

Educational Tourism
Educational tourism is an increasingly popular new trend in the global tourism industry. The concept of a wide range of educational tourism, it has been changing the concept of tourism itself. In other words, the main purpose of educational travel is to obtain knowledge and experience on certain topics, rather than travel itself.
Educational tourism is about learning new things, acquiring new knowledge about culture or history of other destinations. Its main focus is on studying new things, learning about other cultures, study tours, or to apply the learned skills. This is one of the most famous type of tourism activity for past few years, for example people travel to learn foreign languages. Due to the growing popularity of teaching and learning of new knowledge, Educational tourism is growing at a faster speed. Educational tourism has become an alternative of large scale mass tourism.

With the growth of tourism it has led to the emergence of segments within the tourism industry, which includes educational tourism as well. Educational tourism is not a homogenous group; it can vary from person to person or their interest. The number of international students has been steadily increasing over the last 30 years and China, India, and the Republic of Korea are the top three global student providers. The most popular destinations for educational tourism are United States, United Kingdom, Germany,
France, Australia, and Japan. These six countries host around 62% of the world’s total international student population.
In recent past the general increase in the educational level of society has had a profound impact on the tourism market. Educational tourism can take a variety of directions and serve a diversity of visitor interests, “such as satisfying curiosity about other people and their language and culture; stimulating interest in art, music, architecture or folklore; inspiring concerns for natural environments, landscapes, flora and fauna; or, deepening the fascination of cultural heritage and historic places. Educational tourism goes beyond a curiosity, interest or fascination for a particular topic but includes an element of organized learning (Kalinowski & Weiler 1992).
History of Educational tourism
Educational tourism has its roots in the ancient world. Yet, depending on the socioeconomic, political, cultural, and historical circumstances, at different historical stages of its development, it had its own peculiarities.
Educational tourism is not a new concept; it has existence since the 17th, 18th, and much of the 19th centuries. The ‘Grand Tour’ was seen as the beginning of educational tourism, which was undertaken initially by aristocratic British youth as part of their education during 17 th to 19 th century. Many of these were scholars from England, Germans and other countries, travelling on a grand tour of the European Continent.
Educational Tourism from Indian context:
India was an important centre for education in South-Asian countries since the ancient period. Scholars all over the world travelled to India for education. India was a famous destination for advanced learning process and knowledge sharing. Taxila University, Nalanda University, Vikramshila University, Odantapuri, Somapura, Sharada Peeth, Valabhi, and Ratnagiri were among the famous learning centres. The most famous and prestigious centres of learning among all these universities were Nalanda University and Taxila University. The three great personalities of India, Chanakya, Chandragupta and
Charak belong to Taxila University. ‘Arthashastra’ is believed to be written here by Chanakya. Arthashastra is the famous ancient book on economics and polity and it is still famous among the scholars.
Educational tour:
Most of the schools and colleges have educational tour as a part of the academic experience. Educational tours help the students with firsthand experience of various subjects. Example: Educational tours organised by the schools to the zoos and parks to acquaint the students with flora and fauna. This provides the students with an opportunity to see flora and fauna face to face which is quite exciting as compared to see the pictures of these in a book.
Similarly, in order to understand astronomy, a visit to a planetarium is quite beneficial. History students can be taken to places of historic importance or museums with ancient artefacts. Visits to old forts and palaces or the ruins of the ancient kingdoms can make history come alive before us.
Tourism and Education
Tourism and travel activities enhance knowledge because with travelling we come to know about new people, languages, life styles, landscapes, cultures, customs and traditions. This increases our knowledge about the other destinations. Travelling plays an important role in our education and it is essential part of education system. Education without travelling is not complete. Earlier travelling was not easy without facilities but now with the new modes of transportation and scientific improvements it has become quick, easy, cheap, interesting and pleasant. With bthe new modes of transportation like huge ships, fast and comfortable railways, electric vehicals, airplanes the journey has became more interesting and comfortable. Hence travelling has became an important part of education system and it is helpful in in enhancement of knowledge, growing innovative ideas and improving thought process. Travelling provide full knowledge while reading books give half or partial know;edge about things.

Classification of Educational Tourism
Although there is no clearly defined classification of education tourism, we can identify some major types:
- Youth Travelling – It involves school excursions, youth exchanges, and the design and creation for children and adolescents, such as visits to historical, cultural and educational sites, the purpose of the camp of the learning environment, the other tourism projects may also involve access to certain destinations abroad.
2. Tourism Education – Higher liquidity tourism or study can be divided into two types: full-time study program or participate in international exchange program.
3. International research programs- Around the world more and more students decide to complete their degrees in different countries.
4. Student Exchange Program – Due to a variety of higher education reform and the introduction of the European Credit Transfer System (ECTS) University students while studying abroad are still one or two semesters studying at the chance to own universities. Including exchange programs designed for students, such as internships, sports, competitions and summer school mobility plan.
5. Workshop Travels – It usually involves seminars, workshops and Edu-Tourism Symposium. Edu-Tourism Symposium, providing liquidity and travel with the participants , who are not familiar with the subject knowledge as the main purpose . Such a seminar participants are people of any age, the desire to acquire knowledge from experts in specific topics. Travel restrictions within the territory of the country is not necessarily the country, where international transfer may involve seminars. Theme of these workshops may vary, starting from the identification and analysis of marketing policy history book ends. Organization of seminars by the company or the travel supplier, where professionals and students in a common place to gather conduct.
6. Language schools for foreign language learners today to learn the language in a country, it is spoken, and there is the opportunity to become even more important to interact directly with the native language. There are many in the world, provided by language school, which involves not only learning the language, but also to explore the city and country tours.
Benefits of Educational Tourism:
Education tourism is beneficial for the host nation and host community. It has potential for the development of local community, region and nation at large. It can provide global exposure to the host destination, and a niche to explore hidden areas of that destination.

The benefits from Educational Tourism are as follows:
- Development of infrastructure
- New training courses
- More employment opportunities
- Availability of skilled manpower
- Entrepreneurship development
- Exploration of hidden places
- Social welfare and development
- Cultural exchange
- International collaboration
- Image building of region
- Global reorganization of destination
Also read Dark Tourism
You might also like.

Medical Tourism in India

Tourist Decision Making Process

Art Galleries
This post has 4 comments.
Pingback: گردشگری آموزشی چه مزایایی دارد؟ - مدرسه کسب و کار تکاپو
Pingback: londondrugscanada.bigcartel.comlondon-drugs
Pingback: AQWorlds
Pingback: Browser MMORPG
Comments are closed.

What is Educational Tourism: Stats, Benefits, Examples & More

What is educational tourism?
Benefits of educational tourism, types of educational tourism, who is it for, real-life examples.
The global tourism industry is very diverse. With the number of different types of tourism and the number of ways travelers interact with tour packages increasing, it can be pretty hard to keep track of each travel sector’s subdomain.
On the other hand, getting insights from a particular travel sector subdomain can help you make informed decisions, such as whether or not to add new travel products to your offer.
One of the tourism forms that became very popular recently is educational tourism. While it’s not a brand-new tourism concept, educational tourism accumulated enormous interest. To help you understand what it is, we’ve decided to put together an educational tourism ultimate guide that covers everything from its definition to real-life examples.
Educational tourism or edu tourism is a form of tourism. As we mentioned earlier, it’s not a brand-new concept in this vertical – it can be traced back to the 17th century . History records the success of the “Grand Tour,” which marks the beginning of educational tourism as we know it. When it began, it was mainly popular among the aristocratic British youth . It was essential to their education through the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries.
After the UK, other European countries followed, and many scholars traveled to the old continent in search of new knowledge or to learn from their peers and study languages.
It goes beyond the other forms of tourism that mainly offer business or pleasure travel packages. This new trend in the global tourism industry has one purpose – to create opportunities for travelers to obtain new experiences and knowledge on a wide range of topics.
Every travel product that enables travelers to learn about foreign cultures, study new things, engage in study tours, or apply a learned skill is considered an educational tourism’s product. Large-scale mass tourism is still popular, but some travelers seek other options that enable them to travel and yet be able to acquire new knowledge. The shift in travel demands is one of the main factors driving the growth of this sector.
Now, that you understand what educational tourism is, let’s see the current state of the educational tourism market, including recent trends and projections.
Most sectors declined during the past few years, and the educational tourism industry was no exception. The tourism sector has experienced a decline because many countries imposed international travel restrictions. Compared to previous years, foreign tourism decreased by 22% in the first quarter of 2020 and 65% in the first two quarters of 2020 .
However, the sector quickly came back on its feet the moment governments around the globe lifted the travel restrictions. The latest research findings support our previous claim that educational tourism is increasing in popularity.
The global educational tourism market value in 2021 is estimated at $399.8 . It means that the market exhibited a year-on-year growth of 16% . The same research projects that the market will continue to grow with a compound annual growth rate of 17.2% . By 2031 its value is projected to reach $1,947 billion.

According to Future Market Insights , the total number of global educational tourists in 2022 was over 6 million . They’ve identified four main contributing factors to the market growth and increasing popularity of this sector:
- Access to new information;
- Emerging education styles;
- New research techniques;
- Enormous exposure to science.
Furthermore, the FMI report indicates that most inbound educational tourists are interested in obtaining a master’s degree, making students one of the most significant demographic segments driving the sector’s growth. More precisely, the age group of 19–25 years generates a whopping 73% of global educational tourism market revenue. The students alone generate 39% of the overall sector’s revenue .
Educational tourism offers many benefits for all parties involved, including travelers, the host community, and the host nation. It has the power to drive the growth of many sectors and help develop entire regions and communities. With this in mind, let’s see the more specific benefits this type of tourism brings.
Monetization of previously unexplored places
Educational tourism travel can help a region leverage unexplored places and make them available for tours, trips, and excursions . Monetizing these locations can help bring more money to the region and enable it to thrive, make necessary improvements, and attract more travelers in the future.
Improved international collaboration
Governments can recognize the value of educational tourism, especially if they identify travel patterns that indicate their educational tourism offer attracts travelers from a specific country. Governments can improve international collaboration, opening room for more exchange programs, workshop travels, and international scientific research.
Improved image of a city, nation, and country
Educational tourism has the power to improve the image of a city or an entire nation or country. Offering a memorable and pleasant experience to foreign travelers can help a country build a positive image. It can help other tourism sectors attract more visitors and secure stable revenue streams.
Increased number of employment opportunities
The only way to deal with the increasing educational tourism demand in a specific location is to hire more professionals. It’s a great opportunity for countries to lower unemployment rates and offer new employment opportunities in the travel sector to local communities.
New entrepreneurship opportunities
Tourism is one of those industries that can facilitate the growth of other verticals, such as entertainment and hospitality. With the stable influx of educational tourists, there will be plenty of new entrepreneurship opportunities people can pursue to launch successful businesses.
The rapid development of infrastructure
Educational tourism can create the need for new infrastructure in some areas . With the revenue it helps create, local governments can develop new infrastructure plans and have sufficient budgets to build infrastructure to both the local community’s and travelers’ delight.
Lots of benefits for the travelers
Travelers engaging in educational tourism activities stand to gain much more than just exploring new destinations. Educational tourism can help them change their perspective or worldview , increase independence and self-confidence, enhance cultural awareness and dispel stereotypes, and facilitate intellectual and cognitive growth.
Education tourism is a big branch of tourism. Over the years, the market demand has enabled educational travel organizations to develop various educational packages and trips . Some of these packages have many things in common, allowing us to outline several major types of educational tourism.
Language schools
There is no better way to learn a foreign language than to do it by immersing yourself in it. And the best way to do it is to travel to the country where it is spoken. Language schools for foreign languages attract language learners from all over the world.
Learning the native language inside the classroom and then interacting with it outdoors while exploring the cities and country is something language students find attractive. As the final result, we have language schools as one of the major types of educational tourism.
Youth traveling
Youth traveling is the next major type of this tourism branch, involving a wide range of activities mainly developed for children and adolescents. Some youth traveling products include school excursions, youth exchanges, and other programs stimulating creativity and development.
A unique combination of learning and travel e xperiences engages kids and adolescents and invites them to obtain new skills and knowledge while learning about other cultures and exploring iconic sights worldwide.
Workshop travels
Workshop travels include group and individual travels that share one common goal – acquire knowledge from renowned experts while traveling abroad. Workshop travels’ final destinations are often workshops, seminars, and symposiums.
This type of educational tourism is popular among people of any age, which makes it a pretty prominent kind of tourism. Besides individuals, organizations are also common buyers of workshop travel products. It enables businesses to diversify their professional growth and development programs and keep employees engaged.
Student exchange programs
Student exchange programs were always popular. However, student exchange programs became quite popular after introducing systems that enable students to earn credits towards their degree despite where they attend courses, such as the European Credit Transfer System (ECTS).
These programs enable students to work with some of the best professors worldwide and experience their teaching methodologies firsthand. However, these programs don’t exclusively offer students access to courses. They can encompass various camps, internships, and sports competitions as well.
International scientific research programs
Masters and Ph.D. students must research a chosen topic to get a degree. Many choose to do it abroad, working with renowned professors and researchers .
Given the popularity of this type of travel, international scientific research programs make a unique type of educational tourism.
Tourism education
Students seeking knowledge in developing tourism sectors abroad must travel and spend time in a country. The hands-on experience and unique insights complete the tourism education and add additional value to students and operators in a location.
Tourism education helps create more sustainable tourism and encourages young entrepreneurs to start their own tourism businesses.
Educational tourism is not exclusively reserved for any specific demographic group or country . There are examples of very young kids engaging in educational tourism activities . While it is the most popular form of travel among students, older generations benefit from it by visiting seminars and symposiums in foreign countries.
This type of tourism is an excellent opportunity for travel businesses, transportation, and accommodation providers. They can work hand-in-hand with local educational institutions and governments to create attractive programs and enhance the travel experience to invite more people to come and spend their time in a location.
Many organizations exclusively specialize in educational tourism. Let’s take a closer look at some examples to better understand this unique tourism model.
GVI Company
GVI Company specializes in connecting like-minded people to enable them to collaborate on social development programs . They have tailor-made programs for people interested in internships, volunteering, and studying. The company is based in several communities worldwide and works with partners in those communities to deliver the best possible experience to young travelers.
EF Tours has been a go-to company for teachers and parents around the globe for quite a few years now. The company specializes in bringing different student tours at very attractive prices. However, the attractive prices are not the only thing that makes EF Tours so popular.
The company regularly includes new programs to ensure there is an excellent opportunity for all students who go beyond the classroom to pursue new knowledge, no matter how specific their interests might be.
Meridian Overseas
Meridian Overseas is the leader in connecting students eager to study and travel to educational tourism consultants . They help students find the best programs for their needs in the UK, USA, Italy, Canada, New Zealand, Australia, and Germany. The company went even further, enabling students to take IELTS coaching classes to excel in programs where English is their native language.
Global Volunteers
Global Volunteers, as the name suggests, brings numerous volunteer opportunities in the USA and abroad to people who want to be part of the change. The company has a vast network of professionals and partners. Thanks to its extensive networks, the company enables travelers from all possible walks of life to volunteer in various organizations, from classrooms and clinics to childcare centers and farm fields.
ACIS Educational Tours
ACIS stands for the American Council for International Studies. The organization was established back in 1978. Several decades of extensive experience and an extensive network of partners enable ACIS to deliver excellent educational trips to middle and high school students .
The company has branches throughout the US, including those in London and Paris. They offer many unique educational travel products, such as culturally immersive tours, private tours, youth, young women’s leadership tours, STEM-focused tours, and many others.
Educational tourism is one of the rapidly growing tourism industry branches . It offers a unique value – a perfect mix of adventure and learning . There are many types of educational tourism, each one offering specific advantages. Given the range of benefits, it offers to travelers, travel and educational institutions, communities, and countries – it’s safe to assume that this sector has a bright future ahead of it, as is reflected in the projected global educational tourism market growth .
Subscribe to our newsletter
Yay you are now subscribed to our newsletter.
Cristóbal Reali, VP of Global Sales at Mize, with over 20 years of experience, has led high-performance teams in major companies in the tourism industry, as well as in the public sector. He has successfully undertaken ventures, including a DMO and technology transformation consulting. In his role at Mize, he stands out not only for his analytical and strategic ability but also for effective leadership. He speaks English, Spanish, Portuguese, and Italian. He holds a degree in Economics from UBA, complementing his professional training at Harvard Business School Online.
Mize is the leading hotel booking optimization solution in the world. With over 170 partners using our fintech products, Mize creates new extra profit for the hotel booking industry using its fully automated proprietary technology and has generated hundreds of millions of dollars in revenue across its suite of products for its partners. Mize was founded in 2016 with its headquarters in Tel Aviv and offices worldwide.
Related Posts
30 Most Important Travel Industry Events for 2024
30 min. Social share: 2024 is packed with must-attend travel industry events. Stop by to discover all relevant events conveniently grouped by continents with listed dates, themes, and locations! Many travel industry experts believe that travel industry events play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the travel industry. Why is this so? It’s […]
Empowering Equality: Mize Leads the Way in Travel Technology
7 min. Are we all equal? Are we all equally represented in the business world? In some professional sectors, there might still be some under-representation of women, minorities, and the LGBTQIA+ community. The tech sphere is no different, but is the travel tech sector a spark of hope? As the business world becomes more diverse, […]

Slow Tourism Case Studies: Examples to Truly Understand Slow Tourism
14 min. The tourism industry is moving at an ever-accelerating pace. That’s because the tourism industry is perhaps one of the verticals that depend on the most factors. One of the main factors that affect it is social movements, given that tourism brands of all sizes always cater to the needs of consumers. One of […]

What is Educational Tourism? (8 Examples)
Educational tourism is on the rise due to the huge proven benefits to students who take part in it. This article will explain the 8 key types of education in tourism.

Educational tourism isn’t a new concept. In fact, educational tours were popular amongst young British aristocrats in the 17th to 19th centuries. The idea was to expose them to a wide range of experiences and increase their knowledge.
Today, educational tourism continues to enable students to study abroad, learn about foreign cultures, acquire new languages, and have invaluable life experiences. The benefits of such educational endeavours are endless.
What is educational tourism?
Educational tourism is any type of travel that broadens someone’s horizons. This could be a trip organized with education at the forefront, arranged by a university or a school. However, it includes any leisure travel that offers opportunities for learning.
8 types of education in tourism
1. student exchange programs.

Student exchange programs enable students to work with some of the leading academics around the world. They can earn credits towards their degrees with systems like the European Credit Transfer System (ECTS). These programs also offer sports competitions, camps, and internships.
Adjusting to a new culture and language on top of academic commitments can be a struggle. If students are in need of additional academic help, there are online services that can be requested by asking ‘ help me with my homework ‘. External professional help can make the transition to a student exchange program feel more manageable.
2. Language immersion programs

One of the best ways to learn a language is to learn from native language speakers. Language schools in various cities around the globe attract students. They can learn French in Paris and discover the true Paris by speaking with Parisians.
Learning a language lesson from a teacher and then interacting with locals to put it into practice increases understanding and retention.
READ NEXT : Taking a Spanish Course in Salamanca: What to Expect
3. Study abroad programs

There are various study abroad programs that give students the chance to pursue academic courses in foreign countries. They usually provide a combination of learning in the classroom, cultural experiences, and field trips.
Many students choose to do a Master’s Degree or Ph.D. abroad. Whether students want to enroll in a foreign university or advance their business career in London, there are study abroad programs that will assist them.
4. Volunteer opportunities
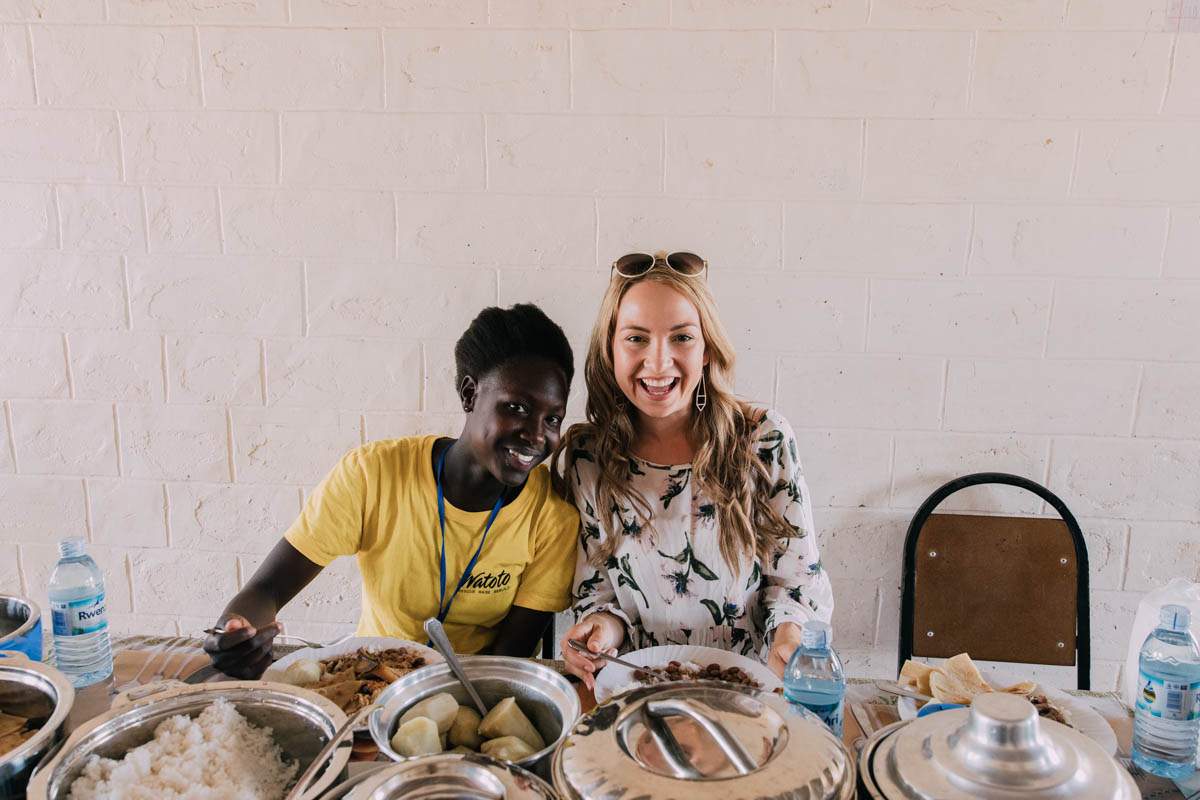

There are companies that offer volunteer opportunities in foreign countries. They usually have a vast network of partners and professionals. Travelers can volunteer to work in many different settings from classrooms and hospitals to farm fields and child care centers.
Working in community service projects enables them to contribute to the betterment of society. They also gain a deeper understanding of global issues.
5. Cultural and historical tours
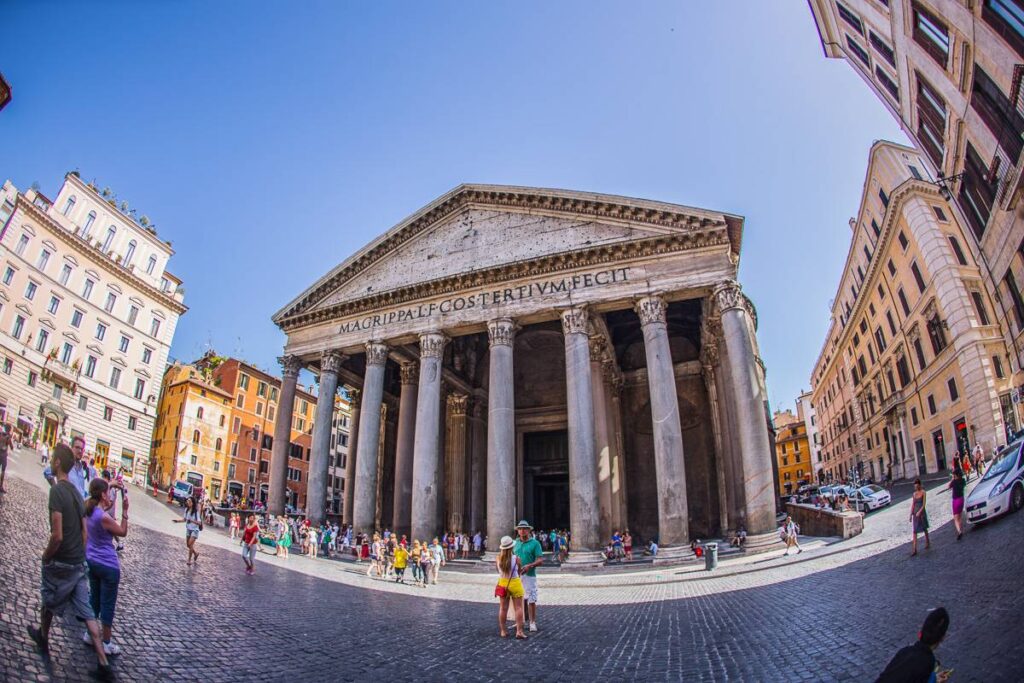

Travelers can take tours to learn more about the history and culture of a particular destination. They will participate in cultural activities and visit monuments, historical sites, and museums.
This helps them to understand the way of life and local traditions. One of the popular places to travel on such a tour is Egypt with its pyramids and other historical attractions.
6. Environmental tours
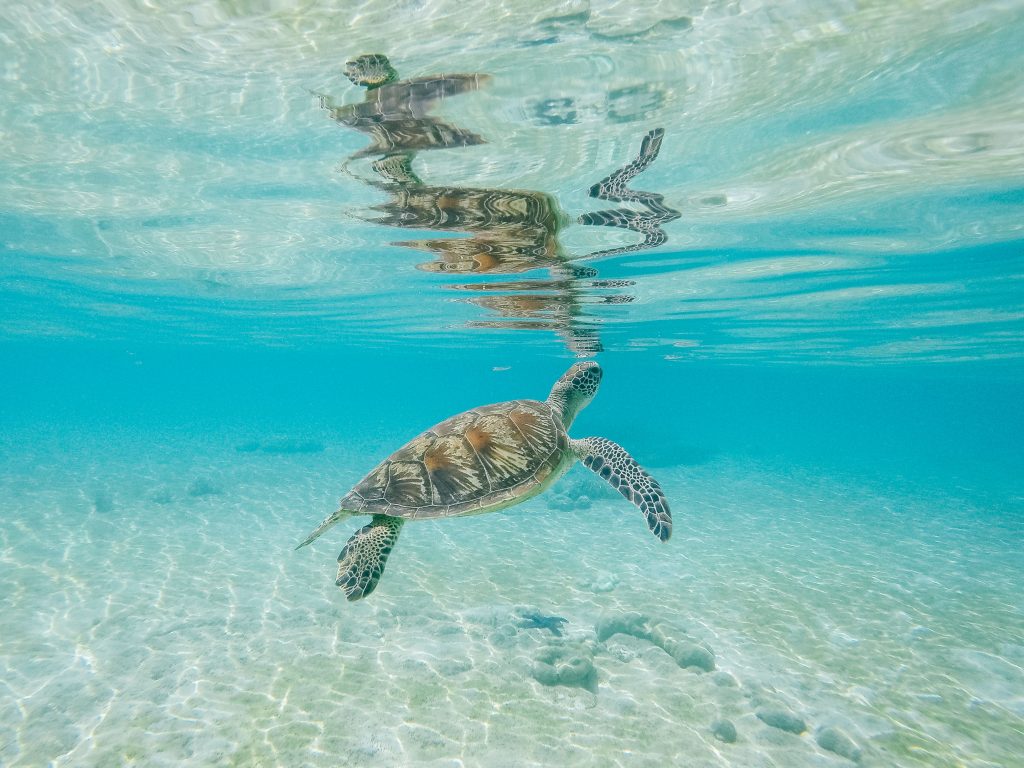

Environmental tours focus on learning about the natural environment. Participants will visit wildlife reserves and national parks.
They will learn more about sustainability and biodiversity through visiting conservation projects. They may participate in activities like spotting wildlife and hiking.
7. Workshops
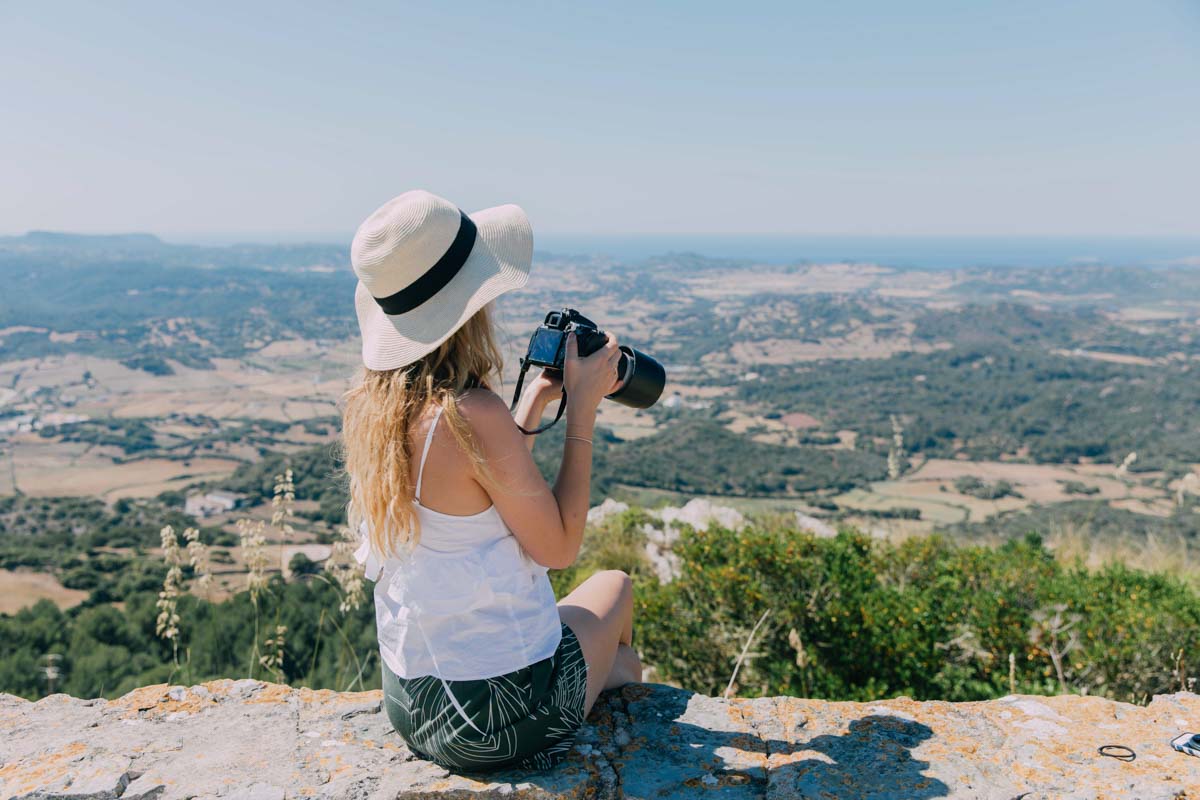

Individuals and groups may travel to attend workshops to acquire knowledge. For example, they may attend workshops or conferences related to their field of interest.
This helps them to gain knowledge and practical exposure. Businesses may invest in a workshop package for employees to help them grow professionally.
8. Tourism Education

Students who want to go into the tourism sector need to get hands-on experience. Traveling to different countries provides them with unique insights and practical experience.
They may become passionate about creating more sustainable tourism. It will also help them to make contacts and establish a network that will assist them in their future career.
No matter what type of educational tourism you choose to take part in, you are bound to see a huge amount of benefits. Whether this is broadening your worldview, increasing cultural awareness or facilitating your intellectual growth- education in tourism is a life-changing industry.
Want more inspiration for educational tourism? Read these articles next:
- 10 Cheap Destinations for Student Holidays
- 10 Tips for Traveling as a Student
Hey, I'm Nicola!
I am a travel + food blogger on a mission to discover the best destinations & dishes in the world. Thanks for joining the adventure!
WANT TO GROW on SOCIAL MEDIA?
Download my FREE pdf guide with 5 simple steps guaranteed to grow your online presence!
Go check your inbox!
sign me up!

Our Dream South of France Wedding
This is what it looks like to have a 3-day wedding in the South of France! On the 23rd of August 2023, James and I finally got to have the wedding celebration of our dreams. We had sixty of our nearest and dearest flying from all over the world to join us for three...

A Guide to Sailing in the Ionian Sea
Find out why the Ionian Sea in Greece is one of the most spectacular places in the world to go sailing! Image source Imagine traveling in a blue sea of calm waters and cool winds on the Western Coast of Greece. The waters lead to a paradise of islands with white sandy...
Turkish Airlines Food: Economy Class Review
Ever wondered what Turkish Airlines food is like in Economy Class? I reviewed everything I ate flying from London to Tbilisi. Normally when I travel short-haul in Europe, I'm flying on a budget airline that basically charge you money for breathing. So it was a real...

Fun Things to Do in Auckland at Night
Image source Auckland is the most populous city in New Zealand and, as such, offers a great deal of activities. No matter what a traveller looks for, they’ll find it here. Auckland is a stunning harbourside city during the day, yet it really turns on its charm when...

Educational tourism- the best way to travel?
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Educational tourism is one of the best types of tourism ! Whether you are going on a school trip, backpacking around South East Asia or going on a round the world cruise, there are always lots of things to learn while travelling. Whilst people used to be content with laying on a beach and reading a book, consumer preferences are changing- people want to experience something different- they want adventure, excitement and education!
What many people don’t realise, is that educational tourism is actually all around us. Whether in a formal or informal context, most types of travel involve an element of education. But how does this work and what does it mean for the travel industry? In this article I will explain exactly what is meant by the term educational tourism, how this occurs and where it is most commonly found. I will also discuss the many advantages of educational tourism, to both the tourist and the tourism industry .
What is educational tourism?
Educational tourism definition, why we need to understand the concept of educational tourism, education first, tourist first, consequential education in travel, how does educational tourism work the theory behind the practice, benefits of educational tourism, educational tourism.
As LaTorre noted in 2011, The world is one’s school. When most people hear the term ‘educational tourism’, they think of school trips to visits to sites such as Auchswitz or Oradour-Sur-Glane . Or they think of educational holidays for adults such as learning to dive in Dahab . or learning to cook in Thailand . However, educational tourism is soooo much more than this. In fact, it is everywhere we look!

Since the origins of tourism and the grand tour (Ritchie et al , 2003) the educational benefit of travel has long been recognised. There are now an abundance of ‘study abroad’ options available to those inclined and the informal educational attributes of travel, for example whilst undertaking volunteer tourism placements, gap years or backpacking trips, are undisputed.
Yet despite such common reference to the educational benefits of travel, educational tourism appears to be under-researched as an academic subject. Literature surrounding educational tourism appears to be sporadically scattered across many fields of study and ironically, this concept that is so commonly identified as a benefit or motivation for touristic activities has been subject to little academic attention to date. This has seen rise to many unanswered questions such as; what are travellers learning; who is learning; where, when and how are they learning? (Falk et al , 2012).
Read the book: Educational tourism by Elizabeth App
Due to the lack of literature addressing the concept of educational tourism there are few attempts at drawing definitional boundaries explaining what constitutes an educational tourist. Ritchie et al (2003) draw upon definitions of tourism and the parameters of educational tourism and conclude that an educational tourist is;
‘A person who is away from their home town or country overnight, where education and learning are either the main reason for their trip or where education and learning are secondary reasons but are perceived as an important way of using leisure time’ (p18)
Ritchie highlights an important point here. He notes that education may be the main reason for tourism. BUT it may also be a secondary motive for tourism. I would like to take this one step further and propose also that education may not be perceived as being an important part of a trip, but in actual fact, it is. I call this consequential education in tourism.

Understanding the concept of educational tourism is important to tourism industry stakeholders . Tourists want to learn. They may not desire a formal learning environment whilst on holiday, but most people are inquisitive about new places and new people. People enjoy learning how elephants are cared for at the elephant sanctuaries in Thailand and they want to know more about how spices are harvested at the spice plantation in Goa , for example.
Falk et al (2012) argue that tourism managers and researchers need to better understand the nature of learning in tourism and leisure contexts. Educational tourism is big business, bigger than most people realise! And the potential for tourism businesses is huge…. understanding the concept of educational tourism can help to inform business plans, marketing, consumer satisfaction and lots more!
The types of educational tourism
Educational tourism comes in many different shapes and sizes. In fact, educational tourism is actually a macro niche tourism , which is subsequently found within many different types of tourism. Types of tourism that commonly facilitate educational tourism include:
- Cultural tourism
- Dark tourism
- Business tourism
- Culinary tourism
- Volunteer tourism
- Special interest tourism
Educational is found is tourism in many different regards. This can be in a formal or informal context (or somewhere in between). Shwayat has attempted to demonstrate this through the diagram below. However, I believe that this is too fragmented to be representative. Yes, sometimes educational tourism is evident to all, but other times it is subtle. So subtle in fact, that even the tourist may not realise they are an ‘educational tourist’.

Similarly, Pogodina (2009) has attempted to visually depict the educational tourism spectrum in the chart below. Here you can clearly see the role of the various stakeholders of educational tourism.

According to Ritchie et al (2013), educational tourism can be divided into two segments. The first is university, college and school tourism, in which the tourist experience is secondary to formal learning and can be described as ‘education first’. The second is edu-tourism, defined as general travel for education and known as ‘tourist first’ (Ritchie et al , 2003). In addition to this, I propose that there should be a third classification: consequential educational travel.
I will explain what each of these mean below.
Education first tourism is the most known form of educational tourism. However, in reality it is actually less common than the other two types of educational tourism, tourist first and consequential educational travel. Education first is the most formal educational tourism setting and can take a number of forms. Examples include:
- Studying abroad at college or university
- Attending a boarding school abroad
- Doing a qualification overseas, e.g. TEFL
- Language exchange programmes
- Taking a course abroad e.g. learning a language/diving/cooking/art etc
- Service learning
- Educational school trips
- Girl guide/Scouts etc trips
- World schooling
- Cultural immersion e.g. working as an au pair
Many people choose to study abroad because they are in search of a new experience or because this provides opportunities to them that are not available at home. Freestone and Geldens (2008) state that as a result of the student having a pre-determined date of returning home, study abroad can be considered a tourist experience. Students are also likely to undertake touristic activities during their free time.
Study abroad has been found to significantly aid learning and is now common practice within schools, colleges and universities (Paige et al , 2009). Abrams (1979) stated some years ago that study abroad is better defined as learning through experience abroad . This is due to the difficulty in determining whether the benefits and outcomes of study abroad are the results of travel, interaction with other cultures, classroom study or a combination. This supports my suggestion that it is difficult to develop linear, segmented models of educational tourism, like the ones included in this article above.
The ‘tourist-first’ experience is when learning is acquired through tourist experiences outside of the classroom. This can take many different forms. For example, it could be learning about the history of the long neck tribe in Thailand during an excursion or visiting the Egyptian museum in Cairo whilst travelling in Egypt .
Some have identified educational tourism as being a form of lifelong learning (e.g. Broomhall et al, 2010; Falk et al , 2012). TEFL teaching (the subject of my PhD- learn more in the video below) is akin with lifelong learning in that the experience consists of formal and informal learning, whether this be in a classroom environment or ‘on the job’ learning, self-motivated learning as they are likely to have opted to undertake their TEFL teaching placement and self-funded learning as many are likely to have funded the trip and placement through their own means. Increasing numbers of people in Western society appear to have a growing appetite for lifelong learning (Falk and Dierking, 2002), and this can lead to assumptions that the likes of TEFL tourism will increase in the future.
An increasing body of research now shows that most learning takes place outside of the formalities of the education system (e.g. Falk and Dierking, 2010; Falk, Storksdieck and Dierking, 2007). In fact, there has been an exponential increase over the past two decades in the amount of learning that derives from self-directed experiences on the Internet or as part of leisure activities (Estabrook et al , 2007).
Pearce and Foster (2007) describe travel as being its own kind of educational institution, with the experiences and knowledge gained representing a kind of parallel to formal education in school or university. In fact, travel offers one of the few opportunities outside of formal education where non-vocational learning about other times, places and people takes place (Werry, 2008). An example of such learning is demonstrated through gap year travel, with many people returning home claiming to have developed intellectually as a result of their experiences, with personal growth and increased life skills being prominent areas of development (Coetzee and Bester, 2009). Others have reported learning of ‘generic skills’ whilst backpacking, such as problem solving and interpersonal skills as well as enhancing their general geographical and cultural awareness (Pearce and Foster, 2007).
Studies on volunteer tourism have highlighted its educational benefits and the ability to foster self-reflection and developments in personality traits and behaviours (e.g. Alexander, 2012; Benson and Wearing, 2012; Broad and Jenkins, 2008; Gray and Campbell, 2009; Sin, 2009; Soderman and Snead, 2008; Wickens, 2011). It has also been known for those involved with international travel to develop skills such as problem solving, time management and communication (Scarini and Pearce, 2012). Although the ‘curriculum’ of such informal learning may not be well organised, there is plenty of information to process and travellers are likely to acquire new skills and perspectives as a result (Pearce and Foster, 2007).
Another emerging type of education that is acquired through travel is the concept of world schooling. World schooling is essentially a means of providing and finding education from the real world. It provides families with the opportunities to travel long-term and to allow their children to learn through their experiences. World schooling removes teachers, classrooms, schools and pre-defined curriculums and allows children to learn through environments, cultures, climates, histories and societies that they naturally encounter on their travels. You can learn more about how world schooling works in practice on the World Travel Family blog .

To further emphasise the value of consequential education through travel, Pearce and Foster (2007, p1286) draw upon a quote from a graduate recruitment advertisement for the Ford Motor Company ascertaining that;
‘Degrees get students a job but the skills determine success’
This highlights that it is the combination of learning derived from formal institutions and qualifications and personal experience that is likely to help the individual be most successful in their chosen career path.
In order to demonstrate the relationship between travel and learning it is necessary to draw upon some of the fundamental theories used in learning and education analysis. Stone and Petrick (2013) pay reference to existential learning, stating that it can be used as a model for explaining how people learn by travelling.
Existential learning is in essence a form of education that takes place as a result of learners uncovering knowledge by themselves, usually as a result of personal experiences and can be defined as ‘meaningful discovery’ (Boydell, 1976, p19).
Kolb’s (1984) model provides a widely used framework for the understanding of existential learning and consequently, evaluating travel learning (Stone and Petrick, 2013). Kolb’s (1984) model essentially outlines the way in which a person will have a concrete experience, reflect on their experience, conceptualise or conclude what has happened and then experiment or try out what they have learnt before having another new concrete experience, and so the cycle continues. This framework is useful not only in understanding existential learning as a result of travel in a formal education context, but can potentially aid in the comprehension of learning of the different areas of the travel industry.

Despite Kolb’s (1984) model having not yet been thoroughly analysed as a way of travel learning (Stone and Petrick, 2013), it does have potential to be utilised in future studies involving travel as a means to learning. To date there have been attempts at linking travel with existential learning (e.g. Novelli and Burns, 2010; Woolley et al , 2011), however these have focussed on travel as part of an educational course, as opposed to freely chosen travel per se. This appears to be an area that is largely under researched to date.
Building on the pedagogy of existential learning and the reflective aspect in particular, Coghlan and Gooch (2011) propose that volunteer tourism organisations should utilise Mezirow’s (1991) theory on transformative learning to inform their operational plans. Mezirow’s (1991) theory describes a shift in one’s assumptions and world beliefs through a series of ten steps and highlights that the individual experiences a deep, structural shift in the basic premises of thought, feelings and actions (O’Sullivan, 2002).

There are many benefits of educational tourism that have been recorded in the academic literature. These include:
- Change in perspective or worldview/ greater awareness of ‘self’ (Dwyer, 2004)
- Increased independence and self-confidence/positive personality changes (Bachner and Zeutschel, 2009)
- Intercultural development/ have cultural experience (Ingraham and Peterson, 2004; Rexeison et al , 2008)
- Global engagement/ enhanced citizenship (Paige et al , 2009)
- Enhanced cultural awareness/dispelling of stereotypes (Freestone and Geldens, 2008)
- Intellectual and cognitive growth/ learning (Chieffo, 2007; Ingraham and Peterson, 2004; Novelli and Burns, 2010; Miller-Perrin and Thompson, 2010; Sutton and Rubin, 2004)
- Opportunity to achieve training and/or qualifications/ develop skills to aid career development
Educational tourism is an important type of tourism that I expect will continue to grow into the future. If you enjoyed reading this article, then I recommend you also take a look at:
- Cultural tourism explained: What, why and where
- MICE tourism: A simple explanation
- 10 jobs in travel and tourism that will be BIG in 2021 and beyond…
- Volunteer tourism: Everything you need to know
- The history of Thomas Cook | Understanding tourism
Liked this article? Click to share!
Educational Tourism: Definitions, Types and Popular Destinations
Educational tourism offers unique opportunities for people to travel and learn by combining the joys of visiting new places with acquiring knowledge. This type of tourism includes various experiences such as study abroad programs, exchange student experiences, and school trips to historical sites or natural wonders. The primary goal is to enrich the learning experience, enhance cultural understanding, and nurture personal development.
As globalization continues to make the world more interconnected, educational tourism has become increasingly popular. People of all ages are eager to broaden their horizons while discovering new environments and cultures. Educational tourists also play a significant role in supporting local economies, fostering cultural exchanges, and contributing to global understanding.
Educational tourism has evolved in response to rising demand and greater availability of diverse travel experiences in recent years. From attending language schools to participating in workshops or seminars, there are endless ways to learn and grow while exploring new destinations. This growth underscores the importance of educational tourism in fostering lifelong learning and bridging cultural divides.
Definitions of Educational Tourism
Defining educational tourism, types of educational tourism, motivations for educational tourism, popular educational tourism destinations, suppliers of educational tourism, educational tourism programs and companies, benefits of educational tourism, challenges of educational tourism, future of educational tourism, what are the examples of edutourism.
Definitions of educational tourists and educational tourism are following as:
An educational tourist (or educational stayover) may be considered as:
a person who is away from their home town or country overnight, where education and learning are either the main reason for their trip or where education and learning are secondary reasons but are perceived as an important way of using leisure time
An excursionist (or same-day educational tourist) is:
a person involved in any educational/learning activity or excursion, which does not include an overnight stay away from their home destination, and for whom education and learning is seen as an important way of using leisure time.
Therefore, educational tourism can be defined as:
tourist activity undertaken by those who are undertaking an overnight vacation and those who are undertaking an excursion for whom education and learning is a primary or secondary part of their trip. This can include general educational tourism and adult study tours, international and domestic university and school students’ travel, including language schools, school excursions and exchange programmes. Educational tourism can be independently or formally organised and can be undertaken in a variety of natural or humanmade settings.
What is Educational Tourism

Educational tourism, also known as edu-tourism or educational travel, is a form of tourism whose primary purpose is gaining knowledge and engaging in cultural exchanges. It involves travelling to a different country or region to learn about various subjects such as history , languages, art, and environmental issues.
Education tourism isn’t limited to academic learning; it can encompass any activity or experience that enriches the traveller’s understanding of the world. The goal is to explore new places, foster personal growth, and broaden one’s perspective.
Several types of educational tourism cater to different interests and age groups. Some of the most common include:
- Language Immersion Programs: These are designed for those who want to learn a new language by visiting a country where the language is spoken. The immersion environment enables participants to practice their language skills and better understand the local culture.
- Cultural Exchange Programs: These programs foster understanding and appreciation of other cultures. Participants live with host families, attend local schools or workshops, and partake in community-based activities to learn about the customs and traditions of the host country.
- Study Abroad Programs: These are popular among college and university students, allowing them to complete a portion of their degree in a different country. It promotes cross-cultural understanding, enhances global awareness, and broadens academic perspectives.
- Eco-Tourism and Sustainable Tourism: Travelers visit natural habitats and engage in activities that support their preservation and conservation . It increases environmental awareness and promotes responsible travel practices.
Educational tourism presents countless opportunities for personal development, academic enrichment, and cultural exploration. As a global phenomenon, it encourages learning from different perspectives and fosters a deeper understanding of our diverse world.

Personal Growth
Educational tourism provides numerous opportunities for personal growth. Travellers are exposed to new environments and experiences that can foster self-discovery, adaptability, and resilience. They can develop interpersonal skills through interactions with diverse groups of people, enabling them to communicate effectively in different cultural contexts. Furthermore, participating in educational trips can also enhance critical thinking and problem-solving abilities as individuals learn to navigate unfamiliar situations.
Professional Growth
Pursuing educational tourism can significantly contribute to professional growth. Acquiring new skills and knowledge, particularly in a global context, can make individuals more competitive in the job market, set them apart from their peers, and increase their chances of employment. Additionally, some educational tourism programs provide opportunities for networking, collaboration, and exposure to industry professionals, which can result in valuable connections and insights that can propel one’s career forward.
Cultural Knowledge
Engaging in educational tourism immerses individuals in the destination country’s local culture, history, and traditions. This exposure to diverse cultures enriches travellers’ understanding of the world and broadens their perspectives. By participating in culturally immersive activities, like workshops, visiting museums or engaging with local communities, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for and understanding of various cultural practices. This increased cultural knowledge promotes tolerance, respect, and empathy towards other cultures.

In Europe, France is a top destination for educational tourism, offering cultural experiences like art galleries and museums and language immersion programs. Italy is another popular choice, known for its history, architecture, and cuisine. Students can visit famous landmarks like the Colosseum or the Leaning Tower of Pisa while learning about the country’s rich heritage. Germany is an ideal destination for learning about its technological advancements and history, with attractions like the Berlin Wall and BMW Museum. Finally, the United Kingdom offers various educational activities, including famous landmarks such as Buckingham Palace and the British Museum.
Japan is a sought-after educational tourism destination in Asia, known for its technological innovations and deep-rooted traditions. Visitors can participate in tea ceremonies, learn about samurai culture, and explore high-tech cities like Tokyo. Thailand provides opportunities for learning about Southeast Asian history, visiting temples and ancient sites, and exploring its rich biodiversity. India is another popular choice, featuring architectural wonders like the Taj Mahal, rich cultural heritage, and diverse traditions.
North America
In the United States , educational tourism spans from historical landmarks, like the Washington Monument and Ellis Island, to scientific institutions, such as NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The US offers numerous educational activities, including visiting national parks and learning about the country’s diverse demographics.
Australia is recognized for its unique flora and fauna, making it an ideal destination for biology and ecology students. The Great Barrier Reef, the Outback, and various wildlife sanctuaries can be visited for learning opportunities in Australia.
Please note that this list is not exhaustive, and plenty of more destinations are available for educational tourism across the globe.
The Canadian Tourism Commission (2001) notes two main components to the supply side of educational tourism: the primary tourist product and secondary or support elements.
A variety of organisations combine to form the primary educational tourism experience, including:
- Attractions and events which provide the venue for learning experiences (e.g. parks, historic sites, zoos, bird and wildlife sanctuaries and archaeological dig sites).
- Resource specialists who are responsible for delivering the learning component of these vacations (e.g. employees, curators, interpreters, lecturers, storytellers, researchers and academics).
- Affinity travel planners from organisations who help plan and develop learning programmes for travellers (e.g. special interest groups, conservation organisations, universities and language schools).
- Tour and receptive operators who package experiences for customers and organisations and provide destination expertise, local knowledge, escort services and marketing services.
However, secondary suppliers or support services are also required for educational travellers, including:
- Transportation such as cruise, bus and train transport as part of an independent trip or package, including travel to and from the departure point.
- Hospitality services , including catering, recreation, entertainment, social activities and accommodation options.
- Travel services , including travel agents, insurance companies, travel media and advertising.
- Destination marketing organisations who operate at a national, regional or local level to promote educational travel and tourism to potential tourists.
It is the combination of primary and secondary suppliers which will create the educational tourist experience consumed by travellers. The continued development of innovative partnerships and product development is critical to the future of the educational tourism industry.
Student Exchange Programs
Student exchange programs are a popular form of educational tourism, allowing students to experience other cultures and improve their language skills. These programs often involve partnerships between universities and schools in different countries. Global Volunteers and GVI Company are examples of organizations that facilitate student exchanges. Participants may stay with host families or in university dormitories, promoting cross-cultural understanding and lifelong connections.
Language Schools
Language schools are another popular option for educational tourism, providing immersive learning experiences. Students can attend classes to improve their language skills while enjoying exploring a new country. EF Tours and ACIS Educational Tours are notable companies that organize language school trips, catering to various age groups and proficiency levels. These tours can include cultural activities, excursions, and opportunities to practice conversation with native speakers.
Workshops and Seminars
Workshops and seminars provide focused learning experiences on specific subjects, usually conducted quickly. Travellers can attend workshops and seminars on topics such as art, cooking, photography, or writing, hosted by experts in the field. These educational tourism experiences often include accommodations, meals, and excursions related to the explored topic. Companies like Workshop Travels specialize in organizing these types of trips, offering unique educational opportunities alongside cultural experiences.
Educational Tours Companies
Educational tour companies often offer tailor-made itineraries for school trips and excursions, providing students with hands-on experiences in various subjects. Examples include exploring historical landmarks, visiting museums, and participating in local customs and traditions. EF Tours, ACIS Educational Tours, and School Excursions are well-known companies that arrange these trips for schools and universities. Packages range from short one-day outings to multi-week adventures catering to diverse educational needs and interests.
In summary, educational tourism programs and companies cater to various learning experiences and fields of interest, offering unique travel opportunities for students, educators, and travellers.

Broadening Cultural Experience
Educational tourism immerses travellers in diverse cultures, art, history, and architecture. This exposure leads to a deeper understanding and appreciation for different ways of life. Tourists broaden their perspectives by visiting historical landmarks, engaging with local communities, and participating in cultural activities. Exploring unique landscapes and learning foreign languages also contribute to culturally enriching experiences.
Enhancing Education and Teaching
Through educational tourism, individuals can enhance their knowledge and skills by learning from experts in various fields. Incorporating hands-on experiences in subjects like history, art, and architecture provides a more engaging and memorable educational journey. As a result, such incidents often stimulate a lifelong passion for learning and a greater appreciation for diverse subjects. Furthermore, educators can bring back valuable insights, tools, and teaching methods to enrich their classrooms and contribute to improved teaching practices.
Boost to Employment and Business
Educational tourism creates a demand for skilled professionals in the tourism industry . This demand increases employment opportunities for local guides, translators, and educators. Moreover, the influx of travellers contributes to the growth of local businesses such as hotels , restaurants, and entertainment venues. Education tourism strengthens the foundation for sustainable growth within the global community by fostering cultural exchange and economic development.
Impact on Local Cultures
Educational tourism offers the opportunity to learn about new cultures and societies but can also significantly impact these communities. Over-tourism can lead to commodifying cultural experiences, with locals feeling pressured to adjust their traditions and customs for tourist consumption. This can result in losing crucial cultural heritage, a decline in authenticity, and socio-cultural tensions between visitors and local populations.
Furthermore, tourists’ motivation to learn about new cultures may sometimes result in intrusive behaviour. The desire to explore and understand can lead to an invasion of privacy or violations of personal boundaries, creating resentment within the local community.
Environmental and Social Issues
Another challenge of educational tourism is the ecological footprint it leaves behind. As tourists travel to remote destinations, they often generate environmental issues such as pollution, littering, and depletion of natural resources. These actions can endanger the ecosystems on which local communities rely for their livelihoods.
Additionally, educational tourism can exacerbate social inequality. Wealthier tourists can consume resources, push up the cost of living, and drive up housing prices in popular destinations, making it increasingly difficult for locals to afford necessities.
To minimize the negative impacts, tourists and educational institutions must be conscious of their actions and strive for sustainable and responsible tourism practices.
Global Trends and Growth
Educational tourism is gaining rapid prominence in the global tourism industry, driven by the increased number of international students, researchers, and individuals exploring new places for learning. The year-on-year growth of educational tourism has been remarkable, indicating its significance and potential for the future of educational tourism . The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of educational tourists globally is expected upward.
With more diverse modes of transportation available, travelling for educational purposes is becoming more accessible to individuals worldwide. As a result, global educational tourists are anticipated to grow exponentially over the coming years. Dark tourism has also garnered attention as an educational sub-sector among the various niche segments. It involves visiting sites associated with death, tragedy, or adverse historical events, encouraging tourists to learn about critical aspects of human history.
International Collaborations
In the age of globalization, international collaborations have become the cornerstone for promoting educational tourism. Universities and academic institutions worldwide have recognized the benefits of global exposure through partnership programs, research initiatives, and exchange opportunities for students and faculty. These collaborations foster cultural exchange, promoting understanding different perspectives and contributing to academic advancements.
International students, in particular, play a pivotal role in boosting educational tourism’s global reach. With increasing interest in studying abroad, greater acceptance of different cultures, and the opportunities offered through international collaborations, international student mobility is expected to rise. Consequently, educational tourism will continue to thrive and evolve, enriching people’s lives with the experiential knowledge they acquire through travel and tourism .

Educational tourism, also known as “edutourism” or “academic tourism,” involves travel experiences designed to provide participants with opportunities for learning, cultural enrichment, and personal growth. Here are some examples of educational tourism:
- Museum Tours: Travelers visit museums, art galleries, science centres, and historical sites to learn about art, history, science, and culture. Guided tours , interactive exhibits, and informative displays help visitors gain insights into various subjects.
- Cultural Exchange Programs: These programs facilitate interactions between travellers and local communities. Participants engage in homestays, language immersion, and cultural workshops to understand different cultures and traditions firsthand.
- Historical Site Visits: Travelers explore historical landmarks, ancient ruins, and heritage sites to learn about past civilizations, events, and architecture. These visits provide insights into the historical context of a region.
- Language Learning Trips: Participants travel to destinations where the target language is spoken. Language immersion programs offer classes, cultural activities, and opportunities to practice language skills in real-life settings.
- Culinary Tours: Travelers explore the local cuisine, visit markets, and participate in cooking classes to learn about food traditions, ingredients, and cooking techniques of a particular region.
- Eco-Tourism and Sustainability Tours: These tours focus on ecological conservation, sustainable practices, and environmental awareness. Participants learn about local ecosystems, wildlife, and efforts to protect the environment.
- Educational Workshops and Retreats: Travelers attend workshops, seminars, and retreats related to personal development, wellness, and skill enhancement. These events provide opportunities for learning new skills and self-improvement.
- Educational Cruises: Cruises often offer onboard lectures, workshops, and field excursions that provide travellers with educational experiences while visiting multiple destinations.
- Academic Conferences and Seminars: Professionals, researchers, and students attend conferences and seminars to present and discuss research findings, share insights, and engage in academic discussions.
- Volunteer Tourism (Voluntourism): Travelers engage in volunteer activities, such as teaching, community development, or conservation efforts, while experiencing the local culture and gaining insights into societal challenges.
- Wildlife and Nature Tours: Participants explore natural habitats, observe wildlife, and learn about biodiversity, conservation, and ecological systems through guided tours and excursions.
- Adventure-Based Learning: Adventure activities such as outdoor expeditions, trekking, and team-building exercises provide opportunities for personal growth, leadership development, and experiential learning.
- Educational Farm Stays: Travelers stay on farms to learn about agriculture, animal husbandry, and sustainable farming practices. They may participate in farm activities and gain an appreciation for rural life.
- University or School Exchange Programs: Students participate in exchange programs to study abroad, gaining exposure to different educational systems, cultures, and perspectives.
- Archaeological Expeditions: Participants join archaeological digs to learn about ancient civilizations and the process of excavation and preservation.
Educational tourism offers participants a chance to learn beyond traditional classroom settings, fostering cultural understanding, personal development, and a broader worldview. The activities and experiences can vary widely, allowing travellers to choose options that align with their interests and learning goals.


Understanding What is the Meaning of Educational Tourism
Table of Contents
Educational tourism encompasses a diverse range of travel experiences that offer unique opportunities for learning and personal growth. It refers to any type of travel that provides opportunities for expanding one’s knowledge and gaining new insights. Educational tourism has been popular since the 17th century and continues to be a valuable experience for students of all ages.
There are various types of educational tourism, including study abroad programs, language schools, volunteer opportunities, cultural tours, environmental tours, and workshops. These experiences allow individuals to immerse themselves in different cultures, learn new languages, engage in hands-on activities, and expand their understanding of various subjects.
Educational tourism offers numerous benefits. It broadens one’s worldview, increases cultural awareness, facilitates intellectual growth, and creates opportunities for personal and professional development. By stepping out of their comfort zones and engaging with new environments, travelers can gain a deeper understanding of the world and themselves.
The global educational tourism market is expected to continue growing in the coming years. According to industry projections, it will reach a value of $1,947 billion by 2031. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for experiential learning, field trips, study abroad programs, and other educational travel opportunities.
Understanding the concept of educational tourism is crucial for tourism industry stakeholders. It can inform business plans, marketing strategies, and customer satisfaction. By embracing educational tourism, individuals and organizations can contribute to the personal and intellectual growth of travelers while also promoting intercultural understanding and global awareness.
As the field of educational tourism evolves, it continues to offer endless possibilities for individuals seeking educational adventures. From exploring historical landmarks to participating in workshops and volunteer projects, there is something for everyone. So, embrace the opportunity to learn, grow, and expand your horizons through educational tourism.
Key Takeaways:
- Educational tourism encompasses diverse travel experiences that provide opportunities for learning and personal growth.
- It includes study abroad programs, language schools, cultural tours, workshops, and more.
- Educational tourism offers benefits such as broadening worldviews, increasing cultural awareness, and facilitating personal and professional development.
- The global educational tourism market is projected to reach a value of $1,947 billion by 2031.
- Understanding educational tourism is important for stakeholders in the tourism industry and can inform business strategies and customer satisfaction.
Exploring Educational Tourism Benefits
Engaging in educational tourism comes with a myriad of benefits that go beyond traditional travel experiences. When you embark on an educational trip, you have the opportunity to expand your knowledge and broaden your worldview. It’s a chance to immerse yourself in new cultures, learn about different perspectives, and gain a deeper understanding of the world around you.
One of the key benefits of educational tourism is the opportunity for personal growth. As you explore new destinations and engage in unique learning experiences, you develop valuable skills such as problem-solving, adaptability, and intercultural communication. These skills not only enrich your personal life but also enhance your professional prospects.
Furthermore, educational tourism fosters cultural awareness and appreciation. By interacting with locals, participating in cultural activities, and visiting historical landmarks, you gain a deeper understanding of diverse cultures and traditions. This cultural competency becomes a valuable asset in an increasingly interconnected world.
Whether you choose to study abroad, attend language schools, or participate in workshops, educational tourism offers a transformative experience. It allows you to step out of your comfort zone, challenge your preconceptions, and create lifelong memories. So why not embrace the educational adventures that await and embark on a journey of knowledge and growth?
Table: Educational Tourism Benefits
Explore more about the exciting world of educational tourism at Exquisitive Education , a platform dedicated to providing unique and enriching educational travel experiences. Immerse yourself in a world of learning and embark on a journey that will expand your horizons and change your life.
Different Types of Educational Tourism
Educational tourism offers a wide range of opportunities to expand knowledge and experience different cultures through immersive programs and activities. Whether you’re a student looking to study abroad, a language enthusiast seeking fluency, or an avid traveler eager to learn about history and art, there is a type of educational tourism that suits your interests and goals. Let’s explore some of the different types of educational tourism below:
Study Abroad Programs
Study abroad programs are a popular choice for students seeking an immersive educational experience in a foreign country. These programs often offer a combination of academic coursework, cultural activities, and language immersion, allowing students to gain a deeper understanding of their chosen field of study and the host country’s culture.
Language Schools
If you’re looking to improve your language skills, attending a language school is a fantastic option. Language schools offer intensive language courses taught by experienced instructors, and many also provide cultural activities and excursions to enhance the learning experience. Whether you want to learn Spanish in Spain, French in France, or Mandarin in China, language schools provide an immersive environment to practice and develop your language skills.
Cultural Tours
Cultural tours are an excellent way to explore different countries and learn about their rich history, art, and traditions. These tours often involve visits to historical sites, museums, and cultural landmarks, as well as interactions with local communities. Cultural tours provide valuable insights into the host country’s heritage, allowing participants to broaden their perspective and deepen their appreciation for diverse cultures.
In addition to formal educational programs, workshops offer hands-on learning experiences in various fields. From cooking classes and art workshops to photography and sustainable agriculture, there are workshops available for a wide range of interests. These practical learning opportunities provide participants with new skills and knowledge while immersing them in a specific subject or craft.
Educational tourism is a dynamic and evolving field that continues to offer enriching experiences for individuals of all ages. Whether you choose to study abroad, learn a new language, embark on a cultural tour, or participate in workshops, educational tourism provides an opportunity to expand your horizons, foster cultural awareness, and gain valuable skills. To explore the diverse world of educational tourism and discover immersive learning experiences tailored to your interests, visit Exquisitive Education .
The Impact of Educational Tourism
Educational tourism has a profound impact on individuals, fostering intercultural understanding and promoting a global perspective. By immersing yourself in different cultures and environments, you gain firsthand experiences and insights that cannot be replicated in a classroom setting. These immersive experiences broaden your worldview and challenge your preconceived notions, allowing you to develop a deeper appreciation for diversity and cultural differences.
One of the key benefits of educational tourism is its ability to foster intercultural skills. As you interact with people from different backgrounds, you learn to navigate cultural nuances, adapt to unfamiliar situations, and communicate effectively across language barriers. These skills are highly valuable in an increasingly interconnected world, where cross-cultural collaboration and global awareness are essential.
Educational tourism also plays a crucial role in promoting personal and intellectual growth. It offers opportunities for self-discovery, self-reflection, and self-development. Whether it’s learning a new language, exploring historical sites, or engaging in meaningful volunteer work, educational tourism allows you to expand your knowledge and skills while gaining a deeper understanding of the world around you.
As the global educational tourism market continues to grow, it presents a wealth of opportunities for individuals seeking to expand their horizons. With a projected value of $1,947 billion by 2031, educational tourism is not only a valuable experience but also a thriving industry. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or a lifelong learner, embracing educational adventures can open doors to new possibilities and empower you with intercultural skills that are highly sought after in today’s globalized society.
Ready to embark on your own educational adventure? Explore the immersive and transformative experiences offered by Exquisitive Education. Click here to learn more and start your journey today!
Popular Educational Tourism Destinations
From historic cities to natural wonders, there are countless destinations around the world that cater to educational tourism. These destinations offer unique opportunities for travelers to learn, explore, and immerse themselves in different cultures and environments. Whether you’re interested in history, art, science, or the natural world, there is a destination that will satisfy your educational curiosity.
1. Rome, Italy
Rome, the eternal city, is a top educational tourism destination that showcases the rich history of the Roman Empire. Visitors can explore iconic landmarks such as the Colosseum, the Roman Forum, and the Pantheon. Additionally, Rome is home to renowned museums like the Vatican Museums and the Borghese Gallery, which house priceless art collections.
2. Kyoto, Japan
Kyoto, the cultural heart of Japan, offers a fascinating blend of tradition and modernity. This city is known for its beautiful temples, serene gardens, and traditional tea houses. Educational tourists can immerse themselves in Japanese history and culture by visiting historic sites like Kinkaku-ji (Golden Pavilion) and Fushimi Inari Shrine.
3. Cape Town, South Africa
Cape Town is a vibrant city that offers a diverse range of educational experiences. Visitors can learn about the country’s complex history by visiting landmarks like Robben Island, where Nelson Mandela was imprisoned, and the District Six Museum. Additionally, Cape Town is a gateway to stunning natural wonders, such as Table Mountain and the Cape of Good Hope.
These are just a few examples of the many educational tourism destinations available worldwide. Whether you’re interested in art, history, science, or nature, there is a destination that will inspire and educate you. So pack your bags, embrace the educational adventures that await, and start planning your next educational journey.
Emerging Trends in Educational Tourism
Educational tourism is continuously evolving, with new trends and approaches shaping the way people engage in learning while traveling. In recent years, there has been a shift towards experiential learning, where participants actively immerse themselves in educational experiences. This hands-on approach allows travelers to gain practical skills and knowledge that can be applied in real-world situations.
One emerging trend in educational tourism is place-based education, which emphasizes learning about the local environment, culture, and history of a destination. This approach encourages participants to engage with the local community, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of the destination. Place-based education often includes field trips to significant landmarks, interactive workshops with local experts, and participation in community service projects.
Hands-on Experiences and Experiential Learning
Another trend in educational tourism is the focus on hands-on experiences. Travelers are seeking opportunities to actively participate in educational activities, rather than passively observing. This can include participating in archaeological digs, working on sustainable farms, or learning traditional crafts from local artisans. By engaging in these immersive experiences, participants gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter and develop practical skills.
The integration of technology is also changing the landscape of educational tourism. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are being used to enhance educational experiences, allowing travelers to explore historical sites, interact with cultural artifacts, and engage in virtual language immersion programs. These technological advancements provide a unique and engaging learning environment that complements traditional educational methods.
Continued Growth and Opportunities
As educational tourism continues to grow, opportunities for both travelers and the tourism industry are expanding. More destinations are recognizing the value of educational experiences and developing programs to attract educational travelers. This growth presents new avenues for collaboration between educational institutions, tour operators, and local communities to provide enriching and diverse learning opportunities.
Whether it’s studying abroad, attending language schools, or participating in cultural tours, educational tourism offers a multitude of benefits. It broadens horizons, fosters cultural awareness, and encourages personal growth. With the ongoing evolution of educational tourism and the emergence of new trends, there is no shortage of educational adventures awaiting those who seek to expand their knowledge while exploring the world.
The Value of Authentic Experiences in Educational Tourism
Authentic experiences are at the heart of educational tourism, providing opportunities for immersive and practical learning. Unlike traditional classroom settings, where knowledge is acquired through textbooks and lectures, educational tourism allows you to engage directly with the subject matter, gaining firsthand knowledge and skills that are applicable in the real world. By stepping out of your comfort zone and experiencing new cultures, environments, and perspectives, you can develop a deeper understanding and appreciation for the topics you are studying.
One of the key advantages of authentic experiences in educational tourism is the ability to apply what you have learned in a practical setting. Whether it’s participating in a community service project, conducting field research, or engaging in workshops and interactive sessions, these hands-on activities allow you to see the real-world applications of the concepts you have studied. This type of experiential learning not only enhances your understanding but also helps build critical thinking, problem-solving, and interpersonal skills that are invaluable in today’s competitive world.
Furthermore, authentic experiences in educational tourism offer a level of cultural immersion that is unmatched by any other form of learning. By actively engaging with the local community, interacting with locals, and participating in cultural activities, you can gain a deeper understanding and respect for different perspectives, traditions, and ways of life. This exposure to diverse cultures not only broadens your worldview but also fosters empathy, global awareness, and intercultural competence, which are increasingly important in our interconnected society.
The Role of Exquisitive Education
If you’re looking for a provider of educational tourism experiences that prioritizes authentic learning, look no further than Exquisitive Education. They offer a range of immersive programs and unique opportunities that combine education with adventure. Their carefully curated itineraries allow you to explore fascinating destinations while learning from experienced guides and experts in various fields. Whether you’re interested in marine biology, archaeology, literature, or any other subject, Exquisitive Education ensures that you have an enriching and unforgettable educational experience.
The Role of Educational Tourism in Cultural Exchange
Educational tourism acts as a catalyst for meaningful cultural exchange, promoting mutual respect and tolerance. By immersing yourself in a different culture, you have the opportunity to gain a deeper understanding of its traditions, values, and way of life. Whether you participate in a study abroad program, join a cultural tour, or engage in volunteer activities, educational tourism provides a unique platform for connecting with people from diverse backgrounds.
During your educational travel experience, you can interact with locals, share knowledge, and exchange ideas. This exchange fosters an appreciation for cultural diversity and breaks down barriers between individuals and communities. You may have the chance to learn about ancient customs, taste traditional cuisine, or witness traditional performances. These experiences not only enrich your own personal growth but also contribute to the preservation and celebration of different cultural heritage.
Moreover, educational tourism helps promote mutual respect and tolerance by challenging stereotypes and prejudices. It provides an opportunity to dispel misconceptions and bridge cultural divides. Through direct engagement with local communities, you can gain a firsthand perspective on their values, beliefs, and challenges. This exposure to different perspectives nurtures empathy, understanding, and acceptance, enhancing your intercultural skills and global citizenship.
The Power of Cultural Exchange
One of the most powerful aspects of educational tourism is the meaningful cultural exchange it facilitates. It allows you to develop authentic connections with individuals from different cultures, fostering mutual understanding and appreciation. By stepping outside your comfort zone and immersing yourself in unfamiliar environments, you can challenge your own preconceptions and broaden your worldview.
These benefits of cultural exchange extend beyond the individual level. They contribute to a more inclusive and interconnected world, where diverse voices are valued and celebrated. Educational tourism serves as a bridge between different cultures, fostering dialogue, collaboration, and cooperation.
So, whether you’re exploring ancient ruins, participating in a language immersion program, or volunteering in a local community, embrace the educational adventures that await you. Engage in educational tourism to not only expand your knowledge but also to be an ambassador for cultural understanding and appreciation.
The Future of Educational Tourism
As the world becomes more interconnected, educational tourism will continue to play a vital role in shaping global citizens equipped with intercultural skills. The value of experiential learning and cultural exchange cannot be overstated, as they provide individuals with the opportunity to broaden their horizons, gain a deeper understanding of different cultures, and develop a global awareness that is crucial in today’s society.
Intercultural skills, such as empathy, adaptability, and open-mindedness, are increasingly sought after by employers and are necessary for navigating an ever-changing global landscape. Educational tourism provides individuals with the chance to immerse themselves in new environments, interact with diverse communities, and challenge their preconceived notions. This exposure fosters the development of intercultural skills, enabling individuals to communicate effectively across cultural boundaries and collaborate with people from different backgrounds.
Embracing the Educational Adventures Awaits!
If you’re looking to embark on an educational adventure, there are countless opportunities available. From studying abroad in prestigious universities to participating in volunteer programs that contribute to local communities, the options are vast. Cultural tours, workshops, and language schools offer immersive experiences that allow for deep cultural immersion and language acquisition. Environmental tours provide opportunities to explore diverse ecosystems and learn about sustainability practices.
As the educational tourism market continues to grow, it is essential for travelers to seek authentic experiences that provide hands-on learning and real-world application. By embracing the educational adventures that await, you can enrich your personal and professional life while contributing to global dialogue and understanding.
So why wait? Start your educational journey today and explore the world with Exquisitive Education, a leading provider of transformative educational experiences that combine learning, adventure, and cultural immersion. Visit https://exquisitiveeducation.com to discover the diverse range of programs available and begin your journey towards becoming a global citizen equipped with intercultural skills.
The Growing Market of Educational Tourism
Educational tourism is a thriving market, encompassing a wide range of experiences such as study abroad programs, field trips, and experiential learning opportunities. As the demand for immersive and enriching educational experiences continues to rise, this sector has seen significant growth in recent years. According to industry projections, the global educational tourism market is expected to reach a value of $1,947 billion by 2031.
One of the key drivers behind this growth is the increasing recognition of the value of hands-on learning and real-world application. Educational tourism offers students the chance to engage with new cultures, languages, and environments, providing them with a unique perspective that cannot be replicated in a traditional classroom setting. Whether it’s exploring historical landmarks, participating in scientific field research, or volunteering in local communities, these experiences foster personal and professional growth while expanding intercultural skills and global awareness.
The Benefits of Educational Tourism:
- Broadens worldview
- Increases cultural awareness
- Facilitates intellectual growth
- Creates opportunities for personal and professional development
As the market for educational tourism continues to grow, it presents a wealth of opportunities for both travelers and industry stakeholders. For educational institutions, it provides a platform to attract international students and expand their global reach. For travel companies and destinations, it opens doors to develop specialized programs, create partnerships, and showcase unique offerings to cater to this specific market segment.
To navigate this thriving market, it is essential for tourism industry stakeholders to understand the concept of educational tourism and its potential impact. By leveraging the power of educational experiences, businesses can develop innovative strategies, improve customer satisfaction, and tap into the immense potential of this diverse and evolving field. For more information on educational tourism and the transformative experiences it offers, visit ExquisitiveEducation.com .
Embrace the Educational Adventures Awaits!
Embrace the transformative power of educational tourism, unlocking new horizons and nurturing your intercultural skills. Educational tourism refers to any type of travel that provides opportunities for learning and expanding one’s knowledge. Whether you embark on a study abroad program, enroll in a language school, or participate in volunteer opportunities, educational tourism offers a wealth of experiences that go beyond traditional classroom learning.
By immersing yourself in different cultures and environments, you broaden your worldview and increase your cultural awareness. You develop a deeper understanding and appreciation of diverse perspectives, fostering empathy and intercultural communication skills. Engaging in educational tourism also facilitates intellectual growth, as it challenges you to think critically, adapt to new situations, and embrace lifelong learning.
As the global educational tourism market continues to grow, it presents a multitude of opportunities for personal and professional development. According to projections, the market is expected to reach a value of $1,947 billion by 2031. This underscores the importance of understanding the concept of educational tourism for tourism industry stakeholders, who can leverage this knowledge to shape their business strategies and ensure customer satisfaction.
So, why wait? Take advantage of the wide array of educational tourism options available and embark on a journey of self-discovery, knowledge, and cultural exchange. Embrace the educational adventures that await and visit Exquisitive Education to explore the exciting opportunities that will expand your horizons and nurture your intercultural skills.
Q: What is the meaning of educational tourism?
A: Educational tourism refers to any type of travel that provides opportunities for learning and expanding one’s knowledge.
Q: What are the benefits of educational tourism?
A: Educational tourism offers numerous benefits, such as broadening one’s worldview, increasing cultural awareness, facilitating intellectual growth, and creating opportunities for personal and professional development.
Q: What are the different types of educational tourism?
A: There are various types of educational tourism, including study abroad programs, language schools, volunteer opportunities, cultural tours, environmental tours, and workshops.
Q: What is the impact of educational tourism?
A: Educational tourism has a positive impact on personal growth, intercultural skills, and global awareness.
Q: What are some popular educational tourism destinations?
A: Some popular educational tourism destinations include historical landmarks, famous universities, and cultural hotspots around the world.
Q: What are the emerging trends in educational tourism?
A: Emerging trends in educational tourism include experiential learning, place-based education, and hands-on experiences.
Q: Why are authentic experiences important in educational tourism?
A: Authentic experiences in educational tourism provide valuable hands-on learning and real-world application opportunities.
Q: How does educational tourism contribute to cultural exchange?
A: Educational tourism facilitates cultural exchange by fostering understanding and appreciation of different cultures.
Q: What is the future of educational tourism?
A: The future of educational tourism lies in promoting global awareness and developing intercultural skills for an increasingly interconnected world.
Q: How big is the market for educational tourism?
A: The global educational tourism market is projected to reach a value of $1,947 billion by 2031, indicating significant growth.
Q: How can I embrace educational adventures through educational tourism?
A: Embrace educational adventures by exploring the diverse range of educational tourism experiences available and seizing the opportunities for personal growth and cultural enrichment.
About The Author
Ethan Emerson
Ethan Emerson is a passionate author and dedicated advocate for the transformative power of education. With a background in teaching and a love for writing, Ethan brings a unique blend of expertise and creativity to his contributions on ExquisitiveEducation.com .His articles are a delightful mix of insightful knowledge and engaging storytelling, aiming to inspire and empower learners of all ages. Ethan's mission is to ignite the spark of curiosity and foster a love for learning in every reader.Ethan Emerson, is your companion in the realm of general education exploration. With a passion for knowledge, He delves into the intricate world of Education Expenses & Discounts , uncovering financial insights for your educational journey. From the vitality of Physical Education to the synergy of Education & Technology , Ethan's here to bridge the gap between traditional and innovative learning methods. Discover the art of crafting impressive Resume & Personal Documentation in Education , as well as insights into diverse Career Paths, Degrees & Educational Requirements . Join Ethan in navigating through a sea of Educational Courses & Classes , exploring the nuances of various Education Systems , and understanding the empowering realm of Special Education . With an eye on Teaching & Teachers , He offers a glimpse into the world of educators who shape minds. Let's unlock Studying Tips & Learning Methods that turn education into a delightful journey of growth with Exquisitive Education .
Related Posts

What is User Education: What You Need to Know

Modern Narratives: Navigating the Dynamics of the New Sociology of Education

Understanding What is Educational Media: A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Architecture and Design
- Asian and Pacific Studies
- Business and Economics
- Classical and Ancient Near Eastern Studies
- Computer Sciences
- Cultural Studies
- Engineering
- General Interest
- Geosciences
- Industrial Chemistry
- Islamic and Middle Eastern Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Library and Information Science, Book Studies
- Life Sciences
- Linguistics and Semiotics
- Literary Studies
- Materials Sciences
- Mathematics
- Social Sciences
- Sports and Recreation
- Theology and Religion
- Publish your article
- The role of authors
- Promoting your article
- Abstracting & indexing
- Publishing Ethics
- Why publish with De Gruyter
- How to publish with De Gruyter
- Our book series
- Our subject areas
- Your digital product at De Gruyter
- Contribute to our reference works
- Product information
- Tools & resources
- Product Information
- Promotional Materials
- Orders and Inquiries
- FAQ for Library Suppliers and Book Sellers
- Repository Policy
- Free access policy
- Open Access agreements
- Database portals
- For Authors
- Customer service
- People + Culture
- Journal Management
- How to join us
- Working at De Gruyter
- Mission & Vision
- De Gruyter Foundation
- De Gruyter Ebound
- Our Responsibility
- Partner publishers

Your purchase has been completed. Your documents are now available to view.
Managing Educational Tourism
- Brent W. Ritchie
- X / Twitter
Please login or register with De Gruyter to order this product.
- Language: English
- Publisher: Channel View Publications
- Copyright year: 2003
- Audience: College/higher education;
- Main content: 304
- Keywords: educational travel ; educational holidays ; educational tourism ; ecotourism ; cultural heritage tourism ; language learning ; student exchanges ; offshore education ; lifelong learning
- Published: January 9, 2003
- ISBN: 9781873150528
- Asia & India
- Europe & Türkiye
- Middle East
- Oceania & Easter Island
- The Americas
- Archived Trips
- Custom Trips
- Tour Scholars
- Guides & Blogs
- (415) 482-8400
- [email protected]
- Request Info
What is Educational Tourism?
Every traveler sets off on their journey with their own unique motivations.
Some travel in search of adventure, while others travel for business. Many are inspired by food, and many more by picture-perfect natural landscapes and cultural attractions.
Educational tourism is a travel style defined by a desire to know more about other cultures – their history, languages, architecture, cuisine, and beyond.
At Far Horizons, we craft adventure-filled trips to extraordinary destinations led by Leading Academics . This means guests enjoy all the excitement and luxury one could want from a vacation, along with a focus on developing historical and cultural knowledge.
Below, we’ll discuss the general features of educational tourism and how travelers can benefit from an educational tourism mindset, especially when exploring the world’s greatest cultural treasures.
And while you’re here, please check our Worldwide Historical Tours . If you have any questions about our tours, please don’t hesitate to get in touch .

Defining Educational Tourism
In its simplest form, educational tourism is travel that broadens our horizons. It’s about venturing to new places with curiosity and openness that will enable learning and personal growth.
You’re on vacation, after all! Educational tourism is enriching, but it is never dry. Studying that is undertaken in the quiet of a library or behind a computer screen has its benefits, but educational tourism is about learning while also savoring the vibrancy of the world around you.
Educational tourism is often divided into two groups: travel organized with education as its driving motivation, such as school trips and university exchange programs, and travel mainly for pleasure but also offering the traveler opportunities for development.
At Far Horizons, our Educational and Archaeological Tours rest somewhere in the middle of educational tourism’s main varieties.
All our tours are guided by Ph.D. scholars – leading experts in their chosen fields. However, our small group tours are also crafted with entertainment and enjoyment in mind.
We want you to arrive home as both a happy and enriched traveler.

Self-Development Through Travel
Educational tourism is a mindset. Travel to a new place with an open mind and unbridled curiosity, and you’re guaranteed to learn plenty about other cultures and even about yourself.
It’s become something of a cliché, but travel is one of the surefire ways to discover what your true passions are in life.
At Far Horizons , our guests tend to join us due to having an intense love for a particular culture or period of history. By joining our experts on a tour, guests can explore their dream destinations while having a specialist close at hand to illuminate the historical sites.
If ancient Egypt has long fascinated you, our Majesty of Egypt Tour is the perfect way to see Egypt’s great tombs and temples in the company of an expert guide and a small group of like-minded individuals.
Have the castles and stately homes of England always seemed enchanting to you? Joining our England’s Castles, Battlements, and Stately Homes tour is guaranteed to be a rewarding experience.
When we began Far Horizons, our focus was mainly on the archaeological sites of the Maya World. However, as more and more travelers joined us and our tour program grew, we began designing educational tours across the globe.
The possibilities of educational tourism are endless. Every journey you make can help expand your knowledge of the world and the story of human history.
And, when bearing the educational potential of travel in mind, our journeys can become the ultimate aid to self-development, providing genuinely transferable skills helpful in the workplace or academic environment.
Travel helps us think big, empathize with others, inspire creativity, and improves our self-confidence.
Within our field of archaeological tourism specifically, there’s no better way to develop confidence in your area of interest than by visiting the sites themselves.

Uncovering World History with Far Horizons
Far Horizons specializes in upscale educational tours worldwide, each led by a renowned scholar who unveils the secrets of the sites we explore. We believe that to truly understand an area of the world, it is important not to be just an observer, a traveler passing through, but we must endeavor to be as much of a participant within that culture as possible.
This is the central purpose of educational tourism. It is about journeying with the curiosity and openness required to truly come away with a meaningful understanding of other cultures.
On our tours, archaeological and historical knowledge boundaries are being tested and pushed ever outward. The scholars who lead our groups are working at the forefront of their chosen fields, and we keep our groups to a maximum size of 14 people to ensure that every guest has the freedom to ask questions.
These smaller group sizes also enable us to enjoy dining experiences in celebrated restaurants, to stay in small accommodations that capture the atmosphere of the country we’re in, and to access historical attractions that would not be possible with a larger group.
Please explore our full range of Educational Tours . If you are still looking for the itinerary right for you, you may want to consider our Custom Tours option.
If you have any questions, we’d be pleased to hear from you – get in touch .
Recent Blogs

- Archived Tours
- Culture & History
- Did You Know?
- Egypt & Africa
- Far Horizons
- Middle East & Arabia
- Turkey & Europe

- IE Corporate Relations
- IE University

Laying the Foundation of Tourism Education
Tourism is one of the leading employers in the world but many of these workers are underskilled, operating in an informal labor market. Natalia Bayona explains how education can create a more sustainable tourism sector and empower young entrepreneurs.

It is well known that the ability of a structure to last over time depends on its foundation and how well it can resist and adapt to adversities and novelties, to expansion and contraction, and, yes, to natural disasters and pandemics. In fact, this principle can be applied to many components of society, from buildings and businesses to personal relationships. Foundations are built on the strength of communities, communications, civility, institutions, social values, economics, politics, and especially education.
For it is through education that individuals acquire the specific skills and knowledge that supports their personal career path and allows them to filter information, develop critical thinking, and add to the betterment of their community and society at large. The education of individuals is a key foundation for economic growth. A prime example of this is how education can positively impact one of the most human economic sectors: tourism.
A variety of skills are needed to be part of a competitive tourism sector, including customer service, marketing, storytelling, innovation, and entrepreneurship, and the ability to identify and harness the power of new technologies such as big data and artificial intelligence. Tourism is considered one of the leading employers in the world; by 2019 the sector had generated 7% of global trade and employed one in 10 people worldwide, especially women and young people. And while the pandemic has put more than 100 million direct tourism jobs at risk , past crises – including the global economic crisis, volcanic eruptions, and the Swine Flu – have shown it to be a dynamically resilient sector.
High school students should have access to tourism-related electives that allow them to create their own businesses.
However, despite the prominence of tourism within the world economy, 50% of its professionals have only acquired secondary or soft skills. This scenario is not a major issue in the medium term. However, stagnated academic formation can perpetuate an informal labor market which is, while a tempting option due to the high percentage of uneducated workers in tourism, simply unsustainable in the long term. Additionally, the current Covid-19 crisis has highlighted the difficulties and shortages experienced by those who live thanks to this informal employment model. And furthermore, 50% of the youth in the tourism sector aspire to be entrepreneurs but most – particularly in emerging tourism destinations such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia – are unable to achieve this goal for lack of opportunity, tools, and resources, and access to academic training.
The solution to tourism’s informal labor market is a lifelong learning methodology in which online education helps scale the way people are educated. In order to create added value jobs and empower young leaders, we must develop an educational model that begins early, with helping kids understand the importance of tourism on society and embedding classes within the curriculum that teach skills related to tourism and hospitality. In addition, in those emerging countries where tourism is part of public policy strategy to become a relevant economic sector, high school students should have access to tourism-related electives that allow them to create their own businesses, and learn about how the industry is connected to or relies upon transport, gastronomy, arts, humanities, commerce, and sustainability.
In most cases, tourism is a complement to education, in contrast to other fields of knowledge that we learn about as early as primary school, such as social sciences, mathematics, languages, economics, arts, etc. Rarely do we encounter elementary schools with tourism-focused vocational curricula, even in those regions with tourism-based economies. There is no reason to wait until students are aged 18 and graduating to start training them in tourism. Furthermore, imagine what would happen if tourism education was digitized accessible to those who have little opportunity?
Colombia is a success case. The country’s national program “ Colegios Amigos del Turismo ” includes tourism in the curriculum of hundreds of public schools in an effort to train Colombian talent in the country’s most important nontraditional economic sector.
The goal of creating a tourism education mindset is key if tourism is to truly play a significant role in driving employment and addressing modern-day needs, let alone lead the discussion of what kind of opportunity and future we want for youth around the world. One way to achieve this is through innovation and sustainable investment.
Israel may not be among the top three tourism destinations, but the country has channeled its strength in entrepreneurship and digital transformation to become one of the world’s top three tourism innovation ecosystems. In this way, new ventures and technology focused on tourism have added valuable jobs to the sector. The importance that Israel lends to training in innovation is embedded in the country’s education mindset – particularly through the compulsory military service – and, yes, this training has a positive effect on the tourism sector. But, what if there were also an education model specifically geared toward tourism? We would be providing future tourism workers with hard skills and primary skills that would render the sector better trained, more competitive, and focused on sustainability, inclusivity, profit, and prosperity.
Another educational framework worth investigating can be found in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, which was closed to tourism until just a few years ago. The government has since created a public policy that prioritizes tourism in an effort to diversify the economy and provide new employment opportunities for citizens. Thanks to the policy, the country has the potential to become a strong touristic hotspot.
If there is no training in tourism, the circle of poverty will continue and young people will be forced to opt for informal, poorly paid, and occasional employment.
Saudi Arabia currently has the most ambitious tourism education strategy, with the government investing in the first global tourism academy in partnership with the United Nations World Tourism Organization. The aim of the partnership is to have national and international talent in Saudi Arabia train with renowned vocational and managerial institutions and practice their skills in the biggest investment tourism project in the world: Qiddiya, a USD10 billion tourist project that includes five-star hotels, amusement parks, cultural attractions, lifestyle, and wellbeing.
It is clear that a strong and educated tourism sector can become drive economic relevance and impact, and sustainable development. Moreover, it has the potential to serve as the livelihood for millions of families seeking to lift themselves out of poverty. But in order for this to happen, a youth-led sustainable tourism model must be in place. This requires access to quality tourism education because if there is no training in tourism, the circle of poverty will continue and young people will be forced to opt for informal, poorly paid, and occasional employment.
It is important to also acknowledge that tourism education is the gateway to sustainability, specifically sustainability as a business. The creation of sustainable tourism businesses is only possible once the sector’s professionals acquire hard-skills, and can take advantage of governmental tax incentives that reduce environmental impact, lower pollution, foster green infrastructure, and curb environmentally damaging behaviors.
For example, Costa Rica is focused on preserving biodiversity, offering economic incentives to investors who bring in responsible companies that work with local communities and empower those communities through education, thereby making the tourism business more impactful, resilient, and inclusive.
For the first time in history, due to Covid-19, international borders were closed. With the lockdown, tourism came to a screeching halt and so did a part of our education. As we now begin to travel again, we have a unique opportunity to rethink and reset the tourism model and empower education as a way to increase training, reduce labor informality, reduce poverty, and enable countries to enter the global market via tourism and hospitality. The priority must be to bring about a more innovative, inclusive, and sustainable tourism sector in which youth are the protagonists.
© IE Insights.
Technology’s Role in the ESG Evolution
Not all stakeholders are created equal: a tribute to michael jensen, retaining talent in the age of resignation, eu elections explainer: what are they and why do they matter, would you like to receive ie insights.
Sign up for our Newsletter
RELATED CONTENT

Rethinking Tourism Beyond the Economic and Environmental Impact
The tourism industry has been badly hit by the current pandemic and here Isabela del Alcazar looks at how the industry, especially in Spain, must focus on sustainability and ethical practices in order to maintain natural ecosystems and create more harmony between ourselves and the planet.

Universities Are Engines of Development

Expert Roundup: the Environment
Latest news, share on mastodon.
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer

share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
UNWTO Ministers Summit in London: Transforming Tourism Through Education and Youth Empowerment
- All Regions
UNWTO celebrated the biggest Ministers Summit on record as it brought tourism leaders together on the opening day of the World Travel Market in London to focus on education and skills development.
Welcoming a record 40 Ministers of Tourism, representing every global region and destinations of all sizes, UNWTO Executive Director Natalia Bayona underscored the vital importance of investing in education.
The Summit, hosted at WTM for the 17th time, also featured inputs from key private sector players and from co-organizer the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC).
Education for a better tourism
According to UNWTO with 1.2 billion people worldwide aged between 15 to 24, tourism can establish itself as a top employer of youth and driver of youth empowerment. However., according to the Office for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) around 10% of that demographic are unemployed and 14% hold only basic qualifications.
Outlining how UNWTO is leading the way in promoting tourism education, Executive Director Bayona emphasised the need to support education and skills development at every stage.
- UNWTO launched its Education Toolkit in October 2023. The landmark resource will enable countries everywhere to introduce tourism as a high school subject.
- The Bachelors Degree in Sustainable Tourism Management offered by UNWTO and the Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts will welcome its first students in 2024.
- Currently, 30 universities worldwide contribute content to the UNWTO Online Academy. And on the ground, the Riyadh School of Hospitality and Tourism in Saudi Arabia and the Tourism Academy in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, train thousands of tourism professionals.
Ministers share education policies
The United Kingdom's Minister for Tourism, Sir John Whittingdale, stressed the importance of platforms like the Ministers Summit to provide a dialogue on how different countries are tackling common challenges, including advancing tourism education. With more than double the number of Ministerial-level participants than 2022 highlighting the strong interest in the topic, participants shared their insights on the place of education in the future of tourism.
- The Ministers of South Africa, Egypt, the Philippines and Jordan all made clear the importance of supporting education at every stage. For example, South Africa has launched a tourism equity fund to bridge the gap between student skills and employer needs, and in the Philippines , tourism education extends from high school to vocational degrees. At the same time, Jordan is working to boost the abilities of tourism workers, including in language skills.
- The Ministers from Mauritius, Malta and Indonesia stressed the vital need to upskill new and existing tourism workers. Mauritius noted that all Least Developed Countries were hit hard by the pandemic and face a challenge to boost literacy and numeracy rates, potentially with bilateral and multilateral support. For Malta, a new Skills Card will aim to elevate professional standards in the sector for better career prospects for workers and service for tourists, while Indonesia will prioritise innovation and adaptation as it creates 5 million tourism jobs in the next decade.
- Highlighting the vital importance of education for tourism sustainability, the Minister for Colombia outlined how the sector is bringing peace, jobs and youth opportunity to areas afflicted by insecurity, while Ethiopia shared its work investing in young people as well as in tourism infrastructure.
Alongside the Ministerial voices, the private sector was represented by leaders from Riyadh Air and JTB (Japan Tourism Bureau) Corp. They echoed the Ministers' focus on the importance of public-private partnerships, stressing that governments need to work with businesses to ensure training meets the needs of employers.
Ministers takeaways from Summit
On the back of the expert inputs from tourism leaders from every global region, Ministers were able to take away key lessons from the London Summit. Chief among them was the shared nature of the challenges facing destinations everywhere, with a common need for more and better-skilled workers. Concluding, UNWTO Executive Director Natalia Bayona noted the urgent need to make tourism an aspirational sector for young people everywhere, with public-private partnerships essentially for bringing the current skills gap in the sector.

Ministers Summit in London

Related links
- Download News Release on PDF
- The Global Education Forum Puts a Spotlight on the Future of Tourism
- Bachelor of Science in International Sustainable Tourism
- World Travel Market
Category tags
Related content.

Winners of 2022-2023 UNWTO Students’ League Grand Final...

Almost Half of all Global Destinations Now Offer Digita...

Opportunity for All: Samarkand Academy Adds to Growing ...

The Global Education Forum Puts a Spotlight on the Futu...

The Role of Pleasure to Improve Tourism Education pp 35–53 Cite as
Tourism Education in Perspective
- Alejandra Zuccoli 3 &
- Maximiliano E. Korstanje 3
- First Online: 02 January 2023
96 Accesses
1 Citations
To some extent, tourism education is facing an unparalleled crisis, probably a terminal crisis. Metrics applied in research and publications are wreaking havoc in the discipline as never before. Many professional researchers are pressed to publish leaving their classrooms to amateur professors. This chapter insights on the genesis and evolution of higher tourism education as well as the curricula formation. At a first glimpse, the indiscipline of tourism research -originally denounced by Tribe- is accompanied by other problems which include high dropout rates, a dissociation between professional research and learning without mentioning low salaries and bad working conditions once the Ba is earned. The present chapter interrogates the present problems of higher tourism education and the future of the discipline in an ever-changing and global world.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Airey, D. (2016). Tourism education: Past, present and future. The Business of Tourism, 17 , 9–12.
Google Scholar
Airey, D., & Tribe, J. (Eds.). (2006). An international handbook of tourism education . Abingdon.
Airey, D., Tribe, J., Benckendorff, P., & Xiao, H. (2015). The managerial gaze: The long tail of tourism education and research. Journal of Travel Research, 54 (2), 139–151.
Article Google Scholar
Akoglu, T. (2015). Walter Hunziker–the founder of academic tourism studies. Anatolia, 26 (3), 501–505.
Almeida, F., & Buzády, Z. (2019). Learning entrepreneurship in higher education through flow theory and FLIGBY game. International Journal of Virtual and Personal Learning Environments (IJVPLE), 9 (1), 1–15.
Almeida, F., Buzady, Z., & Ferro, A. (2021). Exploring the role of a serious game in developing competencies in higher tourism education. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education, 29 , 100347.
Amoah, V. A., & Baum, T. (1997). Tourism education: Policy versus practice. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 9 (1), 5–12.
Ateljevic, I., Harris, C., Wilson, E., & Collins, F. L. (2005). Getting ‘entangled’: Reflexivity and the ‘critical turn’in tourism studies. Tourism Recreation Research, 30 (2), 9–21.
Ateljevic, I., Morgan, N., & Pritchard, A. (Eds.). (2013). The critical turn in tourism studies: Creating an academy of hope (Vol. 22).
Baum, T. (2011). Global tourism higher education: The British Isles experience. In C. Hsu (Ed.), Global tourism higher education: Past, present and future (pp. 27–38). Abingdon.
Beckendorff, P., & Zehrer, A. (2017). Handbook of teaching and learning in tourism . Edward Elgar Publishing.
Book Google Scholar
Belhassen, Y., & Caton, K. (2009). Advancing understandings: A linguistic approach to tourism epistemology. Annals of Tourism Research, 36 (2), 335–352.
Benckendorff, P. (2009). Themes and trends in Australian and New Zealand tourism research: A social network analysis of citations in two leading journals (1994–2007). Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 16 (1), 1–15.
Boley, B. B. (2011). Sustainability in hospitality and tourism education: Towards an integrated curriculum. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Education, 23 (4), 22–31.
Botterill, D. (2001). The epistemology of a set of tourism studies. Leisure Studies, 20 (3), 199–214.
Buzady, Z., & Almeida, F. (2019). FLIGBY—A serious game tool to enhance motivation and competencies in entrepreneurship. Informatics, 6 (3), 27–35.
Carr, N., & Hayes, S. (2017). A comparison of tourism PhD Students’ publication records and university of study. Tourism Management Perspectives, 23 , 151–153.
Caton, K. (2014). Underdisciplinarity: Where are the humanities in tourism education? Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education, 15 , 24–33.
Chon, K., Park, E., & Zoltan, J. (2020). The Asian paradigm in hospitality and tourism. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 44 (8), 1183–1202.
Coles, T. (2009). Tourism studies and the governance of higher education in the United Kingdom. Tourism Geographies, 11 (1), 23–42.
Coles, T., Hall, C. M., & Duval, D. T. (2006). Tourism and post-disciplinary enquiry. Current Issues in Tourism, 9 (4–5), 293–319.
Coles, T., Hall, C. M., & Duval, D. T. (2009). Post-disciplinary tourism. In J. Tribe (Ed.), Philosophical issues in tourism (pp. 80–100). Channel View.
Chapter Google Scholar
Cooper, C. (2002). Curriculum planning for tourism education: From theory to practice. Journal of Teaching in Travel & Tourism, 2 (1), 19–39.
Cooper, C., & Shepherd, R. (1997). The relationship between tourism education and the tourism industry: Implications for tourism education. Tourism Recreation Research, 22 (1), 34–47.
Costa, C., Carvalho, I., Cacador, S., & Breda, Z. (2016). Future higher education in tourism studies and the labor market: Gender perspective on expectations and experiences. In D. Prebežac, C. Schott, & P. Sheldon (Eds.), The tourism education futures initiative: Activating change in tourism education (pp. 193–213). Routledge.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1988). The flow experience and its significance for human psychology. Optimal experience: Psychological studies of flow in consciousness, 2 , 15–35.
Csikszentmihalyi, M., Abuhamdeh, S., & Nakamura, J. (2014). Flow. In Flow and the foundations of positive psychology (pp. 227–238). Springer.
Cunliffe, S. (2002). Forecasting risks in the tourism industry using the Delphi technique. Tourism, 50 (1), 31–41.
Dredge, D. (2015). Tourism and governance. In Education for sustainability in tourism (pp. 75–90). Springer.
Du, J. (2003). Reforms and development of higher tourism education in China. Journal of Teaching in Travel & Tourism, 3 (1), 103–113.
Dwyer, L. (2012). Trends underpinning global tourism in the coming decade. In W. Theobald (Ed.), Global tourism (pp. 542–558). Routledge.
Ertaş, M., & Kozak, M. (2020). Publish or perish: The proportion of articles versus additional sections in tourism and hospitality journals. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 43 , 149–156.
Fernandez Fuster, L. (1967). Teoría y Técnica del turismo. [Theory and practice of tourism] Tomo I . Editorial Nacional.
Fidgeon, P. R. (2010). Tourism education and curriculum design: A time for consolidation and review? Tourism Management, 31 (6), 699–723.
Gopher, D., Well, M., & Bareket, T. (1994). Transfer of skill from a computer game trainer to flight. Human Factors, 36 (3), 387–405.
Gretzel, U., & Bowser, G. (2016). Real stories about real women: Communicating role models for female tourism students. In D. Prebežac, C. Schott, & P. Sheldon (Eds.), The tourism education futures initiative: Activating change in tourism education (pp. 214–227). Routledge.
Gursoy, D., & Sandstrom, J. K. (2016). An updated ranking of hospitality and tourism journals. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 40 (1), 3–18.
Hall, C. M. (2011). Publish and perish? Bibliometric analysis, journal ranking and the assessment of research quality in tourism. Tourism Management, 32 (1), 16–27.
Hall, T., Gray, T., Downey, G., Sheringham, C., Jones, B., Power, A., & Truong, S. (2016). Jafari and transformation: A model to enhance short-term overseas study tours. Frontiers: The Interdisciplinary Journal of Study Abroad, 27 , 33–46.
Houlot, A. (1961). Le Turisme et La Biblie. Revue l’Académie Internationale du Turisme. Monaco.
Hsu, C. H. (2018). Tourism education on and beyond the horizon. Tourism Management Perspectives, 25 , 181–183.
Inui, Y., Wheeler, D., & Lankford, S. (2006). Rethinking tourism education: What should schools teach. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport and Tourism Education, 5 (2), 25–35.
Jafari, J. (2001). The scientification of tourism. In V. L. Smith & M. Brent (Eds.), Hosts and guests revisited: Tourism issues of the 21st century (pp. 28–41). New York.
Jafari, J. (2002). Tourism education and training models-getting to the core of destination planning and management (pp. 29–34). World Tourism Organization.
Jafari, J., & Ritchie, J. B. (1981). Toward a framework for tourism education: Problems and prospects. Annals of Tourism Research, 8 (1), 13–34.
King, B., McKercher, B., & Waryszak, R. (2003). A comparative study of hospitality and tourism graduates in Australia and Hong Kong. International Journal of Tourism Research, 5 (6), 409–420.
Korstanje, M. E. (2007). The origin and meaning of tourism: Etymological study. E-Review of Tourism Research, 5 (5), 100–108.
Korstanje, M. E. (2015). A portrait of Jost Krippendorf. Anatolia, 26 (1), 158–164.
Korstanje, M. E. (2016). Why citation impact is so important for tourism researchers? Advances in Hospitality and Tourism Research (AHTR), 4 (1), 26–31.
Korstanje, M. E. (2022). Tourism imagination: A new epistemological debate. Current Issues in Tourism , 1–13. Ahead of print. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2021.2023481
Korstanje, M. E., & George, B. (2022). The nature and future of tourism: A post-COVID-19 context . Apple Academic Press.
Krippendorf, J. (2010). Holiday makers . Routledge.
Ladkin, A. (2014). Employment and career development in tourism and hospitality education. In D. Dredge, D. Airey, & M. Gross (Eds.), The Routledge handbook of tourism and hospitality education (pp. 427–439). Routledge.
Lam, T., & Xiao, H. (2000). Challenges and constraints of hospitality and tourism education in China. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management., 12 (5), 291–295.
Law, R. (2017). Ranking individuals in tourism and hospitality research. Tourism Recreation Research, 42 (3), 392–397.
Leiper, N. (1979). The framework of tourism: Towards a definition of tourism, tourist, and the tourist industry. Annals of Tourism Research, 6 (4), 390–407.
Leiper, N. (1983). An etymology of "tourism". Annals of Tourism Research, 10 , 277–281.
MacLaurin, D. (2006). Tourism education in Canada: Past, present and future directions. In C. Hsu (Ed.), Global tourism higher education: Past, present and future (pp. 1–26). Abingdon.
McKercher, B. (2002). The future of tourism education: An Australian scenario? Tourism and Hospitality Research, 3 (3), 199–210.
McKercher, B. (2008). A citation analysis of tourism scholars. Tourism Management, 29 (6), 1226–1232.
Moscardo, G. (2011). The role of knowledge in good governance for tourism. In E. Laws, H. Richins, & J. Agrusa (Eds.), Tourist destination governance: Practice, theory and issues (pp. 67–80). CABI.
Nakamura, J., & Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2014). The concept of flow. In Flow and the foundations of positive psychology (pp. 239–263). Springer.
Paris, C. M. (2011). Social constructivism and tourism education. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sports and Tourism Education (Pre-2012), 10 (2), 103–115.
Pearce, P. (2011). Australian tourism education: The quest for status. In C. Hsu (Ed.), Global tourism higher education: Past, present and future (pp. 251–268). Abingdon.
Pechlaner, H., Zehrer, A., Matzler, K., & Abfalter, D. (2004). A ranking of international tourism and hospitality journals. Journal of Travel Research, 42 (4), 328–332.
Prebežac, D., Schott, C., & Sheldon, P. (Eds.). (2016). The tourism education futures initiative: Activating change in tourism education . Abingdon.
Rakić, T., & Chambers, D. (Eds.). (2012). An introduction to visual research methods in tourism . Routledge.
Reichel, A. (2011). Tourism and hospitality higher education in Israel. In C. Hsu (Ed.), Global tourism higher education: Past, present and future (pp. 61–88). Abingdon.
Ryan, C. (2005). The ranking and rating of academics and journals in tourism research. Tourism Management, 26 (5), 657–662.
Sheldon, P. J., Fesenmaier, D. R., & Tribe, J. (2011). The tourism education futures initiative (TEFI): Activating change in tourism education. Journal of Teaching in Travel & Tourism, 11 (1), 2–23.
Stevens, Z. M., Grimwood, B. S., & Caton, K. (2019). Story and moral development in tourism education. Journal of Teaching in Travel & Tourism, 19 (1), 22–38.
Tribe, J. (1997). The indiscipline of tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 24 (3), 638–657.
Tribe, J. (2000). Indisciplined and unsubstantiated. Annals of Tourism Research, 27 (3), 809–813.
Tribe, J. (2001). Research paradigms and the tourism curriculum. Journal of Travel Research, 39 (4), 442–448.
Tribe, J. (2004). The indiscipline of tourism. In S. Williams (Ed.), Tourism: Critical concepts in the social sciences, 2 (pp. 205–226). Routledge.
Tribe, J. (2008). Tourism: A critical business. Journal of Travel Research, 46 , 245–255.
Tribe, J. (2010). Tribes, territories and networks in the tourism academy. Annals of Tourism Research, 37 (1), 7–33.
Wang, J., Ayres, H., & Huyton, J. (2010). Is tourism education meeting the needs of the tourism industry? An Australian case study. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Education, 22 (1), 8–14.
Weber, K., & Ladkin, A. (2008). Career advancement for tourism and hospitality academics: Publish, network, study, and plan. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 32 (4), 448–466.
Xiao, H. (2013). Jafar Jafari: The platform builder. Anatolia, 24 (2), 288–296.
Xu, F., Tian, F., Buhalis, D., Weber, J., & Zhang, H. (2016). Tourists as mobile gamers: Gamification for tourism marketing. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 33 (8), 1124–1142.
Yankholmes, A. K. (2014). Publish or perish: African scholarship in the field of tourism and hospitality studies. Tourism and Hospitality Research, 14 (1–2), 97–107.
Young, T., & Maguire, A. (2017). Indigenization of curricula: Trends and issues in tourism education. In P. Beckendorff & A. Zehrer (Eds.), Handbook of teaching and learning in tourism . Edward Elgar Publishing.
Zhao, W., & Ritchie, J. B. (2007). An investigation of academic leadership in tourism research: 1985–2004. Tourism Management, 28 (2), 476–490.
Zopiatis, A., Theocharous, A. L., & Constanti, P. (2015). ‘The past is prologue to the future’: An introspective view of hospitality and tourism research. Scientometrics, 102 (2), 1731–1753.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economics, University of Palermo, Buenos Aires, Argentina
Alejandra Zuccoli & Maximiliano E. Korstanje
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Zuccoli, A., Korstanje, M.E. (2023). Tourism Education in Perspective. In: The Role of Pleasure to Improve Tourism Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21580-3_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-21580-3_3
Published : 02 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-21579-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-21580-3
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Educational tourism is about learning new things, acquiring new knowledge about culture or history of other destinations. Its main focus is on studying new things, learning about other cultures, study tours, or to apply the learned skills. This is one of the most famous type of tourism activity for past few years, for example people travel to ...
The global educational tourism market value in 2021 is estimated at $399.8. It means that the market exhibited a year-on-year growth of 16%. The same research projects that the market will continue to grow with a compound annual growth rate of 17.2%. By 2031 its value is projected to reach $1,947 billion.
Educational tourism is on the rise due to the huge proven benefits to students who take part in it. This article will explain the 8 key types of education in tourism. Educational tourism isn't a new concept. In fact, educational tours were popular amongst young British aristocrats in the 17th to 19th centuries.
The first is university, college and school tourism, in which the tourist experience is secondary to formal learning and can be described as 'education first'. The second is edu-tourism, defined as general travel for education and known as 'tourist first' (Ritchie et al, 2003).
Defining Educational Tourism. Educational tourism, also known as edu-tourism or educational travel, is a form of tourism whose primary purpose is gaining knowledge and engaging in cultural exchanges. It involves travelling to a different country or region to learn about various subjects such as history, languages, art, and environmental issues.
One emerging trend in educational tourism is place-based education, which emphasizes learning about the local environment, culture, and history of a destination. This approach encourages participants to engage with the local community, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of the destination.
Abstract. Student mobility in higher education has undergone significant growth in recent decades to the point of becoming a global phenomenon. Under certain conditions, higher education students can be considered as visitors to the destination countries and this mobility can be defined as tourism. This chapter clarifies and contextualizes the ...
Tourism is a relative newcomer to education but has developed as a distinct area of study. Its growth was spurred by vocational needs evolving from education for hotel management. The first dedicated programs started in the 1970s at the postgraduate level, and undergraduate programs were introduced shortly after.
Educational tourism is classified as a youth type of tourism that attracts a certain market niche. Therefore, educational tourism is defined as a niche type of tourism. In this type of tourism ...
About this book. This book outlines the main forms of educational tourism, their demand and supply characteristics, their impacts and the management issues associated with them.It argues for adequate research and appropriate management of educational forms of tourism to maximise regional development impacts and personal learning benefits.
All Regions. 26 Oct 2023. The UNWTO General Assembly looked to the future with a focus on tourism education and training. The Global Education Forum brought together Ministers, employers, educators and learners to address the biggest challenges and opportunities for advancing training across every part of the sector.
Educational tourism is a travel style defined by a desire to know more about other cultures - their history, languages, architecture, cuisine, and beyond. At Far Horizons, we craft adventure-filled trips to extraordinary destinations led by Leading Academics. This means guests enjoy all the excitement and luxury one could want from a vacation ...
The education of individuals is a key foundation for economic growth. A prime example of this is how education can positively impact one of the most human economic sectors: tourism. A variety of skills are needed to be part of a competitive tourism sector, including customer service, marketing, storytelling, innovation, and entrepreneurship ...
On the basis of a scoping review of the literature about educational tourism—a type of tourism in which the traveller's primary or secondary objective is learning—this study summarizes views on how Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) can foster local development through educational tourism. The results show that international students can be considered as educational tourists, and their ...
The findings derived from a Scopus meta-data collection pertaining to Historical Tourism in Education over the past two decades indicate that 362 publications on the subject have been produced by 77 different countries. The ten nations that publish the most research on Historical Tourism in Education are illustrated in Fig. 4.
Like many tourism concepts, tourism education is largely an industry-specific example of a more general phenomenon. In its widest context, education is generally positioned as being something different to indoctrination, training, or instruction. Rather, it is to do with the acquisition of knowledge and skills and the development of understanding.
Tourism education is the way tourists destination prepare the human resources to be able to work professionally in the developing the tourism sectors. ... This meaning should also be placed in the ...
Roppolo C. (1996). "International Education: What Does This Mean for Universities and Tourism?" In Tourism and Cultural Change, edited by Robinson M., Evans N., Callaghan P. Sunderland: Centre for Travel and Tourism and Business Editorial Press, pp. 191-201.
Tourism Education in the twenty first century has been characterised by developments in the 16-19 year old age category (Further Education) and the growth of Professional Qualifications. ... His injunction maintains that fundamental questions about the aims and meaning of (tourism) education must be addressed at the outset. This is because it ...
All Regions. 7 Nov 2023. UNWTO celebrated the biggest Ministers Summit on record as it brought tourism leaders together on the opening day of the World Travel Market in London to focus on education and skills development. Welcoming a record 40 Ministers of Tourism, representing every global region and destinations of all sizes, UNWTO Executive ...
To some extent, tourism education is facing an unparalleled crisis, probably a terminal crisis. ... The epistemological tradition struggled to find an all-encompassing definition of tourism. Rather, the economic-centred tradition focused on the management and profits of international destinations. Per this academic tradition, the tourist is the ...
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
The present paper is an attempt to stress upon the education tourism adoption as a growth strategy for the sustainable development of tourism in both the regions. The paper also highlights the hindrances and requirements for creating education tourism as an exclusive part of learning. Keywords: hedonistic, spiritual, education, tourism ...
International Tourism Summit Oyo State 2024 The tower was built in 19 thirty6 in honor of Captain Bauer. It was designed by Robert Taffy Jones, a British architectural engineer.