Prakhar Tyagi


A Guide – How To Start Medical Tourism Business in India
Medical tourism is a rapidly growing industry, with India emerging as a preferred destination for individuals seeking high-quality healthcare services at a fraction of the cost compared to Western countries. If you are considering venturing into the dynamic world of medical tourism in India, this guide will walk you through the essential steps to establish a successful business in this booming sector.
- Market Research:
Begin by conducting thorough market research to understand the demand, competition, and potential target audience. Identify popular medical procedures that attract international patients to India, such as cardiac surgeries, orthopedic treatments, cosmetic surgeries, and fertility treatments. Evaluate the existing competition and identify the unique selling points that can set your business apart.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
Familiarize yourself with the regulatory requirements governing medical tourism in India. Ensure that your business complies with licensing, accreditation, and quality standards set by healthcare authorities. Building a network with reputable healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics is crucial to ensure the delivery of high-quality services.
- Partnerships with Healthcare Providers:
Forge strong partnerships with leading hospitals, clinics, and healthcare professionals. Establishing alliances with reputable institutions not only enhances the credibility of your medical tourism business but also ensures that your clients receive top-notch medical care.
- Customized Packages and Services:
Develop tailor-made medical tourism packages that cater to the diverse needs and preferences of international clients. Include comprehensive services such as medical consultations, travel arrangements, accommodation, local transportation, and post-treatment care. Offering all-inclusive packages simplifies the process for your clients and enhances their overall experience.
- Quality Assurance:
Emphasize the importance of quality assurance and patient safety. Ensure that the healthcare facilities you collaborate with adhere to international standards and possess necessary certifications. Transparent communication regarding treatment procedures, potential risks, and expected outcomes is vital to build trust with your clients.
- Digital Presence and Marketing:
Establish a strong online presence through a professional website and active engagement on social media platforms. Utilize digital marketing strategies such as search engine optimization (SEO), content marketing, and targeted advertising to reach potential clients globally. Highlight success stories, testimonials, and the expertise of the healthcare professionals associated with your business.
- Visa Assistance and Travel Arrangements:
Facilitate the visa application process for international clients and provide assistance with travel arrangements. Collaborate with reliable travel agencies to ensure seamless logistics, airport transfers, and comfortable accommodation during their stay in India.
- Cultural Sensitivity and Language Support:
Train your staff to be culturally sensitive and provide language support to overcome potential communication barriers. Offering multilingual services and hiring interpreters can significantly enhance the overall experience for international clients.
- Insurance Partnerships:
Explore partnerships with international insurance providers to offer comprehensive medical insurance coverage for your clients. This not only provides financial security but also adds an extra layer of assurance to your services.
- Feedback and Continuous Improvement:
Regularly collect feedback from clients and healthcare partners to identify areas for improvement. Implement a system for continuous enhancement of services, ensuring that your medical tourism business remains at the forefront of industry standards.
Conclusion:
Embarking on the journey to start a medical tourism business in India requires careful planning, dedication, and a commitment to delivering exceptional services. By navigating the regulatory landscape, building strong partnerships, and prioritizing the well-being of your clients, you can establish a successful venture in this thriving industry. India’s rich cultural heritage, coupled with world-class healthcare services, positions the country as an ideal destination for medical tourism entrepreneurs looking to make a positive impact on global healthcare.
Connect With Me Today – If You Are Interested To Start Medical Tourism Business In India
Popular Posts

Medical tourism is a rapidly growing industry, with India emerging as a preferred destination for individuals seeking high-quality healthcare services at a fraction of the cost compared to Western countries. If you are considering venturing into the dynamic world of medical tourism in India, this guide will walk you through the essential steps to establish…

The Power of Free Cash Flow : A Key Metric for Financial Health
In the intricate world of finance, businesses rely on various metrics to gauge their financial health and make informed decisions. One such crucial metric that plays a pivotal role in assessing a company’s financial strength is Free Cash Flow (FCF). Free Cash Flow is more than just a number on a financial statement; it serves…

Head Down Execute: A Deep Dive into the Concept
In the fast-paced world of technology and business, staying ahead often requires adopting new methodologies and approaches. One such concept that has gained traction in recent times is “Head Down Execute.” This phrase encapsulates a mindset and a set of practices that are becoming increasingly relevant in various fields. In this blog post, we will…
- Digital Marketing (5)
- Healthcare Marketing (19)
- Startup (4)
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- January 2023
Active Listening (2) AI-generated text (1) AI detection (1) Artificial intelligence (3) Brand Awareness (2) Communication Skills (2) Communication Strategies (2) Competition (2) content marketing (5) Data-driven marketing (2) Data Analysis (2) Digital Marketing (8) Effective Communication (2) email marketing (2) Healthcare advertising (3) healthcare branding (4) healthcare business strategies (2) Healthcare Industry (6) Healthcare innovation (3) healthcare marketing (8) Healthcare Marketing Strategies (3) Healthcare Professional Marketing (1) Healthcare technology (2) identifying AI text (1) India Healthcare (2) international healthcare (2) International Patient Care (2) Marketing Strategies (3) Marketing Strategy (2) medical tourism (3) medical travel (2) Online Presence (2) Online Presence in Healthcare (1) patient acquisition (2) Patient Engagement (6) Patient experience (4) Presentation Skills (2) Return on Investment (ROI) (3) Search Engine Optimization (SEO) (3) social media marketing (4) Target Audience (3) Targeted Healthcare Audience (1) Time Management (2) Trust Building. (2) Video marketing (2)
Get doctor listing on ClinicSpots.
- Best Medical Tourism Companies in India 2024 List
Discover excellence in healthcare with top-rated Medical Tourism Companies in India. Your journey to world-class treatment begins here.
- Dental Treatement
By Pankaj Kamble
17th Apr '20
In India, the medical tourism industry is thriving, serving patients annually. This reflects the global demand for affordable, quality healthcare. India offers various services, including heart and bone surgeries, cosmetic enhancements, and oncology, demonstrating a commitment to excellent healthcare.
Financially, the sector thrives with an impressive 15-20% annual revenue growth, showcasing its robust resilience. Looking ahead, over 2 million jobs are anticipated by 2029, emphasizing the industry's significant role in the nation's workforce.
Let's talk about the best medical tourism companies in India. Interested to know who's leading the pack? Stay with us as we explore the top players that are setting the standard for excellent healthcare experiences. Ready for the inside scoop? Let's dive in!
1. ClinicSpots

- ClinicSpots is among India's top medical tourism companies, operating in major metro cities with a focus on providing excellent medical care assistance.
- They have established tie-ups with renowned hospitals in Mumbai, ensuring access to superior healthcare facilities.
- Offering global medical treatments such as Plastic surgery, IVF, dental implants, and hair transplants in locations like Dubai, Turkey, Bangladesh, etc.
- Prioritizing patient convenience, they streamline procedures for a hassle-free medical journey, allowing patients to focus solely on their treatment.
- Patient support services include assistance in finding accommodation based on budget, airport pick-up and drop services, and facilitating currency exchange/payment options.
- ClinicSpots provides visa assistance, generating request letters for embassies to ensure a smooth process and address potential issues.
2. Peace Medical Tourism

- Connects you with the best doctors and hospitals in India based on your specific needs.
- Offers access to various healthcare specialists, from cardiologists to oncologists.
- Maintains international standards in the medical tourism sector.
- Over 15 years of experience, establishing itself as a trusted name in the industry.
- Provides various services, including free medical invitation visas and fast doctor appointments during emergencies.
- Offers complimentary airport pickup and drop-off, along with assistance in hotel booking and interpreter services.
- The experienced team ensures a seamless experience, providing guides or translators as needed.
- Committed to delivering top-notch service and support throughout your medical journey.
3. TransEarth Medical Tourism

- TransEarth Medical Tourism is known for its highly transparent pricing policy, ensuring clear and honest cost structures for medical tourists.
- The professional team consistently follows international protocols, prioritizing optimal care for patients and setting high standards in the medical tourism landscape.
- The company goes the extra mile to assist patients in finding comfortable accommodation during their stay in India for medical treatment, enhancing the overall experience.
- TransEarth provides comprehensive support, assisting with visa arrangements and airline ticket purchases, ensuring a hassle-free journey for medical tourists. Medical clearance is handled efficiently.
- Beyond medical concerns, TransEarth facilitates patients who wish to explore the beauty of India. Additional services include road ambulance, air ambulance, hospital admission support, private attendants, and special assistance for disabled patients.
4. MedMonks

- MedMonks, a renowned medical tourism company, specializes in providing comprehensive services to medical tourists.
- With a dedicated and efficient team, MedMonks assists patients in finding affordable treatment packages at the best clinics in India.
- Recognizing cost as a major concern for patients seeking treatment abroad, MedMonks addresses this issue proactively.
- Understanding the diverse needs of medical travelers, MedMonks offers additional services, including pre-activated SIM cards or data cards for international patients.
- The company goes the extra mile by providing services such as airport pickup, hospitalization assistance, and the option to extend the trip for rejuvenation.
- MedMonks caters to the ongoing needs of medical travelers, allowing them to purchase follow-up care packages for continued support and assistance.
5. Credihealth

- Credihealth offers online solutions for medical tourism in India with a dedicated team of consultants.
- They provide personalized advice for individuals considering moving to India for medical services.
- The company has earned the trust of patients from various countries, establishing itself as a reliable healthcare partner.
- Patients can easily upload their medical history documents for evaluation by experienced doctors.
- Credihealth ensures transparency by providing cost estimates from the best hospitals for the required medical services.
- Consultants at Credihealth also assist with services related to medical visas and follow-up treatments, offering comprehensive support for international patients.

- Vaidam has earned trust from patients worldwide, including India.
- It is a popular NABH-certified platform, ensuring high-quality healthcare connections.
- Connects patients to top-rated specialists and hospitals internationally.
- Responsive team to address inquiries and provide assistance.
- Consultants assist in securing personalized and cost-effective treatments.
- Vaidam's concierge team helps with medical visa, ensuring seamless travel.
7. MediConnect

- Received the National Tourism Award twice, showcasing reliability and excellence.
- Established connections with renowned hospitals like Apollo and Jaypee.
- In-house team provides multiple healthcare options from different hospitals.
- Simple process to send queries to preferred hospitals for quick and efficient communication.
- Access to check doctors’ qualifications before making informed decisions.
- Dedicated team takes care of post-operative queries, ensuring patient well-being.
- Beyond healthcare, offers assistance for buying flight tickets and other medical tourism needs.
8. MedGinnie

- MedGinnie specializes in providing affordable medical tourism packages for international patients.
- Their services encompass a diverse range of treatments, including joint replacements, weight loss surgeries, and dental procedures.
- The focus is on ensuring quality care while maintaining affordable prices.
9. TourMyIndia

- TourMyIndia provides affordable services, becoming a trusted travel partner for medical tourists.
- They offer 24-hour assistance, addressing concerns from medical treatment opinions to post-treatment services.
- While dedicated to medical tourists, TourMyIndia's platform caters to all types of travelers, showcasing its versatility.
10. Forerunners Healthcare, South Delhi

- Forerunners is a government-registered company in the medical tourism industry.
- International patients benefit from video consultations.
- Highly skilled doctors and qualified nurses are accessible to medical tourists.
- The professional team at Forerunners Healthcare understands healthcare needs and the urgency of treatment.
- The company has a network with hospitals across different Indian cities.
- To find the best doctor, send your medical report to the company.
Rise of Medical Tourism Companies in India
The rise of medical tourism companies in India is an exciting story fueled by a potent mix of factors, transforming the way patients access healthcare on a global scale. Here's a peek into the dynamic landscape:
Key Drivers of Growth:
- Cost-effectiveness: India offers high-quality treatment at a fraction of the cost compared to developed nations, attracting budget-conscious patients worldwide.
Expertise Hub:
- India features a vast pool of skilled doctors, internationally trained and equipped with advanced medical technology.
Specialized Focus:
- Companies are honing in on specific areas like cardiac surgery and oncology, offering top-notch expertise in targeted treatments.
Government Backing:
- The Indian government actively supports medical tourism through simplified processes, infrastructure development, and marketing initiatives.
Technological Strides:
- Telemedicine, AI diagnostics, and virtual reality applications enhance patient convenience and treatment effectiveness.
Wellness Fusion:
- Traditional therapies like Ayurveda blend seamlessly with modern medicine, attracting health-conscious travelers seeking holistic experiences.
Impact on the Scene:
Rising Competition:
- Increasing competition prompts companies to stand out through specialization, patient-centric services, and digital marketing.
Quality Assurance:
- JCI and NABH certifications gain significance, ensuring international standards and building patient trust.
Expanding Horizons:
- Medical tourism facilities extend beyond major cities, reaching smaller towns and rural areas, providing diverse and accessible options.
- Job creation: The booming industry generates significant employment opportunities for healthcare professionals, boosting the economy.
Challenges and Opportunities For Medical Tourism Companies in India
India's medical tourism industry boasts immense potential, attracting patients worldwide with its cost-effective treatments and skilled professionals. However, challenges and opportunities coexist, requiring companies to navigate a complex landscape for sustainable growth.
Challenges:
- Maintaining consistent quality: Diverse healthcare providers across India necessitate robust quality control measures to ensure international standards and patient trust.
- Ethical practices: Transparency in pricing, communication, and treatment options is crucial to avoid exploitation and build patient loyalty.
- Infrastructure limitations: Upgrading infrastructure in smaller towns and rural areas can expand accessibility and cater to a wider patient base.
- Competition: The growing number of companies necessitates differentiation through specialization, patient-centric services, and effective marketing.
- Visa complexities: Streamlining visa processes for medical tourists can enhance convenience and attract more patients.
- Reputation management: Negative reviews or incidents can damage the industry's reputation, requiring proactive communication and crisis management strategies.
Opportunities:
- Embracing technology: Telemedicine, AI-powered diagnostics, and virtual consultations can improve patient access and treatment efficacy.
- Wellness integration: Blending Ayurveda with modern medicine caters to a growing segment seeking holistic healthcare and rejuvenation.
- Specialization and niche markets: Focusing on specific treatments or patient demographics attracts targeted audiences and builds expertise.
- Collaboration and partnerships: Partnering with international hospitals, airlines, and tourism agencies can expand reach and offer comprehensive packages.
- Government support: Increased government initiatives for infrastructure development, marketing, and quality assurance can boost the industry's competitiveness.
- Responsible tourism: Promoting sustainable practices and environmental awareness can attract ethical travelers and build long-term value.
Why Choose Medical Tourism Companies in India?
Choosing medical tourism companies in India can be a great decision for a variety of reasons. Here are some key factors to consider:
Cost-Effectiveness:
- Significantly lower treatment costs: Compared to developed nations, India offers high-quality treatments at a fraction of the price. This can be a major saving for procedures like cardiac surgery, orthopedic surgery, and cosmetic surgery.
- Affordable packages: Many companies offer comprehensive packages that include not only medical treatment but also travel arrangements, accommodation, and post-operative care, making it easier to budget for your trip.
Medical Expertise:
- Highly skilled and experienced doctors: India boasts a large pool of skilled doctors trained in international standards and equipped with advanced medical technology.
- Wide range of specialities: Medical tourism companies can connect you with specialists in various fields, from cardiology and oncology to cosmetic surgery and Ayurveda.
- JCI/NABH accreditations: Many hospitals and clinics in India are accredited by international organizations like JCI and NABH, ensuring adherence to quality standards.
Accessibility and Convenience:
- English widely spoken: Communication is rarely a barrier, as English is widely spoken by medical professionals and hospitality staff.
- Simplified visa processes: Medical visas are streamlined for patients seeking treatment in India.
- Direct flights from major cities: Convenient travel options are available from many countries, making India easily accessible.
Additional Benefits:
- Focus on holistic healthcare: India offers a unique blend of modern medicine with traditional therapies like Ayurveda, catering to a holistic approach to well-being.
- Cultural experiences: Medical tourism in India can be combined with exploring the country's rich culture and diverse landscapes.
- Rejuvenation and relaxation: Many companies offer additional services like yoga and spa treatments, facilitating a complete mind-body rejuvenation experience.
Relevant Blogs

Hip Replacement Hospitals in India: A Comprehensive Guide
Hip pain slowing you down? Transform your mobility with India's top-rated Hip Replacement experts. Experience minimally invasive surgery, affordable costs, exceptional outcomes, cutting-edge technology, compassionate care, & proven results await!

Cancer Treatment in India - Compare Costs, Hospitals & Doctors in 2024
Discover cutting-edge cancer treatment in India. Renowned specialists, advanced technology ensure comprehensive care and better outcomes. Explore options today!
Eye Cancer Treatment in India: Advanced Care Solutions
Explore advanced eye cancer treatment in India. Renowned specialists, state-of-the-art facilities ensure comprehensive care and better outcomes. Discover options today!
Organ Specific Cancer Treatment in India
Cancer can occur in all the organs. The treatment plan will differ for different organs based on their site and the intensity of treatment they require. We have further provided the organ specific treatment options for some of the most common types of cancer affecting people all over the world.

PET Scan in Mumbai
You’ll find all the available details for the PET scan in Mumbai on this page.
Dr. Sandeep Nayak - Best Oncologist in Bangalore
Dr. Sandeep Nayak - Best oncologist in Bangalore. Experience of 19 years. Consults at Fortis, MACS & Ramakrishna. To book an appointment, call @ +91-98678 76979
VISION – A GODS GIFT
If you are looking for tips to keep your eyesight healthy and sharp then below is all your answers.

10 Best Hospitals in Istanbul - Updated 2023
Looking for the best hospital in Istanbul? Here is a compact list for you of the 10 Best Hospitals in Istanbul.
Question and Answers
I have been staying up late for about a week and i started to notice that my vision started to be a little bit blur and that i cant focus is there anything that can be done for this to be corrected
Spending too much time looking at screens might result in eye strain and temporary loss of visual sharpness. In order to avoid negative impacts on vision, it is better to take breaks, change lighting and use the screens with the anti-reflective filter. For further treatment consult a eye specialist
Answered on 21st Mar '24
Dr. Sumeet Agrawal
I have cavity in 10 teeths
I would advise you to visit a dentist as soon as possible for an examination and treatment options. Cavities can lead to further complications if left untreated, such as tooth decay and infection.
Dr. Parth Shah
I have wisdom tooth .. swelling over there unbreable pain its ả important tở extraction ??
Female | 29
Wisdom teeth can cause discomfort and pain if they don't have enough room to grow properly. Visit a dentist they can evaluate your condition and determine the best course of action for your particular situation, which may include extraction.
Answered on 20th Mar '24
I have been experiencing ankle pain for about three months. However with mobility, it stops hurting. There's no swelling. But when I wake up in the morning it becomes stiff snd it hurts. Eventually with some movement it stops hurting.
Female | 26
Pain in the ankle, mostly in the morning, is probably associated with arthritis, gout, or tendinitis. It is best to see an orthopedist who has the experience and capability to diagnose the condition and provide suitable treatment.
Answered on 19th Mar '24
Dr. Pramod Bhor
I think I have osteomyelitis, I burned my hand with a curling iron two weeks ago, it blistered then popped. It got infected, then I started to notice pain in my bone near the infection. The infection is better but the pain in my bone has gotten worse
Female | 12
The symptoms you have mentioned can be suggestive of osteomyelitis which is an infection of the bone. I recommend you to see an orthopedist immediately for a proper diagnosis and a therapy plan.
Answered on 18th Mar '24
Cost Of Related Treatments In Country
Cancer hospitals in other cities, top related speciality doctors in other cities.

Health & Lifestyle
Medical Tourism in India: Benefits, Risks, and Tips

Read Next →

Prevention Through Lifestyle: Healthy Habits for Reducing the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes

What is Anal Cancer? 5 Early Symptoms

Treatments for Men With Low Sperm Count
Table of Contents
India’s medical tourism industry has grown rapidly over the past decade, with nearly 2 million patients visiting from neighbouring countries each year and generating $13 billion in forex annually.
However, to become the top medical travel destination, improvements are needed in the ecosystem surrounding patient experience and accommodation. Investment in medical travel facilitators and standardised guesthouses is crucial, as is pursuing the opportunity for selling Indian health insurance to foreigners, potentially generating an additional $9 billion.
Cross-border telemedicine also presents a large opportunity, given India’s skilled workforce and cost advantage.
In this blog, we will explore the benefits and risks of medical tourism in India, as well as provide tips for those considering travelling to India for medical treatment.
Medical tourism is a growing industry, and India is one of the most popular destinations for medical tourism. India has a well-established healthcare system, and many hospitals in India are accredited by international organisations such as Joint Commission International (JCI) and National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Providers (NABH).
Additionally, India offers world-class medical treatment at a fraction of the cost of Western countries.
How is India becoming a popular medical hub for patients?
India is rapidly becoming a popular medical hub for patients due to a variety of factors.
- Firstly, the country has a world-class healthcare industry that offers top-quality treatment at a fraction of the cost compared to other countries. This is due to the availability of highly skilled doctors and modern hospitals.
- Secondly, India’s traditional systems of medicine, such as Ayurveda, Yoga, and Panchakarma, which are some of the oldest forms of medicine in the world, are gaining immense popularity globally.
The combination of modern and traditional medicine makes India a unique destination for medical tourism, with patients seeking a holistic approach to healthcare.
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has implemented various measures to promote medical tourism in India. These include:
Special provision of Medical Visa available in 165 countries, a feedback mechanism to obtain testimonials from medical tourists, and the ‘Heal in India’ initiative which aims to position the country as a global hub for medical and wellness tourism.
The initiative includes an online portal for foreigners seeking medical treatments, which provides a one-stop-shop for all services from treatment package costs to grievance redressals and feedback.
The initiative also aims to diversify its operations by sending Indian doctors abroad to treat patients.
Benefits of Medical Tourism in India:
- Cost-effective treatment : The cost of medical treatment in India is significantly lower than in Western countries. Patients can save up to 80% of the cost of medical treatment in India compared to the USA.
- Quality healthcare : Indian hospitals offer world-class healthcare facilities and services. Many hospitals in India have internationally trained doctors and nurses, and are equipped with the latest medical equipment and technology.
- No waiting time : In many Western countries, patients have to wait months or even years for medical treatment. However, in India, patients can receive medical treatment immediately, without having to wait.
- Travel and tourism opportunities : Patients can combine their medical treatment with travel and tourism. India is a popular tourist destination, with a rich cultural heritage and diverse cuisine.
Risks of Medical Tourism in India:
- Language barriers : Patients who do not speak the local language may face communication difficulties with doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals.
- Infection control : Infection control standards in some Indian hospitals may not be up to the same standards as those in Western countries.
- Cultural differences : Patients may experience cultural differences in medical treatment and patient care.
- Travel risks : Patients may face travel risks, such as jet lag, long flights, and exposure to different climates and diseases.
Tips for Medical Tourism in India:
- Choose a reputable hospital : Do your research and choose a hospital that is accredited by international organisations such as JCI and NABH.
- Consult with your doctor : Consult with your doctor before travelling to India for medical treatment. Your doctor can advise you on the risks and benefits of medical tourism and help you make an informed decision.
- Plan your trip : Plan your trip in advance and make sure to arrange for transportation, accommodation, and other logistics.
- Communicate effectively : Communicate effectively with healthcare professionals and make sure to ask questions if you do not understand something.
- Follow infection control guidelines : Follow infection control guidelines, such as washing your hands regularly and wearing a mask if necessary.
Conclusion:
India, despite being a developing country, offers world-class and standardised medical services and care, aided by the latest technology.
In conclusion, the demand for the healthcare industry is expected to surge in the post-Covid world, and India has a significant potential to attract medical tourists from around the globe, including Europe and the Americas. The government’s efforts to make India the hub of medical tourism, combined with the increasing demand, are likely to make India a leading destination for medical tourism in the future. This development not only saves lives but also generates valuable jobs and more than $13 billion in forex, highlighting the potential benefits of medical tourism for India’s economy and healthcare sector.
Ayu Health is the largest chain of most trusted hospitals across the country with a team of 3000+ highly skilled doctors and state-of-the-art facilities, we’re committed to provide patients with comprehensive and personalised treatment plans. Whether you are seeking treatment for a chronic condition or simply looking to improve your overall well-being, book a consultation atAyu Health to help you achieve your health goals.
Our Hospital Locations
General Surgery Hospitals in Chandigarh | General Surgery Hospitals in Bangalore | General Surgery Hospitals in Jaipur | General Surgery Hospitals in NCR | General Surgery Hospitals in Hyderabad
Our Doctors
General Surgery Doctors in Chandigarh | General Surgery Doctors in Bangalore | General Surgery Doctors in Jaipur | General Surgery Doctors in NCR | General Surgery Doctors in Hyderabad
About the Author

Dr. S. Goel
Dr. S. Goel is a renowned Internal Medicine Specialist currently practicing at Ayu Health, Bangalore . He is a Specialist in Internal Medicine, Diabetes HTN, Paediatric Care, and Family Medicine.
- Dr. S. Goel #molongui-disabled-link Prevention Through Lifestyle: Healthy Habits for Reducing the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
- Dr. S. Goel #molongui-disabled-link What is Anal Cancer? 5 Early Symptoms
- Dr. S. Goel #molongui-disabled-link Treatments for Men With Low Sperm Count
- Dr. S. Goel #molongui-disabled-link How to Rewire Your Brain: 5 Neuroplasticity Exercises
Share this:
Arvind has been writing health information for the past 8 years. He has extensive experience writing about health issues like sepsis, cancer, mental health issues, and women’s health.

- Back Health (9)
- Cancer Prevention (30)
- Children's Health (21)
- Digestive Health (9)
- Diseases Prevention (45)
- Eye Health (23)
- Hair Care Resources (13)
- Health & Lifestyle (194)
- Healthcare Case Study (5)
- Heart Care (45)
- Kidney Health (12)
- Lung Health & Diseases (6)
- Musculoskeletal System (24)
- Plastic Surgery Care (2)
- Surgery Info (21)
- Uncategorized (2)
- Urology (5)
- Women Fertility (43)
- Womens Health (39)
- Women’s Fertility
- Children’s Health
- Musculoskeletal System
- Plastic Surgery Care
- Back Health
- Healthcare Case Study
- Hair Care Resources
- Digestive Health
- Kidney Health
- Lung Health & Diseases
- Cancer Prevention
- Diseases Prevention
Latest Posts
- Shoulder Pain: What’s Causing It and How to Get Relief Did you know that shoulder pain affects 18–26% of adults in their lifetime? Beyond injuries […]
- Working From Home? Tips to Prevent Low Back Pain The rise of remote work has revolutionized how we work, offering flexibility and freedom, but […]
- Prevention Through Lifestyle: Healthy Habits for Reducing the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Did you know that more than 95% of people with diabetes have type 2 diabetes? […]
- What is Anal Cancer? 5 Early Symptoms Did you know that anal cancer, though rare, is a significant health concern? According to […]
- How to Know if You’re Suffering from Bursitis in the Knees Are you experiencing knee pain that won’t go away? It might be more than just […]
- Ensuring Cardiac Wellness in Bangalore: The Role of ECG Test and Timely Interventions The heart, our tireless companion, beats ceaselessly to keep us alive. Amidst the fast-paced and […]
ColorWhistle
Digital Web Design Agency India

Explore our Market-Fit Services
We ensure to establish websites with the latest trends as we believe that, products whose value satisfies the needs of the market and its potential customers can be efficiently successful.
Quick Links
- About Us – ColorWhistle
- Engagement Models
- Testimonials
- Case Studies
- Agency Services
- Web Development
- Web App Development
- Digital Marketing
- Travel Website Development Services Company
- Real Estate Website Development Services Company
- Education Website Development Services Company
- Healthcare Website Development Services Company
- Hotel and Restaurant Website Development Services

Category: Travel
Date: August 22, 2023
Medical Tourism Business – A Complete Guide
Across the world, there is an emerging class of voyagers who are crossing international borders to obtain a range of medical services from dental care to liposuction. This type of travel is known as medical or healthcare tourism.
Business in this sector is booming. On a global scale, healthcare tourism is higher than oil and gold industry.
If you have plans to enter the medical tourism industry, this blog is for you. We hope that this blog will guide and help you make an informed decision.
What Is Medical Tourism?
Medical tourism involves traveling to another country for the purpose of getting care.
Originally, patients from less-developed countries traveled to developed countries to get treatments that were not available in their homeland.
Today, people from developed countries travel to developing countries to get health care services. This shift is driven by low-cost treatments offered by developing countries, inexpensive flights and the easy availability of online information about medical services.
The word ‘tourism’ is included in this because in most cases people stay in a foreign country to get medical assistance. So, travelers can take advantage of this situation to get to know the country in that short time.
According to the WHO , here are the main drivers of medical tourism.

Here is a graphical representation of a consumer’s path to medical tourism by Deloitte
Types of Medical Tourism
Medical tourism is one of the highly emerging concepts in the tourism industry. There are three main categories in medical tourism.
- Outbound medical tourism – In this type of tourism, a person leaves the country of their origin to another country to get medical help. For example, leaving Denver to get medical care in India
- Inbound medical tourism – In this type of tourism, a person from another country travels to a host country to get medical help. For example, leaving Canada to get medical treatment in the US
- Domestic medical tourism – In this type of tourism, a person travels to another city in the same country to get medical help. For example, leaving Texas to get medical treatment in New York
Top Medical Tourism Destinations in The World
According to Bookimed and Medical Tourism Magazine, here is a list of the top medical tourism destinations in the world.
What Are The Business Models for Medical Tourism?
Here are the different types of business models in medical tourism.
1. Business to Customer
This model involves targeting patients through online marketing and connecting them to the provider. It is also known as direct to patient model
2. Business to Business
This model involves doctors directly referring to other doctors or hospitals. It is also known as provider to provider model
3. Exporting Brand Presence
Exporting brand presence means bringing your brand to the patients directly. For example, many US hospitals want to mark their presence in China
4. Payer Driven
In this model, a payer or employer who is looking to reduce the cost for their insureds will ask them to get medical care away from their homes. The payer or employer may also give incentives for doing it
5. Additional Information
These are some other ways medical tourism businesses earn money.
- Commission – The hospital will pay a fee to the facilitator for sending patients to them
- Revenue – The tourism company will decide the treatment cost of the patient. After the patient makes the payment to the company, it will settle the bill with the hospital. The difference is the actual revenue earned by the company
- Other information – After surgery, people may want to go shopping in the city or even take a vacation. The medical tourism company can also charge a commission for these activities
How to Start a Medical Tourism Service Agency?
If you are planning to start a medical tourism business, here are some points you must consider.
Analyze The Industry and Understand Your Clientele
Analyzing the medical sector of a particular destination will help you to easily determine where you want to target your business. For example, India is famous for heart surgery while Thailand is famous for HIV/AIDS treatment and Spain for neurosurgery.
Understand why certain people prefer to travel for treatment and what type of help you can provide to satisfy their needs.
Additionally, analyze the strong points of the locations you want to choose from. For instance, Germany is known for using cutting-edge equipment and Costa Rica is well known for its world-class plastic surgeons.
Next, you must get a market needs assessment and financial feasibility study from service providers such as The Fox Group . You must also figure out the financial plan. and talk with industry experts to figure out how much to charge for the services you offer.
Certifications, Permits and License
You may be required to undergo training and licensing before opening up the business. Displaying badges from recognized accreditation bodies on your website and other materials will give a message to tourists that your business is properly managed and has undergone rigorous evaluations.
The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) is a prominent healthcare accreditation organization in the US. They formed the Joint Commission International (JCI) to help medical tourism businesses find good healthcare providers around the globe. For example, The Apollo Hospitals was the 1st one in India to get this certification. Click here to view the full list of the medical tourism industry certifications.
Other Points To Keep In Mind
- Insurance is one of the most important elements in the medical tourism business. Make sure that the policy your clients have will cover most of the sections of your business
- To make your client’s medical trip smooth, you have to coordinate and collaborate with the whole medical tourism network. They include travel agencies, hotels, airlines, insurance providers, translators and dealing with the embassy
- Most people find medical tourism-based services online. So, creating a website is important when you are planning to start a medical tourism business A professional website design and development company will have the core expertise to create a customized solution according to your requirements. So, it is highly recommended that you get help from such professionals
- Have a good online marketing plan to spread the word of your business. You can also get help from digital marketing experts to get high-quality results
Medical Tourism Statistics And Facts
Here are some interesting statistics and facts you need to know about the medical tourism industry.
- According to a CII-Grant Thornton study, the Indian medical tourism market is expected to grow from the current $3 billion to around $8 billion by 2020.
- According to MarketWatch, Global Medical Tourism Market will grow at a CAGR of 16.1% during the forecast period 2019-2025
- According to BD Health & Fitness, Medical tourism is one of Turkey’s fastest-growing industries and is estimated to contribute $4 Billion to the country’s economy annually
- According to Statistica, 53% of EU citizens are willing to travel to another country for better quality treatment
- According to CNN, India’s medical tourism industry could grow by 200% by 2020, hitting $9 billion
- According to Statistics, here is the percentage of adults in the U.S. who had traveled abroad specifically to receive medical treatment

- According to Statistica, as of 2019, here is the percentage of adults in the U.S. who had traveled abroad specifically to receive medical treatment and were satisfied with their treatment

- This graph explains the growth of the medical tourism market

Top Medical Tourism Service Providers in The World
Here are some of the top medical tourism companies in the world.
- Bumrungrad International Hospital
- Costa Rica Medical Travel
- Medical Tourism Malaysia
- Seoul Guide Medical
- Ventures Healthcare
- Istanbul Safe Medical
Useful Guides About Medical Tourism
Here are some guides which will help you to get more information about the medical tourism industry.
- Treatment Abroad
- International Medical Travel Journal
- Patients Beyond Borders
- The Medical Tourism Directory For Costa Rica
- Medical Tourism Magazine
- Dr. Prem Medical Tourism Guide
Mobile Apps
Mobile apps are revolutionizing medical tourism and it’s going to be the next big thing in the industry. Here are some of the medical tourism companies that have already created mobile apps and attracting the attention of medical travelers. If you need any help to create a mobile app , you can contact our ColorWhistle team anytime.
- HealthTraveler™
- TaiwanTrade
- HealthTraveler
- PlacidMobile
Drive Conversions and Boost your Business with Expert Travel Website Development.
Medical tourism service providers play a crucial role in making the travel experience easy and comfortable.
Here are some of the basic facilities that a good medical tourism facilitator must provide.
- Custom treatment packages
- Round the clock support and guidance
- Assistance for procuring a medical visa letter
- Timely doctor appointments
- Quick in-patient admissions
- Money exchange
- Safe accommodation
- Provide local sim cards
- Proper end-to-end transportation guidance
- Post-treatment follow-ups
International healthcare services are booming because of the globalization of capital funding and advancement in medical technology. The changing technologies and economic conditions have created many opportunities for patients and businesses in world-wide medical tourism.
The future of medical tourism will be profitable as experts predict the revenue growth to be in billions of dollars in the coming years.
In quest of the Perfect Travel Tech Solutions Buddy?
Be unrestricted to click the other trendy writes under this title that suits your needs the best!
- Types Of Tourism
- Travel Mobile App Features
- Travel Tourism Industry Evolution
- Rezdy Online Booking Software Review
- Computer Reservation System
- Online Travel Agencies
- Travel Meta Search Engine
Related Posts

Exploring the World Through AI and VR in the Travel Industry

How AI-based Travel Booking Applications Can be Developed?

Latest Marketing Trends for Travel Businesses in This New Year
About the Author - Anjana
Anjana is a full-time Copywriter at ColorWhistle managing content-related projects. She writes about website technologies, digital marketing, and industries such as travel. Plus, she has an unhealthy addiction towards online marketing, watching crime shows, and chocolates.
View Our Services
Have an idea? Request a quote
Share This Blog
Impressive writing and content presentation, useful too, hope also keep sharing.
thank you for sharing such a wonderful information.
Very informative. Thank you for sharing
The way you explain a complex topic in an easy-to-understand way is really impressive.
Great Post! Really happy to say that your post is fascinating to read. I never stop myself from saying anything about it. Expecting more blogs.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Ready to get started?
Let’s craft your next digital story

Sure thing, leave us your details and one of our representatives will be happy to call you back!
Eg: John Doe
Eg: United States
Eg: [email protected]
More the details, speeder the process :)
Subscribe Now! Get features like

- Latest News
- Entertainment
- Real Estate
- PBKS vs DC Live Score
- KKR vs SRH Live Score
- Election Schedule 2024
- IPL 2024 Schedule
- Bihar Board Results
- The Interview
- Web Stories
- IPL Points Table
- IPL Purple Cap
- IPL Orange Cap
- Mumbai News
- Bengaluru News
- Daily Digest

Medical Tourism in India: Top destinations, scenarios and all you need to know
India in recent years has emerged as a major hub for medical tourism and is now considered among the top 6 medical value travel destinations in the world. here is all you need to know about it..
Medical Tourism , or Medical Value Travel, refers to the industry where international patients travel across the border for medical, cosmetic, or wellness treatments. India in recent years has emerged as a major hub for medical tourism and is now considered among the top 6 medical value travel destinations in the world. Its rapidly growing medical tourism industry has put Delhi, Chennai, Mumbai and Kochi on the globe for millions of people across Asia and Africa, who turn to these cities for all their surgical needs. Our unrivalled knowledge , top-notch doctors, extensive experience, and premier hospitals enable us to dominate the Indian medical tourism market. The patient can receive affordable treatment packages in India. (Also read: Kerala Tourism focuses on ‘responsible tourism’ to increase the livelihood of locals )

In an interview with HT Lifestyle, Danish Ahmed, Founder, Healthtrip.com, shared important insights regarding medical tourism in India.
Medical tourism scenario in India:
Medical Tourism in India, in mid-2020, was estimated to be worth around USD 9 billion which makes India stand at Number 10 in the Global Medical Tourism Index. Approximately 2 million patients visit India each year from 78 countries for medical, wellness and IVF treatments, generating $6 billion for the industry which is expected to reach $13 billion by 2026 backed by the government’s Heal in India initiative. This not only generates jobs, profits and forex for hospitals but also creates very valuable soft power for India, positioning it as the Healing Center of the world. It also creates demand for high-end equipment, which results in continuous upgradation of Indian healthcare, resulting in a spiral of demand generating quality, generating more demand.
Why do they choose India:
India’s key advantage is the price at which it can deliver the world-class quality of healthcare, along with complementing treatments in Ayurveda, which gives it the unique positioning of Holistic Healthcare. Aptly called, Heal in India, the expected initiatives from the government will ease visa and forex norms for these patients, unlocking the tremendous potential of medical tourism in the country. India is known to be the land of natural medicines to the world. India and Ayurveda have a history that longs back in time.
Where are most medical tourists from:
Most of the tourists are from Asian or African countries such as Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, Maldives, Indonesia and Kenya, among others.
Top 5 medical tourism destinations in India:
Chennai: One of the most well-liked locations in India for receiving medical care. According to research by the Confederation of Indian Industries, almost 40% of patients choose Chennai because of the city's high standard of care. Chennai, the "health capital of India," sees foreign patients annually for hip replacements, eye surgeries, cardiac bypasses, bone marrow transplants, and alternative medical procedures.
Mumbai: It is the city with India's fastest expanding medical tourism industry, and is home to a number of super speciality hospitals as well as a Research and Diagnostic Center for orthopaedic and weight reduction procedures. Mumbai is also well-known for its Ayurvedic therapies and cosmetic surgery.
New Delhi: Numerous outstanding private hospitals, including ones that offer packages for general surgery, eye surgery, heart care, and neurosurgery to foreign patients, can be found in the nation's capital.
Ahmedabad: Ahmedabad is another Indian city that is gradually rising to prominence as a centre for medical tourism. Many non-residents prefer seeking treatment in Ahmedabad because of its hospitals with top-notch amenities.
Bangalore: Due to the vast quantity of top-notch medical facilities and specialists among its medical professionals. These are Bangalore medical tourism's main attractions. There are also doctors in Bangalore who have had advanced training in the west with almost little wait time and quick access to medical care for visitors seeking treatment.
Follow more stories on Facebook & Twitter
Join Hindustan Times
Create free account and unlock exciting features like.

- Terms of use
- Privacy policy
- Weather Today
- HT Newsletters
- Subscription
- Print Ad Rates
- Code of Ethics
- Elections 2024
- India vs England
- T20 World Cup 2024 Schedule
- IPL 2024 Auctions
- T20 World Cup 2024
- Cricket Players
- ICC Rankings
- Cricket Schedule
- Other Cities
- Income Tax Calculator
- Budget 2024
- Petrol Prices
- Diesel Prices
- Silver Rate
- Relationships
- Art and Culture
- Telugu Cinema
- Tamil Cinema
- Exam Results
- Competitive Exams
- Board Exams
- BBA Colleges
- Engineering Colleges
- Medical Colleges
- BCA Colleges
- Medical Exams
- Engineering Exams
- Horoscope 2024
- Festive Calendar 2024
- Compatibility Calculator
- The Economist Articles
- Explainer Video
- On The Record
- Vikram Chandra Daily Wrap
- EPL 2023-24
- ISL 2023-24
- Asian Games 2023
- Public Health
- Economic Policy
- International Affairs
- Climate Change
- Gender Equality
- future tech
- Daily Sudoku
- Daily Crossword
- Daily Word Jumble
- HT Friday Finance
- Explore Hindustan Times
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Subscription - Terms of Use
- Rise of Medical Tourism in India
- Team India Blogs

Over the past decade, India has gained a reputation in providing high quality medical service at low costs to medical tourists travelling from across the globe. However, with the travel bans during the covid-19 pandemic, the influx of medical tourists had dipped. According to the Tourism Ministry , India registered a negative growth of 79.4% over 2020. Although, the situation looks positive once more owing to the efforts made to handle the pandemic situation. Market insights suggest the demand forecast to increase at a robust 19 % CAGR in 2022.
Why is India emerging as the popular medical hub for patients? India’s healthcare industry offers a combination of both modern and traditional forms of medicine which sets the country apart from others. First, it has a set of world-class doctors and hospitals that provide treatment at fractional rates when compared to other countries. Secondly, India’s systems of medicine: AYUSH i.e. Ayurveda, Yoga, Panchakarma, Rejuvenation Therapy, etc, which are the most ancient forms of medicine, are now gaining immense popularity globally. PM Modi also recently announced plans to launch an AYUSH Mark. A mark to provide credibility to AYUSH products in India and promote India’s medical tourism sector. Additionally, the other medical services and facilities are also backed by the World Health Organisation (WHO) and the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA).
To become the No.1 medical travel destination, there is a need for significant investments into making the healthcare industry and equipment attractive for international patients. Patients spend most of their time in guest houses and are prone to further infections from such places. Thus, proper infrastructure and standardisation needs to be brought into the tourism industry and nexus of guest house service providers urgently. Another aspect that needs to be tapped into is the opportunity for selling Indian health insurance to foreigners. This has the capability to generate an additional $9 billion in patient inflow to India.
To maximise the industry’s potential, the government is pulling out all its aces. The aim is to make India the No.1 Destination for Medical Tourism in the world, tripling its revenue to $13 billion within 4 years. The government has also proposed an outlay of US$ 28.7 billion for health and well-being, which is 137% higher than the previous year's budget outlay.
The following measures have been taken up by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare :
- Special provision of Medical Visa has been made for tourists travelling to India for healthcare purposes. This has been made available in 165 countries.
- Setting up a feedback mechanism to obtain testimonials from tourists travelling to the country for medical purposes. This ‘one-step’ portal would add to the convenience and provide credible information for medical tourists coming to India.
- The 'Heal in India' initiative aims to position the country as a global hub for medical and wellness tourism. Under this initiative, foreigners or those seeking medical help will be able to locate the list of hospitals in the country available to provide their choice of medical treatments through an ‘one step’ online portal. It is a one stop shop for all services from the treatment package cost, visa applications to grievance redressals and feedback. The initiative also aims at providing a database of healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and pharmacists and will also include a section where professionals can specify the country in which they are most interested in providing their services. This will allow India to diversify its operations by sending doctors abroad to treat patients.
The following measures have been taken up by the Ministry of Tourism :
- The Marketing Development Assistance Scheme (MDA) offers financial assistance to approved tourism service providers to promote an intricate nexus of facilities for the tourists to stay.
- Publicity materials, such as brochures and CDs, intended to promote medical and health tourism have been circulated in target markets. Yoga/Ayurveda/Wellness has been promoted over the last two years in print, electronic, internet, and outdoor media under the Ministry of Tourism's "Incredible India Campaign''.
To conclude, in the post-Covid world, the demand for the healthcare industry is bound to surge and there is a huge potential for India to realise and aggressively advance towards attracting medical tourists from other parts of the world including Europe and the Americas. With the government making it their priority to make India the hub of medical tourism, the initiatives combined with the surging demand are sure to make India the centre for all medical tourists in the future. Not only will India be the leader in saving millions of lives, but will also simultaneously generate valuable jobs and over $13 billion in forex.
This blog has been co-authored by Priyanka Cardoz and Sanjana Saigal.
We are India's national investment facilitation agency.

For further queries on this subject, please get in touch with us @Invest India. Raise your query
The Economic Times daily newspaper is available online now.
What's medical tourism how it can help indian economy, trends, and challenges.
Medical tourism refers to the practice of traveling to another country for medical treatment, often due to lower costs, better quality care, or shorter waiting times. In India, this industry has witnessed exponential growth, driven by factors such as world-class medical facilities, skilled healthcare professionals, and cost-effective treatments.

Read More News on
Download The Economic Times News App to get Daily Market Updates & Live Business News.
Subscribe to The Economic Times Prime and read the ET ePaper online.

Entire INR25 crore poll bonds purchased by Dangi’s Authum ahead of its Reliance-ADAG buys went to BJP

Retail investors ride momentum in the hunt for multibaggers. How long will the party last?

Indians shell out as much as Americans on transportation. And it’s a worrying sign. Here’s why.

Sebi wants to check fund managers amid a bull market. But MFs assure they are ready.

How Authum purchased INR25 crore electoral bonds before buying two Reliance-ADAG firms

Stock Radar: This IT stock is trading below 50 & 200-DMA. Is it a contra buy?
Find this comment offensive?
Choose your reason below and click on the Report button. This will alert our moderators to take action
Reason for reporting:
Your Reason has been Reported to the admin.

To post this comment you must
Log In/Connect with:
Fill in your details:
Will be displayed
Will not be displayed
Share this Comment:
Uh-oh this is an exclusive story available for selected readers only..
Worry not. You’re just a step away.

Prime Account Detected!
It seems like you're already an ETPrime member with
Login using your ET Prime credentials to enjoy all member benefits
Log out of your current logged-in account and log in again using your ET Prime credentials to enjoy all member benefits.
To read full story, subscribe to ET Prime
₹34 per week
Billed annually at ₹2499 ₹1749
Super Saver Sale - Flat 30% Off
On ET Prime Membership
Sign in to read the full article
You’ve got this prime story as a free gift.
Subscribe Now
(Credit card mandatory)
You can cancel your subscription anytime
(Pay Using Netbanking/UPI/Debit Card)
₹399 /month
Monthly PLAN
Billed Amount ₹399
No Trial Period
₹208 /month
Yearly PLAN
Billed Amount ₹2,499
15 Days Trial + Includes DocuBay and TimesPrime Membership.
₹150 /month
2-Year PLAN
Billed Amount ₹3,599
7 Days Trial
(Save 40.0%)
15 Days Trial
Get ET Prime for just ₹2499 ₹1749/yr
Offer Exclusively For You
Save up to Rs. 700/-
ON ET PRIME MEMBERSHIP
Get 1 Year Free
With 1 and 2-Year ET prime membership
Get Flat 40% Off
Then ₹ 1749 for 1 year
ET Prime at ₹ 49 for 1 month
Holi Offer on ETPrime
Get flat 20% off
To Read the full Story, Subscribe to ET Prime
Access the exclusive Economic Times stories, Editorial and Expert opinion
Unlock this story and enjoy all members-only benefits.
- 8 insight-rich stories published daily
- 4000+ in-depth Stock Reports
- Print Edition, the digital Newspaper
- 2 Stock Researches everyday
90 Days Prime access worth Rs999 unlocked for you

Exclusive Economic Times Stories, Editorials & Expert opinion across 20+ sectors
Stock analysis. Market Research. Industry Trends on 4000+ Stocks
Get 1 Year Complimentary Subscription of TOI+ worth Rs.799/-
Stories you might be interested in
- [email protected]
- +91 99109 32162

Healthcare Beyond Borders: The Rise of Medical Tourism in India
India’s emergence as a premier medical hub: reviving medical tourism post-covid.
The global healthcare landscape has witnessed a remarkable shift in recent years, with India gaining recognition for providing high-quality medical services at significantly lower costs to patients travelling worldwide. However, the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic and subsequent travel bans severely impacted the influx of medical tourists into the country.
The Tourism Ministry reported a staggering negative growth rate of 79.4% in 2020. Despite this setback, the situation is gradually improving as efforts to combat the pandemic yield positive results. Market insights suggest a robust 19% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the demand for medical tourism in India by 2022.
What makes India an increasingly popular destination for medical treatment?
The country’s healthcare industry offers a unique blend of modern and traditional medicine, setting it apart from competitors. Firstly, India boasts world-class doctors and hospitals that provide treatments at a fraction of the cost compared to other nations. Secondly, India’s ancient systems of medicine, known as AYUSH (Ayurveda, Yoga, Panchakarma, Rejuvenation Therapy, etc.), are gaining immense popularity globally.
To further enhance the credibility of AYUSH products and promote India’s medical tourism sector, Prime Minister Modi recently announced plans to launch an AYUSH Mark. India’s medical services and facilities also adhere to standards set by reputable organizations such as WHO, the World Health Organization, and the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA).
Significant investments are required to enhance the healthcare industry’s infrastructure and equipment, making them more appealing to international patients. Proper infrastructure and standardization in the tourism industry, mainly guest house services, are crucial to ensure patients’ safety and minimize the risk of infections. Additionally, there is a vast opportunity to offer Indian health insurance to foreign patients, which has the potential to generate an additional $9 billion in patient inflow to India.
The government is leaving no stone unturned to maximize the potential of the medical tourism industry. The objective is to make India the number one destination for medical tourism, tripling its revenue to $13 billion within four years. To support this vision, the government has proposed an outlay of US$ 28.7 billion for health and well-being, a substantial increase of 137% compared to the previous year’s budget allocation.
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has taken several measures to facilitate medical tourism:
- Special Medical Visas for healthcare purposes have been made available in 165 countries.
- Establishing a feedback mechanism aims to gather testimonials from medical tourists visiting India, providing credible information and convenience.
The ‘Heal in India’ initiative seeks to position the country as a global medical and wellness tourism destination. This initiative will enable foreigners and those seeking medical assistance to access a comprehensive list of hospitals offering their desired treatments through a user-friendly online portal. It will be a one-stop shop, covering treatment package costs, visa applications, grievance redressals, and feedback. Additionally, the initiative aims to create a database of healthcare professionals which includes dedicated doctors, nurses, and pharmacists, allowing them to specify their interest in providing services abroad, thus facilitating India’s diversification of operations.
The Ministry of Tourism has also taken serious steps to promote medical tourism
The Marketing Development Assistance Scheme (MDA) provides financial support to approved tourism service providers, enhancing tourist facilities.
Publicity materials, including brochures and CDs, have been extensively used to promote medical and health tourism under the Ministry of Tourism’s “Incredible India Campaign.” The campaign has successfully showcased the benefits of yoga, Ayurveda, and wellness practices across print, electronic, internet, and outdoor media.
As the world emerges from the Covid-19 pandemic, the demand for healthcare services is expected to surge, presenting India with a tremendous opportunity to attract medical tourists from Europe, the Americas, and beyond.
With the government’s unwavering commitment to making India the hub of medical tourism and the rising demand, the country is poised to become the ultimate destination for all medical tourists. India’s leadership in saving millions of lives will drive job creation and generate over $13 billion in foreign exchange, firmly establishing its position as a global healthcare leader.
How UniMediks can help you?
UniMediks are pivotal in facilitating affordable treatment for foreign nationals in India. Here’s how UniMediks can help:
Extensive Network of Medical Providers: UniMediks has partnered with renowned hospitals, clinics, and healthcare professionals across India. This vast network allows us to connect foreign nationals with the best medical providers offering affordable treatment options without compromising quality.
Customized Treatment Packages: UniMediks understands that each patient has unique healthcare needs. We work closely with medical providers to create customized treatment packages that align with patients’ requirements and budgets. These packages often include comprehensive medical services, accommodation, transportation, and other necessary arrangements, ensuring a hassle-free experience.
Cost Transparency and Negotiation: UniMediks believes in transparency regarding healthcare costs. We provide detailed cost breakdowns of treatment procedures, consultations, medications, and additional services. Our team negotiates with medical providers to secure competitive pricing, helping foreign nationals access affordable treatment options.
Assistance with Visa and Travel Arrangements: Traveling to an international country for medical treatment can be daunting. UniMediks offers guidance and support throughout the visa application process, ensuring a smooth and hassle-free journey for patients. We also assist with travel arrangements, including flight bookings, airport transfers, and accommodation, making the entire experience convenient and stress-free.
Language and Cultural Support: Overcoming language and cultural barriers is essential for foreign nationals seeking treatment in India. UniMediks provides language interpretation services to ensure effective communication between patients and healthcare providers. We also offer cultural guidance, helping patients navigate the cultural nuances and adapt to the local environment.
Post-Treatment Follow-up: UniMediks recognizes the importance of post-treatment care and follow-up. We facilitate regular communication between patients and medical providers, ensuring that patients receive the necessary support and guidance even after returning to their home countries.
Quality Assurance: UniMediks works only with accredited and reputable healthcare providers in India. We carefully evaluate the quality of services and infrastructure our partner hospitals and clinics offer. This commitment to quality ensures that foreign nationals receive safe and effective treatment from trusted medical professionals.
By leveraging our expertise and network, UniMediks strives to make affordable treatment in India accessible to foreign nationals. Our comprehensive support throughout the medical journey, combined with competitive pricing and quality assurance, enables patients to receive the care they need at affordable costs.
Recent Posts

Medical Tourism Companies in India: Indian Companies that Have Transformed Healthcare Access

Discover the Best Orthopedic Hospital in India: A Comprehensive Guide

Best Orthopedic Doctors in India: Expertise and Excellence

Navigating Excellence in Cardiac Care Choosing the Best Cardiac Surgeon in India

Navigating Healthcare: Understanding the Cost of Cancer Treatment in India
A Comprehensive Guide: Uterus Cancer Treatment Cost in India

Seeking the Best Mental Care Spotlight on the Best Mental Hospitals in India
Achieving Healthier Ears, Nose, and Throat: A Look at the Best ENT Hospital in India
A Review of the Top 10 Orthopedic Doctors in India

Unveiling the Economic Aspect of Cancer Treatment in India
Top hospitals.
- Medanta The-Medicity Hospital
- Indraprastha Apollo Hospital
- Fortis Escorts Heart Institute
- Manipal Hospital
- BLK-Max Hospital
- Batra Hospital & Medical Research Centre
- Jaypee Hospital
Top Procedures
- Heart Valve Replacement Surgery in India
- Knee Replacement Surgery In India
- Liver Transplant In India
- Disc Replacement Surgery in India
- Cardiac Valve Replacement Surgery in India
- Whipple Surgery in India
- Brain Cancer Treatment in India
Top Specialities
- Heart Hospital in India
- Orthopaedics Hospital in India
- Neurology Hospital in India
- Urology Hospital in India
- Bone Marrow Transplant Hospital in India
- IVF Treatment Hospital in India
- Gastroenterology Hospital in India
Top Doctors
- Dr. Rana Patir
- Dr. Sudheer Kumar Tyagi
- Dr. Hitesh Garg
- Dr. Puneet Girdhar
- Dr. Z.S Meharwal
- Dr. Yugal Kishore Mishra
- Dr. Shubash Chandra
UniMediks offers the most affordable and finest treatment packages for international patients seeking medical care in India. With our unique patient first strategy, we help you get access to quality facilities that meet your needs without breaking bank accounts or giving up on treatments because they’re too expensive!
- Patient Stories
- Get a free quote

UniMediks Support Online
Subscribe To Our Weekly Newsletter
Find us here.

Welcome to UniMediks
DESTINATION

Brief Introduction to the Country and its Reputation in Medical Tourism
India has long been a captivating destination, not just for its cultural richness and historical grandeur, but increasingly for its advancements in healthcare. Recognized as one of the premier medical tourism destinations, India welcomes hundreds of thousands of medical tourists each year. The combination of cutting-edge technology, highly qualified healthcare professionals, and affordable treatments has solidified India's reputation as a medical tourism powerhouse. From elective procedures to critical surgeries, the country provides an expansive range of high-quality medical services to international patients.
Historical and Cultural Significance in Medicine
The roots of Indian medical practices can be traced back to its ancient systems like Ayurveda, Yoga, and Siddha, which are still prevalent and integrated into modern medicine. The country's historical commitment to medical research and surgery is exemplified by figures like Susruta, an ancient Indian physician often dubbed the "Father of Surgery." Modern Indian healthcare draws from this rich history, amalgamating traditional practices with contemporary medical science.
An International Hub for Medical Excellence
Indian hospitals and healthcare providers are increasingly being accredited by international organizations, underscoring their commitment to quality and excellence. The growth of private hospitals catering specifically to international patients is another feather in India’s medical cap.
Cutting-Edge Innovation and Technology
From robotic surgeries to pioneering techniques in cardiology and oncology, Indian healthcare providers are at the forefront of medical innovation. State-of-the-art facilities and medical equipment are now standard in many Indian hospitals, making the country an attractive option for those seeking advanced medical treatments not available or affordable in their home countries.
Popular Medical Procedures
List and brief descriptions of procedures.
India is especially known for offering quality treatments in the following areas:
- Cardiology (including heart transplants)
- Orthopedic surgeries (like knee and hip replacements)
- Cosmetic surgery
- Dental care
- Oncology (cancer treatments)
- Ophthalmology
Specializations or Pioneering Treatments
India has gained recognition for specialized treatments like Ayurvedic Therapies, stem cell therapy, and minimally invasive surgeries. Hospitals are also engaging in groundbreaking research and offering cutting-edge treatments in neurosurgery and cardiovascular care.
Top Hospitals & Clinics
Renowned hospitals.
- Apollo Hospitals
- Fortis Healthcare
- Max Healthcare
- Medanta - The Medicity
Accreditation and Affiliation Details
Most top-tier hospitals are accredited by the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH) and many have Joint Commission International (JCI) accreditation.
Special Features, Awards, or Recognitions
Many Indian hospitals have won national and international awards for excellence in healthcare delivery and patient safety.
Cost Comparison
Comparative data.
On average, the cost of medical procedures in India is about 60-90% lower than in the United States, without compromising on quality. For example, a heart bypass surgery that costs upwards of $100,000 in the U.S. could cost as low as $5,000 in India.
Price Ranges
The following are approximate price ranges for some popular treatments:
- Knee Replacement: $4,000 - $9,000
- Hip Replacement: $5,000 - $10,000
- Heart Bypass: $5,000 - $8,000
Quality & Safety
Medical standards and practices.
India upholds high standards in medical practices, often on par with Western countries like the United States and the United Kingdom. The country has a rigorous medical education system that produces a large number of highly qualified doctors and nurses each year.
Accreditation Systems and Regulatory Bodies
Apart from international accreditations like JCI, Indian hospitals often seek accreditation from the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH), a constituent board of Quality Council of India. This ensures that the hospitals meet stringent guidelines in terms of quality and patient safety.
Quality Checks and Patient Safety Protocols
Hospitals and clinics in India are equipped with the latest technology to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Patient safety protocols are strictly followed, and quality checks are performed regularly to ensure the highest standards are maintained.
Patient Rights
Patients in India have the right to confidentiality, informed consent, and access to their medical records. Hospitals have dedicated International Patient Services departments that assist foreign patients in navigating healthcare in India.
Medical Visa Information
Guidelines and requirements.
International patients can apply for a Medical Visa, usually designated as ‘Med Visa’, which is specifically intended for medical treatments in India.
Duration, Documentation, and Application Process
A Medical Visa usually has a duration of up to one year or the period of treatment, whichever is less. Required documents often include a letter from a local doctor, a letter from the Indian hospital agreeing to treat you, and proof of financial stability. Online applications are generally processed within a week.
Travel-related Advisories or Restrictions
It is advisable to consult your home country’s embassy or consulate for any travel advisories or restrictions related to India, especially due to the evolving situation with the COVID-19 pandemic.
Cultural Considerations
Local customs and etiquette.
While the hospital staff is usually well-versed in international etiquette, understanding local customs like greetings and modest dress codes can enhance your stay.
Language Barriers
English is widely spoken in Indian medical facilities. However, translators for other languages can usually be arranged by the hospital.
Dietary Considerations
Indian cuisine is diverse and can be spicy. Most hospitals offer international cuisine to cater to the dietary needs of foreign patients.
Travel & Accommodation
Popular and recommended areas to stay.
Areas near major hospitals in cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, and Chennai offer a range of accommodation options, from budget hotels to luxury suites.
Proximity to Medical Facilities
Staying close to the hospital is advisable for convenience, and many hospitals offer in-house accommodation options for international patients.
Transportation Facilities
Public transport in major Indian cities is generally good, with options ranging from taxis to metro services. Private car hire services are also readily available.
Post-procedure Relaxation and Recuperation Spots
India offers a plethora of tourist attractions, from serene beaches in Goa to the peaceful Himalayan regions, ideal for post-procedure relaxation.

Legal & Ethical Considerations
Legal rights of patients.
Patients have the right to legal recourse in case of medical negligence or malpractice, although the legal process can be lengthy.
Medical Malpractice Laws
India has a set of laws dealing with medical malpractice and negligence, aimed at protecting the patient's rights.
Ethical Considerations
Issues like organ transplants are strictly regulated, and only relatives can donate organs, with some exceptions.
Benefits & Risks
The major benefits of choosing India for medical treatment include cost-effectiveness, high quality of healthcare, and the availability of specialized treatments.
Risks or Concerns
Potential risks include varying standards among healthcare providers and long waiting times for certain treatments, though these are not common at leading hospitals.
Post-procedure Care
Post-operative care.
Indian medical institutions offer comprehensive post-operative care, including physical rehabilitation services.
Availability and Quality of Rehabilitation Centers
Several top-notch rehabilitation centers are available for procedures requiring long-term care, such as joint replacements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is it safe to have surgery in India? Yes, if you choose accredited hospitals, patient safety and quality are generally excellent.
- Do doctors in India speak English? In most top-tier hospitals, doctors are fluent in English.
- What is the cost comparison? Medical treatments in India can cost 60-90% less than in Western countries.
- What about aftercare? Comprehensive aftercare and rehabilitation services are available.
Global Provider Members

Hindi and English
Indian Rupee
1,370,825,550
India is typically very hot, with the hottest and driest months lying between March and June. The average temperature during this time is usually 90 degrees Fahrenheit. However, in the western part of India, the average temperature can be much higher. The coolest months are between December and February, with the average daily temperature fluctuating between 50-59 degrees Fahrenheit (10-15 degrees Celsius). The rainy (monsoon) season lasts from March until June. Because the boundaries of India span a large land area, it does not fit into only one climate zone.
Facilitators

New Delhi, India

Haryana, India

Karnataka, India

Mumbai, India

Maharashtra, India

Delhi, India

Uttar Pradesh, India

Telengana, India

Tamilnadu, India

Punjab, India
Maharastra, India

Kerala, India

Gujarat, India
Tamil Nadu, India
Dehli, India
Featured Treatments

MedicalTourism.com
MedicalTourism.com is a free, confidential, independent resource for patients and industry providers. Our mission is to provide a central portal where patients, medical tourism providers, hospitals, clinics, employers, and insurance companies can all find the information they need. Our site focuses on patients looking for specific knowledge in the fields of medical tourism, dental tourism, and health tourism.

Medical Tourism in India: Challenges, Growth, Scope, Suggestions to Develop
- Post last modified: 28 August 2021
- Reading time: 29 mins read
- Post category: Tourism
What is Medical Tourism?
Medical Tourism can be defined as when clients go for medical treatment and choose to travel across international countries for medical services such as dental problems, beauty surgery, and different type of surgery and fertility treatment.
Medical tourism in India is a fast-growing sector. It has been estimated that the current size of the Indian medical tourism industry is a little over $ 3 billion and forecasted that the medical tourism industry will reach India by $ 6billion by 2018.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Medical Tourism?
- 2.1 Competition
- 2.2 Follow-Up Problems
- 2.3 Cultural Proximity
- 2.4 Brain Drain
- 2.5 Quality
- 2.6 Infrastructure
- 3 Growth of Medical Tourism in India
- 4 Treatment Cost Comparison
- 5 Issues to Medical Tourism Industry in India
- 6.1 Product
- 6.4 Promotion
- 6.6 Process
- 6.7 Physical Evidence
- 7.1 Role of Government
- 7.2 Medical Visas
- 7.3 Holistic Medical and Diagnostic Centers
- 7.4 Setting Up National Level Bodies
- 7.5 Integrate Vertically
- 7.6 Joint Ventures or Alliances
It is one of the major drivers of the Indian economy along with biotechnology, software technology, and technology facilitates consumer services.
India has been the most attractive destination for visitors around the globe. But the recent trend in the tourism sector shows a propelling growth in this industry. This is not only because of the heritage attraction of the country but due to growing medical care facilities in India.
Medical tourism is a developing concept and this sector is growing at a very fast rate. India ranks second for medical tourism in the world. In India, people from the world over visiting for their medical and relaxation needs.
It is also offering other medical services like yoga, meditation, and Ayurveda, which is increasingly becoming popular as a non-surgical treatment for various ailments among foreign patients.
The major service providers in Indian medical tourism are the Apollo Hospitals, Escorts Hospital, Fortis Hospitals, Breach Candy, Hinduja, Mumbai’s Asian Heart Institute, Arvind Eye Hospitals, Manipal Hospitals, Mallya Hospital, Shankara Nethralaya, etc.
Challenges of Medical Tourism in India
Medical tourism is not a new field in today’s era but today also it has the potential to nurture. With growing ability, it also tackles many challenges that need to be undertaken.
The challenges faced by medical tourism in India are as follows:
Competition
Follow-up problems, cultural proximity, brain drain, infrastructure.
Medical tourism is not only seeing immense growth in India rather it is seeing extensive growth one has to wait for long times for treatment in these above-said countries. And expectations of foreign customers are also increasing as they want personalized services at an affordable cost.
As the customer is coming from another country for treatment and if they want to follow up, it becomes very difficult for the patient especially in case of surgery, if any complexities occur after operation and the patient has departed to his own place/country.
In that case, it’s very difficult to follow up with the patient, which is also expensive in nature.
One of the biggest barriers in medical tourism is from the cultural and language front. Many patients, doctors, and nurses are not able to understand the language, apart from the specialized doctors and extremely refined medical systems, many doctors and their staff are not able to communicate in their language which makes the system weak and difficulties arise on both the side; patient as well as on staff side.
As our country is full of expert professionals but the main problem is to retain them, which is one of the biggest challenges in front of our country, because of not offering good salaries to them. In other countries, the professionalized and skilled professionals are very less so they hire people from India by offering higher salaries to them.
Quality is the main problem for patients while considering the medical tourism industry as a substitute treatment. Patients need a protected and elevated eminence in medical care. While selecting the other countries for medical treatment their focus is not only on the price but on the quality and safety also.
While choosing the hospitals and countries they also consider the nationalized and worldwide accreditation by quality monitoring bodies like the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (Indian Accreditation Body) and international boards such as Joint Commission International (JCI)/ Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO).
But it’s very sad to say that still, many Indian hospitals don’t have this accreditation.
Before selecting the country, the customer also focuses on the Infrastructure, which is the main concern affecting India as a destination. Bad roads, improper flight connectivity all over the country, lighting problem, water availability are some of the drawbacks which lacking behind India in the race of medical tourism.
Growth of Medical Tourism in India
There are many reasons for the growth of medical tourism in India . The primary reasons cited for this are the cost advantage that the Indian health care sector enjoys in comparison to other countries. Along with cost advantage, the services are offered by internationally experienced specialists.
This mixture of world-class facilities at an affordable cost makes India one of the top five most favored medical tourist destinations in the world. India is also endowed with world-acclaimed tourist destinations.
India provides a wide range of tourist destinations with natural beauties (Jammu, Srinagar, Shimla, Dehradun, Kerala backwaters, beaches of Chennai, Mumbai, Goa, Kolkata, etc.) heritage sites (Western ghats, Sunderbans, Nilgiris, Ajanta, Ellora, and Elephanta caves) spiritual destinations (Varanasi, Haridwar, Bodh Gaya, Ajmer Sharif, Churches of Goa ) and Metropolitan cities (Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, Hyderabad).
This gives the tourists visiting India a variety of options to include along with the treatment of their ailments. Another reason for the growth of medical tourism in India is the comparative cost advantages of India vis-àvis other countries.
This difference in cost is depicted in the table below: The table below depicts the cost difference between India and other countries. When one compares cost between India and the United States of America (USA) it can be seen that there is a huge difference between the two.
For the heart bypass procedure, the difference amounts to $ 1,20,000. Between India and Thailand, the cost difference is not much but India scores well in the state-of-art technology and has world-class hospitals and doctors.
Some other reasons which are cited for the growth of medical tourism in India are:
- In some countries there are long lists for getting treated.
- Favorable exchange rates of developed countries in comparison to India. This makes the travelling and lodging cheap for people from these countries.
- India provides state-of- art facilities because of the specialized doctors, nurses and paramedical staffs.
Treatment Cost Comparison
Issues to medical tourism industry in india.
As various countries are at loggerheads to get a greater share in the medical tourism industry, India needs to carve out a distant place for itself, by leveraging its existing strengths and thereby offering a unique value proposition.
Generally, there are three types of medical tourists:
- Foreigners coming for medical treatment.
- Foreigners seeking treatment and leisure.
- Expatriates.
A country like India is facing the following issues/challenges to become a tourist destination with a competent medical tourism industry. They are:
- Lack of infrastructural facilities like lack of connectivity, lack of coordinating system, poor power supply and poor water supply.
- Most Indian hospitals are also facing the lack of trust from the foreign patients. The hospitals have observed poor hygiene awareness in medical attendants, unhygienic food handling, and lack of proper hospitality services, heterogeneous pricing of services and no industry standards.
- no regulations,
- taxation anomalies,
- bureaucratic roadblocks,
- no works on land reforms,
- lack of long term investor friendly policies and
- instability with respect to terrorism and communal tensions.
- inadequate insurance cover,
- underdeveloped insurance market in India,
- insurance frauds and
- overseas companies refusing reimbursement.
- poor accessibility,
- lack of capital,
- lack of Community participation and awareness,
- lack of involvement from rural sector,
- lack of concern for sustainability,
- complex visa procedures,
- lack of good language translators, and
- poor airport facilities.
- quality accreditations to the Indian hospitals and service providers,
- training and Development to the Doctors, Nurses and Para medical staffs,
- lack of customer oriented approach.
Scope of Medical Tourism in India
India has many advantages. The first and the foremost is the cost advantage. Then, it has many hospitals equipped with international standards. Most Indian doctors and other medical staff have world-class exposure and are fluent in English which is connecting language globally.
India also has a whole lot of natural solutions to health like Ayurveda, and Sidha. It has many exotic tourist spots. Many medical tourists have already chosen India as their destination for treatments.
In the olden days, people used to travel to the USA to get advanced medical treatment. Now the reverse is happening. IT boom and cheaper flights make people to choose alternate health destinations for treatment.
Fast-paced lifestyle increases demand wellness tourism and alternative cures. Health insurance in countries like the USA covers only critical care and not cosmetic care and beauty treatments. Those who seek cosmetic /beauty treatments choose low-cost destinations like India.
Soaring medical costs, high insurance premiums, long waiting lists, a large number of uninsured/underinsured and insured in many advanced nations force people in those nations to be medical tourists. Insurance companies and employers also prefer to send patients to India in order to reduce health care expenses.
The large Indian community living abroad also makes use of a significant part of medical tourism in India. In Japan, the USA, UK, and many other European nations, the proportion of elder people has increased rapidly. At the same time, life expectancy has also increased steadily.
The combined result is significant demand for the natural healthcare system. The inability of many healthcare systems drives many individuals to seek alternatives to domestic healthcare. Demand from countries with underdeveloped healthcare capacities also increases.
The main opportunity presented by medical tourism is its contribution to the growth of health economies. It is a major source for foreign exchange and stimulates economic growth in other sectors including tourism, transport, pharmaceuticals, hotels, food suppliers to hospitals and restaurants.
The labor-intensive nature of the tourism industry makes it an excellent generator of employment. Medical tourism and the competition on the global health market promote technological advances and improved medical infrastructure.
After the SWOT analysis on Indian medical tourism and also interviewing the healthcare service providers in India as well as observing the different websites related to medical tourism’s growth and opportunities, the following marketing strategies may be used by India’s healthcare service providers.
They may be based on the 7 Ps of marketing mix:
Physical Evidence
India has a number of hospitals offering world-class treatments in nearly every medical sector such as cardiology and cardiothoracic surgery, joint replacement, orthopedic surgery, gastroenterology, ophthalmology, transplants, and urology to name a few.
The various specialties covered are Neurology, Neurosurgery, Oncology, Ophthalmology, Rheumatology, Endocrinology, ENT, Paediatrics, Paediatric Surgery, Paediatric Neurology, Urology, Nephrology, Dermatology, Dentistry, Plastic Surgery, Gynaecology, Pulmonology, Psychiatry, General Medicine & General Surgery.
Major healthcare service providers in India have started expanding their business to other countries by investing in and/or operating hospitals or medical centers overseas. These hospitals function as a diagnostic center for screening cases and also for follow-ups in medical treatments.
India’s healthcare service providers have a competitive advantage over their competitors due to its high standard of medical treatments and services offered to the patients at a very competitive price. In India, complicated medical procedures are being done only at one-tenth of the cost in industrialized countries.
But in terms of infrastructure facilities such as roads, sanitation, power backups, accommodations, and public utility services much more is needed for the country to become a medical tourism destination.
Internet is the main means for disseminating information related to medical and non-medical care services offered by each healthcare service provider. It is the most effective and inexpensive way to reach the product to its target customers directly, and at the same time helping patients acquire correct and valuable information allowing them to make an informed decision.
Informative online marketing of each service provider creates awareness of the medical treatments available and reassures potential patients. Interactive communication, treatments description, description of services and facilities, quality assurance other concierge services were also presented on the websites to attract the patient who is on a medical traveling program.
Most healthcare service providers in India particularly big private hospitals participate in travel marts, travel fairs, trade fairs, exhibitions, seminars, conferences, and advertise in travel magazines in countries with support from the government.
Articles, video, news related to their high quality and standard of medical treatments and services, health issues, latest medical technology equipment, quality assurance/awards/accreditation available on their own websites and also to the international media.
These help to create awareness of the available alternative medical treatments as well as to build up a positive image of the high quality and international standard of medical care in India.
Another strategy that Indian healthcare service providers may use is to attract international patients for their low-cost treatments in India as well as to get the medical services by its well–trained medical specialists who have qualified from well-known overseas institutes.
It is well acknowledged that having specialized and qualified doctors and staff gives a competitive advantage for the hospitals. However, shortage of doctors and trained medical staff is treated as the major concern in Medical Tourism in India.
Moreover, due to the misunderstanding of the patients’ culture is still considered a problem and challenge for the medical tourism business in India.
International patients who seek medical treatments are mostly concerned with the quality of treatments and also want that the service providers preferably be accredited by a recognized international organization that audits medical quality.
India has a large pool of doctors (approx 6,00,000), nurses, and paramedics with required specialization and expertise and the language advantage (English speaking skills). The medical education system caters to the ever-increasing demand for the delivery of quality health care services all over the country.
The Joint Commission International (JCI) recognizes and accredits that the standard of the hospital meets or exceeds the standard of medical facilities as compared to the west. India is a popular destination for medical tourists.
In India, big hospitals like Apollo Hospitals, Escorts Hospital, Wockhardt Hospitals, Breach Candy Hospitals Lilavati Hospital, Manipal Hospitals, Mallya Hospital, AMRI Hospitals etc. have a good ambiance in their Infrastructures with spacious, luxury rooms and excellent amenities same as that of a five-star hotel for patients and relatives, and also are equipped with cutting-edge technology.
This is a competitive advantage of India in order to gain the confidence and build up the trust of international patients, making a decision to choose India as their preferred choice.
Suggestions to Develop Medical Tourism
Role of government, medical visas, holistic medical and diagnostic centers, setting up national level bodies, integrate vertically, joint ventures or alliances.
The government of India must act as a regulator to institute a uniform grading and accreditation system for hospitals to build consumers’ trust. It also acts as a facilitator to encourage private investment in medical infrastructure and policy-making for improving medical tourism.
The government should actively promote FDI (Foreign direct investment) in the healthcare sector as well as also enacts conducive fiscal policies providing low-interest rate loans, reducing import/excise duty for medical equipment.
It also facilitates clearances and certification like medical registration numbers, anti-pollution certificates,s, etc. The government should reduce barriers in getting medical visas and institute visa-on-arrival for Patients and also can create medical attachés to Indian embassies that promote health services to prospective Indian visitors.
A simplified system of getting medical visas should be developed in order to make travel across borders smoother. Visas can be extended depending on the condition of the patients.
The procedures for obtaining a medical visa, the subsequent registration and visa extension procedures are complicated and time-consuming. There is a need to simplify and speed up these procedures to make India a more attractive medical tourism destination.
Holistic medical and diagnostic centers within the corporate hospitals: Most of the big tertiary hospitals are opening up holistic centers within the premises, with yoga and meditation programs long with naturopathy, herbal medicine, acupuncture, and homeopathy departments.
The claim is that these enhance treatment. However, these services are charged for and add to additional revenues. The hospitals have small spaces for the relatives to pray in, thereby wedding science with religion and traditional with modern medical practices.
To market India’s specialized healthcare products in the world and also address the various issues confronting the corporate healthcare sector, leading private hospitals across the country are planning to set up a national-level body on the lines of the National Association of Software and Service Companies (NASSCOM), the apex body of software companies in the country.
It is therefore essential to form an apex body for health tourism –the National Association of Health Tourism (NHAT).
Various added services may be offered to the patients. For example, hospitals may have kiosks at airports, offer airport pickups, bank transactions, or tie-ups with airlines for tickets, and may help facilitate medical visas by the government.
With more Arab patients coming in, some hospitals may have hired Arabic interpreters, stocked up on prayer rugs, and opened up a kitchen serving the food preparations in corporate hospitals in India.
To counter increasing competition in the medical tourism sector, Indian hospitals should tie up with foreign institutions for an assured supply of medical tourists. Specifically, they may tie-ups with capacity-constrained hospitals and insurance providers.
The Apollo group has also tied up with hospitals in Mauritius, Tanzania, Bangladesh, and Yemen. In addition, it runs a hospital in Sri Lanka and manages a hospital in Dubai.
As a part of this policy of promoting public and private initiatives, the Indian travel industry and tour operators have also designed packages that include air travel, hotel accommodation, and surgery expenses, claiming savings.
Please Share This Share this content
- Opens in a new window X
- Opens in a new window Facebook
- Opens in a new window Pinterest
- Opens in a new window LinkedIn
- Opens in a new window Reddit
- Opens in a new window WhatsApp
You Might Also Like
Tourist places to visit in telangana (2024), tourist places to visit in punjab (2024), tourist places to visit in srinagar (2024), recreation and leisure: role, facilities, research methods, types of tourism: based on nationality, duration, number of tourists & classification, approaches to tourism, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
A doctor’s guide on medical tourism in India
Medical tourism in india.
Medical tourism has flourished in India over the years. India ranked 10th in the 2020-2021 Medical Tourism Index. And the arrival of foreign tourists for medical purposes has increased from 1.83 lakh in 2020 to 3.04 lakh in 2022. These findings indicate enormous opportunities for doctors to benefit from medical tourism.
The way forward for medical professionals
For medical tourism to have a major impact, healthcare providers must make some investments. Build and maintain a social media profile, a website, and a blog. Collaborate with travel agencies, five-star hotels, and other hospitality service providers. Ensure comfort to international tourists in every aspect. You need to take care of their end-to-end requirements.
Investment in technology, security, and translators is essential to make Indian healthcare become world-class. Loans for doctors are customised financing solutions. You can use these solutions to make necessary investments and cash in on the booming medical tourism market.
Factors attracting medical tourist to India
Medical tourism in India is growing steadily each year. Chennai city is popular as the “Health capital of India”. The city attracts more than 40% of medical tourists due to the number of multi- and super-speciality hospitals. It is estimated that Chennai has approximately 150 international patients every day. The various factors that attract medical tourists to India are:
India provides high-quality healthcare at lower rates. The cost of treatment in India is one-tenth the cost of the same treatment in the US/UK. For example, a heart bypass surgery may cost approximately US$ 1,23,000 in the US, whereas in India, it costs roughly US$ 7,900 or less.
India has 43 JCI-accredited hospitals. The country has the infrastructure to provide high-quality treatment using the latest technologies and techniques.
3. Waiting time
In developed countries like the US, UK, and Canada, patients have to wait for major surgeries. India has no waiting time or very little waiting time for surgeries.
4. Language
Despite linguistic diversity, English is one of the official languages in India. Knowledge of English, a global language, makes communication easy with foreign patients.
The Government of India, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, and the Ministry of Tourism are focusing on making India a more prominent medical destination. For this purpose, a medical visa has been introduced, which allows a medical tourist to be in India for a specific period. A visa on arrival is granted for citizens from a few countries, letting them stay in India for 30 days.
How to attract medical tourists and the cost involved
The cost of hosting an international patient depends upon factors like the medical intervention needed, the hospital, the physician, and the duration of stay. Medical tourism is a competitive sector. You may take a few initiatives to attract medical tourists:
1. Invest in technology
Medical tourists get attracted to world-class healthcare facilities. You need to invest wisely in technology-enabled services and facilities as per global standards. Technology investments depend on the infrastructure and services that you plan to provide. For better accessibility to your services, you can create an app for using the services offered by your hospital or clinic.
2. Have a strong online presence
Online marketing is essential in medical tourism. You need to maintain a user-friendly and easy-to-understand website and blog. The cost of maintaining a CMS website is approximately Rs. 15,000 and a blog page will cost you approximately Rs. 500 per year for a domain name and hosting. You can answer queries with a live chat feature on your website. A live chat feature may cost you approximately Rs. 1,200 per month.
Be active on social media like Instagram, Facebook, LinkedIn, and others. You can invest in paid promotions to promote your web page on social media platforms like Facebook.
3. Collaborate
Medical tourism is a team effort. You need to invest in collaborating with hospitality partners, representatives of international health officials, and others.
Additional services to attract medical tourists
Apart from quality healthcare, you may need to provide additional services to medical tourists. These services can make their travel and stay comfortable. The extra services for medical tourists you can provide are:
1. Quotation assistance
The quotation is a primary concern for a medical tourist. Right from travel and accommodation to doctor appointments and post-treatment arrangements, the tourist has to prepare for all the costs. Physicians should make an approximate quotation as per the medical intervention and hospital stay required.
2. Visa assistance
Foreign nationals require a visa invitation letter to apply for a medical visa to India. Get necessary details such as the full name of the patient, passport number, and other details from the patient. Then, make arrangements for issuing the visa invitation letter to prospective foreign patients.
Medical tourism is a team effort. You need to invest in collaborating with hospitality partners, representatives of the international health offices, etc.
4. Accommodation service
Comfort is essential for medical tourists. Invest in it. You need to provide spacious accommodations to international patients. The room must have 24*7 room service, laundry service, internet, air conditioner, TV, and meals facility. Collaborate with a travel agency, five-star hotels, guest houses, and other external partners, to ensure comfort.
5. Interpretation service
The staff hired for international patients should be fluent in speaking English. You may need to hire translators for non-English speaking patients. The salary for translators can be around 4.2 lakh p.a.
6. Security service
You cannot compromise the safety of medical tourists. To ensure safety, you must make sufficient investments in hiring trained security personnel and using the latest security technologies.
Additional Read: Indemnity Insurance
DISCLAIMER: While care is taken to update the information, products, and services included in or available on our website and related platforms/websites, there may be inadvertent inaccuracies or typographical errors or delays in updating the information. The material contained in this site, and on associated web pages, is for reference and general information purpose and the details mentioned in the respective product/service document shall prevail in case of any inconsistency. Subscribers and users should seek professional advice before acting on the basis of the information contained herein. Please take an informed decision with respect to any product or service after going through the relevant product/service document and applicable terms and conditions. In case any inconsistencies observed, please click on reach us .
*Terms and conditions apply
Related videos

All you need to know about Credit Pass

All you can do with your Flexi Loans

Change Drawdown Bank Account

Features of Doctor Loans

Doctor Loan EMI Calculator

Doctor Loan Interest Rates

Check Doctor Loan Eligibility
Please wait
Your page is almost ready
Advertisement
Framework for Promotion of Medical Tourism: A Case of India
- Published: 28 June 2021
- Volume 16 , pages 103–111, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
- Vinaytosh Mishra ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6360-910X 1 &
- Mohita G. Sharma ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3341-9663 1
7116 Accesses
10 Citations
Explore all metrics
Medical tourism is quickly growing in developing countries. The healthcare players have recognized it as a potential area for economic diversification. The major factors affecting medical tourism in a country are cost, quality, language, and ease of travel. The healthcare services in India cost significantly lower than in western countries and the middle east. That is one of the reasons behind India attracting customers from these countries. The government promotes India as a premier healthcare destination and has made policies to ease travel for medical tourism purposes. Quality has been one of the important criteria for the selection of healthcare providers even for price-conscious customers. This study uses the case of the eastern part of the state of Uttar Pradesh to investigate the reason behind the low penetration of medical tourism in the region. The study identifies factors affecting medical tourism in post-COVID times and maps them with enablers using a focus group discussion. The study further uses SERVQUAL, a multidimensional research instrument to measure service quality by capturing patient’s expectations and perceptions along five dimensions of service quality. The study contributes to the existing literature in two ways. It provides the framework for the promotion of medical tourism in a region. Second, it provides future directions for research in the area of medical tourism in the post-COVID world.
Similar content being viewed by others

Medical Tourism: The Islamic Perspective

Developing Medical Tourism in Bangladesh: Issues, Challenges and Policies
Medical tourism in bangladesh: present scenario and strategic model for one-stop service.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Medical tourism (MT) has been growing enormously in the past few decades. This has been especially favorable for many developing countries especially in Asia wherein there is travel between upper-income countries and lower- and middle-income countries for healthcare purposes (Behrmann & Smith, 2010 ). The drivers for this travel have been prohibitively expensive, inadequate, or unavailable in their high-income home countries and the services could include cosmetic, wellness, and dental treatments, and has been collectively called medical tourism (Connell, 2006 ; Turner, 2011 ). Especially governments and private-sector actors in Asia, Europe, and Latin America have begun to actively promote their countries, cities, and medical facilities as medical tourism destinations to boost and diversify their tourism and healthcare offerings (Wong & Musa, 2012 ). Various governments have also promoted their country as a medical tourism destination through policy interventions. In a recent study, the economic performance of medical tourism is analyzed vis-a-vis overall community satisfaction, health care satisfaction, and attitudes toward medical tourism through a combination of social exchange theory with spillover theory. This is shown in a study where for a particular region the residents’ perceptions of medical tourism’s impact on community wellbeing also affect willingness to pay higher taxes and support for medical tourism development (Suess et al., 2018 ).
If we focus on India, the main driver of the growth of medical tourism has been the highly trained medical fraternity who is adept in English (Crooks et al., 2011 ). India has over the years become the hub of medical tourism which is the confluence of the twin sectors of the tourism industry and health industry (Shanker, 2019 ). This falls under the category of service exports and has been instrumental in earning foreign exchange and huge employment opportunities for the country. Given the fact that the main objective of medical tourists is getting good quality medical treatment at a reasonable cost, the outward focus has to be on competitiveness and the inward focus has to be operational excellence to drive the cost down. In a previous study, Thailand, Singapore and India have been identified as the main players in medical tourism capturing 80% of Asia’s medical tourism market (Mary, 2014 ). A comprehensive definition of medical tourism competitiveness has been given by Ganguli and Ebrahim, ( 2017 ) which can be stated as: “the ability to strategically plan, set viable policy goals, establish effective multi-stakeholder partnerships, maintain an attractive environment; and ensure that all of these capabilities are harmonized to optimize the delivery of medical services that rank high on parameters of quality, innovativeness, affordability, and safety”.
The further reasons which make India an attractive medical tourism destination are ensuing (Bagga et al., 2020 ; Bies & Zacharia, 2007 ; de Arellano, 2007 ).
Demand: Emanating from the long waiting lists in the developed countries has resulted in patients moving to other healthcare destinations.
Affordability and cost: The low cost of medical treatments in India makes it an enticing healthcare destination. In India, costs for complicated surgical procedures are almost one-tenth of the cost as compared to the procedures in the developed countries.
Accessibility: Affordable and access to air routes from every part of the globe make India one of the favored medical tourism destinations. The country has a further favorable exchange rate which makes it an economically viable alternative. The government has even eased the visa rules for tourists visiting the country for medical tourism purposes.
Communication: Indian healthcare workforce is good at English communication. The advancement in telemedicine helps patients in getting follow-up care, rehabilitative care after major surgery. This even eliminates the need for a follow-up visit to the country.
India attracts patients in areas namely wellness tourism, alternative systems of medicine, cosmetic surgery, and advanced and lifesaving healthcare. Thus, the Medical Tourism structure can be broadly classified into the following four categories (Fig. 1 ).
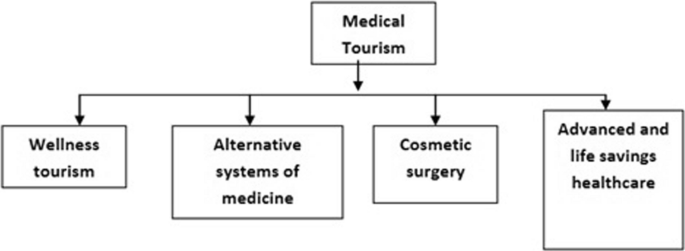
Medical tourism structure in India
Medical tourism is not a simple process. It is a complex decision by an international traveler based on the attributes of the host country, facilities of healthcare professionals, reasonable cost, and the service quality of hospitality and tourism (Chuang et al., 2014 ; Fetscherin & Stephano, 2016 ; Olya & Nia, 2021 ). Some studies are exploring the development of the Medical Tourism Index (MTI) and four dimensions of MTI include country environment, tourism destination, medical tourism costs, and medical facility and services (Fetscherin & Stephano, 2016 ). In a detailed literature review and co-word citation analysis, Hoz-Correa et al. ( 2018 ) suggests that six themes dominate the research: (a) issues regarding ethical implications, trust, and accreditation; (b) health, wellness, spa tourism, and service quality; (c) health-related issues, medical treatments, and tourism; (d) “sensitive” practices in MT; (e) medical tourism destinations and marketing; and (f) globalization, policies and the effect on international patients.
Further, Ebrahim and Ganguli ( 2019 ) and Belladi et al. ( 2019 ) have done a strategic cross-country comparison and have elucidated that the extent of coordination among public and private MT stakeholders and a collaborative; administration efficiency of sectors such as medical, tourism, and economic sectors along with the development of medicine and related human capital contribute to enhancing the growth of the sector. In another cross-country study, exploring the hospital’s website across five dimensions: hospital information and facilities, admission and medical services, interactive online services, external activities, and technical items, it was observed that there were differences between Indian, Malaysian, and Thai hospital websites and suggesting that there was a need for hospital managers to improve their hospitals’ online presence and interactivity (Moghavvemi et al., 2017 ).
Cham et al. ( 2021 ) in their study of Chinese medical tourists to Malaysia have analyzed country-specific factors (country knowledge, safety and security, accessibility, and price reasonableness) and social factors (word-of-mouth and social media) to be significant predictors of the image of Malaysia as a medical tourism destination, which in turn, affect the perceived value and intention to revisit. Another study provides an extended diamond-based pyramid framework of regional competitiveness and can be adopted for the medical tourism sector in a country (Moirangthem & Nag, 2020 ). Ghosh and Mandal ( 2019 ) have cited in a study on India that treatment quality, medical service quality, medical tourism expenses, medical tourism infrastructure, destination appeal, destination culture, and ease of access increase the satisfaction and loyalty of medical tourists. Taking a stream from Hoz-Correa et al. ( 2018 ) of service quality, this study extends this inquiry into understanding the service quality dimensions for medical tourism, especially for India. The study highlights the importance of service quality in achieving operational excellence. The image of India is discolored due to the below-par performance of the health system during the COVID-19 pandemic and may impact the export competitiveness of medical tourism. It is imperative to assess the quality gap and take corrective measures to remain competitive.
The next section lists the objectives of this research followed by the methodology used in this study. Subsequent sections discuss the result and hence the conclusion for the study. In last but not least, the study lists the limitations of the research and the future agenda for the research.
Research Objectives
The objective of this research is threefold: (1) to use the extant literature to identify the factors affecting medical tourism, (2) to provide the framework for the development of medical tourism in a region using focus group discussion, and (3) to use the case of eastern Uttar Pradesh to analyze the service quality gap using established instrument SERVQUAL.
Methodology
The research reviews the extant literature to identify the factors affecting medical tourism in a region. The findings of the reviewed literature are listed in the introduction section of this paper. The first step included using the finding of the literature review and input from the focus group to propose a framework for the development of medical tourism in a region. The study in the second stage uses the SERVQUAL method to evaluate the case region on five dimensions of the service quality.
Services being distinguished by intangibility and consumed simultaneously, the quality of service is understood as the perception of value delivered (Lam et al., 2012 ). Nitecki and Hernon ( 2000 ) defined service quality in terms of “meeting or exceeding customer expectations, or as the difference between customer perception and expectations of service” (Wang & Shieh, 2006 ). SERVQUAL is a multidimensional research instrument designed to measure service quality by capturing respondents’ expectations and perceptions (Parasuraman et al., 2002 ). The instrument has been widely used to assess the quality of services in the industry such as retail, hospitality, and healthcare (Ajam et al., 2014 ; Saleh & Ryan, 1991 ; Zhao et al., 2002 ). Thus for quantitatively assessing it, it is taken as the difference between the customer’s perception of the service and his expectations in his mind. Perception is the comparison between expectations and actual performance. A positive indication of quality is when the performance is higher than expectations and vice versa.
Healthcare is a high involvement service with long-term engagement between the patient and service provider and SERVQUAL has been used to prioritize the dimensions and identify the gaps to be filled to enhance the competitiveness of the delivery process (Al-Neyadi et al., 2018 ; Traipathi & Siddiqui, 2018 ). The SERVQUAL model has five dimensions of service quality namely reliability, assurance, tangibles, empathy, and responsiveness (Fig. 2 ).
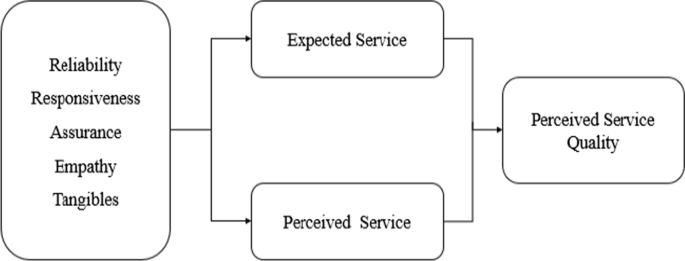
SERVQUAL model for service quality
The description of the five dimensions of service quality is listed in Table 1 (Butt et al., 2010 ; Parasuraman et al., 1988 ).
The researchers have used the established and time-tested SERVQUAL for assessing the service quality in the case of medical tourism (Chou et al., 2012 ; Guiry & Vequist, 2011 ; Qolipour et al., 2018 ).
The focus group used for objective one of the study is the healthcare professionals working in India. The size of the focus group is eight including the researchers as coordinators and passive members. A focus group larger than eight is difficult to manage (Fern, 1982 ). The focus group constituted four healthcare professionals, three doctors, and one healthcare researcher. Focus group discussion is frequently used as a qualitative approach to gain an in-depth understanding of the problem at hand (Nyumba et al. 2018 ). This method uses data from a purposely selected group of individuals rather than from a statistically representative sample of a broader population. Even though the application of this method in management research has been extensive, there are no critical assessments of the application of the technique. In addition, there are no readily available guidelines for researchers. This study uses the Delphi method to gain consensus on the framework. The Delphi method is well suited as a research instrument when there is incomplete knowledge about a problem or phenomenon (Skulmoski, 2007 ). The approach adopted for the Delhi Method is depicted in Fig. 3 (Cooper, 2019 ).
Delphi approach for focus group
The sample size for this exploratory study was taken as 31 and the sampling method was used as purposive sampling. The extant literature suggests that with purposive sampling a sample size of 30 for the exploratory study is adequate (Kowalska & Ostręga, 2020 ). The questionnaire was sent to 50 prospects out of which 31 responded, making the response rate 62%. The characteristics of the respondent are listed in Table 2 .
To summarize, the study first identifies the factors and enablers for medical tourism in the region then uses the focus group’s input to map it. The study then uses SERVQUAL for finding the quality gap. The summary of the research methodology used in the study is depicted in Fig. 4 .
Schematic diagram for the study
Results and Discussion
Based on the research, the study identifies four major factors affecting the penetration of medical tourism in the region. The focus group discussion helped us in identifying cost, quality, language, and ease of travel as the four most important factors affecting the penetration of medical tourism in a region. The study further interviewed the focus group members to identify enablers for these identified factors. Based on the input of the focus group, the study proposes a framework for increasing the penetration of medical tourism in the case region. The secondary research and focus group discussion suggested lean management, use of quality management systems, having National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Providers (NABH) and External Quality Assurance Systems (EQAS), language and soft skills, and ease of travel and visa rules as some of the important enablers for achieving the four factors. Figure 5 summarizes the framework using enablers and factors to increase the medical tourism in the region.
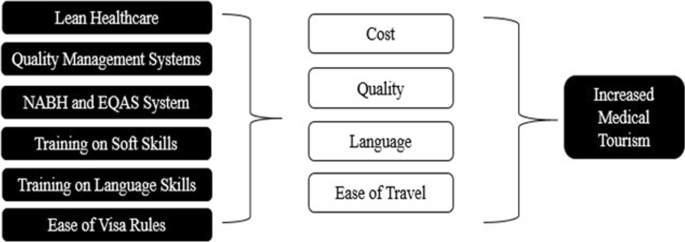
Framework for increasing medical tourism
It can be seen that ease of Travel and Language are environmental factors and external to the control of business whereas Cost and Quality are within the control of the business. Cost and Quality are interlinked and emphasis on quality can reduce the cost of operations thereby achieving operational excellence. Further, as the extant literature and focus group, discussion suggested quality is one of the most important criteria for the selection of a healthcare destination. The study adopted the SERVQUAL model which is a recognized tool to understand the difference between expectations and the perception of the service quality on five dimensions’ reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy, and tangibles. The respondents were asked to give responses to 22 questions on a Likert scale of ten and the average of the score on the subdimensions was taken as a score for a dimension. Thus, the maximum possible score for any dimension is ten. The perception score ( P ) and expectation score ( E ) for the service quality is listed in Table 3 . The difference of P and E gives the gap between expectation and perception, the difference needs to be minimized to increase customer satisfaction (Gounaris et al., 2007 ).
Figure 6 depicts the perception, expectation of maximum value on five dimensions of the service quality. As the figure suggests the largest service gap is for reliability, followed by responsiveness and assurance. The minimum service gap is for the service dimension tangible but there is still a scope of improvement when we compare it with the maximum score possible.
Perception and expectation of service quality
The study also shows that maximum expectation is for dimension reliability, assurance followed by responsiveness and empathy. The gap between expectations and performance is large for Reliability and Assurance Dimensions. The reliability of the service can be enhanced by making the service more process-driven and adhering to management systems. The lesser the non-conformity is, the better the reliability. On the other hand, for ‘assurance’ the focus has to be on providing soft skill training to the personnel and attitude of service in the nurses and paramedical staff. It also depends on the work culture of the organization. The responsiveness of the service is ‘how quickly the problem gets resolved. For addressing this parameter, the capacity of the supporting staff has to be enhanced so that the time of response gets reduced. It is observed that the tangibles and empathy gap is less which is a good sign. The customers are satisfied with the infrastructure and feel that they are understood. Given the fact that the empathy gap is less and the assurance gap is high, an attempt to enhance communication can reduce the assurance gap also.
The increased cost of care in western countries and the middle east has forced patients to look towards the east. Medical tourism is quickly growing in developing countries like India. Recent process innovation and operational excellence in India make it possible to deliver healthcare at a fraction of the cost compared to the western countries. The average cost of open-heart surgery, as reported by Narayana Health, is less than $2000. The same procedure at a US research hospital typically costs more than $100,000. The factors making a destination a preferred medical tourism destination is cost, quality, language, and ease of travel. The extant literature suggests that quality is one of the most important criteria for the selection of a healthcare provider (Mishra et al., 2019 ). A website listing the healthcare tourism destination in India lists only a few healthcare providers from eastern Uttar Pradesh. With the availability of vaccines and mass vaccination in many countries, borders have started opening again. The governments should think about measured to promote medical tourism in post-COVID times. This compelled us to investigate the reason behind the low penetration of medical tourism in the region and what can be done.
Studies have used the SERVQUAL method for quality assessment of private healthcare providers (Butt et al., 2010 ; Pekkaya, 2019 ). There is evidence of recent use of the SERVQUAL method for quality assessment in healthcare in developing countries (AlOmari, 2020 ; Tripathi & Siddiqui, 2018 ). Qolipour et al. ( 2018 ) analyze the patient’s perspective on the quality of medical tourism in Iran. Although there are studies on the evaluation of service quality of medical tourism destinations, there is a lack of studies done on quality assessment of medical tourism as eastern India as the destination, and this study attempts to fill this gap. This study uses a mix of qualitative and quantitative approaches for the development of a framework for promoting medical tourism in the region. The study further uses the SERVQUAL model to find out the patient’s perception and expectation of healthcare services on five dimensions of service quality and identifies the area of improvement. The approach used in the study is simple and easy to follow and does not overwhelm a reader with excessive details. The study uses Radar Chart to visualize the quality gap related to five dimensions. The study will help healthcare providers and policymakers devise strategies for promoting medical tourism in a region. The finding of the study is also useful for healthcare administration to improve service quality in their organization to eventually attract patients from Gulf and Western Countries.
Limitations and Future Directions
The limitations of the study emanate from the model that has been adopted. Despite its strengths and widespread acceptance, SERVQUAL is sometimes disapproved of for its bounded lens and these criticisms are true for this study as well. The focus of the model is from an operations perspective, and so it fails to draw on established economic, statistical and psychological theory. The prime focus remains on service operations and delivery rather than the outcome. Some studies also reflect that the five dimensions of service quality used in the SERVQUAL are not universal (Buttle, 1996 ).
This study is exploratory and uses purposive sampling. A study having a larger sample size and probabilistic sampling will help generalize the finding to a larger population. The study can include samples from countries other than Mauritius, UAE and the US will make the study more inclusive. The majority of the respondents represent prospects from the age group 45–55. This may be one of the limitations of the study. A future study can empirically test the framework proposed in the study for the promotion of medical tourism in a region. Future studies can also include more service dimensions related to healthcare.
Key questions reflecting applicability in real life
What are factors affecting the penetration of medical tourism in a geographical region?
What are the enablers for these factors to attract medical tourists to the region?
What are the healthcare quality dimensions used in existing literature for medical tourism?
How to use the SERVQUAL method to identify and fill the service quality gaps?
Availability of Data and Material
Available on request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Ajam, M., Sadeghifar, J., Anjomshoa, M., Mahmoudi, S., Honarvar, H., & Mousavi, S. M. (2014). Assessing the quality of healthcare service by the SERVQUAL model: A case study of a field hospital. Journal of Military Medicine, 15 (4), 273–279.
Google Scholar
Al-Neyadi, H. S., Abdallah, S., & Malik, M. (2018). Measuring patient’s satisfaction of healthcare services in the UAE hospitals: Using SERVQUAL. International Journal of Healthcare Management, 11 (2), 96–105. https://doi.org/10.1080/20479700.2016.1266804
Article Google Scholar
AlOmari, F. (2020). Measuring gaps in healthcare quality using SERVQUAL model: Challenges and opportunities in developing countries. Measuring Business Excellence . https://doi.org/10.1108/MBE-11-2019-0104
Bagga, T., Vishnoi, S. K., Jain, S., & Sharma, R. (2020). Medical tourism: Treatment, therapy and tourism. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research, 9 (3), 4447–4453.
Behrmann, J., & Smith, E. (2010). Top 7 issues in medical tourism: Challenges, knowledge gaps, and future directions for research and policy development. Global Journal of Health Science, 2 (2), 80.
Beladi, H., Chao, C. C., Ee, M. S., & Hollas, D. (2019). Does medical tourism promote economic growth? A cross-country analysis. Journal of Travel Research, 58 (1), 121–135. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287517735909
Bies, W., & Zacharia, L. (2007). Medical tourism: Outsourcing surgery. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 46 (7–8), 1144–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2007.03.027
Butt, M. M., & de Run, E. C. (2010). Private healthcare quality: Applying a SERVQUAL model. International Journal of Health Care Quality Assurance, 23 (7), 658–673. https://doi.org/10.1108/09526861011071580
Buttle, F. (1996). SERVQUAL: Review, critique, research agenda. European Journal of Marketing, 30 (1), 8–32. https://doi.org/10.1108/03090569610105762
Cham, T. H., Lim, Y. M., Sia, B. C., Cheah, J. H., & Ting, H. (2021). Medical tourism destination image and its relationship with the intention to revisit: A study of Chinese medical tourists in Malaysia. Journal of China Tourism Research, 17 (2), 163–191. https://doi.org/10.1080/19388160.2020.1734514
Chou, S. Y., Kiser, A. I., & Rodriguez, E. L. (2012). An expectation confirmation perspective of medical tourism. Journal of Service Science Research, 4 (2), 299–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12927-012-0012-3
Chuang, T. C., Liu, J. S., Lu, L. Y., & Lee, Y. (2014). The main paths of medical tourism: From transplantation to beautification. Tourism Management, 45 , 49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2014.03.016
Connell, J. (2006). Medical tourism: Sea, sun, sand, and… surgery. Tourism Management, 27 (6), 1093–1100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2005.11.005
Cooper, C. (2019). Critical competencies needed for outside sales managers: A Delphi study . SAGE Publications Ltd.
Book Google Scholar
Crooks, V. A., Turner, L., Snyder, J., Johnston, R., & Kingsbury, P. (2011). Promoting medical tourism to India: Messages, images, and the marketing of international patient travel. Social Science & Medicine, 72 (5), 726–732
Crooks, V. A., Turner, L., Snyder, J., Johnston, R., & Kingsbury, P. (2011). Promoting medical tourism to India: Messages, images, and the marketing of international patient travel. Social Science & Medicine , 72 (5), 726–732.
De la Hoz-Correa, A., Muñoz-Leiva, F., & Bakucz, M. (2018). Past themes and future trends in medical tourism research: A co-word analysis. Tourism Management, 65 , 200–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2017.10.001
De Arellano, A. B. R. (2007). Patients without borders: The emergence of medical tourism. International Journal of Health Services, 37 (1), 193–198. https://doi.org/10.2190/4857-468G-2325-47UU
Ebrahim, A. H., & Ganguli, S. (2019). A comparative analysis of medical tourism competitiveness of India, Thailand, and Singapore. Tourism an International Interdisciplinary Journal, 67 (2), 102–115.
Fern, E. F. (1982). The use of focus groups for idea generation: The effects of group size, acquaintanceship, and moderator on response quantity and quality. Journal of Marketing Research, 19 (1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1177/002224378201900101
Fetscherin, M., & Stephano, R. M. (2016). The medical tourism index: Scale development and validation. Tourism Management, 52 , 539–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2015.08.010
Ganguli, S., & Ebrahim, A. H. (2017). A qualitative analysis of Singapore’s medical tourism competitiveness. Tourism Management Perspectives, 21 , 74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2016.12.002
Ghosh, T., & Mandal, S. (2019). Medical tourism experience: Conceptualization, scale development, and validation. Journal of Travel Research, 58 (8), 1288–1301. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287518813469
Gounaris, S. P., Tzempelikos, N. A., & Chatzipanagiotou, K. (2007). The relationships of customer-perceived value, satisfaction, loyalty, and behavioral intentions. Journal of Relationship Marketing, 6 (1), 63–87. https://doi.org/10.1300/J366v06n01_05
Guiry, M., & Vequist, D. G. (2011). Traveling abroad for medical care: US medical tourists’ expectations and perceptions of service quality. Health Marketing Quarterly, 28 (3), 253–269. https://doi.org/10.1080/07359683.2011.595644
Kowalska, N., & Ostręga, A. (2020). Using SERVQUAL method to assess tourist service quality by the example of the Silesian Museum Established on the post-mining area. Land, 9 (9), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9090333
Lam, S., Lee, V., Ooi, K., & Phusavat, K. (2012). A structural equation model of TQM, market orientation and service quality: evidence from a developing nation. Managing Service Quality, 22 (3), 281–309. https://doi.org/10.1108/09604521211230996
Mary, S. S. (2014). Medical tourism in Asia—an overview. Scholars World-IRMJCR, 2 , 131–136.
Mishra, V., Samuel, C., & Sharma, S. K. (2019). Patient’s utility for various attributes of diabetes care services. IIM Kozhikode Society and Management Review, 8 (1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/2277975218798134
Moghavvemi, S., Ormond, M., Musa, G., Isa, C. R. M., Thirumoorthi, T., Mustapha, M. Z. B., & Chandy, J. J. C. (2017). Connecting with prospective medical tourists online: A cross-sectional analysis of private hospital websites promoting medical tourism in India, Malaysia, and Thailand. Tourism Management, 58 , 154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.10.010
Moirangthem, N. S., & Nag, B. (2020). Developing a framework of regional competitiveness using macro and microeconomic factors and evaluating sources of change in regional competitiveness in India using Malmquist Productivity Index. International Journal of Global Business and Competitiveness, 15 (2), 61–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42943-020-00016-2
Nitecki, D. A., & Hernon, P. (2000). Measuring service quality at Yale university’s libraries. Journal of Academic Librarianship, 26 (4), 259–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0099-1333(00)00117-8
Nyumba, T. O., Wilson, K., Derrick, C. J., & Mukherjee, N. (2018). The use of focus group discussion methodology: Insights from two decades of application in conservation. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 9 (1), 20–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12860
Olya, H., & Nia, T. H. (2021). The medical tourism index and behavioral responses of medical travelers: A mixed-method study. Journal of Travel Research, 60 (4), 779–798. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287520915278
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. (1988). SERVQUAL: A multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality. Journal of Retailing, 64 (1), 12–40.
Parasuraman, A., Berry, L., & Zeithaml, V. (2002). Refinement and reassessment of the SERVQUAL scale. Journal of Retailing, 67 (4), 114–139.
Pekkaya, M., Pulat İmamoğlu, Ö., & Koca, H. (2019). Evaluation of healthcare service quality via SERVQUAL scale: An application on a hospital. International Journal of Healthcare Management, 12 (4), 340–347. https://doi.org/10.1080/20479700.2017.1389474
Qolipour, M., Torabipour, A., Khiavi, F. F., & Malehi, A. S. (2018). Assessing medical tourism services quality using SERVQUAL model: A patient’s perspective. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 47 (1), 103–110.
Saleh, F., & Ryan, C. (1991). Analyzing service quality in the hospitality industry using the SERVQUAL model. Service Industries Journal, 11 (3), 324–345. https://doi.org/10.1080/02642069100000049
Sankar, P. (2019). Medical tourism in India: Issues, opportunities and designing strategies for growth and development. Sociology of Medical Tourism , (pp. 227–240). Chennai: MJP Publishers
Skulmoski, G. J., Hartman, F. T., & Krahn, J. (2007). The Delphi method for graduate research. Journal of Information Technology Education Research, 6 (1), 1–21.
Suess, C., Baloglu, S., & Busser, J. A. (2018). Perceived impacts of medical tourism development on community wellbeing. Tourism Management, 69 , 232–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2018.06.006
Tripathi, S. N., & Siddiqui, M. H. (2018). Assessing the quality of healthcare services: A SERVQUAL approach. International Journal of Healthcare Management . https://doi.org/10.1080/20479700.2018.1469212
Turner, L. G. (2011). Quality in health care and globalization of health services: Accreditation and regulatory oversight of medical tourism companies. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 23 (1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzq078
Wang, I., & Shieh, C. (2006). The relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction: The example of CJCU library. Journal of Information Optimization Services, 27 (1), 193–209. https://doi.org/10.1080/02522667.2006.10699686
Wong, K. M., & Musa, G. (2012). Medical tourism in Asia: Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, and India. Medical tourism: The ethics, regulation, and marketing of health mobility. Routledge.
Zhao, X., Bai, C., & Hui, Y. V. (2002). An empirical assessment and application of SERVQUAL in a mainland Chinese department store. Total Quality Management, 13 (2), 241–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/09544120120102478
Download references
Acknowledgements
The infrastructural support provided by the FORE School of Management, New Delhi is greatly appreciated. The authors are also thankful to the editor and reviewer for their valuable input and comments, which have helped in improving the manuscript significantly.
There is not any funding to report.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
QT and OM Area, FORE School of Management, New Delhi, India
Vinaytosh Mishra & Mohita G. Sharma
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
VM: study planning, data collection and data analysis, and manuscript writing. MoGS: study planning, literature review, and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Vinaytosh Mishra .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
There is not any conflict of interest to report.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Mishra, V., Sharma, M.G. Framework for Promotion of Medical Tourism: A Case of India. JGBC 16 (Suppl 1), 103–111 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42943-021-00027-7
Download citation
Received : 26 April 2021
Accepted : 19 June 2021
Published : 28 June 2021
Issue Date : December 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s42943-021-00027-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Service quality
- Export competitiveness
- Medical tourism
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Business Today
- India Today
- India Today Gaming
- Cosmopolitan
- Harper's Bazaar
- Brides Today
- Aajtak Campus

- Magazine Cover Story Editor's Note Deep Dive Interview The Buzz
- BT TV Market Today Easynomics Drive Today BT Explainer
- Market Today Trending Stocks Indices Stocks List Stocks News Share Market News IPO Corner
- Tech Today Unbox Today Authen Tech Tech Deck Tech Shorts
- Money Today Tax Investment Insurance Tools & Calculator
- Mutual Funds
- Industry Banking IT Auto Energy Commodities Pharma Real Estate Telecom
- Visual Stories

INDICES ANALYSIS
Mutual funds.
- Cover Story
- Editor's Note
- Market Today
- Drive Today
- BT Explainer
- Trending Stocks
- Stocks List
- Stocks News
- Share Market News
- Unbox Today
- Authen Tech
- Tech Shorts
- Tools & Calculator
- Commodities
- Real Estate
- BT-TR GCC Listing
Start-ups are Disrupting the Medical Tourism Space. Here’s How
Medical tourism was always popular in india but now start-ups are entering the fray to offer end-to-end solutions for visa, travel, accommodation, doctor/hospital rankings -- all squeezed into one single package.
- Print Edition: Jul 24, 2022

Jahid Hasnat, 64, was in a fix. The Dhaka resident, who was suffering from cardiac and urology-related ailments, couldn’t decide where to travel to for treatment. Medical facilities in Bangladesh were not up to the mark and an earlier visit to Singapore had burnt a huge hole in his pocket. India was an option, but a previous visit had resulted in a bitter experience.
He approached Dhaka office of HealthTrip, a Delhi-based start-up specialising in medical tourism in India. “A person picked us up at the airport and assisted us in getting a hotel and finally the hospital appointments and tests,” says a relieved Hasnat. “Everything was smooth and much better than our previous trip when we didn’t know where to go after landing in India,” he says, adding that the start-up offered him an all-in-one package.
Hasnat isn’t alone. As many as 495,056 people visited India for medical treatment in 2017, says government data. While the latest statistics are not available, government data for 2020 shows that Bangladesh accounted for nearly 55 per cent of all foreigners coming to India for medical purposes. It was followed by people from Iraq, Maldives, Afghanistan and Oman. Globally, the medical tourism market is booming. According to a report by research firm Global Market Insights, the size of the market globally was over $10 billion in 2020 and set to grow at a CAGR of more than 12 per cent to breach the $37 billion-mark by 2027. It is no wonder that start-ups have spotted the opportunity and jumped in.
A booming segment
But what is medical tourism? Simply put, it refers to the practice of people travelling to other countries for medical treatment. Turkey, India, Thailand and the UAE are among the popular destinations, say industry sources. India scores high because of its cost advantage while providing high-end facilities for all kinds of treatment ranging from cardiology to neurology to bariatric and even transplants. India was ranked 10th among 46 nations on the Medical Tourism Index 2020-21, released by independent information provider MedicalTourism.com; Canada, Singapore and Japan were the top three nations.
The government, too, is aware of the potential of medical tourism. While speaking at the inaugural session of the Global Ayush Investment & Innovation Summit 2022 in April at Gandhinagar, Prime Minister Narendra Modi said that the government would soon introduce a special Ayush visa category for foreigners who want to come to India for traditional medical treatment.
While medical tourism has always been a vibrant segment in India, the entry of start-ups has made it more competitive with such ventures offering convenient end-to-end solutions.
From start to finish
“There is no proper planner for those who travel for medical treatment even though the process involves so many different things,” says Danish Ahmed who along with fellow Co-founders Suneel Kapur and Obaidullah Junaid started HealthTrip—formerly known as HosPals—in 2019. HealthTrip claims to have served nearly 30,000 patients across 38 countries by partnering with 130 hospitals and over 1,000 doctors.

This start-up, like its peers in the segment, offers services that cover the entire gamut of medical tourism, of which finding the right hospital and doctor is just one part. This is how it typically works: Start-ups tie up with hospitals and doctors and list them on their platform with vital details like fees and credentials, among other things. This helps patients and their families to understand their experience and expertise while also giving an idea of the costs involved. Medical tourism, however, involves travel, stay, visa, financial aid and, at times, translators, drivers, cooks and house helps; these start-ups have tied up with all such service providers so that they can offer customers an all-inclusive package.
The scope of growth in the segment can be gauged from the fact that there are nearly 60 such start-ups in the space and while cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru and Gurugram account for the largest share, such ventures are also present in smaller towns and cities such as Malappuram, Mangaluru and Palwal, as per data from Tracxn.
“As an industry grows bigger, it catches the attention of smart and tech-savvy entrepreneurs about how they can catch up with someone who has been running the business through traditional means for 7-10 years. That’s exactly what is happening in medical travel now,” says Pankaj Chandna, Co-founder of Vaidam, a Gurugram-based medical tourism start-up.
Even within the segment, some have found a niche by focussing on a particular treatment. For instance, Meditourz specialises only in regenerative and holistic treatments and has tied up with wellness centres that focus on Ayurveda and yoga, among other things. “We take care of patients’ full rehabilitation with nutrition while also ensuring that they don’t have to stay back in India for long,” says Aashnee Gajaria, Co-founder of Meditourz. Till date, the Mumbai-based start-up has organised over 40 workshops across 18 countries while focussing on the markets of Asia, Southeast Asia and the Middle-East.
Strong growth numbers
If the growth in business volume is anything to go by, then start-ups in this space are having the time of their lives. Since travel was banned for the most part of 2020 and restricted the following year, these start-ups have been seeing real business only in the last one year or so; since then, there has been an explosion in their growth numbers.
“We have grown nearly 12 times in terms of revenue between July last year and now. Due to the pandemic-forced restrictions, there was hardly any travel in 2020 and also till mid-2021 and that created a huge backlog of patients. We are expecting 100 times growth in the next five years,” says Ahmed, adding that his start-up’s annualised revenue has already touched $10 million.
Vaidam says its growth was in multiples of hundred right from the word go. “We have been fortunate to have experienced multi-fold growth since we started. We grew 400 per cent in the second year of our operations followed by 250 per cent in the third year and 200 per cent in the fourth. Then the pandemic happened. Even then, we did multiple new initiatives to keep going and building on our strengths,” says Chandna whose venture has assisted more than 25,000 patients to reach out to over 400 hospitals and 7,000 doctors.

In terms of revenues and profitability, the segment does not have a typical cash burn model as these start-ups earn a commission from either the hospitals or the doctors on every case they facilitate. While exact numbers are not available, sector players say that monthly revenues running into a few lakhs are easily achievable from the first year and given the low-cost structure and funding, profitability is not a difficult target. This is also a reason why, barring a few, most start-ups in the space are still bootstrapped, though in terms of valuations none are close to becoming a unicorn as of now.
The segment has attracted interest from marquee investors. Early-stage institutional investors like IPV, Amity Capital Ventures, Venture Catalysts, Wavemaker Partners, Spiral Ventures, Axilor Ventures and LetsVenture have invested in such start-ups.
Well-known angel investors including Kunal Shah of Cred, Deepinder Goyal of Zomato, Nirav Panchmatia of AUM Financials and Gaurav Singhvi of We Founder Circle have also put money into such ventures.
It may be boom time for these start-ups, but what’s in it for hospitals? “The ecosystem created by these start-ups is very important for hospitals because they are able to reach a larger group and these ventures act as the extended business development arms,” says Shaaz Mehmood, Director of MediJourn, a strategic partner of Apollo Hospitals. “Medical tourism start-ups bring in a lot of value-added services which the hospital cannot, like providing the patient with choice of treatment apart from helping them with paperwork, visa, travel, forex, etc.,” he adds.
Strong vitals ahead
What is fuelling this growth? Apoorva Ranjan Sharma, Co-founder of 9Unicorns & Venture Catalysts, says that the rise of medical tourism start-ups is due to a combination of factors, including supportive government policies, high-quality medical facilities in the country and profitability potential.

“These start-ups are going to further accelerate the growth of the Indian healthcare ecosystem in the next few years and there are high chances of them growing profitably too since this segment is a low cash-burn business,” says Sharma who has invested in this segment.
According to the government, medical tourism in India has huge scope due to a combination of factors including trained doctors/surgeons—many have experience of studying or working in the US or Europe and are also fluent in English—and a huge workforce of trained nurses—there are as many as 1,000 recognised training centres with 10,000 nurses graduating annually.
It appears that medical tourism start-ups are showing a strong pulse for now with their vitals only getting stronger with each passing day.
@ashishrukhaiyar
- #medical tourism
- #medical tourism in India
- #healthcare start-ups
TOP STORIES

- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Press Releases
Copyright©2024 Living Media India Limited. For reprint rights: Syndications Today

Add Business Today to Home Screen
A business journal from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania
Healthy Business: Will Medical Tourism Be India’s Next Big Industry?
June 2, 2011 • 14 min read.
U.S. President Barack Obama recently encouraged Americans to use the country’s health care system for their operations and procedures, instead of going to India and Mexico. But for many, medical tourism is not a matter of choice: They simply cannot afford treatment in the U.S., experts point out. In India, meanwhile, the medical tourism industry is booming, even as controversies erupt over quality and environmental issues.

- Health Care Management

In the past, U.S. President Barack Obama has singled out India for what he sees as the country usurping American jobs and business. In May 2009, he removed some tax incentives for U.S. companies who allegedly preferred to outsource rather than create domestic jobs. “ Buffalo before Bangalore ” was his rallying call at the time. Now, India is back in his crosshairs. In April 2011, he told a town hall gathering in Virginia that Americans shouldn’t have to go to India or Mexico for “cheap” health care. “ I would like you to get it right here in the U.S., “ he said.
“ It’s a 100% political statement, “ Gopal Dabade, convener of the All India Drug Action Network, told weekly newsmagazine India Today . Others in India were equally critical and dismissive. But some have taken more serious objection. “ Not acceptable, “ says federal health minister Ghulam Nabi Azad. Affordable health care does not mean our medicine is inferior to any superpower’s. I would like to say our medicines are indigenous, they are superior, and superiority does not come by escalating costs. “
The bone of contention is the word “ cheap. “ Obama probably used the term in the sense of less expensive. But Indians have interpreted it as meaning “ tawdry and inferior. “ Analysts don’t expect Obama’s political posturing to make any difference to the flow of U.S. medical tourists into India. But there is a lurking fear, nevertheless, that a nascent sector could be hamstrung at birth.
There Is No Choice
“ Patients do not travel to India for health care services because they have a choice and they choose to go to India, “ says Ravi Aron , professor at the Johns Hopkins Carey Business School and a senior fellow at The Mack Center for Technological Innovation at Wharton. “ They travel to India because they have no choice. “ Adds Rana Mehta, executive director, PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) India: “ If patients see value in what India has to offer, they will continue to come. “
Indians feel aggrieved that they have been singled out. In medical tourism, the country is still a bit player. According to a report by the Delhi-based RNCOS, which specializes in Industry intelligence and creative solutions for contemporary business segments, India’s share in the global medical tourism industry will reach around 3% by the end of 2013. The December 2010 report — titled “ Booming Medical Tourism in India “ – says that the industry should generate revenues of around US$3 billion by 2013. “ The Indian medical tourism industry is currently in its early growth stage, “ says RNCOS chief executive Shushmul Maheshwari.
Guess who’s the biggest beneficiary of medical tourism? It’s the U.S. “ The largest segment, with 40% of all medical travelers, seeks the world’s most advanced technologies, “ says a McKinsey & Co paper titled “ Mapping the market for medical travel. “ “ These men and women take their search for high-quality medical care global, giving little attention to the proximity of potential destinations or the cost of care. Most such patients travel to the U.S. ” What worries the Indian industry is that this is not the first attack on Indian medical tourism. In August last year, leading medical journal The Lancet had published an article about a new superbug which it called the New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase 1 (NDM-1). “ The potential of NDM-1 to be a worldwide public health problem is great, and coordinated international surveillance is needed, “ said the article. Later, a co-author noted that some material had been inserted into the article without his knowledge; the editor of The Lancet had to apologize for naming the bug after New Delhi, and the Indian ministry of health had to weigh in. “ The conclusions are loaded with the inference that these resistance genes/organism possibly originated in India and it may not be safe for U.K. patients to opt for surgery in India, “ said the ministry. “ The medical journal’s claim is not supported by any scientific data and thus tarnishes the reputation of the country. “ Rightly or wrongly, the government and many in India’s medical establishment believe that naming the superbug New Delhi was to keep U.K. medical tourists at home. “ The superbug certainly garnered a lot of media attention given its name, “ says Preetha Reddy, managing director of Apollo Hospitals.
It won’t keep medical tourists at home, just as Obama’s appeal is likely to be ignored. “ People will always weigh the cost and the benefit,” says Reuben Abraham . “If there is a 10% saving and there is a danger of the superbug then chances are that people will not want to take it. But if you are offering an 80% discount, it is a different matter. If India continues to offer high quality health care at one-tenth the cost in the U.S. then these things will not make an impact. “
The Next Big Thing
If all this is going to have limited impact, why is India getting so agitated? The answer lies in the potential of medical tourism. It could easily be the next big thing. Unlike business process outsourcing (BPO), which is on the whole very low-tech, health care — particularly sophisticated procedures — is very high-tech. India has not been able to set up an adequate health care infrastructure for its own citizens and it doesn’t have the money to do so. Creation of a sophisticated medical tourism structure will have a trickle-down effect.
“ India has the highest potential in medical tourism in the world, “ says Maheshwari of RNCOS. “ Factors such as low cost, scale and range of treatments differentiate it from other medical tourism destinations. Moreover, growth in India’s medical tourism market will be a boon for several associated industries, including the hospital industry, the medical equipment industry, and the pharmaceutical industry. “ His study shows that CAGR (compound annual growth rates) in revenue in 2011-13 will be 26%. In terms of medical tourists, the number would touch 1.3 million by 2013 at a CAGR of 19%. “ Medical tourism can be considered one of the rapidly growing industries in the Indian economy on the back of various factors, “ he says. “ However, the industry is at a nascent stage and requires a few years to reach the platform already established by the IT sector. ” “ India has been ranked among the top five destinations for medical tourism, “ says Rana Kapoor, founder, managing director and CEO of Yes Bank, which has recently done a study on health and wellness tourism in India along with apex chamber of commerce FICCI. The ranking by Nuwire Investors, an online source for news on alternative investments, puts Panama on top, followed by Brazil, Malaysia and Costa Rica. “ India is looking at exponential growth as far as tourism is concerned, “ continues Kapoor. “ Yes Bank forecasts that there will be an increase in domestic tourist movements over the period (2008-2020) by 118% and foreign tourist inflows over the same period will increase by 71.87%. What the potential for medical tourism from within this growth rate of 71.87% will be depends upon government policies, faith of the patients and many other external factors. We truly believe that this sector will play a significant role as a contributor towards the overall tourism growth in India. “
“ I strongly believe that many developments across the world will put India in a fantastic position, “ says Devi Shetty, cardiac surgeon and chairman of Narayana Hrudayalaya. “ We produce the largest number of doctors, nurses and medical technicians in the world. Also, we have been traditionally linked with western health care because of the British influence on our medical education and the ability to speak English. This is extremely important for developing [global] health care. Our greatest asset is our ability to produce the largest number of technically-skilled individuals. We also have the largest number of USFDA (U.S. Food and Drugs Administration)-approved drug manufacturing units outside the U.S. “
Differences over Terminology
Shetty doesn’t like the term medical tourism. “ Medical care is something that is very stressful and people consider this under tremendous pressure, “ he says. “ It is an event where people are scared of losing their lives. It may not be appropriate to call it tourism. Tourism is a different business altogether. “ Adds Mehta of PwC: “ The tourism component is really very weak. Most foreign patients come to India for chronic and serious medical treatment and I would call it medical value travel. “ Aron of Johns Hopkins has yet another view. “ The world over it is known as the global health care delivery system, “ he says. Reddy of Apollo agrees with Mehta. Says she: “ At Apollo Hospitals, we prefer to term this business opportunity as ‘medical value travel’ as people travel to our hospitals for serious life threatening health conditions, which essentially need highly skilled doctors and medical infrastructure and not mere minor treatments like cosmetic enhancements, dental work or wellness which can be coupled with holidays, as the term ‘medical tourism’ implies. “
The multiplicity of names is accompanied by a wide range of numbers. The confusion was started by the McKinsey study on Mapping the Market mentioned earlier. The May 2008 report said that “ medical travel has captured the world’s attention and imagination “ . But it went on to explain that the McKinsey definition of medical traveler was very different from what many others thought him to be. The first to be knocked off were expats looking for health care in their country of stay. That accounted for 25-30% of the traditional medical tourist pool. Then was the segment categorized under emergencies. These were ordinary tourists caught up in accidents. That eliminated another 30-35%. McKinsey estimated the remaining at “ between 60,000 and 85,000 inpatients a year “ , much lower than generally accepted numbers. For instance, a 2008 Deloitte Center for Health Solutions report on “ Medical Tourism: Consumers in Search of Value “ put the number of Americans who had traveled abroad for medical care in 2007 at 750,000. McKinsey excludes “ wellness “ tourists (acupuncture, spas, yoga, aromatherapy and the like), patients from neighboring countries, and outpatients — those who don’t need to check into hospital.
The Deloitte report says that India is stepping on the gas; the medical tourism sector is expected to grow 30% annually up to 2015. An update on the report says that the U.S. recession is driving more people out of the country for health care; U.S. outbound medical tourism is projected to increase 35% annually from 2010-2012. “ Medical tourism [today] represents the maturation of a cottage industry, “ the report sums up.
Maheshwari of RNCOS agrees that economic problems are driving more Americans abroad for health care. “ Under almost stagnant salary increments, the disposable income and saving considerations of U.S. citizens are still well below the pre-crisis levels, “ he says. “ In this scenario, the low cost treatment and nearly zero waiting time coupled with its proven track record offer convenient procedures for tourist arrivals from various geographical locations including the U.S. “
“ Over the past few years, the medical tourism story has changed dramatically in India, “ says a recent Cover Story in weekly business magazine BusinessWorld . (That it made it to the Cover is a reflection of the growing importance of the sector.) “ Not because the government has figured out the solution. But purely because of private enterprise — with a few corporate hospitals, chemists and freelance agents all working in tandem to build a thriving ecosystem that educates, facilitates and ferries medical tourists from across the world. Last year, this ecosystem was responsible for about 600,000 patients travelling to India and spending US$1 billion in getting treated here. (The numbers are industry estimates as the government does not have any official statistics on the subject.) Corporate hospitals such as Apollo, Fortis Hospital and Max as well as business associations estimate that the business is growing by 40% year-on-year. “ (Obviously, the growth numbers vary depending on who you talk to.)
Other Markets Will Turn to India
“ India’s potential is huge, “ says Mehta of PwC. “ Some 80% of foreign patients coming to India are from the neighboring countries and from Iraq, Afghanistan, the former Soviet Union, etc and now increasingly from Africa. But now with India proving itself as a credible provider of value health care, the western population ageing, and health care becoming more difficult there, I expect more people to come from the U.S. and the U.K. “
Mehta says that some things went wrong with the earlier planning. “ We expected most patients to come from the U.S. and Europe. We expected people to come for cosmetic and regenerative treatment and this is where there is more potential for tourism. But the majority actually came for cardiac treatment, cancer treatment, knee replacement and other serious ailments. Therefore, tourism was not really of importance. We did not get the cost factor right. We thought that typically in India it costs one-tenth of that in the U.S., so we could cost at 5X. But hospitals have not been able to charge very much. At present, with a foreign patient, there is around 20% more earning. “
Cost is, of course, being underplayed in the marketing efforts; this is why the word “ cheap “ rankles. “ The patient is usually acutely aware of the difference in the sticker price for care, “ says Aron. “ There is no reason to draw attention to this. ” That’s an area where India enjoys an advantage over other countries too. According to the BusinessWorld report, a heart bypass surgery costs US$144,000 in the U.S., US$25,000 in Costa Rice, US$24,000 in Thailand, US$20,000 in Mexico, US$13,500 in Singapore, and US$8,500 in India. “ The quality is excellent, “ says Maheshwari. In India, there is also less waiting time and personalized services.
Becoming an Industry
Medical tourism is also taking shape as an industry, though there are some who feel that it will eventually fall in many buckets. (The recent FICCI-Yes Bank study talks of wellness tourism, health tourism…) “ There are over 3,371 hospitals and around 750,000 registered medical practitioners, “ says Maheshwari.
Shetty says it is easier to get loans these days. “ Earlier, it was difficult for us to mobilize huge financial support to create large hospitals. However, things have changed now, “ he explains. Indian companies are also taking over hospital chains in Asia — Fortis has gone on a shopping spree, though it’s not been entirely successful — and setting up front-ends in other countries for marketing purposes. Apollo has facilitation centers in Oman, Nigeria and the U.S. Max is present in Nigeria, Afghanistan, Bangladesh and Nepal. Says Reddy of Apollo: “ There are several key players. Apollo Hospitals continues to attract the largest numbers of international patients followed by Max, Fortis and Workhardt. “
“ Another opportunity that Indian operators are now seeing is that you don’t have to offer these health care services from India, “ says Abraham of ISB. “ For instance you can offer it from say, Cayman Islands or the Bahamas. Ultimately, the innovation is in the process and as long as you can bring the same process innovation, even if the cost goes up a little as compared to offering it from India, it will still be a substantial saving for the patient. “
This is one area where China is no threat. Foreigners in China still rush to Hong Kong when they need treatment because they cannot communicate with local doctors.
But what the budding sector will have to contend with is the Indian government. Take one example. With the intention of making things smoother, the government introduced a medical visa (M visa), which was faster and easier to get. In its wisdom, however, it added a peculiar clause — “ Foreigners coming on M visa will be required to get themselves registered mandatorily well within the period of 14 days of arrival with the concerned Foreigners Regional Registration Office. ” The end result: even patients who have to be carried into India on stretchers are coming on tourist visas. If the government wants medical tourism to be the next big thing, it has to put its house in order.
As for the immediate controversies, Shetty is very clear. “ President Obama’s statement or the New Delhi superbug will not affect medical tourism development in India, “ he says. “ First of all, he was not criticizing India. He was just trying to put his house in order. “
More From Knowledge at Wharton

How Do We Control the Rising Costs of Health Care?

How Early Adopters of Gen AI Are Gaining Efficiencies

How Can AI Improve Health Care?
Looking for more insights.
Sign up to stay informed about our latest article releases.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
Medical Tourism in India
Last updated on January 14, 2023 by ClearIAS Team

Medical tourism is described as any activity that involves a foreign visitor traveling and spending at least one night at the destination to rejuvenate, restore, or maintain health through medical intervention. Since the last decade of the 20th century, India has emerged as a global leader in the medical tourism sector. Read here to learn about the growth of medical tourism in India.
Over the past decade, India has gained a reputation for providing high-quality medical service at low costs to medical tourists traveling from across the globe.
However, with the travel bans during the covid-19 pandemic , the influx of medical tourists had dipped. According to the Tourism Ministry, India registered a negative growth of 79.4% in 2020.
Although, the situation looks positive once more owing to the efforts made to handle the pandemic situation. Market insights suggest the demand forecast to increase at a robust 19 % CAGR in 2022.
Table of Contents
Medical tourism in India
India’s healthcare industry offers a combination of both modern and traditional forms of medicine which sets the country apart from others.
- First, it has a set of world-class doctors and hospitals that provide treatment at fractional rates when compared to other countries.
- Secondly, India’s systems of medicine: AYUSH i.e., Ayurveda, Yoga, Panchakarma, Rejuvenation Therapy, etc, which are the most ancient forms of medicine, are now gaining immense popularity globally.
The government also recently announced plans to launch an AYUSH Mark which is a mark to provide credibility to AYUSH products in India and promote India’s medical tourism sector.

Additionally, the other medical services and facilities are also backed by the World Health Organisation (WHO) and the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA).
India’s healthcare industry has advanced significantly over the past 30 years, as seen by the notable accomplishments it has made.
- One of the industries that have contributed the most to revenue and are expanding quickly is healthcare.
- Both public and private providers support the healthcare industry. Over the past few years, national health policies have been crucial in establishing a more inclusive healthcare system to achieve structured Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- In addition, India provides less expensive treatment alternatives than the US and the UK without sacrificing the standard of healthcare. About one-fourth, less is spent on therapy in India than it is in the United States.
In terms of alternate medical treatment, the Indian medical treatment systems of yoga, ayurveda, rejuvenation therapy, and panchakarma are among the most ancient methods of medical treatment in the world.
The southern state of Kerala has developed medical tourism services as one of its core products for promoting tourism in the region.
Based on the Medical Tourism Index 2020-21, India is ranked 10th out of the top 46 countries, 12th out of the world’s top 20 wellness tourism markets, and 5th out of 10 wellness tourism destinations in Asia-Pacific.
- India boasts 39 Joint Commission International (JCI) accredited and 657 National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH) accredited hospitals.
India holds an advantage as a medical tourism destination due to the following factors:
- Most of the doctors and surgeons at Indian hospitals are trained or have worked at some of the medical institutions in the US, Europe, or other developed nations.
- Most doctors and nurses are fluent in English.
- Top-of-the-line medical and diagnostic equipment from global international conglomerates is available at many Indian hospitals.
- Indian nurses are among the best in the world. Nearly 1000 recognized nurses-training centers in India, mostly attached to teaching hospitals, graduate nearly 10,000 nurses annually.
- Even the most budget-conscious traveler can afford first-rate service and luxury amenities
Most of the tourists are from Asian or African countries such as Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, Maldives, Indonesia, and Kenya, among others.
Chennai, Mumbai, New Delhi, Ahmedabad, and Bengaluru are the top 5 medical tourism destinations in India.
Wellness tourism
Wellness Tourism includes travel for a less stressful lifestyle, promoting a healthier, and finding balance in one’s life.
Ayurveda, Yoga, meditation, Panchakarma, and Rejuvenation Therapy are among the most ancient systems of medical treatment in India and the best way to promote Wellness Tourism.
The Ministry of Tourism has drafted guidelines for wellness tourism. These guidelines address issues regarding making available quality publicity material, training and capacity building for the service providers, participation in international & domestic Wellness related events, etc.
Mushrooming of wellness centers in the country has given rise to the concern for quality service.
- The Guideline for the Accreditation of wellness centers has been developed by National Board for Accreditation of Hospitals & Healthcare Services (NABH) in consultation with AYUSH and released during the workshop on wellness tourism organized by the Ministry of Tourism in 2011.
- The Ministry of Tourism has also extended its Market Development Assistance (MDA) scheme to wellness tourism service providers including accredited wellness centers.
Impact of Covid-19 on medical tourism
Planned hospital operations decreased by as much as 80% during the state-wide lockdown in India caused by the new coronavirus outbreak, while unplanned systems decreased by 66%.
With the government of India’s assistance, the healthcare sector launched a comprehensive response strategy to combat the epidemic.
- Specialized COVID-19 hospitals and isolation facilities were established, and resource mapping using technology was started.
- The Indian government created several programs and used technology to combat the pandemic.
- The Aarogya Setu app was utilized across the nation to improve contact tracing, syndromic mapping, and infection self-evaluation.
- India not only met its own needs but also stepped up to help other nations during these difficult times.
Despite having several initiatives in place, the Medical Tourism industry of the country still faces some serious challenges.
- One of the major challenges that India is facing is promoting and creating awareness about state-of-the-art facilities in India.
- India is witnessing strong competition from destinations like Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Turkey, and South Korea with low-cost options.
- In India, there is a lack of cohesiveness amongst the major players in the industry to come together and represent India on a world platform to acquire newer customers.
- Apart from these, inconsistent fee structure and lack of transparency in billing to foreign patients, and absurdly high margins to trade to refer patients are some of the challenges.
- Most Indian hospitals are also facing a lack of trust from foreign patients. The hospitals have observed poor hygiene awareness in medical attendants, unhygienic food handling, and lack of good hospitality services, heterogeneous pricing of services, and industry standards.
The government can play a vital part to upgrade the medical tourism sector. But the industry is facing the following problems which are caused by the governments. They are:
- no regulations
- taxation anomalies
- bureaucratic roadblocks
- no work on land reforms
- lack of long-term investor-friendly policies
- instability concerning terrorism and communal tensions.
On the part of insurance and allied services, the medical tourism industry in India is also facing some key bottlenecks. They are:
- inadequate insurance cover
- the underdeveloped insurance market in India
- insurance frauds
- overseas companies refusing reimbursement.
The following challenges, due to the infrastructural parts of the medical tourism sector in India, are:
- lack of access
- dearth of capital
- Lack of community participation and awareness
- Non-participation in the rural sector
- lack of concern for sustainability
- complex visa procedures
- lack of good language translators
- airport facilities still being inadequate
Government initiatives for medical tourism
The government has implemented various initiatives to overcome the challenges and push India’s rise as a hub of medical tourism through the promotion of ayurveda, yoga, and other Indian systems of medicine in the international market.
Heal India Initiative:
- Heal in India is a new initiative developed under Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission in which there will be healthcare professionals, and hospital services to help patients seeking medical help in India.
- With this type of initiative, Government aims at promoting Medical Tourism in India via Heal in India Portal.
- It’s another Programme called Heal by India Government that aims to encourage Indian Health care Workers to go abroad and serve patients globally.
Market Development Assistance (MDA) scheme
- MDA scheme offers financial assistance to approved tourism service providers.
Medical Visa provisions
- Special provision has been made for tourists traveling to India for healthcare purposes.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs has introduced a new category of visa, Medical Visa, that can be issued to foreigners traveling to India for healthcare reasons.
Setting up a feedback mechanism to obtain testimonials from tourists traveling to the country for medical purposes.
- This ‘one-step’ portal would add convenience and provide credible information for medical tourists coming to India.
Way forward
To become the top-most medical travel destination, there is a need for significant investments into making the healthcare industry and equipment attractive for international patients.
- Patients spend most of their time in guest houses and are prone to further infections from such places.
- Thus, proper infrastructure and standardization need to be brought into the tourism industry and the nexus of guest house service providers urgently.
- Another aspect that needs to be tapped into is the opportunity for selling Indian health insurance to foreigners. This can generate an additional $9 billion in patient inflow to India.
The government is pulling out all its aces to maximize the industry’s potential. The aim is to make India the No.1 Destination for Medical Tourism in the world, tripling its revenue to $13 billion within 4 years.
The government has also proposed an outlay of US$ 28.7 billion for health and well-being, which is 137% higher than the previous year’s budget outlay.
In the post-Covid world, the demand for the healthcare industry is bound to surge and there is a huge potential for India to realize and aggressively advance towards attracting medical tourists from other parts of the world including Europe and the Americas.
With the government making it their priority to make India the hub of medical tourism, the initiatives combined with the surging demand are sure to make India the center for all medical tourists in the future.
-Article written by Swathi Satish

Module Classes: Join Now!
Csat course.
Join CSAT Course
Current Affairs Course
Join Current Affairs Course
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
Join Prelims Test Series

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

An Assessment of Competitiveness of Medical Tourism Industry in India: A Case of Delhi NCR
Neha malhotra.
Ambedkar University, Delhi, India
Kartik Dave
Associated data.
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Code sharing is not applicable to this study as no new code was created or analysed in this study.
India has emerged as a prominent medical tourism hub, yet the dynamic forces in the regional and global landscape are creating a complex balance of opportunities and risks for the Indian stakeholders. The outbreak of Corona virus pandemic in 2019 has further complicated the market dynamics for the medical tourism industry. This study aims to analyse the key driving factors for the medical tourism industry in India and the issues that Indian stakeholders should address in crafting a winning strategy. A qualitative research design was adopted, and data were collected through semi structured in-depth interviews with practitioners and senior representatives of the hospital management. The study adopted abduction logic and analysed data by means of constant comparison method. The study presents the assessment of the medical tourism industry in India and the scope of opportunity for Indian players.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s42943-022-00060-0.
Introduction
Catalysed by emerging technologies, varying economic and demographic trends and a new age of healthcare consumerism; the worldwide scenario of healthcare is rapidly evolving. Additionally, a growing ageing population, and a swelling burden of diseases is rising the demand and cost of medical services. This evolution in healthcare is driving cross-country and cross-industry convergence (Deloitte Global, 2021 ), resulting in an upsurge in the worldwide medical tourism market. As this trend towards the healthcare is enduring around the world, more and more countries are extending their health systems to access care, not just for their natives but also gaining strength as leading service providers for international patients. While much of the initial focus was on the developed world, the epicentre is now shifting towards the emerging countries. Governments of these developing countries are working towards prioritising their health systems; enhancing productivity, boosting avenues for innovation and entrepreneurship, generating employment opportunities, increasing foreign exchange earnings, and hence driving GDP growth (Rahman, 2019 ).
India has been having its own unprecedented progress in this sector. To counter the emergent health issues, the health system in India has metamorphosed rapidly since the 90 s and has become the focal point of development. With the presence of clinical and technical expertise, international standards and highly competitive prices; India has emerged as a leading contender in the medical tourism industry (Bagga et al., 2020 ). Yet the accelerating shift in the regional and global landscape is making it challenging for the stakeholders to balance opportunities with risks. The industry is showing ramification of rapid disruption and intensified competition. Service providers are facing new playing fields. Recognizing this change alone isn’t enough. Government and entrepreneurs need to become adept at dealing with disruption and adapt the operating models, in a holistic way, to mitigate the outcomes of the shifting paradigm. It is imperative to introspect and identify the capabilities and resources that stakeholders need to realise. This is critical to endure the sophistication and competence of the medical tourism industry in India.
The outbreak of Corona virus pandemic in 2019 has further complicated the market dynamics for the medical tourism industry. Uncertainty over travel restrictions, changing quarantine measures across the world and the overall unprecedentedness of the situation, have made the entire ecosystem of medical tourism industry more precarious. With cross-border travel restrictions and the need to redirect hospital resources to treat COVID-19 patients, healthcare providers have to manage a dual burden of economic and health crises (Stackpole et al., 2021 ). The challenges posed by this pandemic have further demonstrated how crucial it has become for medical tourism industry in India to review their competitive positioning, access deeper competencies and build resilience.
A review of extant literature indicates very little empirical research has been done to done to examine factors of competitiveness of a medical tourism destination (Abubakar & Ilkan, 2016 ; Heung et al., 2010 ; Thayarnsin & Douglas, 2016 ; Yeoh et al., 2013 ). Theoretical understanding around the phenomena requires further academic attention (Chuang et al., 2014 ), specifically with regards to the perspective of medical tourism providers (Taheri et al., 2021 ). Virani et al. ( 2020 ) have also directed our attention to the neglect of policy-relevant research on medical tourism. This study aims to address this gap. By considering the perspective of medical practitioners and senior representatives of hospital management, this study identifies and analyses the key factors driving success in medical tourism industry and the issues that Indian healthcare providers and policymakers should address in crafting a winning strategy. Taking Delhi NCR as the context, this outlook propounds insightful research into the existing state of medical tourism industry in India, explores the dimensions and factors that can help India shape an effective ecosystem for this sector and suggests considerations for an optimum future of medical tourism industry in India.
Literature Review
The literature review encompasses a succinct discussion on the medical tourism industry, its global trends and the current state of Asian and Indian medical tourism industry, along with the key dimensions of medical tourism as highlighted in the literature.
Medical Tourism
Globalisation is restructuring the industries worldwide. Medical tourism is one such manifestation of globalisation in the healthcare industry (Connell, 2013 ; Ganguli & Ebrahim, 2017 ). Broadly it refers to travelling internationally for healthcare. Since its rapid development in 1990s, medical tourism has received a major reflection from both academia and industry. Though the growing interest to study this industry is well evident, there is still no international consent on the definition or measure of this sector. The existing literature addresses the terms health tourism and medical tourism in a loose and disorganised manner. Terms frequently used, and often synonymously, in this regard are ‘ medical tourism ’, ‘health tourism’, ‘medical travel’, ‘health travel’ and ‘cross-border healthcare’. While some researchers have used “medical travel” and “health travel” synonymously (Gola, 2016 ) others refer to health tourism as a wider field with medical tourism as its subset (Carrera & Bridges, 2006 ; Smith & Puczko, 2009 ). In agreement with Smith and Puczko ( 2009 ), this study represents medical tourism distinctly from other subsets of health tourism. The word ‘medical’ here refers to illness, disorder or injuries. As put forth by Jagyasi ( 2008 ), medical tourism is “the set of activities in which a person travels often long distance or across the border, to avail medical services with direct or indirect engagement in leisure, business or other purposes”. Contrarily, health tourism is a wide-ranging phenomenon where travel can be undertaken for a variety of reasons from preventive and health-conductive treatment to rehabilitation and curative forms of travel (Dunets, et al., 2020 ). Other than medical tourism, health tourism encompasses other related fields like—wellness tourism (involving relaxation and exercises) and sports/adventure tourism (involving outdoor recreation) (Hall, 2011 ). Medical tourism itself has sub branches like ‘reproductive tourism’ and ‘dental tourism’. Another emerging term is “domestic tourism” which refers to the act of travelling within one’s own country for medical purposes (Hudson & Li, 2012 ; Reddy, 2010 ). This study focuses primarily on medical tourism and identifies this practice as travelling internationally to receive medical treatment.
Global Medical Tourism Trends
Lack of specific data, novelty of the concept, and the fragmented and unstructured nature of this industry makes it challenging to review this industry and give an estimate of its size (Chambers & McIntosh, 2008 ; de la Hoz-Correa et al., 2018 ). Prominent market research databases have reported global medical tourism market to be worth USD 104.7 billion in 2019, and have projected it to grow at a CAGR of 12.8%, to reach USD 273.7 billion by 2027 (Chhabra et al., 2021 ; Taheri et al., 2021 ).
Even though there is no fixed estimate of this industry, medical tourism is well-considered amongst the most dynamically growing industries today. Trade economists have documented a strong impact of this phenomenon on the global economy (Bookman & Bookman, 2007 ) especially the emerging countries of the world (Lee & Hung, 2010 ; Pafford, 2009 ). It not only adds to their foreign exchange, but also boosts investments in the medical and tourism sector streamlining their services (Ramirez de Arellano, 2007 ). Asia has been specifically considered as a hub for medical tourism (Connell, 2006 ). Countries like Singapore, India, Thailand, Brunei, Cuba, Hong Kong, Hungary, Israel, Jordan, Lithuania, Malaysia, the Philippines, and the United Arab Emirates have emerged as major providers for healthcare services to international patients (Heung, et al., 2010 ). Several other countries like Mexico, Turkey, Brazil, Costa Rica, Argentina and Bolivia are also working toward establishing themselves as major healthcare destinations (Singh, 2008 ).
The global demand and expenditure for healthcare services is on a rise due to factors such as growing and ageing populations, changing disease patterns and rapid transformations in costly digital technologies. With the rising disparity in healthcare costs, governments, corporations and individuals are looking at outsourcing healthcare facilities to emerging markets (Turner, 2007 ), especially those with advance and cost-effective healthcare facilities, and a proximity to developed countries. Medical tourism is also a viable and economical option for uninsured or underinsured patients. On the other hand, there is a substantial disparity in the quality of healthcare services. Patients from countries with limited government spending on healthcare and under developed private sector are forced to look at options beyond their borders. (KPMG, 2014 ).
Medical Tourism Industry in Asia
Last decade has seen Asia as an emerging leader of the medical tourism industry. This growth is fuelled by the availability of a variety of high quality and cost-effective medical procedures in Asia, improved connectivity and infrastructure and along with the presence of attractive locations to explore. The availability of advanced treatments in fields such as cardiology, neurology, orthopaedic, spine, ophthalmology along with aesthetics and alternative treatments like Ayurveda, Unani, Herbal and Yoga, makes Asia a sought-after destination. With private sector as the primary driver of medical tourism in this region, Asia has seen a faster growth of this industry vis-a-vis any other region globally. Many prominent healthcare providers in Asia are internationally accredited and have positioned themselves as distinguished service providers to patients from both within the region and far beyond. A market research on medical tourism industry anticipates the medical tourism market in Asia to cross USD 14 Billion by 2022 (iGATE Research, 2017 ). The research reports that Thailand, Singapore and India account for maximum proportion of international medical tourists in this region, followed by South Korea and Malaysia. Philippines and Taiwan are amongst other fast emerging markets in this sector. International patients contribute to a one-third or more of revenue in these private hospitals, and hence several private hospitals in this region are targeting this global world medical travellers’ market and have also gained a strong position for themselves in the industry (Mooter, 2017 ). An increased focus from government, foreign investment inflows and emerging startups are fueling up the competition not just between countries, but players as well. With the competition becoming stiffer, these countries and players are becoming more proactive in building their unique identifiers. Price is no longer the only factor of differentiation, countries are now looking at founding their proposition on parameters like diverse offerings, niche market, customized offering and even luxury (KPMG, 2014 ).
Medical Tourism Industry in India
Healthcare is amongst the largest and most complex sectors in India and is poised to touch USD 133.44 billion by 2020 (Outlook India, 2019 ). Healthcare in India is becoming one of biggest industries in terms of revenue generation and employment as well. Giving further impetus to this industry is the medical tourism sector which is bolstering the level of enhancements of care services in India. Table A1, as given in Supplementary Appendix file, states some basic facts related to the medical tourism industry in India. With its key differentiating factors of extremely competitive pricing, highly trained doctors, high quality care and availability of a range of treatments, India has realized the potential of medical tourism and positioned itself as one of the largest service providers in this region (Connell, 2013 ; KPMG, 2014 ; Medhekar et al., 2019 ). A study by KPMG India and Google, has pegged the medical travel industry in India at USD 4.8 Billion in 2017 (KPMG India & Google, 2018 ). The pre-Covid estimations expected the Indian medical tourism market to reach USD 13 billion by 2020 (KPMG India & Google, 2018 ). Despite the deliberative effects of Covid-19 on Travel and hospitality industry, the Indian medical tourism was estimated between USD 5–6 billion in 2021 (Financial Express, 2022 ). A right combination of cost efficiency and quality has driven the growth of this sector in India. Table A2, as given in supplementary appendix file, gives a comparative cost chart, for some common procedures, between India and other major medical tourism destination. Further the presence of a robust private sector, with international accreditations, has reinforced India’s standing. India offers a range of treatments from cardiology, neuro, paediatrics, ortho, ophthalmology, urology, gynaecology, general surgery, dental, cosmetics along with traditional healing options (Qadeer & Reddy, 2013 ). As per a report by Ministry of Tourism, Government of India, around 4,95,000 medical tourists travelled to India in 2017, with Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Iraq, Maldives being the top 5 source countries followed by Oman, Yemen, Uzbekistan, Kenya, Nigeria and Tanzania (Ministry of Tourism, 2018 ). In the following years larger share of travel is expected from Africa and GEC countries (KPMG India & Google, 2018 ).Realizing the opportunity, Government of India has taken a few initiatives to promote and encourage the growth of medical travel to the country. These include Government of India’s health tourism policy; setting up a ‘National Medical & Wellness Tourism Promotion Board’ for regulatory, accreditation and marketing issues; accreditation of hospitals under the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals; dedicated website to promote medical and wellness tourism; promotions at international platforms such as World Travel Mart London, ITB Berlin, ATM, etc.; coverage under Ministry of Tourism's ‘Incredible India Campaign’; introducing separate category of medical visas—‘M Visas’; a proposal for setting up tourism circuits, along with a medical circuit which will connect modern medicine centres and Ayurveda; providing fiscal support and other benefits under Market Development Assistance Scheme (MDA); and lowering import duties on medical technology, equipment and machinery (KPMG, 2014 ; Medhekar et al., 2019 ; Ministry of Tourism, 2018 ).
Key Dimensions of Medical Tourism Industry
This section presents the factors, as highlighted in the literature, that impact the development of medical tourism in a region. Cost and quality are considered amongst the most important dimensions of medical tourism industry (Aziz et al., 2015 ; Bagga et al., 2020 ; Cortez, 2008 ). Affordability and service quality of hospitality and tourism have also been considered as important attributes for a medical tourism destination (Chuang et al., 2014 ; Fetscherin & Stephano, 2016 ; Olya & Nia, 2021 ).
Several studies, e.g. Ghosh and Mandal ( 2019 ) and Fetscherin and Stephano ( 2016 ), have highlighted the importance of the type of treatments offered, medical facilities, practitioner competence, service quality and standards of medical care offered by the service providers (Kamassi et al., 2020 ). Technological upgradation and medical innovation are other important factors linked to the success in this sector (Cortez, 2008 ; Velasco et al., 2013 ). Literature also points towards the importance of trust, credibility, perception and hence the need for certification, international standards and accreditation (Debata et al., 2015 ; Hall, 2011 ; Seow et al., 2017 ).
Beladi et al. ( 2019 ) and Ebrahim and Ganguli ( 2019 ) have explored the role of human resource development and administrative efficiency. Infrastructure and facilities with regards to accommodation, transportation, communication are other important dimensions recognized for medical tourism (Heung & Kucukusta, 2013 ; Kamassi et al., 2020 ).
Country specific factors and attributes such as country knowledge, culture, language, accessibility, safety and security, have also been analysed (Bagga et al., 2020 ; Cham et al., 2021 ; Olya & Nia, 2021 ). Crouch and Ritchie ( 2005 ) in their study have highlighted the importance of socio-cultural and political environment of the destination country. Tourism-specific factors of the destination country, such as weather, attractions, culture and exoticness, have also been considered while studying the attractiveness of a medical tourism destination (Fetscherin & Stephano, 2016 ; Lovelock et al., 2018 ).
Medical tourism destination marketing, destination branding and tourism destination image have also been considered important with respect to the development of medical tourism in any region (Hoz-Correa & Muñoz-Leiva, 2019 ).
Studies have also observed public and private coordination and collaboration of the medical tourism stakeholders, to enhance the development of medical tourism sector (Beladi et al., 2019 ; Ebrahim & Ganguli, 2019 ). Government support and a favourable policy framework have been considered as important factors for this industry (Hall, 2011 ; Wang, 2012 ). Snyder et al. ( 2015 ) and Omay and Cengiz ( 2013 ) have specifically advocated the need for a regulatory framework and policy intervention to improve the efficiency coordination, uniformity and standardisation in this sector and promote the medical tourism industry (Momeni et al., 2018 ).
Methodology
Considering the emerging nature of this industry, qualitative approach was exercised to truly analyse the value proposition of India as a medical tourism destination. A qualitative framework encourages both theoretical and applied knowledge and aids in the development of novel and alternate theories (Bygrave, 1989 ; Creswell, 2013 ). Case study method was adopted to classify and analyse the dimensions that can position India as a prominent healthcare service provider for overseas patients. Merriam ( 2002 ) describes case study as a comprehensive description and examination of a phenomenon or a social unit of study. The case being studied becomes the boundary of the research, and by focussing on a single context this approach seeks to offer an extensive enquiry and meaning of the phenomenon under study (Creswell, 2007 ; Miles & Huberman, 1994 ; Yin, 2011 ). For the present research, context was bounded geographically and the problem at hand was thoroughly explored in the Delhi-NCR region. As also suggested by Stake ( 1995 ), a holistic analysis of medical tourism industry in Delhi NCR allowed for an instrumental way to investigate the phenomenon at a broader level in India.
The Case Study Context: Delhi NCR
This study was conducted in Delhi NCR, i.e. National Capital Region of India. It includes Delhi, officially the NCT, National Capital Territory in India and several other regions neighbouring it; Gurugram, NOIDA and Faridabad being the prominent ones. Delhi NCR has witnessed an unprecedented growth in both, the healthcare infrastructure and as well as services in this last decade. The presence of corporate majors like Fortis, Max, Apollo; high-end hospitals like Medanta, Artemis; day care surgery centres and specialised centres, such as for IVF, eye care, birthing centres; has enabled Delhi NCR to emerge as a healthcare hub (Kachhap, 2012 ). Increased activity from the new corporate players have also spurred the existing older players like BLK, Gangaram and Moolchand to revive and widen their portfolio. These healthcare brands are consistently working towards building a strong medical tourism sector. With its robust medical infrastructure, advanced medical specialities, competitive pricing and highly trained doctors, Delhi NCR is amongst the most prominent healthcare destinations in India for international patients. These hospitals provide valuable services to medical tourists, ranging from special wards and lounges for international patients and their companions, translator services, international cuisines, accommodation services and the like. Moreover, its connectivity, location and rich cultural heritage and presence of international standards of hospitality make Delhi NCR a prime tourist destination. These factors make Delhi NCR an important context for exploring the medical tourism industry in India as a whole.
Data Collection
The qualitative approach and exploratory nature of this study maintains that the researcher becomes an agency for data collection. This enables the researcher to get close to the social phenomenon being studied and enable a deeper understanding of the social reality (Bryman, 1988 ; Marshall & Rossman, 1995 ). This also gives researcher the flexibility to delve into the issues that emerge during the study. The qualitative data for this study was collected by the researchers through semi structured in-depth interviews with senior practitioners, and senior members of hospital management. Conducting interviews allowed the researchers to apprehend wide-ranging perspectives and experiences of respondents with regards to medical tourism.
Potential participants for interviews were identified through purposive sampling, to ensure appropriateness, purpose and rich information. Participants were selected from multi-speciality hospitals, offering healthcare services to medical tourists, and through ongoing referrals from interview participants. Table A3, as given in supplementary appendix file, gives a brief profile of the respondents of this study. As a wide-ranging guideline for qualitative design, the study did not look for an increasing number of cases but aimed to collect an extensive detail from each case under study (Creswell, 2007 ). For this research the number of participant cases to be studied was not predetermined. Instead, taking reference from Maykut and Morehouse ( 1994 ), as the study progressed and data was analysed, additional cases required were determined by the extent to which each additional case would contribute to the understanding of the research problem. Data collection was concluded when it was realised that the emerging issues and themes were getting “saturated” and no new data was being found (Creswell, 2007 ; Glaser & Strauss, 1967 ; Strauss & Corbin, 1990 , 1998 ). For this study data saturation occurred within 20 samples. Having a smaller sample size allowed the research to spend an extensive time with each case and encouraged that the understanding, of Delhi-NCR’s competitiveness as a medical tourism destination, which emerged was representative of the practitioners’ perspective (Shaw, 1999 ).
The interviews were conducted in the respondents’ hospitals. The interviews lasted for about 45 min. These were conducted face to face, were audio recorded, after checking with the participants, and later transcribed verbatim. Vital areas of concern were recognised after a thorough literature review on medical tourism and an appraisal of the dimensions of competitiveness of a medical tourism destination, identified by (Malhotra & Dave, 2022 ). These served as the guide for conducting interviews.
Data Analysis
Data was analysed by means of constant comparison method as outlined by Glaser and Strauss ( 1967 ), Strauss and Corbin ( 1990 , 1998 ) and Creswell ( 2007 ). Accordingly, data collection and data analysis were done simultaneously. This allowed the researcher to make necessary adjustment to the research process, such as, sample selection, and testing the emerging themes or concepts with subsequent data (Merriam, 2002 ). This study has adopted the ‘abduction’ logic for data analysis. An abductive analysis approach emphasizes that instead of keeping all predefined theoretical concepts aside, a researcher should enter the field with a broad theoretical understanding and during the research process develop and build upon their theoretical repertoires (Timmermans & Tavory, 2012 ). As also proposed by Lichy et al. ( 2020 ), since the data set for this study was modest in size, coding was conducted manually.
The theoretical background referred to in this paper is a study, by the same authors, on the dimensions and drivers of medical tourism industry. (Malhotra & Dave, 2022 ) previously developed this paper based on a systematic review of empirical studies on the medical tourism industry globally. The purpose of the study was to identify and analyse the factors and dimensions that influence the competitiveness of a country as a medical tourism destination. Figure 1 outlines the dimensions identified by their study. These are structured around the domains of medical tourism opportunity and a country’s positioning, infrastructure and health human resource competence, care delivery, governance and regulatory framework.

Factors influencing a country’s medical tourism industry.
Source: Malhotra & Dave ( 2022 )
This study uses the extant structure to systemize its findings from research work in Delhi NCR that pursues an understanding on how the value proposition of medical tourism industry can be redefined here. This helps us explore the wider relevance of the proposed dimensions in the study by (Malhotra & Dave, 2022 ) and its implications in a specific context. By analysing the experiences of the practitioners from Delhi NCR, the study has able been able to identify an additional dimension that impact a medical tourism destinations’ competitiveness. This dimension is the role of medical facilitators and it has been included in the existing domain of Refined Delivery. Taken together, this has helped to emerge a more comprehensive range of dimensions that are relevant for the development of an advanced medical tourism destination.
This section organises the fieldwork findings around the dimensions outlined in the (Malhotra & Dave, 2022 ) study to identify any contrast and facilitate discussion on Delhi-NCR’s proposition as a medical tourism destination. These dimensions are: assessing a country’s competence as a medical tourism destination, successful positioning and government as a facilitator. While each of these dimensions have been considered independently, for analytical purpose, the apparent correlation between these three domains should be acknowledged. Along with this the discussion also includes respondents’ views on the opportunity assessment of medical tourism for India, its benefits and social implications.
Assessing Medical Tourism as an Opportunity
The ambiguity in the size or figures of the medical tourism market, as highlighted in the literature review, was also reported in the fieldwork of this study. Participants emphasised the concern regarding lack of data on the volume of value of this industry or the market shares. Almost all respondents saw medical tourism as an opportunity for India. They reflected that the market is increasing on a year-to-year basis and that there is a huge potential for the coming 5 to 10 years as well. The major reasons reported for India’s exponential growth in this segment is its clinical expertise, major cost competitiveness over other countries, conducive and friendly environment.
“Reason for the growth is that India has the advantage of being clinically excellent. Technology if not the best is at par with most other countries, our clinicians are trained abroad and they are returning back to practice in India. So clinical excellence has built up” (Respondent 9) “Indian hospitals are clinically sound, environment is conducive, we have a price point advantage over many other countries, then we speak a language that is understood, or getting people who speak their language is easier and cost effective” (Respondent 11)
Some of the respondents also highlighted the evolution in the medical tourism industry, with destination countries getting matured and looking to invest in their own healthcare infrastructure, new medical tourist hubs coming up and a growing impetus of value driven services.
“Very soon you’ll see, facilities there will be developed, clinicians from here will go and train their people. They will still carry back procedures, which cannot be done there, because of the environment, or which require critical post-op care.” (Respondent 14)
Assessing a Country’s Competence as a Medical Tourist Destination
A well-crafted strategy can lay the foundation for a competitive destination for medical tourism and creating an environment of holistic care for medical tourists. The study shows a consensus on the competence of India and specifically Delhi NCR as a healthcare provider.
Healthcare Infrastructure
In the last decade, Delhi NCR has seen the emergence of a robust private healthcare system. Most respondents agreed that Delhi-NCR’s healthcare infrastructure, if not superior, is at par with most other destinations. And that it is one of prominent drivers of medical tourism industry here.
“In purely technical terms of medical infrastructure, I think we are at par with both Singapore and Thailand, or any other country for that matters, where they have an edge over us?? I think it’s in terms of their overall infrastructure…their ethos of cleanliness for example. It takes us an effort to do that, whereas in a place like Singapore it’s given, so that’s the challenge for us Indians” (Respondent 9)
Refined Delivery
Respondents indicate a lack of streamlined and standardised care delivery. This includes not just healthcare services, but service touch points of travel, tourism, airport and hospitality. While Delhi NCR has an appeal over factors such as accommodation, cultural adaptability, language interpreters and general conduciveness, it still has a long way to go.
“Facilities and infrastructure in hospitals are no less than anywhere else, but I think the degree of professionalism can improve a lot. Our systems and processes are not as smooth as how they should be... like the whole process starts when a patient needs medical care in a certain country, so he gets in touch with a local hospital or agent in the source country who in turn gets in tough with the hospital here, that interface could be smoother.” (Respondent 11) “It’s not about their lack of trust on India’s healthcare system, its generally the perception of India as a country and safety of their travel. Say for e.g., patient addressal mechanism could be stronger.” (Respondent 6)
The ‘role of medical facilitators’ was not highlighted in (Malhotra & Dave, 2022 ) original framework. The research work in this study in the Delhi-NCR region, however, raised a number of critical systems impacts and policy implications regarding the role of medical facilitators or middlemen in the Indian medical tourism market. Participants demonstrated a consistent view regarding the prominent role of the facilitators in the medical value chain, in channelizing the international patients towards a particular country and subsequently a healthcare service provider. There was also a prevalent concern regarding the lack of transparency and regulation in the way these middlemen operate, quality of service delivered, corruption or any unethical practices, and most of all a lack of credibility. Participants expressed an apprehension on the way these facilitators impact the quality of care delivery or the overall experience of overseas patients.
“There are these middlemen, also known as facilitators, they form a very important but also the weakest link in this chain. There is no accountability, no regulation… all this can severely impact the service delivery and in turn our name, our credibility goes down” (Respondent 8)
Quality Driven by Standardized Protocols
Most respondents have recognised the importance of accreditation. Issue of safety and quality is a primary concern for the medical tourists. Delhi-NCR hospitals are accredited with both Indian standard of—National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Providers (NABH) and more importantly Joint Commission International (JCI).
“NABH is a recent Indian government initiative to get some sort of quality standardisation in the healthcare industry, it’s not as stringent as JCI, but at least some initiation has been done.” (Respondent 4) “We had our first international accreditation done in 2006 and now second one around 2011–12. The Indian NABH is comparable, but it’s fairly new and not recognised well in international market. Say JCI is well recognised internationally, so we have to get that done if we want to get recognition in the international healthcare industry. Though sometime one is not able to justify the cost incurred on these international accreditations, but still they are very important.” (Respondent 15)
Enhanced Healthcare Human Resource Development
Though Delhi-NCR’s hospitals are clinically competent, lack of skill at the paramedic level was felt by several; respondents. Most respondents reflected the need for superior training programmes for paramedics, and not just in specialities but also in general category and front staff. Only then will service quality standards be met. Respondents expressed the problem of lack of retention of trained paramedics and healthcare workforce.
“Areas of improvement for us would be paramedics. We don’t have training institutes; we need to have a much more vibrant infrastructure for skilling people. Skill development is not there. One excuse given here is the numbers we deal with makes it impossible to work on trainings…” (Respondent 8) “Doctors travel to enhance their skills, where is the exposure for paramedics? On the job training is never enough to improve their service standards.” (Respondent 2)
Coordination and Collaboration for a Superior Care Delivery
Most respondents highlighted a lack of coordination or participation at an industry level. Though several forums like FICCI, CII and the like have been recognised to have some level of representation, however these collaborations and partnerships are still at an early stage. An important reason highlighted was the clash of opinions between players. The industry is still at a fragmented state, where each hospital is strategizing to increase its share in the pie.
Successful Positioning
Most respondents spoke about the individual efforts and strategies, at the group hospital level. Each corporate is trying to position in the international market, in its own capacity. There are some efforts by the government as well in this regard.
“Yes, these corporate groups and other private players are strategizing for capturing medical tourism market, it is a big agenda for them.” (Respondent 5 )
By far, Delhi NCR has been able to position itself as a clinically competent and a cost-effective player. It also scores over other players in terms of its cultural adaptability and soft service skills. Indian doctors are considered more approachable.
“On the price that we are charging, the service that we are giving is very good. We have a patient from Canada, he tells us that our service quality, the kind of attention we give is far better than what they get in west. Because, here we give personal attention, people talk to you, they are ready to go out of their way to help you…” (Respondent 3)
Government as a Facilitator
There was a mixed opinion regarding the role of government as a facilitator. A majority of the respondents felt that government should stay out of the medical tourism sector and the system. They strongly felt that any kind of intervention or regulation by the government would hamper the growth of this industry in India.
“Thankfully govt doesn’t interfere, else the business would go down. As in case of many other sectors... the fact that govt has stayed away from this business like in case of IT sector, has helped the business to come to a certain level... the moment govt steps in, and starts the process of licencing, permits, accreditation. the whole system will come down… let this run as a free market interaction, cause that will bring the best quality at the lowest price… leave the market to its business...” (Respondent 7)
The other opinion recognises the government’s efforts in a positive state. They feel the government has stepped in whenever it needs to, for visa facilitation, rationalisation of visa costs as the like. Initiatives from government and regulatory bodies are required to make the system cleaner and more transparent.
“Regulation is like a double edge sword, it helps you in certain things, it harms you in certain ways. So as long as the regulations are crafted carefully, taking in to the considerations the infrastructure of the institutions…” (Respondent 15)
Social Implications and Benefits of Medical Tourism
The widely shared outlook demonstrated the positive impact of medical tourism on a country’s healthcare and tourism industry. Participants expressed a consistent vision of an overall upgradation of both healthcare and basic infrastructure in the country as a result of the fast-growing competition in the medical tourism market. The participants typically did not express a concern on the social implication of medical tourism industry on the domestic healthcare industry of India, however suggested a holistic outlook to the entire proposition.
“We should not ague on how encouraging medical tourism in India can have a negative impact in our own healthcare burden... If you see we have come a long way, our healthcare system, our medical expertise, technology, has progressed immensely… competition is good for any industry.” (Respondent 12) “If we talk about the impact of medical tourism on Indian healthcare industry, I should say it’s been a positive one… this proposition has added value, credibility and given us a global visibility. One can see a long-term benefit to the domestic industry, not just healthcare but other sectors as well, tourism, logistics, hospitality… Our overall standards of service and hospitality is increasing.” (Respondent 12)
Research aimed at exploring the sources of competitiveness, in a particular industry, for firms competing in international or regional markets (e.g., Momaya, 2019 ; Moon et al., 2015 ; Thompson et al., 2013 ) have emphasised the role of abilities, proprietary knowledge, innovation capability, sustainable business and economic model, technological innovation, pace of internationalisation, quality, business excellence and human resources. Based on our research and taking these factors into consideration, India’s capability as a medical tourism destination is assessed below and gap areas identified. Table Table1 1 provides a synthesis of the growth drivers for India’s medical tourism industry and the opportunity scope.
Medical tourism industry in India—growth drives and opportunity scope.
Source: Compiled by author
With increasing significance of quality and outcomes of the service (Mishra & Sharma, 2021 ), ‘value’ has become the watchword for the healthcare industry. The term to be used here is then medical ‘value’ travel. The addressable market is huge and several countries are strategizing to tap into this opportunity. India’s needs to build a value proposition around the right combinations of cost and quality efficiency.
Clinical expertise and cost are primarily the two important drivers of medical tourism market in India (Ebrahim & Ganguli, 2019 ). It has an edge over other countries with respect to its cost competitiveness. With several prominent super speciality brand names, Delhi NCR has become a hub for medical tourism. The emergence of a robust private sector has significantly enhanced the quality and standards of healthcare. With the presence of clinical and technical expertise, and international standards, Delhi’s credibility as a medical destination is on a rise. Delhi also scores high on the parameters like cultural adaptability and soft skills. The surge in emerging unconventional formats of healthcare delivery and technological revolutions are further fuelling the growth of this industry in India.
Delhi’s holistic appeal as a medical travel destination is hampered by a significantly poor perception on factors such as safety, travel infrastructure, tourism experience and streamlined systems. There have been few initiatives from the government, however much work needs to be done. Regulatory initiatives are specifically required in the areas of transparent accreditation to prevent false claims and substandard care deliveries. Most of all there needs to be a streamlined effort to bring the industry together and work on common grounds of promotion, streamlined systems and travel infrastructure. The medical facilitators play a prominent role in the medical tourism value chain. However, there is an urgent need to define and regularise their position. The channel needs to be streamlined to promote transparency in the process and curtail any unethical and unfair practice that can impact the service outcome and in turn the overall credibility.
Delhi NCR, being the capital and focal point of major developments in the country, has significant scope for improvements in airport and travel infrastructure. As in case of the hospitality industry, service delivery standards need to get streamlined in healthcare industry as well. This would mean investing in training and retaining of paramedics, not just with specialities, but general nurses and staff well.
Industry to focus on brand building initiatives, driven by digital marketing solutions and user specific marketing campaigns. Industry can leverage from collaborative efforts of the stakeholders and public private partnerships to extend potentials of enhancing expertise, efficiency and investment. Most of all it is critical to focus on factors like safety, pollution, drinking water quality, sanitation and corruption to promote a strong positive image of the country that can positively impact medical tourism industry.
As the market is getting matured, industry dynamics are changing. ‘Value’ and ‘Sustainability’ have become the operative words around the world. India and specifically Delhi NCR can look at streamlining the medical value chain by adding and generating value at each touch point, both for India and the source country. With countries which are ready to step up their healthcare facilities, India can explore the option of ‘reverse medical travel’, where in Indian doctors can help set up facilities in the source countries and train their health resources. The complicated and serious procedures will still have to refered back to India, due to the nature of procedure or the critical post-op are required. Such initiatives have already started taking place, but at a minuscule scale. Indian healthcare system needs to take a giant leap towards leveraging the unconventional operating models and technological revolutions, building an ecosystem that encourages and supports innovation. Tapping the international market in a big way will further power this growth.
Limitations and Avenues for Future Research
Case study research has an inherent limitation of generalisability. This research is limited to redefining the value proposition of the medical tourism industry in the Delhi-NCR region only. However, to get an overall perspective of India as a destination, such a study needs to get extended to other major medical tourism hubs as well, such as Chennai, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Mumbai. Also, this study is limited to the surgical aspect of the medical tourism market. Further research could also focus on another growing segment of wellness tourism. Domestic tourism is also an important but a relatively unexplored area. Other micro-niche areas can be super-specialities such as cardiac, ortho, dental, or reproductive services. Facilitators for an important but a very weak link in the medical travel value chain. Further research could focus to either remove or to strengthen this link.
India’s evolution, as amongst the world’s most preferred medical tourist destinations, is expected to sustain a steady growth. This growth is driven by five major factors: cost competitiveness, medical expertise, quality of healthcare services, robust private sector and cultural adaptability. Even as these factors propel India forward, there are some major gaps to bridge. The most pressing concerns in front of the Indian medical tourism industry are paucity of an amenable policy framework, inadequate tourism and logistic infrastructure, unstandardized service quality standards, and India’s poor perception on macroeconomic factors such as corruption, environment quality, safety. To successfully build a future of envisioned growth, India must place a premium on a collaborative effort from all the stakeholders, to address these issues; a commitment to innovation and sustained inclusive growth.
As for the healthcare systems around the world, COVID-19 pandemic has shaken the foundations of Indian healthcare industry as well. With business and health restrictions, medical tourism industry also suffered the initial setback (Ayittey, 2020 ). Government, tourism companies and healthcare providers are struggling to remodel their business to adjust to current realities, withstand the pandemic and accelerate recovery. As the trajectory of the COVID-19 pandemic is not clear, the future remains uncertain. This pandemic and uncertainty around it have further intensified the need for the industry players to direct their focus on realignment and revaluation of their business models and work towards enhancing resilience and agility.
The purpose of this research is to analyse the factors that are crucial for India to identify, create and finally deliver a distinctive value proposition as medical tourism destination. Following a literature review and a qualitative study with Delhi NCR as a case, this research advances the medical tourism body of knowledge. The paper discusses the research process and the methodology adopted for the study in detail. Finally, the report analyses India’s, and specifically Delhi-NCR’s, competence as a medical tourist destination and synthesises the key growth drivers and opportunities for this industry.
Key Questions Reflecting Applicability in Real Life
- What are the critical success factors in medical tourism industry?
- What are the dimensions and factors that can help India increase its competitiveness as a medical tourism destination?
- How can service providers ensure a steady growth of the medical tourism ecosystem, to ensure sustainability and competitiveness?
- What role can policy support play for the medical tourism ecosystem in India and its competitiveness?
- How has the Covid-19 Pandemic affected the medical tourism ecosystem? Which segment of the industry can rebound stronger in which cities?
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their special thanks to all the respondents of this study, who despite their busy schedules and heavy engagements, took time to give us their insights and critical inputs to improve the quality of this research. Besides, the authors wish to acknowledge all the reviewers including the members on the Editorial Board of this journal, whose constructive critique helped in improving the quality of the paper to a great extent.
Biographies
has over 16 years of diverse experience in industry and academics. She has been working as a management consultant offering knowledge-based services to clients in the consumer and retail sector. Neha has also been associated with various universities and institutes as a visiting faculty in the area of marketing, management and retail. Her research interest lies in the area of Marketing, Retail, Luxury, Services, Consumer Behaviour, Education and Employability. Neha Malhotra is a doctoral scholar at Ambedkar University, Delhi. She has done MS in Consultancy Management from BITS Pilani and Postgraduation in Fashion Management Studies from NIFT Bangalore.

is a professor of Marketing and Retail Management area at Ambedkar University, Delhi. He brings in-rich experience of around 23 years in industry and academics. Prof Dave is also Dean of School of Business, Public Policy and Social Entrepreneurship (SBPPSE) at Ambedkar University. He has been serving as an expert for various academic endeavours like selection committees, board of studies, PhD examiner, speaker and trainer at various B-schools and universities. His research interest lies in Marketing, Management, Services, Branding, Luxury, Retailing, Customer Analysis, Internationalization in Higher Education, Management Education in India, Quality and Accreditation issues.

Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by NM and KD. The first draft of the manuscript was written by NM and all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The authors declare that there was no funding from any agency or institution for conducting this study.
Data Availability
Code availability, declarations.
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Neha Malhotra, Email: [email protected] .
Kartik Dave, Email: ni.ca.dua@kitrak .
- Abubakar AM, Ilkan M. Impact of online WOM on destination trust and intention to travel: A medical tourism perspective. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management. 2016; 5 (3):192–201. doi: 10.1016/j.jdmm.2015.12.005. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ayittey FK, Ayittey MK, Chiwero NB, Kamasah JS, Dzuvor C. Economic impacts of Wuhan 2019-nCoV on China and the world. Journal of Medical VIrology. 2020; 92 (5):473. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25706. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aziz A, Yusof RM, Ayob M, Bakar NTA. Measuring tourist behavioural intention through quality in Malaysian medical tourism industry. Procedia Economics and Finance. 2015; 31 :280–285. doi: 10.1016/S2212-5671(15)01179-X. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bagga T, Vishnoi SK, Jain S, Sharma R. Medical tourism: Treatment, therapy and tourism. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research. 2020; 9 (3):4447–4453. [ Google Scholar ]
- Beladi H, Chao CC, Ee MS, Hollas D. Does medical tourism promote economic growth? A cross-country analysis. Journal of Travel Research. 2019; 58 (1):121–135. doi: 10.1177/0047287517735909. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bookman M, Bookman K. Medical tourism in developing countries. Palgrave Macmillan; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bryman A. Doing Research in Organisations. Routledge; 1988. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bygrave W. The entrepreneurship paradigm (I): A philosophical look at its research methodologies. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice. 1989; 14 (1):7–26. doi: 10.1177/104225878901400102. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carrera P, Bridges J. Globalization and healthcare: Understanding health and medical tourism. Expert Review of Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research. 2006 doi: 10.1586/14737167.6.4.447. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cham TH, Lim YM, Sia BC, Cheah JH, Ting H. Medical tourism destination image and its relationship with the intention to revisit: A study of Chinese medical tourists in Malaysia. Journal of China Tourism Research. 2021; 17 (2):163–191. doi: 10.1080/19388160.2020.1734514. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chambers D, McIntosh B. Using authenticity to achieve competitive advantage in medical tourism in the English-speaking Caribbean. Third World Quarterly. 2008; 29 :919–937. doi: 10.1080/01436590802106056. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chhabra A, Munjal M, Mishra PC, Singh K, Das D, Kuhar N, Vats M. Medical tourism in the Covid-19 era: Opportunities, challenges and the way ahead. Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism Themes. 2021 doi: 10.1108/WHATT-05-2021-0078. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chuang TC, Liu JS, Lu LY, Lee Y. The main paths of medical tourism: From transplantation to beautification. Tourism Management. 2014; 45 :49–58. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2014.03.016. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Connell J. Medical tourism: Sea, sun, sand and… surgery. Tourism Management. 2006; 27 (6):1093–1100. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2005.11.005. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Connell J. Contemporary medical tourism: Conceptualisation, culture and commodification. Tourism Management. 2013; 34 :1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2012.05.009. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cortez N. Patients without borders: The emerging global market for patients and the evolution of modern health care. Indiana Law Journal. 2008; 83 :1–24. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell JW. Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches. 2. Sage Publications Inc.; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell J. Qualitative Inquiry & Research Design Choosing among Five Approaches. CA Sage: Thousand Oaks; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Crouch GI, Ritchie JB. Application of the analytic hierarchy process to tourism choice and decision making: A review and illustration applied to destination competitiveness. Tourism Analysis. 2005; 10 (1):17–25. doi: 10.3727/1083542054547930. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- De La Hoz-Correa A, Muñoz-Leiva F. The role of information sources and image on the intention to visit a medical tourism destination: A cross-cultural analysis. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing. 2019; 36 (2):204–219. doi: 10.1080/10548408.2018.1507865. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- De la Hoz-Correa A, Muñoz-Leiva F, Bakucz M. Past themes and future trends in medical tourism research: A co-word analysis. Tourism Management. 2018; 65 :200–211. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2017.10.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Debata BR, Patnaik B, Mahapatra SS, Sree K. Interrelations of service quality and service loyalty dimensions in medical tourism: A structural equation modelling approach. Benchmarking: an International Journal. 2015; 22 (1):18–55. doi: 10.1108/BIJ-04-2013-0036. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Deloitte Global. (2021). Digital transformation and health care delivery model convergence. Retrieved from https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/global/Documents/Life-Sciences-Health-Care/gx-digital-transformation.pdf
- Dunets AN, Yankovskaya V, Plisova AB, Mikhailova MV, Vakhrushev IB, Aleshko RA. Health tourism in low mountains: A case study. Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues. 2020; 7 (3):2213. doi: 10.9770/jesi.2020.7.3(50). [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ebrahim AH, Ganguli S. A comparative analysis of medical tourism competitiveness of India, Thailand and Singapore. Tourism: an International Interdisciplinary Journal. 2019; 67 (2):102–115. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fetscherin M, Stephano RM. The medical tourism index: Scale development and validation. Tourism Management. 2016; 52 :539–556. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2015.08.010. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Financial Express. (2022, March). Medical value tourism in India: What makes the country a leading Medical Tourism Destination. Financial Express.
- Ganguli S, Ebrahim A. A qualitative analysis of Singapore's medical tourism competitiveness. Tourism Management Perspectives. 2017 doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2016.12.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ghosh T, Mandal S. Medical tourism experience: Conceptualization, scale development, and validation. Journal of Travel Research. 2019; 58 (8):1288–1301. doi: 10.1177/0047287518813469. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaser B, Strauss A. The Discovery of Grounded Theory Strategies for Qualitative Research. CA Sociology Press; 1967. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gola S. Medical tourism in India – in whose interest? Journal of International Trade Law and Policy. 2016; 15 (2/3):115–133. doi: 10.1108/JITLP-01-2016-0005. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hall CM. Health and medical tourism: A kill or cure for global public health? Tourism Review. 2011; 66 (1/2):4–15. doi: 10.1108/16605371111127198. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heung VC, Kucukusta D. Wellness tourism in China: Resources, development and marketing. International Journal of Tourism Research. 2013; 15 (4):346–359. doi: 10.1002/jtr.1880. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heung V, Kucukusta D, Song H. A conceptual model of medical tourism: implications for future research. Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing. 2010; 27 (3):236–251. doi: 10.1080/10548401003744677. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hudson S, Li Z. Domestic Medical Tourism: A Neglected Dimension of Medical Tourism Research. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management. 2012; 21 (3):227–246. doi: 10.1080/19368623.2011.615018. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- iGATE Research. (2017). Asia Medical Tourism Market and Forecast To 2022.
- Jagyasi P. Defining medical tourism - Another approach. Medical Tourism Magazine. 2008; 6 :9–11. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kachhap, M. (2012). Developing Delhi - Express Healthcare. Retrieved from www.expresshealthcare.in : https://www.expresshealthcare.in/archive/developing-delhi/563/
- Kamassi A, Abd Manaf NH, Omar A. The identity and role of stakeholders in the medical tourism industry: State of the art. Tourism Review. 2020 doi: 10.1108/TR-01-2019-0031. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- KPMG. (2014). Medical value travel in India. FICCI Heal Conference. KPMG India.
- KPMG India, & Google. (2018). Indian brands going global, A USD39 billion opportunity.
- Lee C, Hung W. Tourism, health and income in Singapore. International Journal of Tourism Research. 2010; 12 (4):355–359. doi: 10.1002/jtr.755. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lichy J, Farquhar JD, Kachour M. Entrepreneurship via social networks–“connected woman” in Lebanon. Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal. 2020 doi: 10.1108/QMR-01-2020-0004. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lovelock B, Lovelock K, Lyons K. The impact of outbound medical (dental) tourism on the generating region: New Zealand dental professionals' perspectives. Tourism Management. 2018; 67 :399–410. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2018.02.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Malhotra N. & Dave K. (2022). Dimensions and Drivers of Medical Tourism Industry: A Systematic Review of Qualitative Evidence. International Journal of Business and Globalisation . 10.1504/IJBG.2022.10042738 (in press).
- Marshall C, Rossman G. Designing Qualitative Research. 2. Sage; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Maykut P, Morehouse R. Beginning Qualitative Research: A Philosophical and Practical Guide. The free press; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Medhekar A, Wong HY, Hall JE. Factors influencing inbound medical travel to India. Journal of Health Organization and Management. 2019 doi: 10.1108/JHOM-08-2018-0234. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Merriam SB. Introduction to qualitative research. In: Merriam SB, editor. Qualitative research in practice: Examples for discussion and analysis. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; 2002. pp. 1–33. [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles MB, Huberman AM. Qualitative data analysis. 2. Sage Publications; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ministry of Tourism. (2018). India Tourism Statistics 2018. Ministry of Tourism, Government of India.
- Mishra V, Sharma MG. Framework for promotion of medical tourism: A case of India. International Journal of Global Business and Competitiveness. 2021; 16 (1):103–111. doi: 10.1007/s42943-021-00027-7. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Momaya KS. The past and the future of competitiveness research: A review in an emerging context of innovation and EMNEs. International Journal of Global Business and Competitiveness. 2019; 14 (1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/s42943-019-00002-3. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Momeni K, Janati A, Imani A, Khodayari-Zarnaq R. Barriers to the development of medical tourism in East Azerbaijan province, Iran: A qualitative study. Tourism Management. 2018; 69 :307–316. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2018.05.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Moon HC, Lee YW, Yin W. A new approach to analysing the growth strategy of business groups in developing countries: The case study of India's Tata Group. International Journal of Global Business and Competitiveness. 2015; 10 (1):1–15. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mooter, B. V. (2017, Nov). Medical Tourism in Asia-Pacific Growing Rapidly. BRINK, The Edge of Risk.
- Olya H, Nia TH. The medical tourism index and behavioral responses of medical travelers: A mixed-method study. Journal of Travel Research. 2021; 60 (4):779–798. doi: 10.1177/0047287520915278. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Omay EGG, Cengiz E. Health tourism in Turkey: Opportunities and threats. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences. 2013; 4 (10):424–424. doi: 10.5901/mjss.2013.v4n10p424. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Outlook India. (2019, July). Heath is Priceless Live Healthy. Outlook.
- Pafford B. The third wave–Medical tourism in the 21st century. Southern Medical Journal. 2009; 102 (8):810–813. doi: 10.1097/smj.0b013e3181aa8ce4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Qadeer I, Reddy S. Medical tourism in india: Perceptions of physicians in tertiary care hospitals. Philosophy, Ethics, and Humanities in Medicine. 2013 doi: 10.1186/1747-5341-8-20. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rahman R. The privatisation of healthcare system in Bangladesh. International Journal of Health Care Quality Assurance. 2019 doi: 10.1108/IJHCQA-11-2017-0217. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramirez de Arellano A. Patients without borders: The emergence of medical tourism. International Journal of Health Services. 2007; 37 (1):193–198. doi: 10.2190/4857-468G-2325-47UU. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reddy GR. Travel for treatment: Students' perspective on medical tourism. International Journal of Tourism Research. 2010; 12 :510–522. doi: 10.1002/jtr.769. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seow AN, Choong YO, Moorthy K, Chan LM. Intention to visit Malaysia for medical tourism using the antecedents of Theory of Planned Behaviour: A predictive model. International Journal of Tourism Research. 2017; 19 (3):383–393. doi: 10.1002/jtr.2120. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shaw E. A guide to the qualitative research process. Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal. 1999; 2 (2):59–70. doi: 10.1108/13522759910269973. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Singh PK. Medical tourism. Kanishka Publishers; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith M, Puczko L. Health and wellness tourism. Elsevier; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stackpole I, Ziemba E, Johnson T. Looking around the corner: COVID-19 shocks and market dynamics in US medical tourism. The International Journal of Health Planning and Management. 2021; 36 (5):1407–1416. doi: 10.1002/hpm.3259. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE. The art of case study research. Sage Publications; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss A, Corbin JM. Basics of qualitative research: Grounded theory procedures and techniques. Sage Publications Inc; 1990. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss A, Corbin JM. Basics of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing Grounded Theory. Sage Publications Inc; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Snyder J, Byambaa T, Johnston R, Crooks VA, Janes C, Ewan M. Outbound medical tourism from Mongolia: A qualitative examination of proposed domestic health system and policy responses to this trend. BMC Health Services Research. 2015; 15 (1):1–8. doi: 10.1186/s12913-015-0849-5. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Taheri B, Chalmers D, Wilson J, Arshed N. Would you really recommend it? Antecedents of word-of-mouth in medical tourism. Tourism Management. 2021; 83 :104209. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104209. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thayarnsin, S. L., & Douglas, A. C. (2016). A Systematic Review of Challenges in Medical Tourism Destination Management . Travel and tourism research association: Advancing tourism research globally
- Thompson A, Peteraf M, Gamble J, Strickland AJ, III, Jain AK. Crafting & executing strategy 19/e: The quest for competitive advantage: Concepts and cases. McGraw-Hill Education; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Timmermans S, Tavory I. Theory construction in qualitative research: from grounded theory to abductive analysis. Sociological Theory. 2012; 30 (3):167–186. doi: 10.1177/0735275112457914. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Turner L. First world health care at third world prices’: Globalization, bioethics and medical tourism. BioSocieties. 2007; 2007 :303–325. doi: 10.1017/S1745855207005765. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Velasco RP, Myint CY, Khampang R, Tantivess S, Teerawattananon Y. Advanced health biotechnologies in Thailand: Redefining policy directions. Journal of Translational Medicine. 2013; 11 (1):1. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Virani A, Wellstead AM, Howlett M. Where is the policy? A bibliometric analysis of the state of policy research on medical tourism. Global Health Research and Policy. 2020; 5 (1):1–16. doi: 10.1186/s41256-020-00147-2. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang HY. Value as a medical tourism driver. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal. 2012; 22 (5):465–491. doi: 10.1108/09604521211281387. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yeoh E, Othman K, Ahmad H. Understanding medical tourists: Word-of-mouth and viral marketing as potent marketing tools. Tourism Management. 2013; 34 :196–201. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2012.04.010. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin RK. Applications of Case Study Research. Sage; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
Breaking Boundaries: Navigating India’s Medical Tourism Landscape with VisasIndia
New Delhi, India, 21st March 2024, In an era defined by seamless global connectivity, the pursuit of medical excellence knows no borders. Today, we unveil a groundbreaking initiative poised to redefine the landscape of medical tourism: India Medical eVisa. Pioneered by VisasIndia, this innovative platform seamlessly integrates cutting-edge technology with unparalleled convenience, presenting a comprehensive guide to navigating the realm of medical tourism in India.
The journey begins with a click: prospective travelers seeking medical care in the vibrant heart of India can now access a comprehensive guide at India Medical eVisa, where every aspect of the process is meticulously demystified. From visa requirements to navigating entry protocols, this digital compendium serves as a beacon of clarity amidst the complexities of international travel.
INDIA MEDICAL EVISA
INDIA VISA AIRPORTS ALLOWED FOR EVISA
WHAT IS REFERENCE NAME IN INDIAN VISA
INDIAN VISA FOR CAMEROONIAN CITIZEN
INDIAN VISA FOR CAPE VERDEAN CITIZENS
Moreover, the voyage to India is further streamlined through the dedicated insights provided by India Visa Airports Allowed for eVisa. As travelers prepare to embark on their transformative medical odyssey, this indispensable resource elucidates the specific entry points sanctioned for eVisa holders, ensuring a seamless transition from departure lounge to Indian soil. Explore more at India Visa Airports Allowed for eVisa.
For those navigating the intricate nuances of visa application, VisasIndia stands as a steadfast ally, offering unrivaled expertise and guidance. Curious minds can delve into the intricacies of reference name requirements with our illuminating discourse on What is Reference Name in Indian Visa. Navigate through the intricacies at What is Reference Name in Indian Visa, and embark on your journey armed with knowledge and confidence.
As the global community converges on the shores of India, we extend a warm embrace to citizens of Cameroon and Cape Verde, illuminating the path to seamless visa acquisition. Discover the streamlined process for Indian Visa for Cameroonian Citizens and Indian Visa for Cape Verdean Citizens, opening doors to a world of unparalleled medical expertise and cultural enrichment. Learn more at Indian Visa for Cameroonian Citizen and Indian Visa for Cape Verdean Citizens.
In a world defined by innovation and interconnectedness, VisasIndia stands as a beacon of excellence, empowering individuals to embark on transformative journeys with confidence and ease. Join us as we unlock the gateway to India, forging new frontiers in the realm of medical tourism and eVisa services.
About VisasIndia:
VisasIndia is a leading authority in facilitating seamless visa acquisition and travel documentation services. With a commitment to excellence and innovation, VisasIndia empowers travelers worldwide to explore new horizons with confidence and convenience. Through cutting-edge technology and unwavering dedication, VisasIndia continues to redefine the landscape of international travel, fostering a world where borders are transcended, and experiences are limitless. Explore more at VisasIndia.org.
Media Contact
+359 2 982 4808
https://www.india-visa-online.org/visa/

Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

National Strategy and Roadmap for Medical and Wellness Tourism
Gs paper 2/3.
Syllabus: Government policies/Issues Relating to Health/Economy
Source: PIB
Context: With an aim to improve medical tourism in the country, the Ministry of Tourism has formulated a National Strategy and Roadmap for Medical and Wellness Tourism (2022).
Background: India has been ranked 10th in the Medical Tourism Index (MTI) for 2020-2021 out of 46 destinations in the world by the Medical Tourism Association.
Medical vs wellness tourism:
- Medical tourism (valued at $60-80 billion globally) primarily addresses the “ poor health ” end of the market, with patients travelling to another place for specific medical treatments.
- Wellness tourism (~$639 billion), on the other hand, attracts those seeking destinations that extend their wellness lifestyle and help them proactively maintain and improve their health and well-being.
- As far as medical tourism is concerned, India currently has a $5-6 billion market (2019 figure) that may rise to $13 billion by 2026.

Govt. efforts to boost the medical tourism sector in India:
Streamlining Medical Value Travel (MVT) : A segment that attracted 0.7 million foreign tourists in pre-pandemic 2019.
- MVT is a specialised service by Hospitals and Wellness centres including both modern as well as traditional systems of medicine.
- It involves healthcare service providers, VISA requirements, insurance, MVT facilitators, etc.
National Strategy and Roadmap for Medical and Wellness Tourism (2022): Key pillars for the development of MVT in the country:
- Develop a brand for India as a wellness destination
- Strengthen the ecosystem for medical and wellness tourism
- Enable digitalization by setting up an Online Medical Value Travel (MVT) Portal
- Enhancement of accessibility for Medical Value Travel
- Promoting Wellness Tourism
- Governance and Institutional Framework
Heal in India Initiative: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Ministry of Ayush have been working with C-DAC and the Services Export Promotion Council for developing a One Step Heal in India portal for the Promotion of MVT.
Champion Service Sector Scheme: The Ministry of Ayush developed a Central Sector Scheme for MVT to incentivise private investors for the establishment of Super Specialty Hospitals, etc.
e-Tourist Visa scheme: It was liberalised and renamed as an e-Visa scheme and at present, it has e-Medical Visa and e-Medical Attendant Visa as sub-categories of e-visa.
National Medical & Wellness Tourism Board (NMWTB): The Ministry of Tourism constituted the Board in 2015 to provide a dedicated institutional framework to take forward the cause of promotion of Medical and Wellness Tourism.
Insta Links: Heal in India

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

Update on improving Medical Tourism in the country India ranks 10th in Medical Tourism Index (MTI) for 2020-2021 out of 46 destinations of the world Foreign Tourists Arrival on medical purpose increases from 1.83 lakh in 2020 to 3.04 lakh in 2021
India has been ranked 10 th in Medical Tourism Index (MTI) for 2020-2021 out of 46 destinations of the world by Medical Tourism Association. As per information provided by Ministry of Tourism, foreign tourist arriving in India for medical purpose are as below:
With an aim to improve medical tourism in country, Ministry of Tourism has formulated a National Strategy and Roadmap for Medical and Wellness Tourism in 2022. The strategy has identified following key pillars for the development of medical value travel in the country:
- Develop a brand for India as a wellness destination
- Strengthen the ecosystem for medical and wellness tourism
- Enable digitalization by setting up Online Medical Value Travel (MVT) Portal
- Enhancement of accessibility for Medical Value Travel
- Promoting Wellness Tourism
- Governance and Institutional Framework
Union Ministry of Health & Family Welfare is coordinating with other Ministries viz Ministry of Home Affairs, Tourism, AYUSH, External Affairs, Civil Aviation, State Governments and other stakeholders to promote Medical Value Travel (MVT) in the country. An institutional approach in coordination with other Ministries like Ministry of Tourism, AYUSH, Home Affairs, External Affairs, Civil Aviation, State Governments and other relevant stakeholders is adopted for promotion of medical value travel. Several rounds of stakeholder consultations have been conducted with line Ministries, Hospitals, MVT facilitators, Insurance Companies and National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH) to identify the challenges and opportunities in the sector.
The Union Minister of State for Health and Family Welfare, Dr. Bharati Pravin Pawar stated this in a written reply in the Rajya Sabha today.
HFW/ Update on improving medical tourism in the country /2h1 March 2023/4
Overview of Travel Insurance Coverage
What does travel insurance cover, what does credit card travel insurance cover, what travel insurance coverage do you need to pay more for, choosing the right travel insurance, what does travel insurance cover frequently asked questions, understanding what travel insurance covers.
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate insurance products to write unbiased product reviews.
The information for the following product(s) has been collected independently by Business Insider: Chase Freedom Flex℠. The details for these products have not been reviewed or provided by the issuer.
- Travel insurance is intended to cover risks and financial losses associated with traveling.
- Coverage can include trip cancellation, baggage protection, medical care, and emergency evacuation.
- When filing a claim, be specific and comprehensive in your documentation to ease the process.
Whether it's a trip across the world or a trip across the state, having travel insurance provides major relief if things go awry. Flight delays, lost baggage, illness, injuries, and other unforeseen events can disrupt even the best-laid plans. With a major disruption comes the potential for unanticipated expenses.
Travel insurance and the coverage it offers can help keep you protected and save you money in the long run.
Travel insurance policies protect travelers from financial losses should something go wrong during their trip. You can customize which coverages you want to include, and there are several to choose from.
"Common types of coverage include trip cancellation, trip interruption, baggage protection, coverage for medical care if you get sick or hurt during your trip, and emergency medical evacuation," says Angela Borden, a travel insurance expert and product strategist for travel insurance company Seven Corners.
Travel insurance plans offer nonrefundable payments and other trip-related expenses. While monetary compensation is a primary benefit, there is another valuable perk of travel insurance. It can provide peace of mind.
Your specific travel insurance plan (and its terms and conditions) will determine the minutia and specifics of what is covered. As with most other forms of insurance, a general rule of thumb is the more you spend, the better your coverage.
"Travel insurance can be confusing, so it's best to research a reputable company that specializes in travel insurance and has a long history of successfully helping travelers all over the world," says Borden.
Trip cancellation and interruptions
A travel insurance policy can reimburse you for a prepaid, nonrefundable trip if it is canceled for a covered event, such as a natural disaster or a global pandemic.
Trip interruption insurance covers you if you're already on your trip and you get sick, there's a natural disaster, or something else happens. Make sure to check with your travel insurance providers to discuss any inclusions, coverage, and more.
Travel delays and missed connections
Travel delay insurance coverage provides reimbursement for any expenses you incur when you experience a delay in transit over a minimum time. Reimbursements can include hotels, airfare, food, and other related expenses.
Medical emergencies and evacuations
Typically, US healthcare plans are not accepted in other countries. So travel insurance with medical coverage can be particularly beneficial when you are abroad. Medical coverage can also help with locating doctors and healthcare facilities.
Medical transportation coverage will also pay for emergency evacuation expenses such as airlifts and medically-equipped flights back to the US. Out of pocket, these expenses can easily amount to tens of thousands of dollars. Certain plans may even transport you to a hospital of choice for care.
Travel insurance generally does not include coverage for pre-existing conditions. That said, you can obtain a pre-existing condition waiver, which we will talk about later.
Baggage and personal belongings
Most airlines will reimburse travelers for lost or destroyed baggage, but be prepared for limitations. Travel insurance plans will typically cover stolen items, such as those stolen out of a hotel room. This may not include expensive jewelry, antiques, or heirloom items. Typically, airlines have a few days to recover your bag.
In the meantime, you can make a claim to pay for items like certain toiletries and other items you need to pick up. If your bag is truly lost or you don't get it for an extended period, you can file a true lost baggage claim.
A major perk on several travel credit cards is embedded credit card travel insurance . Typically, you will need to use the specific card for the transaction (at least with partial payment) for travel coverage to kick in.
Each card has specific rules on what exactly is covered. But one of the industry leaders is the $550-per-year Chase Sapphire Reserve credit card. Here's a snapshot of what is covered with this specific card:
- Baggage delay: up to $100 reimbursed per day for up to five days if a passenger carrier delays your baggage by more than six hours.
- Lost and damaged baggage: up to $3,000 per passenger per trip, but only up to $500 per passenger for jewelry and watches and up to $500 per passenger for cameras and other electronic equipment.
- Trip delay reimbursement: up to $500 per ticket if you're delayed more than six hours or require an overnight stay.
- Trip cancellation and interruption protection: up to $10,000 per person and $20,000 per trip for prepaid, nonrefundable travel expenses.
- Medical evacuation benefit: up to $100,000 for necessary emergency evacuation and transportation when on a trip of five to 60 days and traveling more than 100 miles from home.
- Travel accident insurance: accidental death or dismemberment coverage of up to $100,000 (up to $1,000,000 for common carrier travel).
- Emergency medical and dental benefits: up to $2,500 for medical expenses (subject to a $50 deductible) when on a trip arranged by a travel agency and traveling more than 100 miles from home.
- Rental car coverage: primary coverage for damages caused by theft or collision up to $75,000 on rentals of 31 days or fewer
More protections are included with cards with an annual fee, but there are exceptions. The no-annual-fee Chase Freedom Flex, for instance, includes up to $1,500 per person (and up to $6,000 per trip) in trip cancellation and trip interruption coverage.
However, there are some differences between credit card travel coverage and obtaining coverage from a third party.
"Credit card coverage does not typically provide travel medical benefits," Borden says. "For protection if you get sick or hurt while traveling, you'll want a travel insurance plan with medical coverage."
Whether you get your travel insurance in a standalone policy or through a credit card, it's important to review your plan details carefully. In either case, there may be exclusions and other requirements such as deadlines when filing a claim, Borden notes.
Knowing what travel insurance doesn't cover is as important as knowing what it does cover.
"Travelers should understand that travel insurance benefits come into play only if a covered reason occurs," Borden says. Most standard travel insurance plans won't reimburse you for the following:
Cancel for any reason (CFAR)
Cancel-for-any-reason travel insurance covers a trip cancellation for any reason, not just a covered event. your standard benefits won't kick in unless it's a covered event. For instance, you'll be reimbursed simply for changing your mind about taking a trip.
That said, CFAR travel insurance is not without its downsides. For one, it's more expensive than traditional insurance, and most CFAR policies will only reimburse you for a percentage of your travel expenses. Additionally, CFAR policies aren't available for annual travel insurance .
You can find our guide on the best CFAR travel insurance here.
Foreseen weather events
Sudden storms or unforeseen weather events are typically covered by standard travel insurance plans. There are exceptions to be aware of. For example, an anticipated and named hurricane will not be covered.
Medical tourism
If you're going to travel internationally for a medical procedure or doctor's visit, your travel insurance plan will not cover the procedure itself. Most medical travel plans also won't cover you if something goes wrong with your procedure.
Pre-existing conditions and pregnancy
Those with specific pre-existing conditions, such as someone with diabetes and needing more insulin, will not be covered by most plans. In addition, pregnancy-related expenses will likely not be covered under most plans.
That said, you can obtain a pre-existing condition waiver for stable conditions. In order to obtain a wavier, you will need to purchase travel insurance within a certain time frame from when you booked your trip, usually two to three weeks, depending on your policy.
Extreme sports and activities
Accidents occurring while participating in extreme sports like skydiving and paragliding will typically not be covered under most plans. However, many plans offer the ability to upgrade to a higher-priced version with extended coverage.
Navigating claims and assistance
When a trip goes awry, the first thing you should do is document everything and be as specific as possible with documentation. This will make the claims process easier, as you can substantiate and quantify your financial losses due to the delay.
For example, your flight home has been delayed long enough to be covered under your policy, you'll want to keep any receipts from purchases made while waiting. For instances where your luggage is lost, you will need to file a report with local authorities and document all the items you packed.
Cancellation protection also requires meticulous attention to detail. If you're too sick to fly, you may need to see a doctor to prove your eligibility. If an airline cancels a flight, you'll also need to document any refunds you received as travel insurance isn't going to reimburse you for money you've already gotten back.
Part of the benefit of CFAR insurance is the reduced paperwork necessary to file a claim. You'll still need to document your nonrefundable losses, but you won't have to substantiate why you're canceling a trip.
Each plan should be personalized to meet the insured party's needs. Some travelers prefer to stick to the bare minimum (flight cancellation benefits through the airline). Others want a comprehensive plan with every coverage possible. Before you buy anything, set your destination. Are there any travel restrictions or changes pending? Does your destination country require emergency or other medical coverage?
If the destination airport is known for lost or delayed luggage, travelers should keep important items in carry-ons. Lost or delayed luggage coverage protects insured parties in the event of a significant delay or total loss.
Second, check current credit card travel benefits to avoid redundancies. Savvy travelers don't need to pay for the same coverage twice.
Finally, consider your individual needs. Do you have a chronic medical condition, or do you feel safe with emergency-only medical coverage? Keep in mind, this does not include coverage for cosmetic surgery or other medical tourism. Do you have a budget limit for travel insurance? Asking and answering these important questions will help every traveler find the right product.
Most travel insurance plans are simple, and Business Insider's guide to the best travel insurance companies outlines our top picks. Remember, read your policy and its specifics closely to ensure it includes the items you need coverage for.
No one likes to dwell on how a trip might not go as planned before even leaving. However, at its core, travel insurance provides peace of mind as you go about your trip. While the upfront cost may seem significant, when you compare it to the potential expenses of a canceled flight, emergency evacuation, or a hefty medical bill, it's a small price to pay in the grand scheme of things.
Coverage for pandemics vary from policy to policy. Some travel insurance companies have specific provisions for pandemic-related cancellations, while others may exclude them entirely.
Sports injuries are often covered under travel insurance, but high-risk or adventure sports might require additional coverage or a special policy.
Travel advisories have different effects on your travel insurance depending on your policy. Traveling to a country already under travel advisory may invalidate your coverage, but if you're already traveling when a travel advisory is announced, you may be covered.
Travel insurance usually covers the cost of emergency medical evacuations to the nearest suitable medical facility, and sometimes back to your home country, if necessary.
Many travel insurance policies provide coverage for the cost of replacing lost or stolen passports during a trip.
Editorial Note: Any opinions, analyses, reviews, or recommendations expressed in this article are the author’s alone, and have not been reviewed, approved, or otherwise endorsed by any card issuer. Read our editorial standards .
Please note: While the offers mentioned above are accurate at the time of publication, they're subject to change at any time and may have changed, or may no longer be available.
**Enrollment required.

- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are some steps you can follow to get started: Research the market: Look into the demand for medical tourism in India and the types of treatments and procedures most popular with foreign tourists. Get started with the best Medical Tourism software. Develop a business plan: Outline your goals, target market, budget, and marketing strategy.
Familiarize yourself with the regulatory requirements governing medical tourism in India. Ensure that your business complies with licensing, accreditation, and quality standards set by healthcare authorities. Building a network with reputable healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics is crucial to ensure the delivery of high-quality services.
1. ClinicSpots. ClinicSpots is among India's top medical tourism companies, operating in major metro cities with a focus on providing excellent medical care assistance. They have established tie-ups with renowned hospitals in Mumbai, ensuring access to superior healthcare facilities.
Benefits of Medical Tourism in India: Cost-effective treatment: The cost of medical treatment in India is significantly lower than in Western countries. Patients can save up to 80% of the cost of medical treatment in India compared to the USA. Quality healthcare: Indian hospitals offer world-class healthcare facilities and services.
According to a CII-Grant Thornton study, the Indian medical tourism market is expected to grow from the current $3 billion to around $8 billion by 2020. According to MarketWatch, Global Medical Tourism Market will grow at a CAGR of 16.1% during the forecast period 2019-2025.
India's medical tourism has grown rapidly in recent years, with an increase in foreign tourists from 183,000 in 2020 to 304,000 in 2021. HFS expects the medical tourism market to grow at a CAGR of more than 20% between 2023 and 2027 to more than US $35 billion from its current US $6 billion. The medical tourism ecosystem comprises healthcare ...
India in recent years has emerged as a major hub for medical tourism and is now considered among the top 6 medical value travel destinations in the world. Here is all you need to know about it.
The aim is to make India the No.1 Destination for Medical Tourism in the world, tripling its revenue to $13 billion within 4 years. The government has also proposed an outlay of US$ 28.7 billion for health and well-being, which is 137% higher than the previous year's budget outlay.
Our medical tariffs are lower when you value them in dollars or pounds. For example, a root canal costs about INR 1,500 in India, while the same procedure costs about INR 10,000-15,000 (at least ...
According to Industry estimates, the total revenue of medical tourism was valued over $310 million in 2005-06 with a record 1 million foreign medical tourists visiting the country every year and is expected to grow to $7-8 billion by 2020. Visitors from 55 countries come to India for treatment but the biggest growth in business is from the UK ...
Prime Exclusives. Medical tourism refers to the practice of traveling to another country for medical treatment, often due to lower costs, better quality care, or shorter waiting times. In India, this industry has witnessed exponential growth, driven by factors such as world-class medical facilities, skilled healthcare professionals, and cost ...
The Tourism Ministry reported a staggering negative growth rate of 79.4% in 2020. Despite this setback, the situation is gradually improving as efforts to combat the pandemic yield positive results. Market insights suggest a robust 19% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the demand for medical tourism in India by 2022.
Discover medical tourism in India: a hub of excellence for affordable procedures. Explore top hospitals, procedures, costs, safety measures, and cultural considerations for a seamless medical journey. Medical Tourism India, Top Hospitals in India, Affordable Medical Procedures, Healthcare Quality India, Cultural Considerations Medical Travel.
Challenges of Medical Tourism in India. Medical tourism is not a new field in today's era but today also it has the potential to nurture. With growing ability, it also tackles many challenges that need to be undertaken. The challenges faced by medical tourism in India are as follows: Competition. Follow-Up Problems.
Medical tourism has flourished in India over the years. India ranked 10th in the 2020-2021 Medical Tourism Index. And the arrival of foreign tourists for medical purposes has increased from 1.83 lakh in 2020 to 3.04 lakh in 2022. These findings indicate enormous opportunities for doctors to benefit from medical tourism.
Medical tourism is quickly growing in developing countries. The healthcare players have recognized it as a potential area for economic diversification. The major factors affecting medical tourism in a country are cost, quality, language, and ease of travel. The healthcare services in India cost significantly lower than in western countries and the middle east. That is one of the reasons behind ...
Medical tourism was always popular in India but now start-ups are entering the fray to offer end-to-end solutions for visa, travel, accommodation, doctor/hospital rankings -- all squeezed into one ...
According to a report by the Delhi-based RNCOS, which specializes in Industry intelligence and creative solutions for contemporary business segments, India's share in the global medical tourism ...
The southern state of Kerala has developed medical tourism services as one of its core products for promoting tourism in the region. Based on the Medical Tourism Index 2020-21, India is ranked 10th out of the top 46 countries, 12th out of the world's top 20 wellness tourism markets, and 5th out of 10 wellness tourism destinations in Asia-Pacific.
Travel Healthcare is a growing sector in India. In 2022, India's travel healthcare sector was estimated to be worth US$9 billion. [1] Approximately 2 million patients visit India each year from 78 countries for medical, wellness and IVF treatments, generating $6 billion for the industry which is expected to reach $13 billion by 2026 backed by ...
Abstract. India has emerged as a prominent medical tourism hub, yet the dynamic forces in the regional and global landscape are creating a complex balance of opportunities and risks for the Indian stakeholders. The outbreak of Corona virus pandemic in 2019 has further complicated the market dynamics for the medical tourism industry.
Today, we unveil a groundbreaking initiative poised to redefine the landscape of medical tourism: India Medical eVisa. Pioneered by VisasIndia, this innovative platform seamlessly integrates cutting-edge technology with unparalleled convenience, presenting a comprehensive guide to navigating the realm of medical tourism in India. ...
governments. Apart from the cost factor the increase of medical tourism is due to availability of easy access to such Abstract: Medical tourism in India has made its mark since mid-1990s. Medical tourism is a kind of combination of rendering medical service along with a wellness tour in a country other than the country of origin of the patient.
Govt. efforts to boost the medical tourism sector in India: Streamlining Medical Value Travel (MVT): A segment that attracted 0.7 million foreign tourists in pre-pandemic 2019.. MVT is a specialised service by Hospitals and Wellness centres including both modern as well as traditional systems of medicine.; It involves healthcare service providers, VISA requirements, insurance, MVT facilitators ...
With an aim to improve medical tourism in country, Ministry of Tourism has formulated a National Strategy and Roadmap for Medical and Wellness Tourism in 2022. The strategy has identified following key pillars for the development of medical value travel in the country: Develop a brand for India as a wellness destination
Travel accident insurance: accidental death or dismemberment coverage of up to $100,000 (up to $1,000,000 for common carrier travel). Emergency medical and dental benefits: up to $2,500 for ...