurva Tripping, alias Kurva Arus Waktu, bisa menjadi topik yang menakutkan. Tujuan dari makalah singkat ini adalah untuk memperkenalkan Anda pada konsep Kurva Tripping dan menjelaskan cara membaca dan memahaminya.
Apakah UL itu?
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) didirikan pada tahun 1894 sebagai Biro Kelistrikan Penjamin Emisi Efek, sebuah biro Badan Penjamin Emisi Kebakaran Nasional. UL didirikan terutama untuk memberikan pengujian dan sertifikasi independen untuk keselamatan kebakaran produk listrik. Produk tersebut termasuk perangkat perlindungan sirkuit yang dibahas dalam makalah ini.
Perangkat Perlindungan Sirkuit
Perlindungan sirkuit digunakan untuk melindungi kabel dan peralatan listrik dari kerusakan jika terjadi kelebihan beban listrik, korsleting, atau gangguan arde. Badai petir, stopkontak yang kelebihan beban, atau lonjakan arus listrik yang tiba-tiba dapat mengakibatkan situasi berbahaya yang berpotensi menyebabkan kebakaran, kerusakan peralatan, atau cedera diri.
Perlindungan sirkuit dirancang untuk menghilangkan risiko ini sebelum terjadi dengan memutus aliran listrik ke sirkuit.
Apa itu Kurva Tripping?
Sederhananya, Kurva Tripping adalah representasi grafis dari perilaku yang diharapkan dari perangkat perlindungan sirkuit. Perangkat perlindungan sirkuit tersedia dalam berbagai bentuk, termasuk sekering, pemutus sirkuit miniatur, pemutus sirkuit cetakan, pelindung tambahan, pemutus sirkuit pelindung motor, relai beban berlebih, sekring elektronik, dan pemutus sirkuit udara.

Kurva Tripping menggambarkan waktu interupsi perangkat arus berlebih berdasarkan level saat ini. Kurva Tripping disediakan oleh produsen perangkat perlindungan sirkuit untuk membantu pengguna memilih perangkat yang memberikan perlindungan dan kinerja peralatan yang tepat, sambil menghindari gangguan gangguan.
Mengapa kita membutuhkan Kurva Tripping yang berbeda?
Pemutus sirkuit harus berjalan cukup cepat untuk menghindari peralatan atau kegagalan kabel, tetapi tidak terlalu cepat untuk menyebabkan kesalahan, atau perjalanan yang mengganggu.
Untuk menghindari perjalanan gangguan, pemutus sirkuit harus berukuran tepat untuk mengimbangi arus masuk. NEMA mendefinisikan lonjakan puncak sesaat sebagai transien arus sesaat yang terjadi segera (dalam setengah siklus AC) setelah penutupan kontak, untuk memahami rating Circuit Breaker silahkan baca Circuit Breaker Adalah | Penjelasan Serta Ratingnya
Arus masuk inilah yang menyebabkan lampu meredup di rumah saat motor, seperti pada pengering pakaian atau penyedot debu dinyalakan.
Seperti yang ditunjukkan grafik, arus masuk yang disebabkan oleh menghidupkan motor adalah 30A. Ini jauh lebih tinggi daripada arus operasi atau kondisi tunak. Puncak arus masuk, kemudian mulai membusuk saat motor berputar.
Kami membutuhkan Kurva Tripping yang berbeda untuk menyeimbangkan jumlah yang tepat dari perlindungan arus berlebih terhadap pengoperasian alat berat yang optimal.
Memilih pemutus arus dengan Kurva Tripping yang trip terlalu cepat dapat mengakibatkan gangguan tersandung. Memilih pemutus arus yang terlambat trip dapat menyebabkan kerusakan besar pada mesin dan kabel.
Bagaimana cara kerja MCB?
Untuk memahami Kurva Tripping, akan sangat membantu untuk memahami bagaimana fungsi pemutus sirkuit miniatur, atau perangkat proteksi arus lebih. Untuk mengetahui bagaimana cara kerja circuit breaker silahkan baca Circuit Breaker adalah | Penjelasan, Jenis dan Cara Kerjanya
Dengan strip bi-logam dan kumparan magnet / solenoid , pemutus sirkuit miniatur dapat menjadi dua jenis perangkat perlindungan sirkuit yang terpisah menjadi satu.
Strip bi-metal memberikan perlindungan beban berlebih sebagai respons terhadap arus berlebih yang lebih kecil, biasanya 10X arus pengoperasian. Strip logam terdiri dari dua strip logam yang berbeda, dibentuk bersama, yang mengembang dengan kecepatan berbeda saat dipanaskan.
Dalam situasi kelebihan beban, strip bimetalik menekuk dan gerakan ini menggerakkan mekanisme trip dan memutus (membuka) sirkuit. Strip mengubah perubahan suhu menjadi perpindahan mekanis.
Kumparan magnet atau solenoida bereaksi terhadap arus lebih yang cepat dan lebih tinggi yang disebabkan oleh korsleting, biasanya lebih besar dari 10X arus operasi - hingga puluhan atau ratusan ribu ampere. Arus tinggi menyebabkan medan magnet dibangkitkan oleh koil, menggerakkan piston internal dengan cepat (dalam mikrodetik) untuk trip mekanisme aktuator dan memutus rangkaian, Untuk mengetahui jenis jenis circuit breaker silahkan baca Perbedaan antara MCB, MCCB, RCCB, ELCB
Kurva Tripping
Bagan Kurva Tripping.
- Sumbu X mewakili kelipatan arus operasi pemutus sirkuit.
- Sumbu Y mewakili waktu tersandung. Skala logaritmik digunakan untuk menunjukkan waktu dari 0,001 detik hingga 10.000 detik (2,77 jam) pada kelipatan arus operasi.
Tiga komponen utama Kurva Tripping adalah:
- Kurva Tripping Termal. Ini adalah Kurva Tripping untuk strip bi-metalik, yang dirancang untuk arus lebih yang lebih lambat agar dapat masuk saat terburu-buru / memulai, seperti dijelaskan di atas.
- Kurva Tripping Magnetik. Ini adalah Kurva Tripping untuk kumparan atau solenoid. Ini dirancang untuk bereaksi cepat terhadap arus berlebih yang besar, seperti kondisi korsleting.
- Kurva Tripping Ideal. Kurva ini menunjukkan Kurva Tripping yang diinginkan untuk strip bi-logam. Karena sifat organik dari strip bi-logam, dan kondisi lingkungan yang berubah, sulit untuk secara tepat memprediksi titik trip yang tepat.
Bagaimana Kurva Tripping berhubungan dengan pemutus arus yang sebenarnya?
Bagian atas grafik menunjukkan Kurva Tripping termal untuk strip bi-logam. Ini memberi tahu kita bahwa pada 1,5X arus pengenal, pemutus sirkuit tercepat akan trip adalah empat puluh detik (1). Empat puluh detik pada 2X arus pengenal adalah yang paling lambat saat pemutus sirkuit akan trip (2).
Bagian bawah grafik adalah untuk perjalanan magnet koil / solenoida; 0,02 hingga 2,5 detik pada 3X arus pengenal adalah paling cepat pemutus sirkuit akan trip (3). Durasi yang sama, 0,02 hingga 2,5 detik, pada 5X arus pengenal, adalah yang terpanjang yang akan membuat pemutus sirkuit trip (4).
Area yang diarsir di antaranya adalah Tripping Zone.
PENTING: Kurva trip menunjukkan prediksi perilaku pemutus arus dalam keadaan dingin (suhu ruangan sekitar). Kondisi dingin adalah ketika strip bimetalik berada dalam suhu pengoperasian sekitar yang ditentukan untuk pemutus.
Jika pemutus telah mengalami perjalanan termal baru-baru ini, dan tidak mendingin ke suhu sekitar, pemutus dapat lebih cepat tersandung.
Menyatukan semuanya
Catat secara khusus Zona Tersandung di mana pemecah bisa tersandung atau tidak. Pikirkan ini sebagai area Kucing Schrödinger. Di dalam zona, sampai peristiwa arus lebih terjadi, kita tidak tahu persis kapan / apakah pemutus akan tersandung (Kucing Schrödinger = mati) atau apakah pemutus tidak akan tersandung (Kucing Schrödinger = hidup).
Sekarang setelah kita menyatukan semuanya, jelas bahwa memilih pemutus sirkuit kurva 10A, B dapat mengakibatkan gangguan perjalanan karena pemutus memasuki zona tersandung pada 30A. (Lihat gambar 8, di bawah ini.)
Pemutus kurva D adalah pilihan yang paling umum untuk motor listrik, meskipun terkadang Pemutus kurva C dapat dipilih untuk aplikasi yang memiliki beban campuran pada sirkuit yang sama.
Tiga kurva trip yang paling umum untuk Miniature Circuit Breaker adalah B, C dan D. Dengan meletakkan ketiganya pada satu grafik, kita dapat melihat bagaimana bagian termal dari kurva tersebut mirip satu sama lain, tetapi ada perbedaan bagaimana kurva magnet (koil / solenoid), dan dengan demikian fungsi pemutus sirkuit.
Singkatnya:
Perlindungan sirkuit digunakan untuk melindungi kabel dan peralatan listrik dari kerusakan jika terjadi kelebihan beban listrik, korsleting, atau gangguan arde.
Sambaran petir, stopkontak yang kelebihan beban, atau lonjakan arus listrik yang tiba-tiba dapat mengakibatkan situasi berbahaya yang berpotensi menyebabkan kebakaran, kerusakan peralatan, atau cedera diri. Perlindungan sirkuit dirancang untuk menghilangkan risiko ini sebelum terjadi dengan memutus aliran listrik ke sirkuit.
Perangkat perlindungan sirkuit termasuk sekering, pemutus sirkuit miniatur, pemutus sirkuit berbentuk kotak, pelindung tambahan, pemutus sirkuit pelindung motor, relai beban berlebih, sekring elektronik, dan pemutus sirkuit udara.
Kurva Trip memprediksi perilaku perangkat proteksi sirkuit dalam kondisi arus berlebih yang lebih lambat, lebih kecil, dan lebih besar, lebih cepat daripada kondisi saat ini.
Memilih Kurva Tripping yang benar untuk aplikasi Anda memberikan perlindungan sirkuit yang andal, sambil membatasi perjalanan yang salah atau gangguan.
Makalah ini adalah gambaran singkat dari Kurva Tripping. Ini tidak dimaksudkan sebagai jawaban akhir tentang topik ini.
Masih banyak lagi yang harus dipelajari, termasuk jenis Kurva Tripping dan koordinasi pemutus sirkuit lainnya. Dengan dasar-dasar yang sekarang tercakup, seseorang dapat dengan percaya diri mendekati topik tersebut.

Share this post
0 Response to "Memahami Kurva Tripping Pada Circuit Breaker"
Post a comment, iklan atas artikel, iklan tengah artikel 1, iklan tengah artikel 2, iklan bawah artikel.


Pengantar Circuit Breaker: Fungsi dan Prinsip Kerjanya
Pernahkah Anda mengalami pemadaman listrik di rumah atau tempat kerja Anda? Jika ya, Anda mungkin pernah mendengar istilah “circuit breaker”. Tapi apa sebenarnya circuit breaker itu dan bagaimana cara kerjanya?
Circuit breaker adalah komponen penting dari sistem kelistrikan apa pun, karena membantu melindungi dari kelebihan beban listrik dan korsleting. Tanpa mereka, risiko kerusakan pada peralatan listrik dan bahkan kebakaran meningkat secara signifikan.
Circuit breaker bisa menjadi bagian dari sistem kontrol otomatis yang menggunakan produk-produk Omron . Misalnya, circuit breaker bisa digunakan sebagai bagian dari sistem proteksi kelebihan arus yang menggunakan relay atau saklar produksi Omron untuk mendeteksi kelebihan arus dan memutuskan aliran listrik.
Pada artikel ini, kita akan membahas cara kerja circuit breaker, termasuk tujuan, jenis, dan cara kerjanya. Baik Anda seorang pemilik rumah atau teknisi listrik, memahami circuit breaker sangat penting untuk menjaga sistem kelistrikan yang aman dan andal. Jadi, mari selami dan pelajari semua tentang komponen listrik yang penting ini.
Pemahaman Umum Tentang Circuit Breaker
Circuit Breaker, atau dalam Bahasa Indonesia disebut sebagai pemutus arus, adalah perangkat penting dalam sistem kelistrikan yang bertujuan untuk melindungi sirkuit listrik dari kerusakan yang mungkin disebabkan oleh beban berlebih atau hubungan singkat (short circuit). Prinsip dasar kerja circuit breaker sama dengan saklar, yaitu memutus dan menghubungkan arus listrik. Namun, perbedaannya terletak pada fungsinya yang lebih kompleks, yakni melindungi sistem kelistrikan.

Fungsi dan Tujuan Circuit Breaker
Circuit breaker, atau pemutus sirkuit, merupakan alat penting yang digunakan dalam sistem kelistrikan dan elektronik. Fungsi utama dari circuit breaker adalah untuk melindungi peralatan dan sistem listrik dari kerusakan akibat over current atau arus berlebih, yang biasanya terjadi akibat short circuit (hubungan pendek) atau overload (beban berlebih).
Berikut adalah beberapa fungsi dan tujuan dari circuit breaker:
- Perlindungan dari Overcurrent: Overcurrent terjadi ketika arus yang mengalir melebihi kapasitas maksimal yang dapat ditoleransi oleh sistem atau peralatan. Hal ini bisa terjadi karena berbagai alasan, seperti kesalahan dalam wiring atau peningkatan tiba-tiba dalam beban listrik. Circuit breaker akan memutuskan aliran listrik saat mendeteksi kondisi ini, melindungi peralatan dari kerusakan.
- Perlindungan dari Short Circuit: Short circuit atau hubungan pendek adalah kondisi di mana arus listrik mengalir melalui jalur yang memiliki resistansi rendah, biasanya akibat kawat listrik yang bertemu langsung tanpa adanya resistansi. Hal ini dapat menyebabkan peningkatan arus yang sangat tinggi, yang dapat merusak peralatan dan bahkan menyebabkan kebakaran. Circuit breaker mendeteksi dan memutus aliran listrik dalam kondisi ini.
- Memungkinkan Manual Disconnect: Circuit breaker juga memungkinkan pemutusan sirkuit secara manual. Ini sangat berguna dalam situasi di mana pemeliharaan atau perbaikan perlu dilakukan pada sistem kelistrikan, memungkinkan sirkuit untuk diputus dan menghilangkan resiko sengatan listrik.
- Menyediakan Fault Clearing: Dalam kasus gangguan atau ‘fault’ dalam sistem, circuit breaker tidak hanya memutus aliran listrik tetapi juga membantu dalam proses ‘fault clearing’. Ini berarti mereka membantu dalam mengisolasi bagian sistem yang bermasalah.
Jadi, tujuan utama dari circuit breaker adalah untuk memastikan keselamatan sistem kelistrikan dan peralatan yang terhubung dengannya, serta mencegah terjadinya situasi yang berpotensi berbahaya seperti kebakaran akibat korsleting atau arus berlebih.
Cara Kerja Circuit Breaker
Ketika terjadi overload atau arus listrik yang melebihi kapasitas, circuit breaker akan memutus sirkuit secara otomatis. Hal ini dilakukan untuk mencegah terjadinya kerusakan lebih lanjut pada perangkat atau bahkan kebakaran. Setelah insiden tersebut diatasi, circuit breaker dapat di-reset (dihidupkan kembali) secara manual atau otomatis, tergantung pada jenisnya.
Klasifikasi Circuit Breaker
Ada berbagai klasifikasi circuit breaker, dan setiap klasifikasi memiliki metode kerja yang sedikit berbeda:
1. Magnetic Circuit Breakers
Pada jenis ini, solenoid (jenis kumparan listrik) di dalam circuit breaker akan memutus sirkuit saat terjadi peningkatan arus secara tiba-tiba atau yang melebihi kapasitas.
2. Thermal Circuit Breakers
Berfungsi dengan memanfaatkan efek termal atau panas dari arus listrik. Ketika terjadi overload, panas yang dihasilkan akan memicu perangkat untuk memutus sirkuit.
3. Thermal-Magnetic Circuit Breakers
Ini adalah gabungan dari dua jenis sebelumnya. Saat terjadi lonjakan arus, solenoid akan memutus sirkuit, sementara dalam kondisi overload, elemen termal akan bekerja.
Jenis-Jenis Circuit Breaker
Berikut adalah beberapa jenis circuit breaker yang paling umum digunakan:
1. Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
MCB umum digunakan dalam instalasi listrik rumahan atau komersial berskala kecil. MCB dapat memutuskan sirkuit saat terjadi over current atau short circuit tanpa memerlukan penggantian komponen, seperti yang diperlukan oleh sekering.
2. Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
MCCB sering digunakan dalam instalasi komersial atau industri. Mereka mirip dengan MCB tetapi memiliki kapasitas penanganan beban yang lebih tinggi. Beberapa MCCB juga memiliki fitur adjustable yang memungkinkan mereka untuk mengatur nilai trip sesuai kebutuhan.
3. Air Circuit Breaker (ACB)
ACB biasanya digunakan dalam aplikasi industri dan utilitas berskala besar, di mana mereka mengendalikan dan melindungi listrik tegangan tinggi. Mereka menggunakan udara sebagai medium pemadaman busur listrik.
4. Vacuum Circuit Breaker (VCB)
Dalam VCB, pemutusan arus terjadi di dalam kamar vakum tertutup. Mereka biasanya digunakan untuk aplikasi tegangan menengah, dan memiliki umur panjang dan pemeliharaan yang minimal.
5. Sulfur Hexafluoride Circuit Breaker (SF6)
SF6 circuit breaker menggunakan gas sulfur hexafluoride sebagai medium pemadaman busur. Mereka biasanya digunakan untuk aplikasi tegangan tinggi, dan memiliki keuntungan seperti kecepatan operasi tinggi dan resistensi terhadap lingkungan yang keras.
6. Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
ELCB adalah jenis circuit breaker khusus yang dirancang untuk mencegah kejadian sengatan listrik dengan memutuskan sirkuit saat mendeteksi kebocoran arus ke tanah.
7. Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) atau Residual Current Device (RCD)
Seperti ELCB, RCCB/RCD dirancang untuk mencegah sengatan listrik. Mereka memonitor arus listrik yang masuk dan keluar dari suatu sirkuit dan memutuskan sirkuit saat mendeteksi adanya perbedaan, yang menunjukkan kebocoran arus.
8. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
GFCI, yang sering digunakan dalam aplikasi rumah tangga, berfungsi mirip dengan RCCB/RCD. Mereka memutuskan sirkuit saat mendeteksi kebocoran arus ke tanah, sering kali dalam hitungan milidetik untuk mencegah sengatan listrik.

Simbol Circuit Breaker
Simbol-simbol dalam rangkaian listrik, termasuk circuit breaker, adalah representasi visual standar yang digunakan dalam diagram dan skema listrik untuk menggambarkan komponen-komponen dan bagaimana mereka terhubung satu sama lain. Mengenali dan memahami simbol-simbol ini sangat penting untuk merencanakan, membaca, dan memecahkan masalah dalam sistem kelistrikan.
Circuit breaker memiliki beberapa simbol, tergantung pada jenisnya dan fungsinya dalam rangkaian. Beberapa simbol umum untuk circuit breaker adalah sebagai berikut:
- Circuit Breaker Umum : Biasanya digambarkan sebagai titik kontak berbentuk huruf T yang dapat dibuka dan ditutup. Jika breaker dalam keadaan “off” atau terbuka, garis akan terputus di titik kontak.
- Circuit Breaker Dua Pola : Digunakan untuk rangkaian listrik dua fasa, simbolnya hampir sama dengan circuit breaker biasa, tetapi dengan dua titik kontak.
- Circuit Breaker Tiga Pola : Digunakan untuk rangkaian listrik tiga fasa, simbolnya memiliki tiga titik kontak.
- Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) : ELCB adalah jenis circuit breaker yang memutus arus ketika mendeteksi arus bocor ke tanah. Simbolnya biasanya adalah simbol circuit breaker biasa dengan tambahan simbol arus bocor (seringkali berbentuk gelombang atau panah melingkar).
- Residual Current Device (RCD) atau Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) : Jenis circuit breaker ini memutus arus saat mendeteksi perbedaan arus antara kawat netral dan kawat hidup. Simbolnya biasanya adalah simbol circuit breaker biasa dengan tambahan simbol arus residual.
Ingatlah bahwa simbol-simbol ini dapat berbeda-beda tergantung pada standar yang digunakan (misalnya, ANSI, IEC, dll.). Oleh karena itu, penting untuk merujuk pada legenda atau daftar simbol yang biasanya disediakan dalam setiap diagram atau skema listrik.
Pentingnya Circuit Breaker
Circuit breaker sangat penting dalam sistem kelistrikan, baik di rumah, gedung, hingga industri. Peran utamanya adalah melindungi perangkat dan sistem listrik dari potensi kerusakan yang dapat disebabkan oleh arus berlebih. Selain itu, circuit breaker juga dapat mencegah terjadinya kebakaran yang bisa disebabkan oleh hubungan singkat atau overload.
Pada akhirnya, pemilihan dan pemasangan circuit breaker yang tepat dan sesuai dengan kebutuhan sistem kelistrikan sangatlah penting. Karena itu, dianjurkan untuk berkonsultasi dengan tenaga pro
Kesimpulannya, pemutus arus adalah langkah keamanan penting yang melindungi sistem kelistrikan dari kerusakan yang disebabkan oleh kelebihan beban dan korsleting. Mereka bekerja dengan secara otomatis mematikan aliran listrik saat mendeteksi adanya masalah, dan dapat disetel ulang setelah tersandung. Dengan berbagai jenis pemutus arus yang tersedia, penting untuk memilih yang tepat untuk kebutuhan spesifik Anda untuk memastikan keamanan sistem kelistrikan Anda.
Mitrainti Sejahtera Eletrindo (Misel) merupakan distributor resmi Omron di Surabaya, kami menyediakan berbagai macam produk Omron yang otentik dengan kualitas terbaik. Segera hubungi kami untuk mempelajari lebih lanjut tentang solusi otomatisasi. Tim kami siap membantu Anda.
Related Posts

Mengenal Temperature Controller dan Cara Kerjanya

Mengenal Definisi, Jenis, dan Fungsi Actuator Dalam Sistem Otomatisasi

Linear dan Rotary Actuator, Apa Saja Perbedaannya?

Mengenal Lebih Dalam: Limit Switch dan Prinsip Kerjanya
- Penyedia Alat -Alat Electrical dan safety
- email: [email protected], WA: 0821-2198-5207
Sign up for Newsletter
Signup for our newsletter to get notified about sales and new products. Add any text here or remove it.

- Pencarian untuk:
- Tentang Kami
- Hubungi Kami
electrical , hioki , kelistrikan , Review Alat
Investigasi penyebab trip pada circuit breaker di lokasi konstruksi dan solusinya.

Trip Pada Circuit Breaker Tidak Hanya Karena Alasan Listrik
Panel listrik berisi Circuit Breaker yang dirancang untuk trip dan menghentikan aliran arus ke sirkuit dan peralatan tertentu jika ada kesalahan atau kelebihan beban pada sistem untuk melindungi sirkuit dari kerusakan. Namun, Circuit Breaker juga diketahui terjadi trip ketika ada titik yang parah atau getaran yang kuat, terutama Circuit Breaker magnetik yang menggabungkan pemicu logam berengsel yang menutup sebagai respons terhadap pergerakan kumparan magnet internal, membuatnya sangat rentan terhadap getaran.

Trip pada Circuit Breaker dapat mengganggu alur kerja, tetapi ini adalah gangguan peringatan yang benar-benar memperingatkan pengguna bahwa beban terlalu banyak untuk ditangani sistem kelistrikan. Lain halnya ketika alasan yang tidak terkait dengan penggunaan listrik menyebabkan trip pada Circuit Breaker dan mengganggu alur kerja, menurunkan produktivitas.
Guncangan tiba-tiba dan getaran kuat sering dialami di lokasi konstruksi yang dioperasikan oleh bor, forklift, truk semen, jackhammers, dan alat berat lainnya. Getaran dari mesin ini dapat menyebabkan Circuit Breaker pada sistem kelistrikan, yang mungkin sudah mendekati kapasitasnya terjadi trip.
Hal pertama yang dilakukan teknisi listrik di lokasi untuk mengatasi Circuit Breaker yang nge-trip adalah selalu mengidentifikasi peralatan yang menyebabkan kelebihan beban, yang lebih mudah disimpulkan dengan meninjau urutan pengoperasian mesin. Namun, mungkin lebih sulit untuk menyimpulkan secara akurat apakah getaran dan gerakan fisik di lokasi adalah penyebab sebenarnya dan peralatan jika ada kesalahan atau kelebihan beban pada sistem untuk melindungi sirkuit dari kerusakan.
Solusi Cepat dan Mudah untuk Memastikan Penyebab Trip

Untuk menemukan penyebab sebenarnya dari trip di lokasi konstruksi, kombinasi peralatan uji yang mencakup Logger (pencatat data), (pengukur getaran), probe diferensial, dan Current Clamp (klem arus) akan membantu dalam memantau karakteristik fisik dan kelistrikan dalam jangka panjang. Ketika trip pada Circuit Breaker , teknisi listrik dapat kembali ke data yang dicatat untuk menganalisis semua sinyal getaran, tegangan dan arus pada sumbu waktu yang sama untuk mengidentifikasi penyebabnya dan mengusulkan pencegahan atau tindakan pencegahan.
Penyetelan Alat Ukur
Ilustrasi di bawah ini menunjukkan bagaimana peralatan pengujian dan pengukuran HIOKI, yang dipasangkan dengan Vibration meter yang tersedia , dapat disiapkan untuk aplikasi ini:
- HIOKI LR8410 Wireless Logging Station + Hioki LR8510 Wireless Voltage / Temp dari jarak jauh (secara remote) menangkap data tegangan, arus, dan getaran sekaligus melalui Bluetooth
- 3 unit HIOKI LR8513 Wireless Clamp Logger yang dipasangkan dengan 2 x CT6500 Clamp On Sensor masing-masing mengukur 6 saluran arus di panel listrik
- P9000-02 Diferensial Probe x 3 mengukur 3 fase tegangan pada panel
- Vibration meter yang tersedia dipasaran dengan keluaran analog, contoh disini seperti Showasokki Model-2502 atau 25908

Tindakan Penanggulangan untuk Mengatasi Trip Secara Tidak Sengaja
Dengan mengukur karakteristik arus, tegangan dan getaran pada panel listrik secara bersamaan, teknisi dapat mengisolasi penyebab utama dari trip dengan cepat dan mudah. Alat praktis seperti probe diferensial dan clamp sensor memungkinkan Anda membuat sambungan yang aman ke kabel pada panel listrik, dan semua data yang dikumpulkan di Hioki LR8410 Wireless Logging Station dapat dianalisis sebagai satu kumpulan data.
Kemampuan menghubungkan Circuit Breaker yang nge-trip dengan sumber getaran dan guncangan tertentu yang dibuat oleh peralatan konstruksi dapat membantu manajer fasilitas merencanakan penggunaan peralatan dengan cara yang lebih efisien untuk menghindari gangguan pada catu daya dan pada akhirnya, waktu henti produksi.
Oke, cukup sampai disini artikel tentang masalah trip di lokasi konstruksi. Jika ada yang kalian ingin tanyakan lebih lanjut tentang artikel ini atau alat-alat logger Hioki terkait jangan sungkan untuk bertanya melalui komentar dibawah, maupun langsung melalui Whatsapp kami dipojok kanan bawah. Jangan lupa untuk share artikel ini di medsos kalian jika artikel ini bermanfaat. Sekian dan terima kasih 🙂
Sumber: https://www.hioki.com/en/products/introduction/detail/?dbid=113474
Tinggalkan Balasan Batalkan balasan
Alamat email Anda tidak akan dipublikasikan. Ruas yang wajib ditandai *
Simpan nama, email, dan situs web saya pada peramban ini untuk komentar saya berikutnya.
Nama pengguna atau alamat email *
Kata sandi *
Ingat saya Masuk
Kehilangan kata sandi?

- [ 22/02/2024 ] Pengertian IoT (Internet of Things) dan Konsep Dasarnya Perangkat Elektronika
- [ 07/02/2024 ] Pengertian NPU (Neural Processing Unit) dan Fungsinya Komponen Elektronika
- [ 12/01/2024 ] Pengertian BIOS dan Fungsi BIOS Komponen Elektronika
- [ 14/12/2023 ] Pengertian Data dalam Statistik dan Jenis-jenis Data Ilmu Statistika
- [ 13/11/2023 ] Cara Kerja Barcode Scanner dan Komponen Utamanya Perangkat Elektronika
Pengertian MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) dan Prinsip kerjanya

Pengertian MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) dan Prinsip kerjanya – MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) atau Miniatur Pemutus Sirkuit adalah sebuah perangkat elektromekanikal yang berfungsi sebagai pelindung rangkaian listrik dari arus yang berlebihan. Dengan kata lain, MCB dapat memutuskan arus listrik secara otomatis ketika arus listrik yang melewati MCB tesebut melebihi nilai yang ditentukan. Namun saat arus dalam kondisi normal, MCB dapat berfungsi sebagai saklar yang bisa menghubungkan atau memutuskan arus listrik secara manual.
MCB pada dasarnya memiliki fungsi yang hampir sama dengan Sekering (FUSE) yaitu memutuskan aliran arus listrik rangkaian ketika terjadi gangguan kelebihan arus. Terjadinya kelebihan arus listrik ini dapat dikarenakan adanya hubung singkat (Short Circuit) ataupun adanya beban lebih (Overload). Namun MCB dapat di-ON-kan kembali ketika rangkaian listrik sudah normal, sedangkan Fuse/Sekering yang terputus akibat gangguan kelebihan arus tersebut tidak dapat digunakan lagi.
Prinsip kerja MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
Pada kondisi Normal, MCB berfungsi sebagai sakelar manual yang dapat menghubungkan (ON) dan memutuskan (OFF) arus listrik. Pada saat terjadi Kelebihan Beban (Overload) ataupun Hubung Singkat Rangkaian (Short Circuit), MCB akan beroperasi secara otomatis dengan memutuskan arus listrik yang melewatinya. Secara visual, kita dapat melihat perpindahan Knob atau tombol dari kondisi ON menjadi kondisi OFF. Pengoperasian otomatis ini dilakukan dengan dua cara seperti yang terlihat pada gambar dibawah ini yaitu dengan cara Magnetic Tripping (Pemutusan hubungan arus listrik secara Magnetik) dan Thermal Tripping (Pemutusan hubungan arus listrik secara Thermal/Suhu).
a. Thermal Tripping (Pemutusan Hubungan arus listrik dengan Suhu Tinggi)
Pada saat kondisi Overload (Kelebihan Beban), Arus yang mengalir melalui Bimetal menyebabkan suhu Bimetal itu sendiri menjadi tinggi. Suhu panas tersebut mengakibatkan Bimetal melengkung sehingga memutuskan kontak MCB (Trip).
b. Magnetic Tripping (Pemutusan Hubungan arus listrik secara Magnetik)
Ketika terjadi Hubung Singkat Rangkaian (Short Circuit) secara mendadak ataupun Kelebihan Beban yang sangat tinggi (Heavy Overload), Magnetic Trippping atau pemutusan hubungan arus listrik secara Magnetik akan diberlakukan. Pada saat terjadi hubungan singkat ataupun kelebihan beban berat, Medan magnet pada Solenoid MCB akan menarik Latch (palang) sehingga memutuskan kontak MCB (Trip).
Sebagian besar MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) yang digunakan saat ini menggunakan dua mekanisme pemutusan hubungan arus listrik ini (Thermal Tripping dan Magneting Tripping).
Jenis-jenis MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
MCB atau Miniatur Pemutus Sirkuit ini dapat diklasifikasikan menjadi tiga jenis utama berdasarkan karakteristik pemutusan sirkuitnya. Tiga jenis utama tersebut adalah MCB Tipe B, MCB Tipe C dan MCB Tipe D.
1. MCB Tipe B
MCB Tipe B adalah tipe MCB yang akan trip jika arus beban lebih besar 3 sampai 5 kali dari arus maksimum yang tertulis pada MCB (arus nominal MCB). MCB Tipe B ini umumnya digunakan pada instalasi listrik di perumahan ataupun di industri ringan.
2. MCB Tipe C
MCB Tipe C adalah tipe MCB yang akan trip jika arus beban lebih besar 5 sampai 10 kali dari arus maksimum yang tertulis pada MCB (arus nominal MCB). MCB Tipe C ini biasanya digunakan pada Industri yang memerlukan arus yang lebih tinggi seperti pada lampu penerangan gedung dan motor-motor kecil.
3. MCB Tipe D
MCB Tipe C adalah tipe MCB yang akan trip jika arus beban lebih besar dari 10 hingga 25 kali dari arus maksimum yang tertulis pada MCB (arus nominal MCB). MCB Tipe C ini biasanya digunakan pada peralatan listrik yang menghasilkan lonjakan arus tinggi seperti Mesin Sinar X (X-Ray), Mesin Las, Motor-motor Besar dan Mesin-mesin produksi lainnya.
Arus Nominal MCB yang umum adalah 6A, 10A, 13A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 50A, 63A, 80A, 100A dan 125A.
- Daya Listrik
Related Articles

Cara Menghitung Daya Listrik yang diperlukan Rumah
Cara Menghitung Daya Listrik yang diperlukan Rumah – Setiap rumah yang sudah dialiri listrik pasti dilengkapi dengan Meter Listrik dan MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) yang dipasang oleh PLN. Fungsi Meter Listrik tentunya adalah mengukur seberapa besar […]
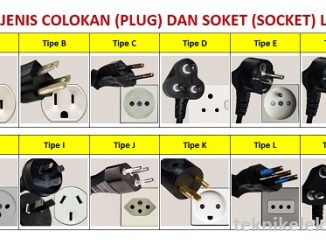
Jenis-jenis Colokan Listrik dan Soket Listrik
Jenis-jenis Colokan Listrik dan Soket Listrik – Untuk menghubungkan peralatan listrik dengan sumber daya listrik AC (arus bolak-balik), diperlukan suatu komponen listrik yang biasanya kita sebut dengan Colokan Listrik atau dalam bahasa Inggris disebut dengan […]
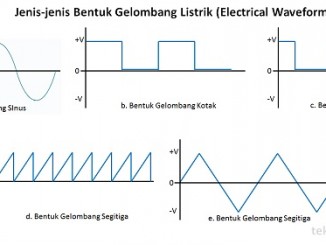
Pengertian Electrical Waveform (Bentuk Gelombang Listrik) dan Jenis-jenisnya
Pengertian Electrical Waveform (Bentuk Gelombang Listrik) dan Jenis-jenisnya – Electrical Waveform atau dalam bahasa Indonesia disebut dengan Bentuk Gelombang Listrik merupakan bagian dari Gelombang Elektromagnetik yang tidak memiliki bentuk fisik. Untuk mempermudah melihat bentuk gelombang tersebut, […]
Copyright 2022 Teknik Elektronika
Minggu, Desember 25
Perbedaan rip current dan longshore current.
Share with your friends
Bimbingan OSN Free

Join My Class

Postingan Terpopuler
- Pembahasan Kunci Soal OSN-K Geografi 2023 No 1-5
- Pembahasan Kunci Simulasi OSN-K Kebumian 2024 (Soal 2023) No 1-5
- Pembahasan Kunci Simulasi OSN-K Kebumian 2024 (Soal 2023) No 91-100
- Pembahasan Kunci Simulasi OSN-K Kebumian 2024 (Soal 2023) No 81-90
- Pembahasan Kunci Soal OSN-K Geografi 2023 No 21-25

- Mode Terang
- Gabung Kompas.com+
- Konten yang disimpan
- Konten yang disukai
- Berikan Masukanmu

- Megapolitan
- Surat Pembaca
- Kilas Daerah
- Kilas Korporasi
- Kilas Kementerian
- Sorot Politik
- Kilas Badan Negara
- Kelana Indonesia
- Kalbe Health Corner
- Kilas Parlemen
- Konsultasi Hukum
- Infrastructure
- Apps & OS
- Tech Innovation
- Kilas Internet
- Elektrifikasi
- Timnas Indonesia
- Liga Indonesia
- Liga Italia
- Liga Champions
- Liga Inggris
- Liga Spanyol
- Internasional
- Sadar Stunting
- Spend Smart
- Smartpreneur
- Kilas Badan
- Kilas Transportasi
- Kilas Fintech
- Kilas Perbankan
- Tanya Pajak
- Sorot Properti
- Tips Kuliner
- Tempat Makan
- Panduan Kuliner Yogyakarta
- Beranda UMKM
- Jagoan Lokal
- Perguruan Tinggi
- Pendidikan Khusus
- Kilas Pendidikan
- Jalan Jalan
- Travel Tips
- Hotel Story
- Travel Update
- Nawa Cahaya
- Ohayo Jepang
- Kehidupan sehat dan sejahtera
- Air bersih dan sanitasi layak
- Pendidikan Berkualitas
- Energi Bersih dan Terjangkau
- Penanganan Perubahan Iklim
- Ekosistem Lautan
- Ekosistem Daratan
- Tanpa Kemiskinan
- Tanpa Kelaparan
- Kesetaraan Gender
- Pekerjaan Layak dan Pertumbuhan ekonomi
- Industri, Inovasi & Infrastruktur
- Berkurangnya Kesenjangan
- Kota & Pemukiman yang Berkelanjutan
- Konsumsi & Produksi yang bertanggungjawab

Arti dan Tanda Munculnya Rip Current, Arus Balik Laut yang Mematikan
Topik untukmu:, kompas.com travel travel tips, wasti samaria simangunsong ,, ni nyoman wira widyanti.
Tim Redaksi
Wasti Samaria Simangunsong
Penulis ni nyoman wira widyanti.
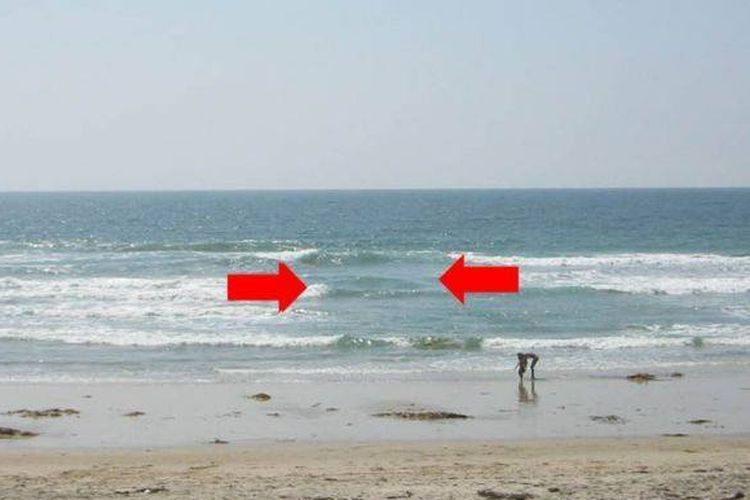

Daryono menjelaskan bahwa rip current rawan terjadi di permukaan pantai yang berbentuk teluk-teluk kecil, atau bentuk pantai yang membusur seperti bulan sabit.
Di sisi lain, tidak ada waktu pasti terkait kapan kemunculan rip current , sebab bisa terjadi sewaktu-waktu, selama ada angin topan yang membangkitkan ombak.
- 6 Tips Hindari Klitih Saat Wisata di Yogyakarta
- 4 Tips Aman Bawa Uang Tunai Saat Liburan
- 6 Tips Cegah Tersesat Saat Mendaki Gunung dan Kesalahan Fatal yang Sering Dilakukan
Kendati demikian, tanda kemunculan rip current bisa dikenali, misalnya saat permukaan laut cenderung lebih tenang daripada gelombang di sekitarnya yang menuju pantai.
"Perhatikan buih ombak yang datang, bila ada celah di antara buih-buih gelombang itu, maka kemungkinan di sekitar area itu sedang terjadi rip current atau arus pecah," ujarnya.
Kemudian untuk ciri lainnya, yakni saat warna air laut cenderung lebih keruh dibanding sekitarnya.
Tag rip current adalah fenomena rip current antisipasi rip current apa itu rip current mengenal rip current rip current atau arus laut terjadinya rip current bagaimana proses terjadinya rip current ciri pantai yang rawan rip current Mengenal rip current, arus balik laut yang mematikan tanda kemunculan rip current tanda rip current tanda awal kemunculan rip current Apa yang dimaksud dengan rip current? Apa itu rip current dan bagaimana proses terjadinya? Bagaimana rip current terbentuk? penyebab rip current adalah rip current di indonesia tanda rip current

10 Tips Traveling saat Cuaca Panas agar Tidak Tepar

9 Tips Semangat Kerja Setelah Libur Panjang Lebaran 2022

6 Tips Wisata Naik Motor Jarak Jauh, Jangan Begadang

3 Tips Dapat Hotel Murah Ala Manajer Pegipegi, Tahu Waktu Terbaik

10 Tips Aman Mendaki Gunung Rinjani yang Buka Lagi 16 Maret 2022

7 Tips Aman Wisata Air Terjun Saat Musim Hujan, Perhatikan Hal Ini

6 Tips Liburan di Musim Hujan agar Tetap Nyaman

10 Tips Hemat Saat Traveling Bareng Grup, Anti-boros


TTS Eps 135: Serba Serbi Ramadhan

TTS - Jenis-jenis Keju

TTS - Tokoh-tokoh Berpengaruh di Dunia

TTS - Sambut Pemilu 2024

TTS - Eps 131 - Acakata: Hewan Melata!

Games Permainan Kata Bahasa Indonesia

TTS - Serba serbi Demokrasi

TTS Eps 130 - Tebak-tebakan Garing

TTS - Musik Yang Paling Mengguncang
Berita terkait.

Terkini Lainnya

Alasan Tiket Pesawat Domestik Mahal Versi Pengamat, Ada Banyak Faktor

Jumlah Pesawat Indonesia Masih Belum Bertambah sejak Pandemi Covid-19

Sandiaga Optimistis Kenaikan PPN 12 Persen Tidak Timbulkan Gejolak

Hanya 40 Persen Turis Asing di Bali yang Bayar Retribusi Rp 150.000

Ingat, Tiket Kapal Ferry ASDP Sudah Tidak Bisa Dibeli di Pelabuhan

Ngabuburit Unik, Naik Kereta Majapahit Kelas Ekonomi Rasa Eksekutif dari Malang

15 Kapal Pesiar dari Luar Negeri Angkut 11.912 Pengunjung ke TN Komodo, Januari-Maret 2024

4 Hotel Dekat Umbul Brintik, Harga mulai Rp 200.000-an Per Malam

Daftar Promo THR dari Tiket.com, dari Transportasi sampai Akomodasi

Rute Menuju ke Umbul Brintik, 15 Menit dari Alun-alun Klaten

Syarat agar Anak Bisa Naik Pesawat Tanpa Orangtua

Harga Tiket Masuk di Umbul Brintik, Wisata Terapi Kesehatan

Daftar Tempat Termahal dan Termurah di Dunia untuk Wisata 2024

Aktivitas yang Bisa Dilakukan di Umbul Brintik, Ada Kolam Terapi

Kenapa Desain Jendela Pesawat Semua Sama?
3 pemandian air panas di pacet mojokerto untuk healing, sumber nyolo, pemandian air di malang konon bikin awet muda, pesawat tambahan ke indonesia timur mulai terbang april 2024, jumlah penumpang di bandara internasional komodo cukup banyak pada "low season" ramadhan, now trending.

Peran Jokowi Susun Kabinet Prabowo-Gibran

Menhan AS Bicara ke Menhan Israel: Jumlah Korban Jiwa di Gaza Terlalu Banyak

Gerindra: Prabowo dan Megawati Bertemu dalam Waktu Dekat

Jokowi Bangga Lihat Serangan Timnas Saat Kalahkan Vietnam

Hasil Spanyol Vs Brasil 3-3, Berhias Gol Titisan Ronaldo

Nasib Tragis Lansia Asal Cimahi, Curi Mi Instan lalu Dikeroyok hingga Tewas dan Mayatnya Dibuang di Karawang

Kubu Anies dan Ganjar Minta Prabowo-Gibran Didiskualifikasi, TKN: 96 Juta Orang Pilih 02, Enggak Dihargai?

Prakiraan BMKG: Wilayah yang Berpotensi Hujan Lebat, Petir, dan Angin Kencang pada 27-28 Maret 2024
Mungkin anda melewatkan ini.

Waspadai Rip Current yang Mematikan Saat Liburan ke Pantai

Ajaibnya Air Terjun Pangkadari di Manggarai NTT, Mirip Sungai di Inggris

Di Depan PBB, Menparekraf Sebut Indonesia Jadi Acuan Dunia dalam Kebangkitan Pariwisata

Wisawatan Minta Pemerintah Aceh Perbaiki Akses Jembatan Gunung Salak, Aceh Utara

Kabar Baik Sandiaga Uno dari Singapura, Akan Tambah Penerbangan
- Entertainment
- Pesona Indonesia
- Artikel Terpopuler
- Artikel Terkini
- Topik Pilihan
- Artikel Headline
- Harian KOMPAS
- Kompasiana.com
- Pasangiklan.com
- Gramedia.com
- Gramedia Digital
- Gridoto.com
- Bolasport.com
- Kontan.co.id
- Kabar Palmerah
- Kebijakan Data Pribadi
- Pedoman Media Siber
Copyright 2008 - 2023 PT. Kompas Cyber Media (Kompas Gramedia Digital Group). All Rights Reserved.

Segera lengkapi data dirimu untuk ikutan program #JernihBerkomentar .

What Is Overcurrent? (Causes, Effects, and Protection)
Overcurrent is a destructive fault that can damage small, as well as, large motors, electric devices, and home appliances.
In this article, I will discuss the current increase (overcurrent) and answer the most important questions about it. let’s get started.
Table of Contents
what is overcurrent?
Overcurrent refers to an electrical condition in a circuit where the current flowing through the conductors exceeds the rated or designed current-carrying capacity of the components, such as wires, fuses, circuit breakers, and other protective devices.
Overcurrent can occur due to various factors and can have different consequences, including overheating, component damage, fires, or circuit malfunction.
Overcurrent example
A clear overcurrent example is, when a motor with a rated current of 35A, you can find rated current on the motor nameplate, draws 55A for any reason, it can be a mechanical loading as I discussed in the article Motor Overcurrent , this motor is an overcurrent situation.
Another example is if a current of 167A passes through a cable with a current ampacity of 135A, this cable is over the current situation.
In general, any electrical equipment has a rated current, whenever the current exceeds this value, it’s an overcurrent situation.
Overcurrent effects

Uncontrolled electric overcurrent leads to excessive heat generation and can damage or burn equipment.
A circuit wiring overheats when an overcurrent occurs. There is a possibility that the insulation could melt, and fire can break out as a result.
Circuit overload causes the breaker to trip, opening up and shutting off the power supply. The overload could cause the wiring to overheat and melt, causing a short circuit and leading to a house fire.
In addition to the heat loss from increasing current, the rising current can also:
- Damage the circuit
- Burn resistors and electronic components
- Damage to electric equipment and home appliances
- And even cause fire to break out around the circuit.
What causes overcurrent in a circuit?
Overcurrent in electrical circuits can occur for various reasons, and it is important to identify and address the underlying causes to maintain the safety and proper functioning of electrical systems. Here are some common causes of overcurrent:
Excessive Load : One of the most common causes of overcurrent is simply overloading a circuit. This happens when the total electrical load connected to a circuit exceeds its designed capacity. Examples include plugging too many appliances into a single outlet or running too many devices on a circuit.
Short Circuits : A short circuit occurs when there is a low-resistance path between two conductors, causing a rapid and excessive flow of current. This can result from damaged insulation, exposed wires, or loose connections. Short circuits are particularly dangerous and can lead to electrical fires.
Ground Faults : Ground faults occur when an unintended electrical connection is established between a live conductor and the ground (earth). This can happen due to damaged insulation or faulty equipment. Ground faults can lead to overcurrent situations and pose safety hazards.
Equipment Malfunctions : Malfunctions within electrical equipment, such as motors, transformers, and appliances, can cause overcurrent. This can be due to internal faults, mechanical issues, or electrical problems within the equipment itself.
Power Surges : Sudden and temporary increases in voltage, known as power surges or voltage spikes, can cause overcurrent in circuits. These surges can result from lightning strikes, utility grid fluctuations, or switching events.
Inrush Current : Some devices, particularly motors and transformers, experience high inrush currents when they are initially energized. Inrush current can temporarily exceed the normal operating current and may trip protective devices if not accounted for in the design.
Circuit Imbalances : In three-phase electrical systems, imbalances in current between the phases can lead to overcurrent in one or more phases. This can occur due to unequal loads or issues with the supply system.
Faulty Wiring and Connections : Poorly installed or deteriorated wiring and connections can increase electrical resistance, leading to overheating and overcurrent. This can be a result of corrosion, loose connections, or inadequate wire size.
Environmental Factors : Environmental factors, such as extreme temperatures, humidity, or exposure to corrosive substances, can degrade wiring and insulation over time, potentially causing overcurrent issues.
Circuit Design Flaws : Errors or flaws in the initial design of electrical circuits, including the selection of protective devices and wire sizes, can lead to overcurrent problems if the circuit is not properly matched to its intended use.
To prevent overcurrent and its associated risks, electrical systems are designed with protective measures, including circuit breakers, fuses, and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs).
These devices are selected based on the expected load and potential risks associated with the circuit.
Regular maintenance and inspections are also essential to identify and address any issues that may lead to overcurrent.
How can you prevent over-current?
Electrical circuits have circuit breakers , surge protectors, and electrical fuses to prevent potential disasters.
The concept of preventing a power outage due to an overcurrent is quite straightforward: you should avoid overloading a circuit in the first place.
There are typically separate circuits for each room of the house, with heavy-duty appliances like an electric dryer or oven requiring a separate dedicated line.
In order to prevent your circuits from overcurrent, let us take a look at how you can do it.
Your circuit load should be calculated
For the workplace, never run any power tool or electrical equipment before you check its power rating, and verify the power source is suitable for it.
Only authorized persons are allowed to add new loads to any power source.
All authorized departments should participate when choosing new equipment. For example, when choosing a new pump, electrical and mechanical engineers should cooperate to make sure the pump and the motor ratings are the same, to prevent motor overloading.
For home circuits, the majority of circuits are rated for 15 to 20 amps, and if you understand how much current your lights and appliances use, you can roughly estimate how much current is safe to put in.
It may be necessary to move the light strand to another room if your load is approaching 80% before plugging in the next strand to avoid overcurrent.
- Never use extension cords without asking an authorized electrician.
- Never overload the outlet with a lot of appliances.
- Ask for advice before connecting any new appliance.
- If you buy a new house, hire an authorized electrician to check its circuits and wiring.
Use large appliances with caution
When searching for a location to plug your lights in, it’s a good idea to stay away from spaces that already include a lot of equipment, such as the kitchen.
To make more current available for those priceless decorations, you may disconnect any equipment or devices you don’t intend to use to avoid overcurrent.
Make LED lighting a priority
Investing in LED lights is one method to make your current setup considerably more festive.
LED lights consume significantly less power than conventional bulbs, saving you money on your electricity bill and easing the pressure on your wiring to avoid overcurrent.
Use Protection devices
The built-in defense against overcurrent in your home is the circuit breaker. They are housed in your electrical panels and turn off electricity to particular areas of the structure if they detect erratic electrical currents.
You may protect yourself against short circuits, when necessary, by doing routine circuit breaker maintenance to make sure it is operating correctly.
Why does the current increase when the load increases?
Each load requires its own current, the more connected loads, the higher the current they draw. To explain it to you, suppose the electrical circuit is a pipeline, the loads are faucets, and the more faucets you open the more water you draw.
In the case of electrical Motors
In case we have a motor (the load), this motor requires electric current depending on its power rating.
If the motor starts with no load, it draws a no-load current, it’s smaller than the full-load current.
By increasing the mechanical load, the motor needs to provide more torque to overcome this load, and of course, it will draw more current .
In case of home loads
In case of connecting more loads on home or a building outlet. Electrical loads are typically connected in parallel.
If you have a load raised, it means the added load is connected in parallel with the existing load.
Parallel connections always decrease the equivalent impedance. Therefore, the current increases.
When loads are connected in parallel, each load draws its own currency from the circuit according to the requirements of that load. Therefore, the current increases when the load is increased.
How can I tell if my electrical panel is overloaded?
If your panel main circuit breaker trips , and when you turn it on again it works for a while and then trips again, it’s a clear sign of a possible overloaded panel.
But, keep in mind that there are other reasons for circuit breaker tripping, you can hire an electrician to measure the currents of the panel, check the man circuit breaker rating, and make sure it’s overloaded.
If you know how to use a current clamp, you can measure the current by it, check the circuit breaker rating, and make sure the CB rating is greater than the measured one.
Make sure to switch on all loads during the measuring process, this is the only way to have a clear idea about the panel load.
One more thing, an electrical engineer can calculate the panel loads, check the circuit breaker’s ratings, and make sure it’s not overloaded.
It’s crucial to watch out for clues that your electrical panel could be generating an excessively high level of electricity when you start putting in more and more appliances for any reason.
To assist you in recognizing when this could be happening, we’ve listed a few telling indications.
Panel Overheating, the overheating that might result from excessive current flowing through your breakers or cables is also a sign of an overloaded panel.
In my workplace, we use thermal imaging to check that panels are not overloaded.
What happens when an electric current increases?
When the electric current increases, the following points can happen:
In the case of electric motors
The higher the current, the higher it temperature rise. This temperature increase can cause the motor insulation to fail, and lead to an internal short circuit between windings and complete damage if the protection device fails to trip the circuit.
In the case of home wiring
Excessive current trips the circuit breaker of your home panel. Of course, it will increase the temperature of the wiring, the panel, and the circuit breaker.
If the increased current is caused by an appliance, the appliance will get damaged if the CB fails to trip.
Ready to dive in? Check out my comprehensive article Avoiding Overcurrent Situations: Tips to Keep Your Circuits and Devices Safe now
In the case of electric cables
Cable temperature rise can cause the insulation to get damaged. When the insulation gets damaged, the live phase and the neutral or another phase will get in touch and a short circuit happens.
In the case of an electric generator

The generator will heat up, its winding insulation will melt and a short circuit occur between its phases. Yep, it’s complete damage.
We can say, that an overcurrent could cause the circuit wiring, as well as the electrical equipment to overheat. This could lead to, equipment damage or melting of the insulation and a possible fire.
The heat loss from increasing current can cause damage to the circuit, burn resistors, damage electrical equipment and home appliances, or even cause fire to the surroundings.
Circuits are designed to work with a particular voltage and resistance . If the excessive current flows in a conductor , the results will be very bad if the protection device fails to trip the circuit.
Why does the current increase in temperature?
From a physics point of view.
Electric current is the flow of electrons in a conductor. As the current increases, the electron flow will increase.
Due to the increased flow of electrons, the collision of electrons will intensify generating heat energy and power losses. This is why the electric current increases the temperature.
From an electricity point of view,
any conductor has a resistance, when current flows through the conductor it faces its resistance.
From the power equation we have, Power = I 2 *R, which means that increasing ‘I’ and the ‘R’ increases the power loss in the shape of heat and raises the temperature.
The temperature rise beyond the allowed limits on any device is directly linked to the fact that you have exceeded power consumption higher than the rated value.
Any equipment is designed to meet a specific power consumption, if the limit is exceeded its power, gets heated.
ِAny electric current value causes produce temperature, the more current the higher the temperature rise.
Starting from the equipment-rated current to the overcurrent and ending at the short circuit current. All these currents produce heat, and the value of the temperature rise differs from one currency to another.
Read also my article about Electric transformer temperature rise . and the other one , Motor temperature rise causes and limits.
Why does an increase in current increase power losses?
Power loss is a result of the conductor resistance that the current faces while passing through the conductor.
As you can see, from the below power loss equation, the power is proportional to the square of the current. So, if the current increases, the power losses will increase much faster.
As we know, Power = I 2 × R, This means, the higher the current the higher energy loss in the conductor in the form of heat . As I mentioned above.
The increase of power loss in the conductor increases the conductor’s temperature. We don’t have an ideal conductor with zero resistance, if we do its power loss will be zero.
What is Overcurrent Protection?
Overcurrent protection is a fundamental aspect of electrical safety that involves the use of devices and measures to detect and limit excessive electrical current in a circuit.
The primary purpose of overcurrent protection is to prevent electrical circuits and equipment from being subjected to current levels that exceed their designed capacity, which can lead to overheating, damage, fires, and safety hazards.
Overcurrent protection is achieved through various protective devices and strategies, including:
Fuses : Fuses are passive overcurrent protection devices that consist of a wire or element that melts or breaks when subjected to excessive current. When a circuit experiences an overcurrent condition, the fuse element melts, opening the circuit and disconnecting power. Fuses are available in various ratings to match the current-carrying capacity of the protected circuit.
Circuit Breakers : Circuit breakers are automatic overcurrent protection devices that can be reset after they trip. They consist of a switch-like mechanism that opens the circuit when an overcurrent condition is detected. Circuit breakers are available in different types, including thermal-magnetic and electronic, and they can be designed to provide protection against short circuits, overloads, or both.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) : GFCIs are specialized overcurrent protection devices used to prevent electrical shock hazards. They detect imbalances in current flow between the hot and neutral conductors and trip the circuit if a ground fault is detected. GFCIs are commonly used in locations where electrical devices may come into contact with water, such as bathrooms and kitchens.
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) : AFCIs are designed to detect and interrupt arcing faults, which can lead to electrical fires. They monitor the circuit for abnormal arcing conditions and trip the circuit if such conditions are detected, reducing the risk of fire.
Motor Overload Relays : These are used to protect electric motors from overcurrent conditions that can occur during motor startup or due to mechanical problems. Overload relays monitor the motor’s current and trip the circuit if the current exceeds a specified threshold for an extended period.
Current Limiting Devices : These devices are designed to limit the magnitude of fault currents in a circuit, reducing the potential damage caused by short circuits and overcurrent events.
Selective Coordination : In complex electrical systems, selective coordination is a strategy that involves coordinating the settings of protective devices (e.g., circuit breakers and fuses) to ensure that only the device closest to the fault opens, minimizing downtime and disruptions in the event of an overcurrent condition.
Proper Circuit Design : Ensuring that circuits are appropriately designed with proper wire sizes, protection devices, and load considerations is essential for overcurrent protection. Designing circuits to match the expected loads and operating conditions helps prevent overcurrent situations.
Overcurrent protection devices and strategies are critical for electrical safety, as they help prevent electrical fires, equipment damage, and electrical hazards.
The selection and installation of the appropriate protective devices depend on the specific requirements and characteristics of the electrical circuits and equipment being protected.
Over-current protection importance
In order to keep yourself and others safe from many risky situations, overcurrent protection is important.
Every electric circuit must have circuit overcurrent protection. If the current levels of an electric circuit exceed the safe limits for which they were built, the circuit may be harmed or even destroyed.
Circuit wires may become too hot if there is an overcurrent. In turn, fire and insulation melting might result due to this situation.
There may be serious consequences if a circuit is not equipped with overcurrent protection. An electrical shock, fire, or electrocution can result from overcurrent, which can destroy unprotected electronic devices and cause human injury and fatality.
The purpose of an overcurrent protection device is to protect against dangerously high temperatures in conductors or their insulation . It is crucial to match the conductor size and current rating of the protection device.
We can say, that overcurrent protection is essential because it protects humans and equipment as well against destructive and fatal accidents.
Is current protection and surge protection the same?
No, it’s different; overcurrent protection protects the excessive current flow in the circuit, and surge protection protects against excessive voltage or spikes of voltage to the circuit.
Overcurrent protection is the protection against excessive currents beyond the acceptable current rating of the equipment. It generally operates instantly.
Magnetic circuit breakers, fuses , and overcurrent relays commonly provide overcurrent protection.
High and low-voltage power distribution systems, as well as control systems, frequently incorporate overcurrent protectors.
On the other hand, Surge protection protects equipment against power surges and voltage spikes while blocking voltage over a safe threshold.
When a threshold is an overrated voltage, a surge protector shorts to ground voltage or blocks the voltage.
Low-voltage power distribution systems frequently utilize SPD, sometimes referred to as surge protector, lightning protector, and lightning arrester, as a lightning protection device.
It is often linked to the line in parallel or series to discharge the wave.
Difference Between Overcurrent and Overload Protection
Overloading equipment causes it to draw an overcurrent. We, electrical engineers, usually use the word overload in case the equipment gets more load, electrical or mechanical, than it’s designed to handle.
For example, a motor is overloaded means its mechanical load is greater than the motor-rated power so, it draws an overcurrent.
Another example is when a cable is overloaded, it means the cable load, electrical load, draws current greater than the cable current carrying capacity, so the cable has over current passing through it.
Overcurrent protection is the protection against excessive currents beyond the acceptable designed current rating of equipment or an electric device . Short circuits, arc faults,s, and earth faults are overcurrent types.
On the other hand, overload protection is protection against overloading equipment that causes it to face an overcurrent situation, and would cause the equipment to overheat.
A well-designed circuit and periodical inspection of loads can help prevent overload
Hence, an overload is also some kind of overcurrent. Slow-acting fuses and overload relays are commonly used for overload protection devices.
A thermal-magnetic CB as well as the dual element fuse has both thermal and magnetic elements which means that it could provide both overcurrent and overload protection.
How does overcurrent protection work?
According to the circuit current rating of equipment or circuit, overcurrent protection devices have a current rating.
In case of any fault, when the circuit current exceeds the rating current of protection devices, it cuts the circuit’s supply, by the thermal or magnetic effect of the overcurrent. As you know, current has both thermal effects, and if the current passes through a coil it will produce a magnetic effect.
The thermal effect can melt a fuse to protect the circuit and can trigger the mechanical mechanism of a circuit breaker to trip the circuit.
The magnetic effect also can trigger the circuit breaker faster than the thermal effect. By using this working principle, overcurrent protection devices protect equipment or circuits.
The thermal effect is used for overload protection, lower values of overcurrent, while the magnetic effect, the faster, is used for protection against the short circuit over currents.
Fuse and circuit breakers are overcurrent protection devices that contain time/current characteristics (TCC) that specify how long it takes to clear the fault for a specific value of fault current. The higher the overcurrent value, the faster the tripping time of the circuit breaker.
The fuse’s metal strip or wire melts when too much current flows across it, cutting off the current flow. Fuses are sacrificial components, which means an overcurrent destroys them.
On the other hand, circuit breakers turn off when they face any fault or a short circuit, unlike fuses, which melt to break the circuit. Circuit breakers can therefore be reused.
Can overcurrent damage an overcurrent protection device?
Yes, overcurrent can potentially damage an overcurrent protection device, such as a fuse or a circuit breaker, if the device is subjected to current levels exceeding its rated capacity for an extended period.
While these protection devices are designed to withstand short-term overcurrent conditions and perform their protective function, they are not invulnerable and can be damaged under certain circumstances:
- Sustained Overloads : If a circuit experiences a sustained overload, where the current exceeds the device’s rated capacity for an extended period, it can cause overheating of the protection device. Prolonged overheating may damage the device, affecting its ability to function properly in the future. For example, a fuse may blow or a circuit breaker may trip due to overheating.
- Fault Currents : In the case of a short circuit or a severe fault current event, the magnitude of the current can be extremely high. While protection devices are designed to handle these situations and quickly interrupt the fault current, the stress from such high current levels can potentially damage the internal components of the device.
- Inadequate Device Rating : Using a protection device with an inadequate current rating for the circuit it is intended to protect can result in the device being damaged during an overcurrent event. For instance, if a lower-rated fuse or circuit breaker is used in a circuit with a consistently high current load, it may trip or blow repeatedly, leading to damage.
- Device Wear and Tear : Like any mechanical or electrical component, overcurrent protection devices can experience wear and tear over time. Frequent tripping, exposure to adverse environmental conditions, or improper handling can contribute to device degradation and reduce their effectiveness.
It’s essential to select protection devices with appropriate current ratings for the circuits they are intended to protect.
Regular maintenance and inspection of protection devices are also important to ensure their continued reliability and performance.
Damaged or malfunctioning protection devices should be replaced promptly to maintain electrical safety and prevent potential hazards.
Can over-current damage a circuit breaker?
Yes, overcurrent can potentially damage a circuit breaker, but circuit breakers are designed to withstand and interrupt overcurrent conditions within their specified ratings.
However, there are limits to their capacity, and extreme overcurrent events or sustained overloads can lead to damage or failure.
Here are some considerations regarding overcurrent and circuit breaker damage:
To prevent damage to circuit breakers and ensure their reliable operation, it’s important to adhere to the following practices:
- Select circuit breakers with appropriate current ratings for the circuits they protect.
- Avoid overloading circuits beyond their designed capacity.
- Properly maintain and inspect circuit breakers to identify signs of wear or damage.
- Replace damaged or malfunctioning circuit breakers promptly.
- Ensure that circuit breakers are operated within their specified voltage and current ranges.
While circuit breakers are designed to provide overcurrent protection and are more robust than fuses, they are not immune to damage under extreme or improper operating conditions.
Regular maintenance and adherence to electrical safety standards are essential to maintain the integrity and reliability of circuit breakers in electrical systems.
For more information about Why circuit breakers go bad, read my article.
What happens if an over-current protection device is oversized?
If an over-current protection device (such as a fuse or circuit breaker) is oversized for the circuit it is meant to protect , it can lead to several potential issues and compromises in electrical safety and equipment protection. Here are some consequences of using an over-sized protection device:
- Reduced Protection : The primary purpose of an over-current protection device is to safeguard the circuit and connected equipment from excessive current levels, which can cause overheating, fires, and equipment damage. When an oversized device is used, it may not trip or open the circuit as intended when overcurrent conditions occur. This means that the circuit and equipment may not be adequately protected from short circuits, overloads, or faults.
- Increased Fault Energy : An oversized protection device can allow excessive fault currents to flow without tripping or interrupting the circuit. This can result in higher fault energy levels in the event of a short circuit, increasing the potential for electrical arc flash incidents and equipment damage.
- Equipment Damage : Oversizing protection devices can lead to damage to downstream equipment. For example, if a circuit breaker with a much higher current rating than the circuit’s load capacity is used, the equipment connected to the circuit may not be adequately protected from overcurrents. This can lead to overheating and damage to the equipment, including motors, transformers, and wires.
- Inefficiency : Oversized protection devices can be less efficient in terms of energy consumption. They may allow unnecessarily high currents to flow for longer periods before tripping, leading to increased energy losses and potentially higher operating costs.
- Violation of Electrical Codes and Standards : Oversizing protection devices can lead to non-compliance with electrical codes and standards. Electrical codes specify the correct sizing and selection of protection devices based on the characteristics of the circuit and equipment being protected. Using an over-sized device may result in non-compliance and regulatory violations.
- Misleading Fault Analysis : Oversized protection devices can make it challenging to identify and analyze faults or overcurrent events within a circuit. Since the device does not operate as expected under fault conditions, troubleshooting and diagnosing electrical issues can become more complex.
To ensure proper electrical safety and equipment protection, it is crucial to select and install protection devices with current ratings that match the circuit’s load and characteristics.
The selection of protection devices should be in accordance with electrical codes and standards. Additionally, regular maintenance and testing of protection devices are essential to verify their proper operation and compliance with safety requirements.
Oversized protection devices should be replaced with appropriately sized ones to maintain electrical safety and equipment protection.
What if an overcurrent protective device opens slower than expected?
If an overcurrent protective device, such as a circuit breaker or a fuse, opens slower than expected, it can have several implications and potential consequences, depending on the specific circumstances and the nature of the overcurrent condition:
- Equipment Damage : Slower tripping of the protective device can allow excessive current to flow through the circuit for a longer duration. This prolonged overcurrent can result in overheating of wiring, equipment, and components, potentially causing damage or degradation.
- Fire Hazard : Overcurrents can generate heat, and if the protective device does not trip promptly, the prolonged overcurrent can increase the risk of electrical fires. Electrical components and insulation may become damaged due to excessive heat.
- Safety Hazards : Slower tripping of protective devices can pose safety hazards to individuals in the vicinity. For example, if a fault condition occurs and the circuit breaker does not trip quickly, it may expose people to electrical shock hazards.
- Compromised Protection : The primary purpose of overcurrent protection is to prevent electrical circuits and equipment from being subjected to current levels that exceed their designed capacity. When a protective device opens slower than expected, it compromises the protection provided by that device.
To address the situation when an overcurrent protective device is not operating as expected, here are some steps to consider:
- Investigation : Identify the cause of the slow operation. It could be due to a malfunctioning protective device, loose connections, or other issues within the electrical circuit.
- Immediate Shutdown : If there is an ongoing overcurrent condition and the protective device is not responding as expected, it is essential to de-energize the circuit immediately to prevent further damage or hazards. Disconnect power at the main switch or circuit breaker panel if necessary.
- Professional Inspection : Seek the assistance of a qualified electrician or technician to inspect the protective device, the circuit, and any associated equipment. They can diagnose the issue and recommend appropriate corrective actions, such as repairing or replacing the protective device.
- Maintenance and Testing : Regularly maintain and test protective devices to ensure they operate within their specified response times. Periodic testing and maintenance can help identify potential issues before they become critical.
- Replacement : If the protective device is found to be faulty or not operating correctly, it should be replaced promptly with a properly rated and functioning device to restore adequate protection.
Ensuring that overcurrent protective devices operate correctly and promptly is crucial for electrical safety and equipment protection.
Any signs of malfunction or unexpected behavior should be addressed promptly to prevent potential hazards and equipment damage.
Install my Free Android App on Google Play :
Electrical Cables Most Common Tables “Electrical Cables Tables”
And, my Electrical Calculations App “ Fast Electrical Calculator ”
Discover more great content by subscribing to My channel
Looking to stay ahead of the game in the world of electrical engineering? Subscribe to my YouTube channel and gain access to exclusive content you won’t find anywhere else!
Are You An Electrical Engineer or Electrician?
Install my Free Electrical Cables Tables App On Google Play Now! It’s 100% Free
The staff I recommend (Amazon Affiliate Links to products I believe are high quality):
- Economy 120 Volt/60Hz AC Power Source – Step-Down Voltage & Frequency Converters 1800W
- UNI-T Digital Multimeter Tester UT139C
- 50-Amp Extension Cord for RV “100ft”
- Voltage Stabilizer 110/220v
- Hair Dryer “best selling “
- TOSHIBA EM131A5C-BS Countertop Microwave Ovens
Disclaimer : This contains affiliate links to Amazon products. I may earn a commission for purchases made through these links.
You Might Also Like
Gfci vs circuit breaker: understanding the differences.

What Is MCC Meaning in Electrical? Read This First!
Prevent electrical fires with gfcis: here’s how they work, what is electrical resistance – answers you should know, electrical thermal current rating (ith) of contactors.
- AWS Pelabuhan Tanjung Priok 241218/12:00UTC, Suhu 30°C Angin SSW 5 knots Water Level 15 m Pressure 1002 hPA Humidity 95%
- AWS Pelabuhan Tanjung Perak 241218/12:00UTC, Suhu 30°C Angin SSW 5 knots Water Level 15 m Pressure 1002 hPA Humidity 95%
- 27-03-2024 08:50:06 WIB
- 27-03-2024 09:50:06 WITA
- 27-03-2024 10:50:06 WIT

- Pengendalian Transportasi Jalur Laut Natal 2023 dan Tahun Baru 2024
- 24 Jam ke Depan
- Prospek Gelombang Mingguan
- Bulletin for Shipping
- Tujuh Hari ke Depan
- Perairan Padat Aktifitas Pelayaran
- Area Pelayanan
- Area Pelabuhan
- Area Wisata Pantai
- Area Jalur Penyeberangan
- Area Provinsi
- Gelombang Tinggi
- Banjir Pesisir (Rob)
- Analisis Bulanan
- Peta Analisis
- Peta OFS Static
- Peta OFS Interaktif
- Indeks Kepuasan Masyarakat
- Lepas Pantai
- Rip-currents
- RIP Currents
Apa itu RIP Current ?
Rip Current adalah arus kuat dari air laut yang yang bergerak menjauh dari pantai. Mereka bahkan dapat menyapu perenang terkuat sekalipun ke laut.
Apa yang menyebabkan terjadinya RIP Current ?
RIP Current disebabkan karena adanya pertemuan ombak yang sejajar dengan garis pantai sehingga menyebabkan terjadinya arus balik dengan kecepatan arus yang tinggi.
Kecepatan arusnya bervariasi tergantung pada kondisi gelombang, pasang surut dan bentuk pantai. Rip Current yang telah diukur kecepatannya dapat melebihi 2 m/ detik. Sehingga tentu saja sangat amat berbahaya bagi pengunjung pantai.
- Angin Permukaan
- El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
- Gelombang Signifikan Tertinggi Absolut
- Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)
- Keadaan Laut
- Kecepatan angin
- Kecepatan Arus
- Madden Julian Oscillation (MJO)
- Peringatan Angin Kencang
- Peringatan Dini Gelombang Tinggi
- Primary Periode Swell
- Primary Swell
- Primary swell period
- Proses Terbentuknya Siklon Tropis
- Pusat Tekanan Rendah
- Saran Keselamatan Berlayar
- Sebaran Hujan
- Siklon Tropis
- Suhu Muka Laut
- Voluntary Observing Ship (VOS)
- Voluntary Observing Ship (VOS)
- Wind direction change
KANTOR PUSAT
Pusat Meteorologi Maritim Jl. Angkasa I No.2 Kemayoran Jakarta Pusat, DKI Jakarta 10720 P.O. Box 3540 Jkt.
Tel. 0812-9086-3118
- Analisis Klimatologis Bulanan
- Gelombang Signifikan
- Kecepatan Gust
- Observasi Kapal Laut
- Observasi Lepas Pantai
- Observasi Pelabuhan
- Peringatan Dini Banjir Rob
- Periode Swell
- Peta Analisis Klimatologis Bulanan
- Peta Prakiraan
- Prakiraan Gelombang dan Hujan 24 jam
- Prakiraan Jalur Mudik Laut
- Prakiraan Jalur Penyeberangan
- Prakiraan Pelabuhan Utama/Laut
- Prakiraan Tujuh Hari kedepan
- Prakiraan Wilayah Pelayanan
- Prakiraan Wisata Pantai
- Tinggi Swell
- Weather Bulletin for Shipping
- Disabilitas
Current Artinya Saat Ini dalam Bahasa Indonesia, Ini Definisi Lengkap dan Contohnya
Diperbarui 04 Sep 2023, 11:54 WIB Diterbitkan 04 Sep 2023, 10:45 WIB
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/1447530/original/021812300_1482828485-Badan_Bahasa_1.jpg)
Liputan6.com, Jakarta - Arti kata current dalam bahasa Inggris yang diterjemahkan dalam bahasa Indonesia adalah situasi saat ini. Istilah ini sering digunakan untuk merujuk kepada keadaan, peristiwa, atau informasi yang tengah berlangsung atau berlaku pada waktu yang sedang dialami.
Enough Artinya Cukup, Begini Contoh Penggunaannya Dalam Kalimat
Disable artinya dalam bahasa indonesia dan contoh penggunaannya, caption bahasa inggris dan artinya, ketahui fungsi dan jenisnya.
Advertisement
Dalam hal ini, current artinya istilah yang bisa membantu menyampaikan ide tentang sesuatu yang relevan dengan kondisi terkini. Bisa pula menggambarkan situasi yang sedang berlangsung.
Misalnya, ketika berbicara tentang current events. Ini artinya sedang merujuk kepada berita atau peristiwa yang tengah terjadi pada saat ini. Ini adalah cara untuk menjelaskan situasi sosial, politik, atau ekonomi yang sedang berlangsung dan memiliki relevansi dalam waktu dekat.
Selain itu, dalam penggunaan sehari-hari, kata current dapat merujuk kepada hal-hal seperti cuaca saat ini, nilai tukar mata uang saat ini, atau status proyek yang sedang berjalan. Dalam semua konteks ini, current membantu untuk memahami dan berkomunikasi tentang situasi saat ini dengan jelas dan tepat.
Berikut Liputan6.com ulas lebih mendalam tentang current artinya dalam bahasa Indonesia lengkap contoh kalimatnya, Senin (4/9/2023).
Dites Bahasa Inggris, Jawaban Bocah Ini Kocak Banget
* Follow Official WhatsApp Channel Liputan6.com untuk mendapatkan berita-berita terkini dengan mengklik tautan ini .
Gambaran Situasi Saat Ini
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/1442120/original/021660800_1482307795-20161220-Wawancara-Khusus-Kepala-Badan-Pengembangan-dan-Pembinaan-Bahasa-Tebe-10.jpg)
Istilah current artinya dalam bahasa Indonesia mengarah pada makna "saat ini." Kata ini adalah hasil terjemahan dari bahasa Inggris dan sering digunakan dalam beragam situasi untuk menggambarkan keadaan atau peristiwa yang sedang berlangsung pada waktu yang tengah dialami.
Pustaka Digital Indonesia menjelaskan kata current artinya sekarang ini, berkelanjutan, aktual, zaman sekarang, dan masih banyak lagi lainnya.
Penggunaan istilah current sangat erat kaitannya dengan dimensi temporal, yaitu waktu, serta relevansi dalam konteks tertentu. Ketika merujuk kepada sesuatu yang bersifat current dalam bahasa Indonesia, itu artinya sedang mencerminkan fakta-fakta atau peristiwa yang tengah berlangsung.
Contohnya, dalam dunia penulisan berita, berita yang bersifat current adalah berita yang merujuk kepada peristiwa yang terjadi pada saat ini atau dalam beberapa hari terakhir. Dalam dunia kerja, pekerjaan yang bersifat current artinya masih menjadi pekerjaan yang saat ini dilakukan.
Kata current artinya memang digunakan untuk menggambarkan sesuatu yang masih berlaku atau relevan dalam situasi saat ini. Ini bisa mencakup hukum, peraturan, atau informasi lain yang tetap berlaku dan memiliki relevansi pada saat sekarang. Misalnya, buku panduan yang disebut current adalah buku panduan yang mengandung informasi terbaru dan masih relevan dengan situasi yang tengah dihadapi.
Lebih lanjut, istilah current artinya juga sering digunakan untuk menggambarkan sesuatu yang aktual atau sesuai dengan perkembangan terkini. Ini berarti sesuatu tersebut sesuai dengan perubahan atau evolusi yang terjadi dalam waktu yang dekat. Sebagai ilustrasi, prediksi cuaca current akan memberikan informasi tentang kondisi cuaca yang diantisipasi dalam beberapa hari mendatang.
Kesimpulannya, penggunaan kata current dalam bahasa Indonesia mencerminkan konsep waktu dan relevansi dengan situasi yang sedang berlangsung atau berlaku pada waktu tersebut. Istilah ini membantu dalam menjelaskan sesuatu yang tengah berlangsung atau masih memiliki relevansi dalam konteks tertentu dengan menyoroti aspek temporal dan aktualitasnya.
Dalam berbagai situasi, current artinya alat efektif untuk menyampaikan informasi tentang keadaan atau peristiwa yang terjadi pada saat ini. Menggambarkan hal yang masih berlaku, serta merujuk kepada aktualitas yang selaras dengan perkembangan terkini.
20 Contoh Kalimatnya
- The current situation in the stock market is quite volatile. (Situasi saat ini di pasar saham sangat fluktuatif.)
- The current economic policies aim to stimulate growth. (Kebijakan ekonomi terkini bertujuan untuk merangsang pertumbuhan.)
- The current government regulations need to be updated. (Peraturan pemerintah yang masih berlaku perlu diperbarui.)
- The current weather forecast predicts rain for the weekend. (Prakiraan cuaca saat ini memprediksi hujan pada akhir pekan.)
- The current generation is more tech-savvy than ever before. (Generasi zaman sekarang lebih mahir dalam teknologi daripada sebelumnya.)
- I'm reading a current bestseller novel. (Saya sedang membaca novel terbaru yang laris.)
- The current pandemic has changed the way we work. (Pandemi saat ini telah mengubah cara kita bekerja.)
- His research is focused on current trends in the fashion industry. (Penelitiannya berfokus pada trend terbaru dalam industri fashion.)
- The current exchange rate favors foreign investors. (Nilai tukar yang berlaku saat ini menguntungkan investor asing.)
- She is well-informed about current events around the world. (Dia sangat paham tentang berita-berita terkini di seluruh dunia.)
- The current project is running behind schedule. (Proyek yang sedang berlangsung saat ini sedikit terlambat.)
- The current CEO has implemented several changes in the company. (CEO yang sekarang telah menerapkan beberapa perubahan dalam perusahaan.)
- The current legislation addresses environmental concerns. (Legislasi yang berlaku saat ini mengatasi masalah lingkungan.)
- Please provide me with the current status of the project. (Mohon berikan saya status saat ini dari proyek tersebut.)
- The current educational system needs reform. (Sistem pendidikan yang sedang berlangsung saat ini perlu direformasi.)
- The current market conditions are favorable for investors. (Kondisi pasar saat ini menguntungkan bagi para investor.)
- Her research focuses on current developments in the field of medicine. (Penelitiannya berfokus pada perkembangan terkini di bidang kedokteran.)
- The current technology allows for faster communication. (Teknologi yang sedang berlaku saat ini memungkinkan komunikasi yang lebih cepat.)
- The current regulations require all employees to undergo safety training. (Peraturan yang berlaku saat ini mengharuskan semua karyawan menjalani pelatihan keselamatan.)
- The current trend in interior design leans towards minimalism. (Trend zaman sekarang dalam desain interior cenderung minimalis.)
* Fakta atau Hoaks? Untuk mengetahui kebenaran informasi yang beredar, silakan WhatsApp ke nomor Cek Fakta Liputan6.com 0811 9787 670 hanya dengan ketik kata kunci yang diinginkan.
current artinya
Current artinya apa, current artinya adalah, current artinya bahasa indonesia.
Mau Ganti HP Pas THR Cair, Ini Daftar HP Terbaru Poco yang Diskon
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4717781/original/034747100_1705404517-20240116-Paparan_Kinerja_KPK-ANG_1.jpg)
KPK Peringatkan PNS dan Penyelenggara Negara Dilarang Memungut THR
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/1533266/original/000310500_1489154768-mbak_ita_pecat.jpg)
THR ASN Pemkot Semarang Disiapkan, Mbak Ita Berharap Banyak
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/3147468/original/046003900_1591677975-20200609-Ojek-Online-Gunakan-Pelindung-Pembatas-Antar-Penumpang-1.jpg)
Tak Jadi Terima THR Lebaran, Ojol Dapat Insentif Isinya Bingkisan Biskuit
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/1045213/original/057155400_1446724551-151105-THR-PNS-05-Grafis-Abdillah.jpg)
Segini Besaran THR 2024 Anggota DPRD DKI Jakarta, Jangan Kaget!
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4656568/original/073882700_1700533929-IMG-20231121-WA0002.jpg)
Menaker: THR Lebaran untuk Ojol Itu Tidak Wajib
Kate middleton.
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/2396414/original/030748900_1540948935-1.jpg)
Top 3 Berita Hari Ini: Teman Pangeran Harry dan Meghan Markle Tuduh Kate Middleton Berbohong soal Mengidap Kanker
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4781737/original/004768400_1711147329-k11ate_1.jpg)
Kate Middleton Singgung Jalani Kemoterapi Preventif, Ahli: Itu Bukan Istilah Medis
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4421808/original/083367700_1683690655-AP23129555000841.jpg)
Momen Pangeran Wiliam Tahu Kate Middleton Didiagnosis dengan Kanker, Langsung Batal Hadiri Acara Penting
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/1661063/original/039431500_1501158850-531391716_33064891.jpg)
Respons Pribadi Pangeran William terhadap Pesan Pangeran Harry Usai Kate Middleton Didiagnosis Kanker
Video kate middleton soal pengumuman diagnosis kanker mengandung simbol tersembunyi, maknanya mengharukan.
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/1812306/original/052937000_1514253725-20171225-Meghan-Markle-di-Perayaan-Natal-Kerajaan-AP-1.jpg)
Teman Pangeran Harry dan Meghan Markle Tuduh Kate Middleton Berbohong soal Mengidap Kanker
Ramadhan 2024.
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4784653/original/001924300_1711434412-Screenshot_2024-03-26_122221.jpg)
Kisah Atlet MMA Jadikan Ramadhan Ajang Mengingat Kembali Tujuan Hidupnya di Dunia
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4785731/original/044705700_1711491751-DSC09661.JPG)
Berkah Ramadan, Pupuk Kaltim Salurkan Bantuan Rp 3,47 Miliar ke Warga Bontang
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/3279875/original/073055400_1603801467-PEUGEOT_3008_2016_281_UK_Fogging.jpg)
Momen Ramadan 2024, Industri Pengharum Kendaraan Incar Pasar Indonesia
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4401948/original/049872700_1681943680-Pemudik-Manfaatkan-Kemacetan-di-Tol-MBZ-untuk-Beristirahat-Sejenak-Herman-5.jpg)
Mudik Lebaran 2024, Pemerintah Siapkan Skema Cegah Kendaraan Menumpuk di Rest Area
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4755596/original/074870500_1709072542-AP24058761858331.jpg)
Klub Liga Inggris Luton Town Gelar Acara Buka Bersama buat Umat Muslim di Kenilworth Road
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4146216/original/065707700_1662292786-000_9WX226.jpg)
FIFA: VAR Bisa Mulai Digunakan pada Championship Series BRI Liga 1 2023/2024
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4370769/original/022786700_1679670599-20230324BL_BRI_Liga_1_2022-2023_Persib_Bandung_vs_Bhayangkara_FC_2.jpg)
Jadwal BRI Liga 1 2023/2024 pada Pekan Ketiga Ramadhan 2024
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/3538569/original/015307700_1629173438-LIGA_BRI_LIGA_1.jpg)
Hasil BRI Liga 1 2023/2024: Bali United Gagal Kalahkan RANS, Persis Bungkam PSIS
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4774804/original/035005600_1710600277-IMG_7980.JPG)
Hasil BRI Liga 1 2023/2024: Persija Sikat Persik Kediri, Radja Nainggolan Cetak Gol Perdana
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4767662/original/012911700_1709993382-20240309IQ_Persib_Bandung_vs_Persija_Jakarta_09.JPG)
Jadwal BRI Liga 1 2023/2024 di Pekan Pertama Ramadhan 2024
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4767537/original/062622200_1709984258-20240309151940_2R8A9903.JPG)
Klasemen BRI Liga 1: Persib Bandung Segera Rebut Tiket Championship Series, PSM Nyaris Mustahil Pertahankan Gelar
English for Adults
Daftar program
Kantor dan sekolah
:quality(90)/f/78828/1920x750/1ea5099802/ef_blog_header_beda_travel_tour.jpg)
Perbedaan "Trip", "Travel", "Tour", dan "Journey" dalam Bahasa Inggris
Sebagai pengguna bahasa Inggris, kamu tentu mengenal kata “trip”, “travel”, “tour” dan “journey”. Bahkan, kamu mungkin pernah menggunakannya saat berkomunikasi dalam bahasa Inggris , baik dengan berbicara, maupun menulis. Biasanya, keempat kata tersebut digunakan untuk menjelaskan bahwa kamu sedang liburan. Lalu, bagaimana cara membedakan waktu penggunaannya? Nah, berikut ini adalah penjelasan lengkap dari masing-masing kata dan contoh penggunaannya yang tepat:
Secara harfiah, kata “trip” artinya adalah sebuah perjalanan, biasanya bolak-balik ke suatu tempat. Meski bisa digunakan untuk perjalanan jauh, kata “trip” akan lebih sesuai digunakan untuk perjalanan singkat yang sengaja dilakukan untuk kesenangan atau menyenangkan diri sendiri. Dalam bahasa Inggris, kamu bisa menggunakan kata “trip” yang berupa kata benda atau noun untuk menceritakan perjalanan kerja ( business trip ), liburan singkat ( short trip ), atau liburan sekolah ( school trip ). Agar lebih jelas bagaimana menggunakan kata “trip” dengan tepat, berikut adalah beberapa contoh kalimat yang bisa kamu pelajari:
We had a short trip to Bandung last week. (Kami melakukan perjalanan singkat ke Bandung minggu lalu.)
He’s gone to Paris for a business trip . (Dia pergi ke Paris untuk melakukan sebuah perjalanan bisnis.)
He went with me to my overseas trip last year. (Dia ikut bersamaku melakukan perjalanan ke luar negeri tahun lalu.)
She’s planning a trip to Singapore. (Dia merencanakan sebuah perjalanan ke Singapura.)
Kata “travel” dalam bahasa Inggris biasanya bisa diartikan sebagai “bepergian”. Itu sebabnya, saat kamu jalan-jalan ke berbagai tempat dalam jarak yang cukup jauh, kamu bisa disebut sedang travelling. Kata ini sebenarnya tidak berbeda jauh maknanya dengan kata “trip”. Akan tetapi, jika “trip” adalah kata benda atau noun , kata “travel” termasuk sebagai kata kerja atau verb . Dalam bahasa Inggris, kamu bisa menggunakan kata “travel” untuk menunjukkan aksi atau kegiatan yang dilakukan dan berkaitan dengan bepergian. Jika kegiatan tersebut sedang berlangsung saat kamu mengatakannya, kamu bisa menggunakan kata “travelling” sebagai present participle dari kata “travel”.
Untuk lebih memahami penggunaan kata ini dengan tepat, simak beberapa contoh kalimat berikut ini.
I traveled abroad a lot last year. (Aku sering bepergian ke luar negeri tahun lalu.)
We love to travel by train. (Kami suka bepergian menggunakan kereta api.)
My parents enjoy travelling around Asia continent. (Orangtua saya sangat menikmati bepergian keliling benua Asia.)
Sama halnya dengan kata trip, kata tour juga termasuk sebagai kata benda atau noun . Kata yang satu ini memiliki makna “perjalanan yang dilakukan ke beberapa tempat, bisa daerah, kota, hingga negara”. Hal ini bisa digunakan untuk mendeskripsikan sebuah perjalanan yang menyenangkan dan dilakukan secara berkelanjutan ke beberapa tempat. Meski demikian, kata ini sebenarnya juga bisa difungsikan sebagai verb layaknya “travel”. Biasanya, jika digunakan sebagai kata kerja, tour bermakna aktivitas bepergian yang dilakukan ke beberapa tempat secara berkelanjutan.
Berikut adalah contoh penggunaan kata “tour” sebagai noun dan kata “tour” sebagai verb dalam kalimat Bahasa Inggris yang tepat.
Kata “tour” sebagai noun
They embarked on a tour around the country. (Mereka melakukan perjalanan keliling negara ini.)
When I was in Europe, I rode a bus tour. (Saat aku berada di Eropa, aku naik tur bus.)
Kata “tour” sebagai verb
She’s currently touring with her theatre club . (Dia saat ini sedang berkeliling dengan klub teaternya.)
He’s toured the country promoting his new album. (Dia bepergian keliling negara ini untuk mempromosikan album barunya.)
Sedikit berbeda dengan ketiga kata lainnya, journey yang tergolong sebagai kata benda atau noun ini memiliki makna “sebuah perjalanan panjang yang jauh dan memakan waktu lama.” Biasanya, kata journey juga bisa digunakan untuk mengatakan “perjalanan hidup” dalam bahasa Inggris.
Jika kamu ingin menggunakan kata journey saat berkomunikasi dalam bahasa Inggris, pastikan kamu sudah menggunakannya secara tepat. Berikut ini adalah beberapa contoh kalimat yang menggunakan kata “journey” sesuai konteks.
Lani had a very thoughtful journey in Africa. (Lani mengalami perjalanan yang berat di Afrika.)
She has a wonderful journey touring across the world. (Dia mengalami perjalanan yang sangat indah saat berkeliling dunia.)
My journey was tiring. (Perjalananku sangatlah melelahkan.)
Nah, dari penjelasan lengkap di atas, kini kamu sudah paham bukan bagaimana menggunakan keempat kosakata tersebut?
Current Weather
Latest Weathercast
Interactive Radar
NBC 10 I-Team: One former official accepts ethics fine, second vows to fight allegations
by BRIAN CRANDALL, NBC 10 NEWS

PROVIDENCE, R.I. (WJAR) — Two former high-ranking Rhode Island state employees met behind closed doors with the state Ethics Commission Tuesday as part of the fallout from a scandalous business trip to Philadelphia a year ago.
One emerged agreeing to pay a fine.
The other will fight the allegations.
After a months-long investigation, the Ethics Commission found probable cause that David Patten and James Thorsen, who both had influence over the awarding of state contracts, violated multiple ethics rules by accepting a $500 lunch at a fancy restaurant paid for by their hosts, who were trying to secure a state contract to redevelop the Cranston Street Armory.
Patten, who was the director of Capital Asset Management and Maintenance at the time, agreed to pay a $5,000 ethics fine, a fraction of what he could have faced.
He was accused by the hosts of the Philly trip of making racist and sexist comments.
Patten did not respond to questions from reporters Tuesday as he left the Ethics Commission.
His attorney, Michael Lynch, spoke instead, saying, “I had said a while ago, Mr. Patten has been apologetic for the events and for the conduct that resulted from this event.”
Patten and his boss, then-state Administration Director James Thorsen, were visiting Scout, the company trying to secure a $55 million contract for the armory project.
An email from Scout executives detailing the alleged inappropriate comments and demanding behavior became public months later.
Lynch told reporters Tuesday, as he did in a statement in the wake of the email’s release, that Patten suffered a medical episode.
“The result, unfortunately, of a medical event, a medical crisis that occurred back then. He’s received the treatment that he’s needed,” Lynch said.
The night before the trip, after a work dinner, a co-worker messaged Thorsen that Patten may be having a manic episode, according to the Ethics Commission report.
Scout executives claimed Patten messaged them that same night demanding Diet Cokes for Thorsen, the best croissants in the city, and lunch at a closed restaurant, while saying they had three hours to try to win the state contract.
Patten then took items like sneakers, glassware, and vegan cheese along their tour of a Scout development.
Thorsen repaid part of the lunch bill days later, allegedly only after learning of Scout's complaints.
Thorsen is going to fight the Ethics Commission allegations at an upcoming hearing.
Asked by the NBC 10 I-Team on Tuesday if he thought he did anything wrong, Thorsen replied, “If I thought I did wrong, I wouldn’t be here right now. It would have been settled a long time ago.”
“I believe I behaved in a responsible manner and took the appropriates steps, reported to HR and contacting the governor’s chief of staff,” Thorsen maintained, repeating his previous assertion that he notified others of Patten’s behavior upon returning from the trip.
Asked by NBC 10 News if there was anything he would have done differently, Thorsen replied, “Yes, of course. It was a difficult trip. And we’ll have more to say about that later.”
The Ethics Commission did not address Patten’s alleged racist and sexist comments on the trip.
“The Ethics Commission doesn’t have jurisdiction to impose penalties for offensive behavior or inappropriate behavior. We have to enforce the code of ethics,” Ethics Commission Executive Director Jason Gramitt said.
McKee ultimately canceled the deal with Scout.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Short-time pickup is adjustable from 1.5 to 10 times the trip unit ampere setting (Ir). For example, a 1000 ampere frame can be adjusted to trip anywhere from 1500 to 10,000 amps. The switch also has an "OFF" position to eliminate short-time pickup and short-time delay. Short-time pickup used for selective tripping.
Time-current curves are shown as bands, and the actual performance of any one breaker can fall anywhere within the band. Using the example CFD6 breaker and 200 ampere trip unit, the time the breaker will trip for any given overload can easily be determined using the same procedure as previously discussed. For example, the breaker will trip ...
In = Rated Current adalah arus rating kontinyu/arus nominal pada CB. Icu = Rated Ultimate Breaking Capacity adalah kemampuan CB untuk dapat memutuskan arus hubung singkat maksimum tanpa menyebabkan kerusakan/meleleh pada contact contacnya. FLC Full Load Current : arus kontinyu beban tanpa menyebabkan CB trip.
The trip curve of an MCB (B, C, D, K, and Z curves) tells us about the trip current rating of Miniature Circuit breakers. The trip current rating is the minimum current at which the MCB will trip instantaneously. It is required that the trip current must persist for 0.1s. Table of contents. Definition.
The standards state that they should trip at 12.5 times the rated current but will trip anywhere between 10 to 20 times the rated current. The tripping characteristics of this circuit breaker is called a D Curve. D Curve. Type K. Lets move on to Type K. This circuit breaker is specifically designed for air conditioning and heat pump systems ...
Ir (dalam A) adalah fungsi dari In, yang menyatakan proteksi tripping dikarenakan pengaruh thermal. Ir dikenal sebagai proteksi waktu panjang (Long Time Protection LTP). 3. Isd atau Im (short time delay current / Arus magnetic) Isd (dalam kA) adalah fungsi dari Ir, menyatakan proteksi hubung pendek.
The thermal-trip relays are generally adjustable from 0.7 to 1.0 times In, but when electronic devices are used for this duty, the adjustment range is greater; typically 0.4 to 1 times In. Example (see Fig. H27) A NSX630N circuit-breaker equipped with a 400 A Micrologic 6.3E overcurrent trip relay, set at 0.9, will have a trip-current setting ...
Di bawah adalah kurva trip tiap jenis MCB. Mari kita lihat perbedaan tiap jenis: Miniature Circuit Breaker : Jenis A. MCB yang sangat sensitif adalah MCB jenis A, yang mana cukup jarang dimanfaatkan. Mereka dibuat untuk trip secara instan ketika arus melebihi 2-3 kali arus yang ditetapkan. Hasilnya, mereka terbatas untuk perangkat yang sensitif.
Bagian bawah grafik adalah untuk perjalanan magnet koil / solenoida; 0,02 hingga 2,5 detik pada 3X arus pengenal adalah paling cepat pemutus sirkuit akan trip (3). Durasi yang sama, 0,02 hingga 2,5 detik, pada 5X arus pengenal, adalah yang terpanjang yang akan membuat pemutus sirkuit trip (4). Area yang diarsir di antaranya adalah Tripping Zone.
The trip unit is the part of the circuit breaker that determines when the contacts will open automatically. In a thermal-magnetic circuit breaker, the trip unit includes elements designed to sense the heat resulting from an overload condition and the high current resulting from a short circuit. In addition, some thermal magnetic circuit ...
Time Current Curve TCC pada Trip Unit. Untuk menggambarkan karakteristik besar arus (I ) terhadap waktu (t). Gambar 3. TCC Electronic Trip Unit ACB 4 kA, 65 kA ... Ring setting pada contoh switch trip unit dibawah ini adalah antara 1.5 - 10 kali Ir. • Delay STD ( dalam second) / tsd : Settingan waktu tsd terkait dengan settingan arus pick ...
Circuit breaker, atau pemutus sirkuit, merupakan alat penting yang digunakan dalam sistem kelistrikan dan elektronik. Fungsi utama dari circuit breaker adalah untuk melindungi peralatan dan sistem listrik dari kerusakan akibat over current atau arus berlebih, yang biasanya terjadi akibat short circuit (hubungan pendek) atau overload (beban ...
Both should be considered. If your device must have a minimum current, then look at holding current. And if it must trip at some point, then look at trip current. Unlike Harper, I'm assuming you're talking about poly-resettable fuses. when the current is between the hold and trip current, what happens to the fuse is uncertain.
Solusi Cepat dan Mudah untuk Memastikan Penyebab Trip. Untuk menemukan penyebab sebenarnya dari trip di lokasi konstruksi, kombinasi peralatan uji yang mencakup Logger (pencatat data), (pengukur getaran), probe diferensial, dan Current Clamp (klem arus) akan membantu dalam memantau karakteristik fisik dan kelistrikan dalam jangka panjang.
Tiga jenis utama tersebut adalah MCB Tipe B, MCB Tipe C dan MCB Tipe D. 1. MCB Tipe B. MCB Tipe B adalah tipe MCB yang akan trip jika arus beban lebih besar 3 sampai 5 kali dari arus maksimum yang tertulis pada MCB (arus nominal MCB). MCB Tipe B ini umumnya digunakan pada instalasi listrik di perumahan ataupun di industri ringan. 2. MCB Tipe C
Rip current adalah arus air laut yang membalik arah menuju laut lepas atau tegak lurus dengan garis pantai. Arus ini biasanya akah hilang tidak jauh dari pantai dan memiliki lebar kurang dari 25 m. Rip current biasanya punya kecepatan 1 hingga 2 kaki per detik. Namun beberapa penelitian telah mencatat kecepatan tertinggi arus ini ada di kisaran ...
"Secara ilmiah, rip current adalah arus balik yang terkonsentrasi pada sebuah jalur sempit, yang memecah zona empasan gelombang hingga melewati batas zona gelombang pecah," jelas Koordinator Mitigasi Gempa Bumi dan Tsunami Badan Meteorologi, Klimatologi, dan Geofisika (BMKG), Daryono, kepada Kompas.com, Selasa (10/5/2022).
Circuit overload causes the breaker to trip, opening up and shutting off the power supply. The overload could cause the wiring to overheat and melt, causing a short circuit and leading to a house fire. In addition to the heat loss from increasing current, the rising current can also: Damage the circuit; Burn resistors and electronic components
RIP Current disebabkan karena adanya pertemuan ombak yang sejajar dengan garis pantai sehingga menyebabkan terjadinya arus balik dengan kecepatan arus yang tinggi. Kecepatan arusnya bervariasi tergantung pada kondisi gelombang, pasang surut dan bentuk pantai. Rip Current yang telah diukur kecepatannya dapat melebihi 2 m/ detik. Sehingga tentu ...
Chyntia Sami Bhayangkara Suara.Com. Selasa, 15 Februari 2022 | 15:44 WIB. apa itu RIP Current (Phys.org) Suara.com - Sebanyak 11 orang di Pantai Payangan, Jember, Jawa Timur, tewas setelah tersapu ombak ketika menggelar ritual, pada Minggu (13/2/2022). Ternyata, peristiwa naas tersebut diduga disebabkan oleh Rip Current.
Contohnya, dalam dunia penulisan berita, berita yang bersifat current adalah berita yang merujuk kepada peristiwa yang terjadi pada saat ini atau dalam beberapa hari terakhir. Dalam dunia kerja, pekerjaan yang bersifat current artinya masih menjadi pekerjaan yang saat ini dilakukan.. Kata current artinya memang digunakan untuk menggambarkan sesuatu yang masih berlaku atau relevan dalam situasi ...
Kata ini sebenarnya tidak berbeda jauh maknanya dengan kata "trip". Akan tetapi, jika "trip" adalah kata benda atau noun, kata "travel" termasuk sebagai kata kerja atau verb. Dalam bahasa Inggris, kamu bisa menggunakan kata "travel" untuk menunjukkan aksi atau kegiatan yang dilakukan dan berkaitan dengan bepergian.
Rip Currents digadang-gadang menjadi biang utama kecelakan di pantai. Dalam bahasa yang mudah dimengerti, Rip Currents lebih dikenal sebagai ombak penggulung di tepi pantai yang menimbulkan ancaman bagi siapa saja yang tidak menyadari terbentuknya sirkulasi tersebut. Di Amerika Serikat, Rip Currents tercatat sebagai salah satu penyumbang ...
Former Rhode Island state official David Patten agrees to pay a $5,000 ethics fine over his behavior on a business trip to Philadelphia, his lawyer said. ... Current Weather . Cranston. Cloudy. 38 ...