

IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Test 1 Reading Passage 1, Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website; with best solutions, explanations and bonus tips
This IELTS Reading post deals with a total solution package for IELTS Cambridge 13 Reading test 1 passage 1 . This is a targeted post for candidates who have major difficulties in finding and understanding Reading Answers. This post can guide you the best to understand every Reading answer easily and without much difficulty. Finding IELTS Reading answers is a step-by-step process and I hope this post can help you in this respect.

Reading Passage 1 :
The headline of the passage: case study: tourism new zealand website.
Questions 1-7 ( Completing table with ONE WORD ONLY):
In this type of question, candidates are asked to write only one word to complete a table on the given topic. For this type of question, first, skim the passage to find the keywords in the paragraph concerned with the answer, and then scan to find the exact word.
[ TIPS: Here scanning technique will come in handy. Target the keywords of the questions to find the answers. Remember to focus on Proper nouns, random Capital letters, numbers, special characters of text etc.]
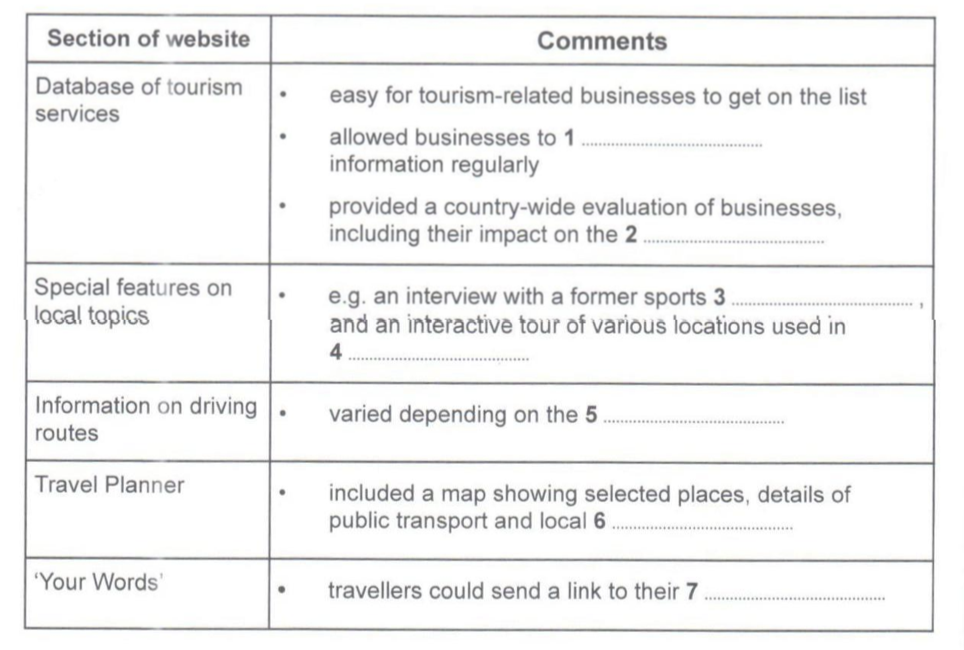
Question 1: allowed businesses to ______ information regularly.
Keywords for these answers: database, allowed businesses, information, regularly,
In paragraph no. 2, we find the mention of the word ‘database’ in the third line. Here, lines 8 & 9, the writer mentions, “In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis….”.
Here, details = information
So, the answer is: update
Question 2: provided a country-wide evaluation of businesses, including their impact on the _________.
Keywords for this answer: database, country-wide evaluation, impact on
The last line of paragraph no. 2 has the answer. Here, the writer suggests, “As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.”
Here, effect = impact
So, the answer is: environment
Question 3: e.g. an interview with a former sports __________.
Keywords for this answer: special features, interview, a former sports
The answer can be found in paragraph 3, lines 1-3. The words ‘interview’ and ‘former’ are formed in line number 2. The writer says, “.. .. . One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga.”
Here, rugby = sports
So, the answer is: captain
Question 4: and an interactive tour of various locations used in ________.
Keywords for this answer: interactive tour, various locations
The answer is in paragraph 3, lines 4-5. The lines say, “…… was an interactive journey through a number of locations chosen for blockbuster films …… ..”.
Here, journey = tour,
A number of locations = various locations,
Chosen for = used in,
So, the answer is: films
Question 5: varied depending on the __________.
Keywords for these answers: driving routes, varied, depending on
Paragraph 3, lines 8-9 has the answer to this question. The lines say, “…. . .the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season ….. . .”.
Here, different = varied,
according to = depending on,
So, the answers are: season
Question 6: including a map showing selected places, details of public transport and local _______.
Keywords for this answer: travel planner, a map, public transport, local
The answer lies in paragraph no. 4, line 4. The paragraph begins with ‘travel planner’. In the subsequent lines, we can find the mention of ‘public transport’. In line no. 4 it says, “… . There were also links to accommodation in the area.”
Here, the phrase ‘in the area’ can be replaced with the word ‘local’.
So, the answer is: accommodation
Question 7: travelers could send a link to their ________.
Keywords for this answer: ‘Your Words’, travelers, send, link to,
The answer is in paragraph no. 4. ‘Your Words’ is the name of a section of the website www.newzealand.com. We can see that the phrase ‘Your Words’ is present in line 6 of paragraph 4. So, we need to read lines 6 & 7 to find the answer.
The author says, “ ….. . . The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.”
Here, anyone could submit = travelers could send a link to
So, the answer is: blog
Questions 8-13: (TRUE/FALSE/NOT GIVEN)
In this type of question, candidates must find out whether:
The statement in the question matches with the account in the text- TRUE The statement contradicts the account in the text- FALSE There is no clear connection of the statement with the account in the text- NOT GIVEN
Question 8: The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
Keywords for this answer: the website, aimed, itineraries, travel packages
To find the answer to this question, look for the words itineraries and travel packages. The answer is in Paragraph 6. Here, lines 1 and 2 say, “ The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organizations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests.”
This means that the aim of the website was to allow individuals and travel organizations to do their work on their own, the website did not provide any ready-made itineraries and travel packages.
The statement clearly contradicts the text.
So, the answer is: FALSE
Question 9: It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
Keywords for this answer: started searching, geographical location
The answer is not anywhere in the passage. The question is about starting the search in the website.
In paragraph 6 line 3, the author says, “…… visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical locations, but also by the particular nature of the activity.” However, nowhere it says anything about starting the search.
So, the answer is: NOT GIVEN
Question 10: According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
Keywords for this answer: 26%, visitor satisfaction, accommodation
** Special answer-finding technique:
There is a number in the question (26%). If the answer is TRUE, 26% has to be in the text. For FALSE, the number will be different; or, the number will be 26% (but it will be related to other matters). If the number is still 26%, yet it doesn’t match with other keywords, the answer will be NOT GIVEN.
The answer is in lines 4, 5 & 6 of paragraph no. 6. Here, the writer says, “This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction , while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26% .”
Here, the lines clearly contradict the question. Transportation and accommodation account for 26%. Visitor satisfaction accounts for 74%. If only accommodation accounted for 26%, we could write TRUE.
Question 11: Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture.
Keywords for this answer: like to, involved, local nature
The answer lies in lines 7-9 of paragraph 6. The author says, “…. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn more about traditional life.”
It means that visitors like to engage in local culture.
So, the answer is: TRUE
Question 12: Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
Keywords for this answer: like staying, small hotels
In paragraphs 6 & 7, there is no mention of staying in hotels. There is no comparison between small and large hotels also.
So the answer is: NOT GIVEN
Question 13: Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
Keywords for this answer: feel, unlikely, will return, after their visit
The answer is in paragraph 7. Here, lines 4 and 5 states, “Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit .”
Here, the phrase ‘often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit’ means that there is a very low possibility that the visit will happen again.
So the answer is: TRUE
Bonus tips:
You must pay attention to WORD LIMIT. For instance, if you have to complete a sentence using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS; and the correct answer in the text is ‘dress made of cotton’, you cannot write the answer as ‘dress made of cotton’. You need to change it to ‘cotton dress’.
If you like this post, and need any assistance about IELTS Reading, please make comments below.
Click here for solutions to Cambridge 13 Reading Test 1 Passage 2
Click here for solutions to Cambridge 13 Reading Test 1 Passage 3
Important vocabulary with explanations for Cambridge 13 Test 1 Reading Passage 1, 2, 3
59 thoughts on “ IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Test 1 Reading Passage 1, Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website; with best solutions, explanations and bonus tips ”
- Pingback: IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Test 1 Reading Passage 2; with best solutions and explanations | IELTS Deal
- Pingback: IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Reading Test 1; Passage 3; Artificial artists; with top solutions and explanations | IELTS Deal
thanku really it’s very helpfull
Thank you for help
it was very helpful, thanks!.
Thank u ???
i although questions were all completely explained, i did n’t understand question number 10.
The question asks you to decide whether 26% visitor satisfaction is related to accommodation. We find in the passage, 26% visitor satisfaction is related to accommodation and transport. So, here in the question, transport is missing. This is why the answer is “FALSE’.
u meant that 26% is divided in transportating and accommodation acc. to passage.
There is a number in the question (26%). If the answer is TRUE, 26% has to be in the text. If it is FALSE, the number will be different; or, the number will be 26% (but it will be related to other matters). If the number is still 26%, yet it doesn’t match with other key-words, the answer will be NOT GIVEN.
The answer can be found in lines 4, 5 & 6 of paragraph no. 6. Here, the writer says, “This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%.”
In there,it was written like transport AND accommodation account for remaining 26%. Not ooonly accommodation account for 26% of visitor satisfaction. It is with transport
Thank you so much, it is very helpful
Plzz Sir mainu tusi mcq diya teps diyo reading diya v te listening diya v plzz mainu bht jada problem aa rhi aa ohna nu solve krn ch te ik headings diya v
Hello Kamaljeet, I don’t understand Punjabi much and I didn’t get clearly from what you wrote. But as far as I can understand you, I think you have problems in MCQs. Plz follow my other lessons and surely you’ll get help in this question type. For Headings, I have some good works available in this website.
Hlo sir mainu mcq ch bht problem aa rhi aa te heading ch v plzz mainu ehna dona diya tips dedo menumeration listening ch v mcq di hi problem aundi a jada plzz help me
Super helpful! Thank you so much!
If i add some explanations,
The reason NG isn’t the correct answer: As far as the ‘transport’ was mentioned along with accommodation as one of the factors contributing to the 26% of visitors satisfaction on the paraghagh, we cannot ignore transport’s contribution to the 26%. So, it means there is definitely certain percent related to ‘transport’. And, this means accommodation cannot account for the whole 26%, which is contradicting the sentence of No.10 question. Thereby the evidence to decide whether the No.10 sentence is right or wrong is clearly given on the paragragh, and the answer is F.
I figured it out this way. Hope this helpful to you.
Dear Kimmy, the way you explained can be considered correct. The way I explained it can also be taken as correct.
Hello sir My reading scores had stucked on 5.5 bands and I have exam on 29th June pls share me some tips to crack my ielts.
Dear Rikta, Try to follow these suggestions. 1. give importance in synonyms. 2. learn the tricks of paraphrasing. 3. do not take more than 1 minute in each question. 4. Try to guess some answers. 5. Be careful about proper nouns and use of capital letters. 6. try to practice some mock tests before your exam. 7. Remember you can’t solve all types of questions. so give importance on the types you are comfortable with.
Is it okay to write all your answers in capital letters?
YES, for Reading and Listening. Not for Writing.
Thank you so much! It’s really helpful ??
Its really a most helpful website
I need tips in paragraph type questions nad match the heading
Please share some techniques regarding solving list of heading or match the statement with paragraph…please!
Sir I don’t understand Question 13 What does the question mean ?
Dear Yoon, Thanks for the question. Question 13: Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit. This question means that many visitors fear that they may not return to New Zealand after their visit.
I’m very confused between not given and false. Please give me some tips.
http://ieltsdeal.com/ielts-reading-how-to-find-answers-for-true-false-not-given-or-yes-no-not-given-questions-best-strategies-methodstricks-and-tips/
Thank you Najib for useful support. It is rare that anyone who gives explanation of IELTS reading with tips. Everybody gives simple tips only, what makes difference between you and them. Request explanation on rest of the Cambridge books. Its really really helpful and useful. Your website is unique.
Welcome! And I request you to pray for me. And the rest is coming. Work is going on.
i didn’t understood the answer of quest 10.. can u plz hlp me.. i have doubt that why it is false because it clearly said that 26 % accounts for transport and accommodation
26% = accommdation + transportation, not accommodation alone. Our key word here is’ accommodation’ and it is very much necessary to understand the clear and exact meaning of each question for true/false questions in general.
- Pingback: IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Test 1 Reading Passage 2, Why being bored is stimulating and useful, too; with best solutions, explanations and bonus tips | IELTS Deal
Hlo sir muja heading ma bhut didn’t aa Rahe ba
Can you write that in English, please?
hi guys , i have a question is that if i use the word blockbusters instead of films , is it correct ?
blockbusters = films which have broken all sorts of records
It’s really very helpful.
I’m delighted to hear that. Thank you. Here’s my YouTube channel for your consideration: https://www.youtube.com/c/IELTSDeal
where are you from sir?
I’m from Bangladesh.
What is the main different between yesnong and truefalseng?
Thanks alot, this is really explanatory and I find it helpful
Welcome! You can follow my YouTube Channel as well: https://www.youtube.com/c/IELTSDeal/
In fact your website has been of a tremendous help to me. I understood true, false and not given from your website.. But I still need help in the other part too, writing listening n speaking My date is very close that is 2nd Dec n 5th
Thank you so much, it’s really helpful for me!!!
GREAT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
very helpful
- Pingback: IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Reading Test 1; Passage 3; Artificial artists; with top solutions and explanations - IELTS Deal
Thanks for your clear explanation. It really helps to deal with reading tasks. I really appreciate you.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Academic IELTS Reading: Test 2 Passage 1; The Dead Sea Scrolls; with top solutions and best explanations
This Academic IELTS Reading post focuses on solutions to an IELTS Reading Test 2 passage 1 that has a passage titled ‘The Dead Sea Scrolls’. This is a targeted post for Academic IELTS candidates who have major problems locating and understanding Reading Answers in the AC module. This post can guide you the best to understand […]

Academic IELTS Reading: Test 1 Reading passage 3; To catch a king; with best solutions and explanations
This Academic IELTS Reading post focuses on solutions to an IELTS Reading Test 1 Reading Passage 3 titled ‘To catch a king’. This is a targeted post for IELTS candidates who have great problems finding out and understanding Reading Answers in the AC module. This post can guide you the best to understand every Reading answer […]
Welcome Guest!
- IELTS Listening
- IELTS Reading
- IELTS Writing
- IELTS Writing Task 1
- IELTS Writing Task 2
- IELTS Speaking
- IELTS Speaking Part 1
- IELTS Speaking Part 2
- IELTS Speaking Part 3
- IELTS Practice Tests
- IELTS Listening Practice Tests
- IELTS Reading Practice Tests
- IELTS Writing Practice Tests
- IELTS Speaking Practice Tests
- All Courses
- IELTS Online Classes
- OET Online Classes
- PTE Online Classes
- CELPIP Online Classes
- Free Live Classes
- Australia PR
- Germany Job Seeker Visa
- Austria Job Seeker Visa
- Sweden Job Seeker Visa
- Study Abroad
- Student Testimonials
- Our Trainers
- IELTS Webinar
- Immigration Webinar
Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website – IELTS Reading Answers
10 min read
Updated On Feb 13, 2024

Share on Whatsapp
Share on Email
Share on Linkedin

Recent IELTS Reading Test with Answers - Free PDF
The IELTS Reading Module offers a fantastic chance to achieve excellent scores. It assesses a candidate’s reading comprehension skills in English. You must comprehend the various question types in order to perform at your best in this area. Ideally, you should not spend more than 20 minutes on a passage.
The Academic passage, Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website reading answers, appeared in an IELTS Test. Try to find the answers to get an idea of the difficulty level of the passages in the actual reading test. If you want more passages to solve, try taking one of our IELTS reading practice tests.
Let’s see how easy this passage is for you and if you can solve it in 20 minutes.
The question types found in this passage are:
- Table Completion (Q. 1-7)
- True/False/Not Given (Q 8-13)
Do you want to revise the steps to solve the Matching Features questions for IELTS Academic Reading?
Check out IELTS Reading Matching Features Questions !
Reading Passage
Case Study: Tourism New Zealand Website
A New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places, and the experiences. In 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
B A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism service to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme whereby organisations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
C To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travelers devise their own customised itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
D Later, a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ places or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out to take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
E The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
F The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organizations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travelers enjoy such learning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
G It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere – the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
Questions 1-7
Questions 8-13.
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write –
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information, FALSE if the statement contradicts the information, NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this.
8 The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
9 It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
10 According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
11 Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture.
12 Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
13 Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
‘ Case Study Tourism New Zealand website ’ IELTS Reading Answers With Location and Explanation
1 Answer: update
Question type: Table Completion
Answer location: Paragraph B
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 8th and 9th lines that, “In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis….”.
2 Answer: environment
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the last line that, “As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.”
3 Answer: Captain
Answer location: Paragraph C
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 1-3 lines that, “….One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga.”
4 Answer: films
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 4th and 5th lines that, “…… was an interactive journey through a number of locations chosen for blockbuster films …….”.
5 Answer: season
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 8th and 9th lines that, “…. the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season…..”.
6 Answer: accommodation
Answer location: Paragraph D
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 4th line that, “….. There were also links to accommodation in the area.”
7 Answer: blog
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 6th and 7th lines that, “ ….. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.”
8 Answer: FALSE
Question type: TRUE/FALSE/NOT GIVEN
Answer location: Paragraph F
Answer explanation: The response lies in Paragraph 6. The initial two lines indicate that the website’s purpose was to empower individuals and travel organizations to create their own travel plans. The website did not offer pre-packaged itineraries and travel packages.
This assertion directly opposes the information in the passage.
Hence, the answer is FALSE.
9 Answer: NOT GIVEN
Answer explanation: The answer cannot be located within the text. The question pertains to initiating a search on the website.
In Paragraph 6, line 3, the author mentions, “…visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical locations, but also by the particular nature of the activity.” However, there is no information provided regarding how to start a search.
As a result, the answer is NOT GIVEN.
10 Answer: FALSE
Answer explanation: The answer can be found in lines 4, 5, and 6 of paragraph 6.
In these lines, it is evident that the question is contradicted. Transportation and lodging makeup 26%, while visitor satisfaction makes up 74%. If only lodging constituted 26%, we could affirm that it is TRUE.
Therefore, the correct answer is FALSE.
11 Answer: TRUE
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in lines 7-9 that, “…. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn more about traditional life.”
12 Answer: NOT GIVEN
Answer location: Paragraphs F & G
Answer explanation: Staying in hotels is not discussed, and there is also no comparison made between small and large hotels.
Therefore, the answer is NOT GIVEN.
13 Answer: TRUE
Answer location: Paragraph G
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 4th and 5th lines that, “Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit.”
Tips for Answering the Question Types in the ‘Case Study Tourism New Zealand website’ IELTS Reading Answers
Let us check out some quick tips to answer the types of questions in the ‘Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website’ Reading Answers passage.
Table Completion:
The way to solve the table completion questions of the IELTS Reading is similar to Summary Completion. You will be asked to fill in the blanks in a small passage given in the form of a note with the relevant words or numbers. So, let us revise the strategies.
- Read the instructions carefully. It will help you determine the word limit (no more than two, one word, etc.) and important terms like ‘using words from the text’ or ‘from the text’. You have to follow these strictly.
- Go through the incomplete table first. Also, think about keywords and how they could be represented by synonyms or paraphrasing.
- Locate where the information is by scanning quickly . If you can’t, move on.
- Study the reading text by using the skimming and scanning techniques . It will help to establish the answer quickly. When scanning for your answer, make sure you are thinking about paraphrasing and synonyms.
- The answers appear in the same order as the questions . Also, check your spelling and remember that your answer should be grammatically correct.
True/False/Not Given
In IELTS Reading , ‘True, False, Not Given’ questions are based on facts. Several factual statements will be provided to you, and it is up to you to determine whether or not they are accurate by reading the text.
To answer this type of question, you can use the following strategies:
- Read the question and identify the keywords – Before reading the material, have a look at your list of True, False, and Not Given questions.
- Scan the passage for synonyms or paraphrased words of the keywords – When you have highlighted the keywords, swiftly read the text to look for paraphrases or synonyms.
- Match the highlighted words in the questions with their synonyms in the text – Once you find both sets of keywords, cross-check them to find the answer.
Identify the answer – If the facts match, the answer is TRUE, and in case it doesn’t match, it is FALSE. If you are unable to find the answer or unsure of it, mark it NOT GIVEN.
Great work on attempting to solve the ‘Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website’ IELTS reading passage! To crack your IELTS Reading in the first go, try solving more of the Recent IELTS Reading Passages.
Also, check :
- In Praise Of Amateurs IELTS Reading Answers
- The True Cost Of Food Reading Answers
- Climate Change And The Inuit Reading Answers
- Zoo Conservation Programmes Reading Answers
- A Workaholic Economy Reading Answers
Practice IELTS Reading based on question types

Start Preparing for IELTS: Get Your 10-Day Study Plan Today!
Smruti is a passionate and highly skilled content writer working in this field for the past 2 years. She is known for her ability to craft compelling and engaging content. With a keen eye for detail and a deep love for words, Smruti has expertized herself with the latest industry trends. Her commitment to producing high-quality content that resonates with audiences is highly valued.
Explore other Reading Actual Tests

Nehasri Ravishenbagam

Post your Comments
Recent articles.

Raajdeep Saha

Kasturika Samanta

Our Offices
Gurgaon city scape, gurgaon bptp.
Step 1 of 3
Great going .
Get a free session from trainer
Have you taken test before?
Please select any option
Get free eBook to excel in test
Please enter Email ID
Get support from an Band 9 trainer
Please enter phone number
Already Registered?
Select a date
Please select a date
Select a time (IST Time Zone)
Please select a time
Mark Your Calendar: Free Session with Expert on
Which exam are you preparing?
Great Going!
Case Study: Tourism New Zealand Website Answers
IELTS Academic Test – Passage 01: Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website reading with answers explanation, location and pdf. This reading paragraph has been taken from our huge collection of Academic & General Training (GT) Reading practice test PDF’s.

Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website
New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product, and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places and the experiences. In 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism services to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme whereby organisations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travellers devise their own customised itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
Later a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ : paces or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organisations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travellers enjoy such earning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with a reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere-the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
Questions 1-7
Complete the table below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer. Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
Questions 8-13
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1? In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information FALSE if the statement contradicts the information NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8. The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
9. It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
10. According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
11. Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture.
12. Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
13. Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
________________
1) IELTS 13 READING PASSAGE – WHY BEING BORED IS STIMULATING ↗
2) IELTS 13 READING PASSAGE – ARTIFICIAL ARTISTS ↗
3) IELTS 13 READING PASSAGE – BRINGING CINNAMON TO EUROPE ↗
4) IELTS 13 READING PASSAGE – OXYTOCIN ↗
5) IELTS 13 READING PASSAGE – MAKING THE MOST OF TRENDS ↗
Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website Answers
Check out Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website reading answers below with explanations and locations given in the text.
- ENVIRONMENT
- ACCOMMODATION
If you want the pdf summary of Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website reading passage and answers, please write your email in the comment section below. We’ll send it across at the speed of light.

ALL THE BEST !
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
IELTS TEST TYPES
✓ IELTS Academic
✓ IELTS General Training
USEFUL LINKS
✓ IELTS Full Form
✓ IELTS Band Score
✓ IELTS Vocabulary
✓ IELTS Grammar
CONNECT WITH US
Pinterest ↗
IELTS® is a registered trademark of The British Council, IDP- IELTS Australia and the University of Cambridge ESOL Examinations (Cambridge ESOL). This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, IELTS Progress Check, and IDP Education Australia. "IELTS Progress Check" is the name of the official IELTS online practice test and is in no way affiliated with this website. To find out more about the official IELTS online practice test please visit https://www.ieltsprogresscheck.com/.
ABOUT US | PRIVACY POLICY | DISCLAIMER | TERMS | CONTACT US
© 2023 IELTSPROGRESS.COM | All Rights Reserved
‘Case study: Tourism New Zealand website’- Reading Answer Explanation- CAM- 13

Here are explanations of the Questions of passage named ‘Case study: Tourism New Zealand website’, which is from the Cambridge 13 book. The Questions that have been asked are True/False/Not Given and Blanks. You will find the locations of the Reading Answers, Keywords( highlighted and underlined) and justifications.
READING PASSAGE 1: Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website
Questions 1-7
Complete the table below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
Questions 8-13
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8 The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
Location: 6 th paragraph
Explanation: The main keyword ‘ready-made itineraries’ helps to locate the answer in the first line of the paragraph. ‘The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organisations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests…’The question statement contradicts the passage statement. ‘Create itineraries’ is opposite to the ‘ready-made itineraries’. Thus, the answer is very clear.
Answer: False
9 It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
Explanation: The answer to this question is in the second line of the passage. ‘Visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity…’Here, the writer does not give information about the starting of search. Hence, no information available.
Answer: Not Given
10 According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
Explanation: The main keyword ‘visitor satisfaction’ is in the fourth line of the paragraph. ‘Visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%…’Here, transportation and accommodation account for 26%.But in question statement 26% accounts for accommodation only. Thus, the answer is False.
11 Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture. Location: 6 th paragraph
Explanation: The location of the answer is in the middle line of the paragraph. ‘It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive…’Here, ‘like to become involved in’ is visible as ‘enjoy cultural activities…’Thus, the answer is clear.
Answer: True
12 Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
Location: Last paragraph
Explanation: Though the writer talks about the visitors in New Zealand. But there is no information regarding hotels in the New Zealand. Thus, no information available.
13 Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
Explanation: The location of the answer is in the second last line of the paragraph. ‘Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit…’Here, ‘often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit…’ makes it clear that there is less possibility that they will return. Thus, the answer is True.
‘About Marine debris or ocean trash’- Reading Answers Explanation- CAM -14
Canada Study Visa Fraud 2023!! Girl to be Deported due to fake offer letter… Click here
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You cannot copy content of this page
Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content

Reading Actual Tests
Download PDF ielts reading test
Listening Recent Tests
Download PDF ielts listening test
english-practice.net
Practice English Exercises to Improve Your Skills
english-exercises.net
Practice More English Exercises to Improve Your Skills
englishpracticetest.net
Practice More English Tests to Improve Your Skills
Cambridge Practice Test
Practice Cam Listening Test with Answer & Transcript
Listening Practice Test
Practice Listening Test with Answer & Transcript
Practice Cambridge Reading Test with Answer
Practice Reading Test
Practice Reading Test with Answer
Practice Reading Mock Test with Answer
Speaking Practice Test
Speaking Practice Test with with Band 8-9 Samples
42 Common Topics for ielts Speaking Part 1
100 TOPICS for ielts Speaking Part 2 with Band 8 Sample
70 TOPICS for ielts Speaking Part 2 with Band 8+ Sample Recordings
Vocabulary Words
Most Common Vocabulary Topics for ielts Speaking
Writing Practice Test
Writing Practice Test with Band 8-9 Samples
Writing Mock Test with Band 8-9 Samples
Writing Task 2 Topics with Band 7-8-9 Samples
General Reading Tests
Practice General Reading Test with Answer
Answers and Explanations for Cam 13 Reading Test 1
Cambridge ielts reading with explanations
Question: allowed businesses to 1……… information regularly
Key words: businesses, information, regularly
Based on the question and particularly the key words, we need to find the information about an activity that businesses usually conduct in the database section of the website. In paragraph 2, when referring to the database of tourism services, the author mentions: “because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis , the information provided remained accurate.” From this, it can be safely concluded that the activity we are looking for is updating information.
– information = details
– regularly = on a regular basis
The answer is update.
2. environment
Question: provided a country-wide evaluation of businesses, including their impact on the 2…………….
Key words: country-wide, evaluation, impact
Looking for the key words in the passage, we find them at the end of paragraph 2: “Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme whereby organisations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered”. This paragraph is all about the website, as we can see from the first sentence. All the organisations/businesses on the site were evaluated, including their impact on the environment.
– impact = effect
The answer is environment.
Question: e.g. an interview with a former sports 3………………
Key words: interview, former, sports
The answer is in paragraph 3, when the author speaks of features relating to famous people and places: “One of the most popular was an interview with the former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga”.
– sports = rugby
So, the answer is captain.
Question: an interactive tour of various locations used in 4……………
Key words: interactive, tour, locations
Remember that paragraph 3 refers to famous people and places/locations. We find the answer in the middle of paragraph 3: “Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for block buster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop”.
– tour = journey
– various = a number of
The answer is films.
Question: Information on driving routes varied depending on the 5…………..
Key words: driving routes, varied, depending on
The answer is given at the end of paragraph 3: “To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times”.
– driving = motoring
– depending on = according to
The answer is season.
6. accommodation
Question: Travel Planner: included a map showing selected places, details of public transport and local 6………………..
Key words: Travel Planner, map, public transport, local.
Travel Planner is discussed in paragraph 4: “Later, a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ places or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area”.
– local = in the area
The answer is accommodation.
Question: ‘Your Words’: travellers could send a link to their 7……………….
Key words: Your Words, travellers, send
‘Your Words’ is also referred to in paragraph 4: “The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website”.
So, anyone travelling in New Zealand could go to the website ‘Your Words’ and use the link to send a blog of their travels, to be included on the website.
– send = submit
The answer is blog.
Question: The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
Key words: ready-made, itineraries, packages, travel companies, individual tourists
At the beginning of paragraph 6, the author refers to the aim of the website, which: “…was set up to allow both individuals and travel organisations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests ”.
The website therefore was designed NOT to provide ready-made packages for travellers or for travel companies. It was designed, on the contrary, for everyone to create their own holidays, according to their own interests.
Also, in paragraph 3 it is stated that: “As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travellers devise their own customised itineraries ”.
– travel companies = travel organisations
– individual tourists = individuals/independent travellers
– ready-made # to suit their own needs and interests
Therefore, the statement is FALSE.
9. NOT GIVEN
Question: It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
Key words: visitors, started searching, geographical location
As many paragraphs discuss the website, finding the correct place in the passage is not easy. However, in paragraph 6, we find: “On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity”. Two pieces of information are not given – we don’t know if visitors started searching on the website by geographical location. We only know that visitors can use the website to search by geographical location if they wish. Secondly, we don’t know what most visitors did when they entered the website.
So, the answer is NOT GIVEN.
Question: According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation
Key words: research, 26%, satisfaction, accommodation
Percentages are only given in paragraphs 5 and 6, so it is not difficult to find the information in paragraph 6: “… research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26% ”.
The figure of 26% refers to those visitors who say they are satisfied with the transport or with their accommodation. This percentage does NOT refer to accommodation alone, so we cannot say that 26% of visitor satisfaction is related only to their accommodation – some of this proportion will relate to transport.
For this reason, the statement is FALSE.
Question: Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture
Key words: visitors, involved, local culture
We find the answer in paragraph 6 again: “It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive , such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life”.
– like = enjoy
– become involved in = interactive
The statement is TRUE.
12. NOT GIVEN
Question: Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones
Key words: visitors like, small hotels, larger
Looking for one of the key words – ‘hotels’ – this is not mentioned in any of the paragraphs. Accommodation is referred to in paragraph 6 and ‘the smallest bed and breakfast’ is mentioned in paragraph 2, but there is nothing to refer to the statement in the question.
The answer is NOT GIVEN .
Question: Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit
Key words: visitors, unlikely, return
In the final paragraph, we find: “Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit ”.
To reach New Zealand, a long flight is usually necessary, so people often visit only once. They stay for an average of 20 days, and they try to see as much as they can, because they may not visit again.
– unlikely that they will return = a once-in-a-lifetime visit.
So, the statement is TRUE.
Paragraph A.
In this paragraph the author introduces the subject of boredom, indicating that: “…defining boredom so that it can be studied in the lab has proved difficult ”. Defining an object to be studied, and then studying it in the laboratory/lab are both elements of a scientific approach, but there are problems. It is difficult. So, the correct heading is: ‘problems with a scientific approach to boredom’.
– problems ~ difficult
Paragraph B.
In the first sentence of Paragraph B, the author states: “By asking people about their experiences of boredom, Thomas Goetz and his team at the University of Konstanz in Germany have recently identified five distinct types : indifferent, calibrating, searching, reactant and apathetic”. The system used by the researchers to measure these types is then described. A two-axes chart is used to arrange the types, with one axis recording level of arousal and the other axis recording positive or negative feelings . So, the main idea of Paragraph B is ‘creating a system of classification for feelings of boredom’.
Paragraph C.
This paragraph is about the positive aspects of boredom. The findings of the psychologist Sandi Mann are discussed: “ Mann has found that being bored makes us more creative. ‘We’re all afraid of being bored but in actual fact it can lead to all kinds of amazing things’ , she says. So, the correct heading is: ‘The productive outcomes that may result from boredom’.
Paragraph D.
In contrast, psychologist John Eastwood considers that boredom is negative: “In my view, by definition boredom is an undesirable state ’. The paragraph continues: “For Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is a failure to put our ‘attention system’ into gear……Perhaps most worryingly , says Eastwood, repeatedly failing to engage attention can lead to a state where we don’t know what to do any more, and no longer care ”.
So, when we are bored, the biggest worry is that we may no longer pay attention or care about the things we do. The most appropriate heading is: “A potential danger arising from boredom”.
– potential = can lead to
Paragraph E.
This paragraph is about certain characteristics of personality, and how these tend to be associated with boredom. Eastwood’s team think that: “ Boredom proneness has been linked with a variety of traits. People who are motivated by pleasure seem to suffer particularly badly. Other personality traits, such as curiosity, are associated with a high boredom threshold . More evidence that boredom has detrimental effects comes from studies of people who are more or less prone to boredom”.
A link has been made, therefore, between boredom and people with certain characteristics. The correct heading is: “Identifying those most affected by boredom”.
– affected by = prone to
Paragraph F.
The author discusses psychologist Francoise Wemelsfelder’s view that: “…our over-connected lifestyles might even be a new source of boredom ”. So, we need less mental stimulation, not more, and: “…perhaps we should leave our phones alone, and use boredom to motivate us to engage with the world in a more meaningful way”.
So, this is a new explanation of one reason why we become bored, and a new cure – less stimulation – is proposed. The correct heading is: “A new explanation and a new cure for boredom”.
Peter Toohey
We can quickly find this name in Paragraph A: Toohey compares boredom with disgust, which is: “…an emotion that motivates us to stay away from certain situations. ‘If disgust protects humans from infection, boredom may protect them from infectious social situations ’, he suggests”.
Toohey’s idea is that boredom may actually protect us from bad situations or experiences.
– avoid = stay away from
– an unpleasant experience = infectious social situations
The answer is E.
Thomas Goetz
Goetz is mentioned in both Paragraph B and Paragraph E. We already know (from Q15) that Paragraph B is about the classification of types of boredom by Goetz and his team. This matches B in the list of ideas: “ Of the five types, the most damaging is ‘reactant’ boredom with its explosive combination of high arousal and negative emotion”.
So, ‘reactant’ boredom is the worst of all five types of boredom, because it is ‘the most damaging’.
– sort = type
The answer is B.
John Eastwood
Eastwood is mentioned in Paragraph D and Paragraph E. Starting to look for the answer in Paragraph D, we find a discussion of boredom as a failure to put our attention system into action: “This causes an inability to focus on anything, which makes time seem to go painfully slowly. What’s more, your efforts to improve the situation can end up making you feel worse ”.
– trying to cope with boredom = your efforts to improve the situation
– increase its negative effects = making you feel worse
The answer is D .
Francoise Wemelsfelder
Her name is mentioned in the last paragraph. She believes that: “ In modern human society there is a lot of overstimulation but still a lot of problems finding meaning ”.
Our modern lifestyles, therefore, tend to stimulate us too much, without enabling us to find any meaning for what we do.
– today = modern
The answer is A.
Question: For John Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is that people cannot 24…………., due to a failure in what he calls ‘the attention system’, and as a result they become frustrated and irritable.
Key words: Eastwood, central, failure, attention system
Using the key words, we find the answer in Paragraph D: “For Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is a failure to put our ‘attention system’ into gear. This causes an inability to focus on anything ….”
Thus, when people are bored, they are not able to focus on anything.
– as a result = causes
– cannot = inability to
The answer is focus.
25. pleasure
Question: His team suggests that those for whom 25……………. is an important aim in life may have problems in coping with boredom.
Key words: aim, problems, coping
The answer is found in Paragraph E, again using the key words. Here, it is stated that: “Boredom proneness has been linked with a variety of traits. People who are motivated by pleasure seem to suffer particularly badly ”.
So, people who are motivated by pleasure try to achieve pleasure as an important aim in life. They soon seem to get bored and have problems, suffering badly.
The answer is pleasure.
26. curiosity
Question: … whereas those who have the characteristic of 26…………….. can generally cope with it.
Key words: characteristic, cope with
In the next sentence, we learn about the people who cope well with boredom: “Other personality traits, such as curiosity , are associated with a high boredom threshold ”.
If people have a ‘high boredom threshold’, that means that they are not easily bored. These are people who have the characteristic of curiosity.
– characteristic = personality trait
The answer is curiosity.
Question: What is the writer suggesting about computer-produced works in the first paragraph?
Key words: suggest, computer-produced, works
In paragraph 1, the writer tells us about how successful works of art have been which have been produced using the computer: “ Classical music by an artificial composer has had audiences enraptured… Artworks painted by a robot have sold for thousands of dollars and been hung in prestigious galleries. And software has been built which creates art that could not have been imagined by the programmer”.
All of this indicates answer B: A great deal of progress has already been attained in this field.
The answer is B .
Question: According to Geraint Wiggins, why are many people worried by computer art?
Key words: Geraint Wiggins, worried
Looking for the key words, we find the name ‘Geraint Wiggins’ in paragraph 2. If creative acts can be translated into computer code, this means that human creativity is no longer a special quality of being human. Computers can do the same thing. “ It scares a lot of people. They are worried that it is taking something special away from what it means to be human ”. In other words, when computer art performs the same creative acts as humans, then people are worried that: ‘It undermines a fundamental human quality” – by taking away (=undermining) the unique (=special) human ability to be creative.
– worried = scared
The answer is C.
Question: What is a key difference between Aaron and the Painting Fool?
Key words: difference, Aaron, Painting Fool
Aaron is mentioned in paragraphs 3 and 4. In paragraph 3, the writer explains what Aaron is and what it can do: “It is still little more than a tool to realise the programmer’s own creative ideas”. In paragraph 4, Aaron is compared with the Painting Fool: “ Unlike earlier ‘artists’, such as Aaron, the Painting Fool only needs minimal direction and can come up with its own concepts by going online for material ”.
As a result, we are told, the Painting Fool is beginning to develop its own imagination. So, the difference is that Aaron only follows the programmer’s ideas, while the Painting Fool can create its own ideas independently, going online for material (= subject matter). The difference is ‘the source of its subject matter’
– key difference = unlike
The answer is C .
Question: What point does Simon Colton make in the fourth paragraph?
In paragraph 4, Colton’s ideas on computer-produced art are presented. “The software runs its own web searches and trawls through social media sites. It is now beginning to display a kind of imagination too, creating pictures from scratch… While some people might say they have a mechanical look, Colton argues that such reactions arise from people’s double standards towards software-produced and human-produced art ”.
If people have ‘double standards’ they have moral principles which are unfair, because they judge human art in one way and computer-produced art in a different way.
The answer is that: ‘People tend to judge computer art and human art according to different criteria (= ‘double standards’).
Question: The writer refers to the paintings of a chair as an example of computer art which…
Key words: paintings, chair, computer art
This is a tricky question, so be careful or you will end up with the wrong answer. The Painting Fools paintings of a chair are discussed at the end of paragraph 4. Here, the writer refers to ‘software bugs’ and ‘a technical glitch’. However, these problems do not necessarily have bad results. In the case of the chair paintings: “Some of the Painting Fool’s paintings of a chair came out in black and white, thanks to a technical glitch. This gives the work an eerie, ghostlike quality”.
So, these technical problems resulted in paintings of a chair which had an unexpected and ‘eerie and ghostlike quality’ – in other words they had a ‘striking’ effect on people who saw them. The paintings produced by computer art thus: “achieved a particularly striking effect”.
Question: Simon Colton says it is important to consider the long-term view when…
Key words: Simon Colton, long-term view
At the beginning of paragraph 5, we find the statement that: “ Researchers like Colton don’t believe it is right to measure machine creativity directly to that of humans ‘ who have had millennia to develop our skills ’ ”. This refers to the creativity (=artistic achievements) of computers and humans and how important it is to consider the element of time.
– long-term = millennia
Question: David Cope’s EMI software surprised people by…
Key words: Cope, EMI, surprised
In paragraph 5, David Cope and his EMI program are mentioned. His software created (=generated) music in the style of various classical composers. Then, people’s reactions are described: “Audiences were moved to tears, and EMI even fooled classical music experts into thinking they were hearing genuine Bach ”.
Thus, people were not able to distinguish between the work of a famous human classical composer and the work of the EMI program. The EMI program generated: “work that was virtually indistinguishable from that of humans”.
– surprised = moved to tears
The answer is A .
Question: Geraint Wiggins criticised Cope for not…
Key words: Wiggins, criticised Cope
We find why Wiggins criticised Cope in paragraph 5. “ Some, such as Wiggins, have blasted Cope’s work as pseudoscience, and condemned him for his deliberately vague explanation of how the software worked ”.
So, Wiggins claimed that Cope did not explain clearly (= reveal) how the software (= program) worked (= the technical details).
– criticised = blasted, condemned
The answer is E .
Question: Douglas Hofstadter claimed that EMI was…
Key words: Douglas Hofstadter, EMI
The answer can be found in paragraph 5. “ Douglas Hofstadter of Indiana University said EMI created replicas which still rely completely on the original artist’s creative impulses ”. Thus, EMI just made copies, “producing work entirely dependent on (= rely on) the imagination (= creative impulses) of its creator (= original artist)”.
Question: Audiences who had listened to EMI’s music became angry after…
Key words: audiences, EMI’s music, angry
At the end of paragraph 5, the author states that: “ When audiences found out the truth they were often outraged with Cope, and one music lover even tried to punch him ”. When they first listened to EMI’s music, people did not know that it had been produced by a computer program. When they found out (= ‘discovered’) the truth, they became angry.
– angry = outraged
The answer is G .
Question: The participants in David Moffat’s study had to assess music without…
Key words: participants, David Moffat, assess
The name David Moffat is in paragraph 6. His study is described: “ The participants weren’t told beforehand whether the tunes were composed by humans or computers, but were asked to guess , and then rate how much they liked each one”. So, listening to pieces of music, the participants in the study did not know if they were “the work of humans or software”.
– music = tunes
Question: Moffat’s research may help explain people’s reactions to EMI
Key words: Moffat, explain, reactions, EMI
At the beginning of paragraph 6, the writer asks: “…why did so many people love the music, yet recoil when they discovered how it was composed? We then learn that Moffat’s study helps to provide an answer to this question: “ A study by computer scientist David Moffat of Glasgow Caledonian University provides a clue ”.
Thus, people’s reactions to music composed by a computer required some explanation. Their reaction was either to love the music or to recoil. The study provided a clue.
– research = study
– help explain = provide a clue.
The answer is YES.
39. NOT GIVEN
Question: The non-experts in Moffat’s study all responded in a predictable way
Key words: non-experts, Moffat, predictable
Moffat asked both experts and non-experts to take part in his study by listening to six pieces of music (paragraph 6). The writer tells us that: “ People who thought the composer was a computer tended to dislike the piece more than those who believed it was human. This was true even among the experts, who might have been expected to be more objective in their analysis ”.
We learn that everyone in the study (experts and non-experts) generally disliked a piece of music more when they thought the composer was a computer. The writer was surprised that even the music experts reacted in the same way as the non-experts.
Non-experts are not mentioned again, so we don’t know if they all responded in a predictable way.
Question: Justin Kruger’s findings cast doubt on Paul Bloom’s theory about people’s prejudice towards computer art
Key words: Kruger, doubt, Bloom, prejudice
Paul Bloom and Justin Kruger are mentioned in the final paragraph. “Where does this prejudice come from? Paul Bloom of Yale University has a suggestion: he reckons part of the pleasure we get from art stems from the creative process behind the work… Meanwhile, experiments by Justin Kruger of New York University have shown that people’s enjoyment of an artwork increases if they think more time and effort was needed to create it”.
They both have theories about why people might be prejudiced against computer art. Bloom believes that people get pleasure partly from appreciating the creative process of making art. Kruger thinks that people enjoy an artwork more if they think that a lot of time and effort went into creating it.
So, Kruger’s findings do not contradict Bloom’s theory – the creative process can be appreciated because humans have spent time and effort to create a work of art.
The answer is NO.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download ebooks

Fulfilling Your Dreams
Cambridge IELTS 13 Academic Reading Test 1 Answer Key
Cambridge 13 reading test 1 answers, reading passage - 1, case study: tourism new zealand website.
Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website reading answers
- environment
- accommodation
Reading Passage - 2
Why being bored is stimulating - and useful, too.
Why being bored is stimulating - and useful, too reading answers
Reading Passage - 3
Artificial artists.
Artificial artists reading answers
Essay questions Join our one to one IELTS online classes Follow us on Instagram Essay model answers IELTS listening answer key
Note: The above content is copyrighted by Cambridge University Press and Cambridge English Language Assessment. We posted this content at the request of IELTS students.
Privacy Overview
Luyện thi IELTS – TP Vinh
CAMBRIDGE IELTS 13 – TEST 1 PASSAGE 1 – CASE STUDY: TOURISM NEW ZEALAND WEBSITE

New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product, and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places and the experiences. In 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism service to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme whereby organisations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travelers devise their own customised itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
Later, a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ places or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out to take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organisations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travelers enjoy such learning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with a reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere – the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
Questions 1-7
Complete the table below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
Questions 8-13
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8 The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
9 It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
10 According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
11 Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture.
12 Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
13 Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
Related News


CAMBRIDGE IELTS 13 – TEST 2 PASSAGE 3 – MAKING THE MOST OF TRENDS

CAMBRIDGE IELTS 13 – TEST 2 PASSAGE 2 – OXYTOCIN
You may have missed.

HỌC IELTS SPEAKING NHƯ THẾ NÀO CHO HIỆU QUẢ?

HỌC IELTS LISTENING NHƯ THẾ NÀO CHO HIỆU QUẢ?

TASK 1 WRITING – GIẢI ĐỀ THI NGÀY 15/03/2022 SAND DUNES

GIẢI ĐỀ WRITING TASK 2 – 12/03/22 – FARMING WORK AMONG YOUNG PEOPLE
- Full IELTS Practice Tests
- Practice Tests
- View Solution
Solution for: Tourism
Answer table.
Found a mistake? Let us know!
Share this Practice Test
Exam Review

Questions 1-5
Reading Passage has 6 paragraphs (A-F).
Choose the most suitable heading for each paragraph from the list of headings below.
Write the appropriate numbers ( i-ix ) in boxes 1-5 on your answer sheet Paragraph D has been done for you as an example.
NB There are more headings than paragraphs so you will not use all of them.
You may use any heading more than once .
Questions 6-10
Do the following statements agree with the views of the writer in Reading Passage? In boxes 6-10 write
YES if the statement agrees with the writer
NO if the statement contradicts the writer
NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this
Example
People who can’t afford to travel watch films and TV. Answer: NOT GIVEN
6 YES NO NOT GIVEN Tourism is a trivial subject. 6. Answer: NO Locate
7 YES NO NOT GIVEN An analysis of deviance can act as a model for the analysis of tourism. 7. Answer: YES Locate
8 YES NO NOT GIVEN Tourists usually choose to travel overseas. 8. Answer: NOT GIVEN
9 YES NO NOT GIVEN Tourists focus more on places they visit than those at home. 9. Answer: YES Locate
10 YES NO NOT GIVEN Tour operators try to cheat tourists. 10. Answer: NOT GIVEN
Questions 11-14
Chose one phrase (A-H) from the list of phrases to complete each key point below. Write the appropriate letters ( A-H ) in boxes 11-14 on your answer sheet.
The information in the completed sentences should be an accurate summary of points made by the writer.
NB There are more phrases A-H than sentences so you will not use them all. You may use any phrase more than once .
11 Our concept of tourism arises from A B C D E F G H 11. Answer: D Locate
12 The media can be used to enhance A B C D E F G H 12. Answer: B Locate
13 People view tourist landscapes in a different way from A B C D E F G H 13. Answer: F Locate
14 Group tours encourage participants to look at A B C D E F G H 14. Answer: H Locate
Other Tests
- 6 - TRUE-FALSE-NOT GIVEN
- 7 - Summary, form completion
The life and work of Marie Curie
- 0 unanswered
- 5 - YES-NO-NOT GIVEN
- 5 - Matching Information
- 4 - Sentence Completion
The psychology of innovation
- 4 - Multiple Choice
- 6 - YES-NO-NOT GIVEN
- 4 - Summary, form completion
The nature and aims of archaelogy
- 6 - Matching Headings
- 4 - Matching Information
The meaning and power of smell
- 3 - Matching Information
- 6 - Sentence Completion
Early occupations around the river Thames
- 6 - Plan, map, diagram labelling
The electric revolution
- Short Practice
Found a mistake? Let us know!
Please descibe the mistake as details as possible along with your expected correction, leave your email so we can contact with you when needed.
Describe what is wrong with the practice test:
Please enter description
Enter your name:
Enter your email address:
Please enter a valid email


Cambridge IELTS 13 Academic Reading Test 1 with Answers
Cambridge ielts 13 academic reading test 1, reading passage 1, case study: tourism new zealand website.
New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product, and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places and the experiences. In 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism service to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme whereby organisations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travelers devise their own customised itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
Later, a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ places or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out to take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organisations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travelers enjoy such learning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with a reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere – the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
Questions 1-7
Complete the table below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
Questions 8-13
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information FALSE if the statement contradicts the information NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8 The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists. 9 It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location. 10 According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation. 11 Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture. 12 Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones. 13 Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
READING PASSAGE 2
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 14-26 which are based on Reading Passage 2 below.
Why being bored is stimulating – and useful, too
This most common of emotions is turning out to be more interesting than we thought
We all know how it feels – it’s impossible to keep your mind on anything, time stretches out, and all the things you could do seem equally unlikely to make you feel better. But defining boredom so that it can be studied in the lab has proved difficult. For a start, it can include a lot of other mental states, such as frustration, apathy, depression and indifference. There isn’t even agreement over whether boredom is always a low-energy, flat kind of emotion or whether feeling agitated and restless counts as boredom, too. In his book, Boredom: A Lively History , Peter Toohey at the University of Calgary, Canada, compares it to disgust – an emotion that motivates us to stay away from certain situations. ‘If disgust protects humans from infection, boredom may protect them from “infectious” social situations,’ he suggests.
By asking people about their experiences of boredom, Thomas Goetz and his team at the University of Konstanz in Germany have recently identified five distinct types: indifferent, calibrating, searching, reactant and apathetic. These can be plotted on two axes – one running left to right, which measures low to high arousal, and the other from top to bottom, which measures how positive or negative the feeling is. Intriguingly, Goetz has found that while people experience all kinds of boredom, they tend to specialise in one. Of the five types, the most damaging is ‘reactant’ boredom with its explosive combination of high arousal and negative emotion. The most useful is what Goetz calls ‘indifferent’ boredom: someone isn’t engaged in anything satisfying but still feels relaxed and calm. However, it remains to be seen whether there are any character traits that predict the kind of boredom each of us might be prone to.
Psychologist Sandi Mann at the University of Central Lancashire, UK, goes further. ‘All emotions are there for a reason, including boredom,’ she says. Mann has found that being bored makes us more creative. ‘We’re all afraid of being bored but in actual fact it can lead to all kinds of amazing things,’ she says. In experiments published last year, Mann found that people who had been made to feel bored by copying numbers out of the phone book for 15 minutes came up with more creative ideas about how to use a polystyrene cup than a control group. Mann concluded that a passive, boring activity is best for creativity because it allows the mind to wander. In fact, she goes so far as to suggest that we should seek out more boredom in our lives.
Psychologist John Eastwood at York University in Toronto, Canada, isn’t convinced. ‘If you are in a state of mind-wandering you are not bored,’ he says. ‘In my view, by definition boredom is an undesirable state.’ That doesn’t necessarily mean that it isn’t adaptive, he adds. ‘Pain is adaptive – if we didn’t have physical pain, bad things would happen to us. Does that mean that we should actively cause pain? No. But even if boredom has evolved to help us survive, it can still be toxic if allowed to fester.’ For Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is a failure to put our ‘attention system’ into gear. This causes an inability to focus on anything, which makes time seem to go painfully slowly. What’s more, your efforts to improve the situation can end up making you feel worse. ‘People try to connect with the world and if they are not successful there’s that frustration and irritability,’ he says. Perhaps most worryingly, says Eastwood, repeatedly failing to engage attention can lead to state where we don’t know what to do any more, and no longer care.
Eastwood’s team is now trying to explore why the attention system fails. It’s early days but they think that at least some of it comes down to personality. Boredom proneness has been linked with a variety of traits. People who are motivated by pleasure seem to suffer particularly badly. Other personality traits, such as curiosity, are associated with a high boredom threshold. More evidence that boredom has detrimental effects comes from studies of people who are more or less prone to boredom. It seems those who bore easily face poorer prospects in education, their career and even life in general. But of course, boredom itself cannot kill – it’s the things we do to deal with it that may put us in danger. What can we do to alleviate it before it comes to that? Goetz’s group has one suggestion. Working with teenagers, they found that those who ‘approach’ a boring situation – in other words, see that it’s boring and get stuck in anyway – report less boredom than those who try to avoid it by using snacks, TV or social media for distraction.
Psychologist Francoise Wemelsfelder speculates that our over-connected lifestyles might even be a new source of boredom. ‘In modern human society there is a lot of overstimulation but still a lot of problems finding meaning,’ she says. So instead of seeking yet more mental stimulation, perhaps we should leave our phones alone, and use boredom to motivate us to engage with the world in a more meaningful way.
Questions 14-19
Reading Passage 2 has six paragraphs, A-F Choose the correct heading for each paragraph from the list of headings below.
Write the correct number, i-viii , in boxes 14-19 on your answer sheet.
List of Headings
i The productive outcomes that may result from boredom
ii What teachers can do to prevent boredom
iii A new explanation and a new cure for boredom
iv Problems with a scientific approach to boredom
v A potential danger arising from boredom
vi Creating a system of classification for feelings of boredom
vii Age groups most affected by boredom
viii Identifying those most affected by boredom
14 Paragraph A 15 Paragraph B 16 Paragraph C 17 Paragraph D 18 Paragraph E 19 Paragraph F
Questions 20-23
Look at the following people (Questions 20-23 ) and the list of ideas below.
Match each person with the correct idea, A-E .
Write the correct letter, A-E , in boxes 20-23 on your answer sheet.
20 Peter Toohey
21 Thomas Goetz
22 John Eastwood
23 Francoise Wemelsfelder
List of Ideas
A The way we live today may encourage boredom.
B One sort of boredom is worse than all the others.
C Levels of boredom may fall in the future.
D Trying to cope with boredom can increase its negative effects.
E Boredom may encourage us to avoid an unpleasant experience.
Questions 24-26
Complete the summary below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 24-26 on your answer sheet.
Responses to boredom
For John Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is that people cannot 24 ……………………………, due to a failure in what he calls the ‘attention system’, and as a result they become frustrated and irritable. His team suggests that those for whom 25 ……………………….. is an important aim in life may have problems in coping with boredom, whereas those who have the characteristic of 26 ……………………….. can generally cope with it.
READING PASSAGE 3
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 27-40 which are based on Reading Passage 3 below.
Artificial artist?
Can computers really create works of art?
The Painting Fool is one of a growing number of computer programs which, so their makers claim, possess creative talents. Classical music by an artificial composer has had audiences enraptured, and even tricked them into believing a human was behind the score. Artworks painted by a robot have sold for thousands of dollars and been hung in prestigious galleries. And software has been built which creates are that could not have been imagined by the programmer.
Human beings are the only species to perform sophisticated creative acts regularly. If we can break this process down into computer code, where does that leave human creativity? ‘This is a question at the very core of humanity,’ says Geraint Wiggins, a computational creativity researcher at Goldsmiths, University of London. ‘It scares a lot of people. They are worried that it is taking something special away from what it means to be human.’
To some extent, we are all familiar with computerised art. The question is: where does the work of the artist stop and the creativity of the computer begin? Consider one of the oldest machine artists, Aaron, a robot that has had paintings exhibited in London’s Tate Modern and the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art. Aaron can pick up a paintbrush and paint on canvas on its own. Impressive perhaps, but it is still little more than a tool to realise the programmer’s own creative ideas.
Simon Colton, the designer of the Painting Fool, is keen to make sure his creation doesn’t attract the same criticism. Unlike earlier ‘artists’ such as Aaron, the Painting Fool only needs minimal direction and can come up with its own concepts by going online for material. The software runs its own web searches and trawls through social media sites. It is now beginning to display a kind of imagination too, creating pictures from scratch. One of its original works is a series of fuzzy landscapes, depicting trees and sky. While some might say they have a mechanical look, Colton argues that such reactions arise from people’s double standards towards software-produced and human-produced art. After all, he says, consider that the Painting Fool painted the landscapes without referring to a photo. ‘If a child painted a new scene from its head, you’d say it has a certain level of imagination,’ he points out. ‘The same should be true of a machine.’ Software bugs can also lead to unexpected results. Some of the Painting Fool’s paintings of a chair came out in black and white, thanks to a technical glitch. This gives the work an eerie, ghostlike quality. Human artists like the renowned Ellsworth Kelly are lauded for limiting their colour palette – so why should computers be any different?
Researchers like Colton don’t believe it is right to measure machine creativity directly to that of humans who ‘have had millennia to develop our skills’. Others, though, are fascinated by the prospect that a computer might create something as original and subtle as our best artists. So far, only one has come close. Composer David Cope invented a program called Experiments in Musical Intelligence, or EMI. Not only did EMI create compositions in Cope’s style, but also that of the most revered classical composers, including Bach, Chopin and Mozart. Audiences were moved to tears, and EMI even fooled classical music experts into thinking they were hearing genuine Bach. Not everyone was impressed however. Some, such as Wiggins, have blasted Cope’s work as pseudoscience, and condemned him for his deliberately vague explanation of how the software worked. Meanwhile, Douglas Hofstadter of Indiana University said EMI created replicas which still rely completely on the original artist’s creative impulses. When audiences found out the truth they were often outraged with Cope, and one music lover even tried to punch him. Amid such controversy, Cope destroyed EMI’s vital databases.
But why did so many people love the music, yet recoil when the discovered how it was composed? A study by computer scientist David Moffat of Glasgow Caledonian University provides a clue. He asked both expert musicians and non-experts to assess six compositions. The participants weren’t told beforehand whether the tunes were composed by humans or computers, but were asked to guess, and then rate how much they liked each one. People who thought the composer was a computer tended to dislike the piece more than those who believed it was human. This was true even among the experts, who might have been expected to be more objective in their analyses.
Where does this prejudice come from? Paul Bloom of Yale University has a suggestion: he reckons part of the pleasure we get from art stems from the creative process behind the work. This can give it an ‘irresistible essence’, says Bloom. Meanwhile, experiments by Justin Kruger of New York University have shown that people’s enjoyment of an artwork increases if they think more time and effort was needed to create it. Similarly, Colton thinks that when people experience art, they wonder what the artist might have been thinking or what the artist is trying to tell them. It seems obvious, therefore, that with computers producing art, this speculation is cut short – there’s nothing to explore. But as technology becomes increasingly complex, finding those greater depths in computer art could become possible. This is precisely why Colton asks the Painting Fool to tap into online social networks for its inspiration: hopefully this way it will choose themes that will already be meaningful to us.
Questions 27-31
Choose the correct letter, A , B , C or D .
Write the correct letter in boxes 27-31 on your answer sheet.
27 What is the writer suggesting about computer-produced works in the first paragraph?
A People’s acceptance of them can vary considerably. B A great deal of progress has already been attained in this field. C They have had more success in some artistic genres than in others. D the advances are not as significant as the public believes them to be.
28 According to Geraint Wiggins, why are many people worried by computer art?
A It is aesthetically inferior to human art. B It may ultimately supersede human art. C It undermines a fundamental human quality. D It will lead to a deterioration in human ability.
29 What is a key difference between Aaron and the Painting Fool?
A its programmer’s background B public response to its work C the source of its subject matter D the technical standard of its output
30 What point does Simon Colton make in the fourth paragraph?
A Software-produced art is often dismissed as childish and simplistic. B The same concepts of creativity should not be applied to all forms of art. C It is unreasonable to expect a machine to be as imaginative as a human being. D People tend to judge computer art and human art according to different criteria.
31 The writer refers to the paintings of a chair as an example of computer art which
A achieves a particularly striking effect. B exhibits a certain level of genuine artistic skill. C closely resembles that of a well-known artist. D highlights the technical limitations of the software.
Questions 32-37
Complete each sentence with the correct ending, A-G below.
Write the correct letter, A-G , in boxes 32-37 on your answer sheet.
32 Simon Colton says it is important to consider the long-term view then
33 David Cope’s EMI software surprised people by
34 Geraint Wiggins criticized Cope for not
35 Douglas Hofstadter claimed that EMI was
36 Audiences who had listened to EMI’s music became angry after
37 The participants in David Moffat’s study had to assess music without
A generating work that was virtually indistinguishable from that of humans.
B knowing whether it was the work of humans or software.
C producing work entirely dependent on the imagination of its creator.
D comparing the artistic achievements of humans and computers.
E revealing the technical details of his program.
F persuading the public to appreciate computer art.
G discovering that it was the product of a computer program
Questions 38-40
Do the following statements agree with the claims of the writer in Reading Passage 3?
In boxes 38-40 on your answer sheet, write
YES if the statement agrees with the claims of the writer NO if the statement contradicts the claims of the writer NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this
38 Moffat’s research may help explain people’s reactions to EMI.
39 The non-experts in Moffat’s study all responded in a predictable way.
40 Justin Kruger’s findings cast doubt on Paul Bloom’s theory about people’s prejudice towards computer art.
Cambridge IELTS 13 Academic Reading Test 1 Answers
1. update 2. environment 3. captain 4. films 5. season 6. accommodation 7. blog 8. FALSE 9. NOT GIVEN 10. FALSE 11. TRUE 12. NOT GIVEN 13. TRUE 14. iv 15. vi 16. i 17. v 18. viii 19. iii 20. E
Practice with Expert IELTS Tutors Online
Apply Code "IELTSXPRESS20" To Get 20% off on IELTS Mock Test
Also Check: Cambridge IELTS 14 Academic Reading Test 4 with Answers
Practice: Practice Cambridge IELTS 4 Listening Test 4 with Answers ca
Oh hi there! It’s nice to meet you.
Sign up to receive awesome content in your inbox, every week.
We promise not to spam you or share your Data. 🙂
Check your inbox or spam folder to confirm your subscription.
Oh Hi there! It’s nice to meet you.
We promise not to Spam or Share your Data. 🙂
Related Posts

Pacific Navigation and Voyaging IELTS Reading

The Accidental Scientists IELTS Reading with Answers

Cambridge IELTS 18 Academic Reading Test 4
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Yes, add me to your mailing list
Start typing and press enter to search
Case study tourism New Zealand website Reading Ielts Answers and Questions
The Blog post contains the following IELTS Reading Questions
Stay informed and prepared for success – Explore our comprehensive Reading Test Info page to get valuable insights, exam format details, and expert tips for mastering the IELTS Reading section .
- IELTS Reading True/False/Not given

Case study tourism New Zealand website
New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places and the experiences. In 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism services to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organized a scheme whereby organizations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travelers devise their own customized itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site cataloged the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
Later, a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ places or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out to take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog about their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly, perhaps, the growth of tourism in New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organizations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travelers enjoy such learning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with a reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere – the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
Unlock your full potential in the IELTS Reading section – Visit our IELTS Reading Practice Question Answer page now!
Recommended Questions:
Renewable Energy IELTS Reading Question with Answer
Questions 1-7
- Complete the table below.
- Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
- Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
Questions 8-13
- Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
- In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
- TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
- FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
- NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8 . The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
9. It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
10. According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
11. Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture.
12. Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
13. Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
Enhance your skills in identifying information as True, False, or Not Given . Click here to discover expert strategies and techniques for mastering this question type in the IELTS Reading section.
Answers for case study tourism New Zealand
1. Answer: Update
2. Answer: Environment
3. Answer:Captain
4. Answer: Flims
5. Answer: Seasons
6. Answer: Accommodation
7. Answer: Blog
8. Answer: False
9. Answer: Not given
10. Answer: False
11. Answer: True
12. Answer: Not given
13. Answer: True
We hope you found this post useful in helping you to study for the IELTS Test . If you have any questions please let us know in the comments below or on the Facebook page.
The best way to keep up to date with posts like this is to like us on Facebook , then follow us on Instagram and Pinterest . If you need help preparing for the IELTS Test, join the IELTS Achieve Academy and see how we can assist you to achieve your desired band score. We offer an essay correction service, mock exams and online courses.
Related Posts

Essay on Importance of English language Reading Questions and Answers
IELTS Reading passage – Essay on Importance of English language Essay on Importance of English…

Keep taking the tablets Reading Ielts Answers and Questions
The Blog post contains the following IELTS Reading Questions: Keep Taking the Tablets Reading Passage …

Ielts Reading-Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website | IELTS reading Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website with answers
by Navita Thakur | Apr 8, 2020

You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 1-13 which are based on Reading Passage 1 below.
READING PASSAGE 1 – Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website

New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabita nts, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product, and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places and the experiences. In 1999 , Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism service to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme whereby organisations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travelers devise their own customised itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
Later, a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ places or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out to take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organisations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travelers enjoy such learning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with a reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere – the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 14-26 which are based on Reading Passage 2 below.
READING PASSAGE 2 – Why being bored is stimulating – and useful, too

This most common of emotions is turning out to be more interesting than we thought
We all know how it feels – it’s impossible to keep your mind on anything, time stretches out, and all the things you could do seem equally unlikely to make you feel better. But defining boredom so that it can be studied in the lab has proved difficult. For a start, it can include a lot of other mental states, such as frustration, apathy, depression and indifference. There isn’t even agreement over whether boredom is always a low-energy, flat kind of emotion or whether feeling agitated and restless counts as boredom, too. In his book, Boredom: A Lively History , Peter Toohey at the University of Calgary, Canada, compares it to disgust – an emotion that motivates us to stay away from certain situations. ‘If disgust protects humans from infection, boredom may protect them from “infectious” social situations,’ he suggests.
By asking people about their experiences of boredom, Thomas Goetz and his team at the University of Konstanz in Germany have recently identified five distinct types: indifferent, calibrating, searching, reactant and apathetic. These can be plotted on two axes – one running left to right, which measures low to high arousal, and the other from top to bottom, which measures how positive or negative the feeling is. Intriguingly, Goetz has found that while people experience all kinds of boredom, they tend to specialise in one. Of the five types, the most damaging is ‘reactant’ boredom with its explosive combination of high arousal and negative emotion. The most useful is what Goetz calls ‘indifferent’ boredom: someone isn’t engaged in anything satisfying but still feels relaxed and calm. However, it remains to be seen whether there are any character traits that predict the kind of boredom each of us might be prone to.
Psychologist Sandi Mann at the University of Central Lancashire, UK, goes further. ‘All emotions are there for a reason, including boredom,’ she says. Mann has found that being bored makes us more creative. ‘We’re all afraid of being bored but in actual fact it can lead to all kinds of amazing things,’ she says. In experiments published last year, Mann found that people who had been made to feel bored by copying numbers out of the phone book for 15 minutes came up with more creative ideas about how to use a polystyrene cup than a control group. Mann concluded that a passive, boring activity is best for creativity because it allows the mind to wander. In fact, she goes so far as to suggest that we should seek out more boredom in our lives.
Psychologist John Eastwood at York University in Toronto, Canada, isn’t convinced. ‘If you are in a state of mind-wandering you are not bored,’ he says. ‘In my view, by definition boredom is an undesirable state.’ That doesn’t necessarily mean that it isn’t adaptive, he adds. ‘Pain is adaptive – if we didn’t have physical pain, bad things would happen to us. Does that mean that we should actively cause pain? No. But even if boredom has evolved to help us survive, it can still be toxic if allowed to fester.’ For Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is a failure to put our ‘attention system’ into gear. This causes an inability to focus on anything, which makes time seem to go painfully slowly. What’s more, your efforts to improve the situation can end up making you feel worse. ‘People try to connect with the world and if they are not successful there’s that frustration and irritability,’ he says. Perhaps most worryingly, says Eastwood, repeatedly failing to engage attention can lead to state where we don’t know what to do any more, and no longer care.
Eastwood’s team is now trying to explore why the attention system fails. It’s early days but they think that at least some of it comes down to personality. Boredom proneness has been linked with a variety of traits. People who are motivated by pleasure seem to suffer particularly badly. Other personality traits, such as curiosity, are associated with a high boredom threshold. More evidence that boredom has detrimental effects comes from studies of people who are more or less prone to boredom. It seems those who bore easily face poorer prospects in education, their career and even life in general. But of course, boredom itself cannot kill – it’s the things we do to deal with it that may put us in danger. What can we do to alleviate it before it comes to that? Goetz’s group has one suggestion. Working with teenagers, they found that those who ‘approach’ a boring situation – in other words, see that it’s boring and get stuck in anyway – report less boredom than those who try to avoid it by using snacks, TV or social media for distraction.
Psychologist Francoise Wemelsfelder speculates that our over-connected lifestyles might even be a new source of boredom. ‘In modern human society there is a lot of overstimulation but still a lot of problems finding meaning,’ she says. So instead of seeking yet more mental stimulation, perhaps we should leave our phones alone, and use boredom to motivate us to engage with the world in a more meaningful way.
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 27-40 which are based on Reading Passage 3 below.
READING PASSAGE 3 – Artificial artist?

Can computers really create works of art?
The Painting Fool is one of a growing number of computer programs which, so their makers claim, possess creative talents. Classical music by an artificial composer has had audiences enraptured, and even tricked them into believing a human was behind the score. Artworks painted by a robot have sold for thousands of dollars and been hung in prestigious galleries. And software has been built which creates are that could not have been imagined by the programmer.
Human beings are the only species to perform sophisticated creative acts regularly. If we can break this process down into computer code, where does that leave human creativity? ‘This is a question at the very core of humanity,’ says Geraint Wiggins, a computational creativity researcher at Goldsmiths, University of London. ‘It scares a lot of people. They are worried that it is taking something special away from what it means to be human.’
To some extent, we are all familiar with computerised art. The question is: where does the work of the artist stop and the creativity of the computer begin? Consider one of the oldest machine artists, Aaron, a robot that has had paintings exhibited in London’s Tate Modern and the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art. Aaron can pick up a paintbrush and paint on canvas on its own. Impressive perhaps, but it is still little more than a tool to realise the programmer’s own creative ideas.
Simon Colton, the designer of the Painting Fool, is keen to make sure his creation doesn’t attract the same criticism. Unlike earlier ‘artists’ such as Aaron, the Painting Fool only needs minimal direction and can come up with its own concepts by going online for material. The software runs its own web searches and trawls through social media sites. It is now beginning to display a kind of imagination too, creating pictures from scratch. One of its original works is a series of fuzzy landscapes, depicting trees and sky. While some might say they have a mechanical look, Colton argues that such reactions arise from people’s double standards towards software-produced and human-produced art. After all, he says, consider that the Painting Fool painted the landscapes without referring to a photo. ‘If a child painted a new scene from its head, you’d say it has a certain level of imagination,’ he points out. ‘The same should be true of a machine.’ Software bugs can also lead to unexpected results. Some of the Painting Fool’s paintings of a chair came out in black and white, thanks to a technical glitch. This gives the work an eerie, ghostlike quality. Human artists like the renowned Ellsworth Kelly are lauded for limiting their colour palette – so why should computers be any different?
Researchers like Colton don’t believe it is right to measure machine creativity directly to that of humans who ‘have had millennia to develop our skills’. Others, though, are fascinated by the prospect that a computer might create something as original and subtle as our best artists. So far, only one has come close. Composer David Cope invented a program called Experiments in Musical Intelligence, or EMI. Not only did EMI create compositions in Cope’s style, but also that of the most revered classical composers, including Bach, Chopin and Mozart. Audiences were moved to tears, and EMI even fooled classical music experts into thinking they were hearing genuine Bach. Not everyone was impressed however. Some, such as Wiggins, have blasted Cope’s work as pseudoscience, and condemned him for his deliberately vague explanation of how the software worked. Meanwhile, Douglas Hofstadter of Indiana University said EMI created replicas which still rely completely on the original artist’s creative impulses. When audiences found out the truth they were often outraged with Cope, and one music lover even tried to punch him. Amid such controversy, Cope destroyed EMI’s vital databases.
But why did so many people love the music, yet recoil when the discovered how it was composed? A study by computer scientist David Moffat of Glasgow Caledonian University provides a clue. He asked both expert musicians and non-experts to assess six compositions. The participants weren’t told beforehand whether the tunes were composed by humans or computers, but were asked to guess, and then rate how much they liked each one. People who thought the composer was a computer tended to dislike the piece more than those who believed it was human. This was true even among the experts, who might have been expected to be more objective in their analyses.
Where does this prejudice come from? Paul Bloom of Yale University has a suggestion: he reckons part of the pleasure we get from art stems from the creative process behind the work. This can give it an ‘irresistible essence’, says Bloom. Meanwhile, experiments by Justin Kruger of New York University have shown that people’s enjoyment of an artwork increases if they think more time and effort was needed to create it. Similarly, Colton thinks that when people experience art, they wonder what the artist might have been thinking or what the artist is trying to tell them. It seems obvious, therefore, that with computers producing art, this speculation is cut short – there’s nothing to explore. But as technology becomes increasingly complex, finding those greater depths in computer art could become possible. This is precisely why Colton asks the Painting Fool to tap into online social networks for its inspiration: hopefully this way it will choose themes that will already be meaningful to us.
Your email address:
Happy Reading!!!

बंद करने के लिए ESC दबाएँ

पर्यटन न्यूज़ीलैंड वेबसाइट केस स्टडी उत्तर पढ़ना: अपनी आईईएलटीएस तैयारी को बढ़ावा देने का तरीका
For now, we have talked a lot about the speaking & listening sections of the IELTS examination. Today, let’s move forward to know more about the IELTS reading section.
The आईईएलटीएस पढ़ना section is an extremely important yet tough exams but it is not possible for one to not crack it in time. All you need is the right reading practice and by that we mean, a lot of it to make sure that you do not cease anywhere while you’re giving the exam during the final attempt. Along with this, you need to tackle a lot of reading passage’s questions and increase your difficulty level every day to make sure that you are easily able to solve all these questions, no matter what type or any sort of questions you’re presented with.
So, today let’s move forward to know more about it.
Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website Reading Answers
The IELTS reading passage topic: Tourism New Zealand Website” is a very common yet interesting topic in the IELTS examination. In the sections below, this topic is divided into different parts to help you practice in a better yet easy manner for this passage.
पर्यटन New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Answers: Part 1
New Zealand is a small country with a minimum of just four million inhabitants that are spread across the country in a peaceful manner.
Currently, the total GDP of the country has the highest percentage of tourism in it. Tourism contributes to making up to 9% of this country’s GDP and is the largest export sector of the country. Unlike all the other export sectors, tourism is one such sector in this country which helps to bring a lot of its customers to this country. And while we talk about the other products of this country – they are just people, places, and the experiences that are taken out of it.
In the year 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a great campaign which was there to help communicate a new brand position to the world. This campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, its exhilarating outdoor activities and the authentic Maori culture that is being followed here which helps in making it the most powerful yet the strongest brands in the world.
यह भी पढ़ें एक अच्छा आईईएलटीएस स्कोर क्या है? क्या 7.5 एक अच्छा आईईएलटीएस स्कोर है? यहां वह सब कुछ है जो आपको जानना आवश्यक है

पर्यटन New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Answers: Part 2
A key feature of this campaign was the website that was launched during this period for this country, www.newzealand.com. This website helped in providing great potential visitors to the country with a single gateway to each and everything that the destination had to offer to its people.
But the heart of the business is the database of tourism services operators, both of which are based in New Zealand as well as abroad which helps in providing great tourism services to the country. So, any tourism-related form can be filled easily without taking anybody’s help at all. Further, to maintain the standards and improve them, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme with the help of which organisations that appear on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of the national standards of quality that they all agreed on. And due to this, the effect it had on each of the businesses was considered too.
पर्यटन New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Answers: Part 3
Further, to communicate the New Zealand experience, this site also carried forward various features related to the famous people and places which was one of the most popular interviews that this country had with the former New Zealand All Blacks Rugby Captain “Tana Umaga.”
Another such feature that helped in increasing a lot of attention towards his country is through the help of those blockbuster films that were made here which helps in providing people with an interactive journey through a number of some amazing yet extremely beautiful locations.
A Travel Planner feature was also added to this list which helped the visitors to click and bookmark the places of attraction for them so that when they visit this country, they’ll have a long list of places to roam around. This planner also helps in suggesting routes and public transport options to the readers in order to easily choose between the locations that they have chosen for them.
यह भी पढ़ें: एक सितारे का जीवन चक्र: एक आईईएलटीएस रीडिंग उत्तर विषय जिसमें हल किए गए प्रश्न शामिल हैं
पर्यटन New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Answers: Part 4
New Zealand is not just any typical destination where people could come and roam around; it’s an emotion, a feeling for all those four million people residing here. New Zealand is just a small & pretty country with little less population in it and it creates a visitor economy for the tourists which is generally composed of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with reliable transport infrastructure. And because of the long-haul flights, most visitors have to stay for a long period of time in this country, let’s say, for about a period of 20 days so that they can see as much of the country as is possible for them on a one-time long visit to this country.
पर्यटन New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Questions
Complete the table below.
Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
#1. Easy for Tourism-related business to get on the list
#2. Allowed businesses to _____________ information regularly
#3. Provided a countrywide evaluation of businesses, including their impact on the _________________
#4. Special features on local topics
Example – an interview with a former sports _________________, and an interactive tour of various locations used in ____________________________
#5. Information on driving routes that varied depending on the ___________________________
#6. Travel Planner • included a map showing selected places, details of public transport and local ________________
#7. ‘Your Words’ • travelers could send a link to their ________________________
#2. Environment
#3. Captain
#6. Accommodation
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, mention
TRUE – if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE – if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN – if there is no information on this
#8. The website “ www.newzealand.com ” created by the tourism department of New Zealand has been aiming to provide some great deals, itineraries, and good-deal packages for the travel companies as well as for all those travel enthusiasts.
#9. Many of the visitors out of these were found to be searching for the information that they want on the official website by the geographical location of the area.
#10. According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
#11. Many-a-times, it has been noticed that many of the visitors to this country become more involved in the local culture of the country and enjoy it a lot.
#12. Many visitors like staying in small hotels as they like the vibe of such hotels a lot rather than those big, grand, and new ones recently built in the country.
#13. Visitors feel it unlikely to return to the country after their first visit here.
#9. Not Given
#12. Not Given
आईईएलटीएस Preparation Tips: Reading Section
#1.the two “s”.
By the two S here, we mean Skimming and Scanning, that is to skim and scan the lines of the passage. This requires an individual to go through the reading passage in order to get a general understanding of the content and what could be the answers to the questions that follow behind it.
#2.Good Reading Speed
While practising for the IELTS reading section, an individual is asked to read as many passages as he/she can in order to increase their reading speed. This can further help an individual a lot in the future.
#3.Don’t Understand the Full Passage
While sitting in the exam hall, the aim of an individual should not be to understand the entire passage completely because this will put the ability to answer the questions in a timely manner to the test. And after all, your only aim should be to just find the correct answers to the questions.
After reading the above paragraph, we hope that you might have understood it well and have got an idea of how you can further solve the questions related to it or find out the different answers for the various questions being provided. If you have any doubts in your mind regarding the same, just feel free to comment down below and let us know all about it so that we can help you with that in the future because we’ll be more than happy to help you out through this.
Also, if you want more help in any of these reading passages, don’t forget to just check out our other blogs that will help you with the same.
यह भी पढ़ें: पुरातत्व की प्रकृति और उद्देश्य: आईईएलटीएस रीडिंग टेस्ट के लिए रीडिंग उत्तर खोजें

helped alott
प्रातिक्रिया दे जवाब रद्द करें

आलेख साझा करें:
लेखक के बारे में
साक्षी बचानी.
साक्षी बचानी एक फ्रीलांस कंटेंट राइटर और टीचर हैं। उन्होंने दिल्ली विश्वविद्यालय से स्नातक की डिग्री पूरी की है। वह पिछले पांच वर्षों से एक स्वतंत्र शिक्षिका हैं और उन्होंने छोटे बच्चों को उनके सपने हासिल करने में मदद करने की दिशा में काम किया है। उन्होंने एक एनजीओ के साथ इंटर्न टीचर के तौर पर भी काम किया था। लिखने और पढ़ाने के अलावा, वह वास्तव में संगीत, जानवरों और पौधों का आनंद लेती हैं। उसका अपना छोटा सा बगीचा भी है जिसे वह बहुत प्यार करती है और कभी-कभी उसे अपने लिए और पौधे खरीदते हुए भी देखा जा सकता है।
आप इसे भी पसंद कर सकते हैं

माइट हार्वेस्टमेन उत्तर पढ़ना: आइए आईईएलटीएस मॉक टेस्ट और आईईएलटीएस अभ्यास टेस्ट के साथ तैयारी करें!

उत्तर पढ़ने वाले चींटियों के नमूने एकत्र करना: आइए आईईएलटीएस परीक्षा में सफल होने की तैयारी करें

जैविक खेती और रासायनिक उर्वरक उत्तर पढ़ना: आइए आईईएलटीएस परीक्षा में अच्छा स्कोर करें!
अन्य कहानियाँ, क्या आईईएलटीएस स्पीकिंग टेस्ट आमने-सामने है यहां बताया गया है कि आप इसमें कैसे सफल हो सकते हैं और 8+ बैंड स्कोर हासिल कर सकते हैं, ऊबना क्यों उत्तेजक और उपयोगी भी है आईईएलटीएस उत्तर पढ़ना.

free ielts tests - online simulation - practice with solution
Cambridge 13 IELTS Academic Reading Test 1
READING PASSAGE 1
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 1-13 which are based on Reading Passage 1 below.
Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website
New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product, and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places and the experiences. In 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism service to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme whereby organisations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travelers devise their own customised itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
Later, a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ places or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out to take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organisations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travelers enjoy such learning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with a reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere – the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
READING PASSAGE 2
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 14-26 which are based on Reading Passage 2 below.
Why being bored is stimulating – and useful, too
This most common of emotions is turning out to be more interesting than we thought
We all know how it feels – it’s impossible to keep your mind on anything, time stretches out, and all the things you could do seem equally unlikely to make you feel better. But defining boredom so that it can be studied in the lab has proved difficult. For a start, it can include a lot of other mental states, such as frustration, apathy, depression and indifference. There isn’t even agreement over whether boredom is always a low-energy, flat kind of emotion or whether feeling agitated and restless counts as boredom, too. In his book, Boredom: A Lively History , Peter Toohey at the University of Calgary, Canada, compares it to disgust – an emotion that motivates us to stay away from certain situations. ‘If disgust protects humans from infection, boredom may protect them from “infectious” social situations,’ he suggests.
By asking people about their experiences of boredom, Thomas Goetz and his team at the University of Konstanz in Germany have recently identified five distinct types: indifferent, calibrating, searching, reactant and apathetic. These can be plotted on two axes – one running left to right, which measures low to high arousal, and the other from top to bottom, which measures how positive or negative the feeling is. Intriguingly, Goetz has found that while people experience all kinds of boredom, they tend to specialise in one. Of the five types, the most damaging is ‘reactant’ boredom with its explosive combination of high arousal and negative emotion. The most useful is what Goetz calls ‘indifferent’ boredom: someone isn’t engaged in anything satisfying but still feels relaxed and calm. However, it remains to be seen whether there are any character traits that predict the kind of boredom each of us might be prone to.
Psychologist Sandi Mann at the University of Central Lancashire, UK, goes further. ‘All emotions are there for a reason, including boredom,’ she says. Mann has found that being bored makes us more creative. ‘We’re all afraid of being bored but in actual fact it can lead to all kinds of amazing things,’ she says. In experiments published last year, Mann found that people who had been made to feel bored by copying numbers out of the phone book for 15 minutes came up with more creative ideas about how to use a polystyrene cup than a control group. Mann concluded that a passive, boring activity is best for creativity because it allows the mind to wander. In fact, she goes so far as to suggest that we should seek out more boredom in our lives.
Psychologist John Eastwood at York University in Toronto, Canada, isn’t convinced. ‘If you are in a state of mind-wandering you are not bored,’ he says. ‘In my view, by definition boredom is an undesirable state.’ That doesn’t necessarily mean that it isn’t adaptive, he adds. ‘Pain is adaptive – if we didn’t have physical pain, bad things would happen to us. Does that mean that we should actively cause pain? No. But even if boredom has evolved to help us survive, it can still be toxic if allowed to fester.’ For Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is a failure to put our ‘attention system’ into gear. This causes an inability to focus on anything, which makes time seem to go painfully slowly. What’s more, your efforts to improve the situation can end up making you feel worse. ‘People try to connect with the world and if they are not successful there’s that frustration and irritability,’ he says. Perhaps most worryingly, says Eastwood, repeatedly failing to engage attention can lead to state where we don’t know what to do any more, and no longer care.
Eastwood’s team is now trying to explore why the attention system fails. It’s early days but they think that at least some of it comes down to personality. Boredom proneness has been linked with a variety of traits. People who are motivated by pleasure seem to suffer particularly badly. Other personality traits, such as curiosity, are associated with a high boredom threshold. More evidence that boredom has detrimental effects comes from studies of people who are more or less prone to boredom. It seems those who bore easily face poorer prospects in education, their career and even life in general. But of course, boredom itself cannot kill – it’s the things we do to deal with it that may put us in danger. What can we do to alleviate it before it comes to that? Goetz’s group has one suggestion. Working with teenagers, they found that those who ‘approach’ a boring situation – in other words, see that it’s boring and get stuck in anyway – report less boredom than those who try to avoid it by using snacks, TV or social media for distraction.
Psychologist Francoise Wemelsfelder speculates that our over-connected lifestyles might even be a new source of boredom. ‘In modern human society there is a lot of overstimulation but still a lot of problems finding meaning,’ she says. So instead of seeking yet more mental stimulation, perhaps we should leave our phones alone, and use boredom to motivate us to engage with the world in a more meaningful way.
READING PASSAGE 3
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 27-40 which are based on Reading Passage 3 below.
Artificial artist?
Can computers really create works of art?
The Painting Fool is one of a growing number of computer programs which, so their makers claim, possess creative talents. Classical music by an artificial composer has had audiences enraptured, and even tricked them into believing a human was behind the score. Artworks painted by a robot have sold for thousands of dollars and been hung in prestigious galleries. And software has been built which creates are that could not have been imagined by the programmer.
Human beings are the only species to perform sophisticated creative acts regularly. If we can break this process down into computer code, where does that leave human creativity? ‘This is a question at the very core of humanity,’ says Geraint Wiggins, a computational creativity researcher at Goldsmiths, University of London. ‘It scares a lot of people. They are worried that it is taking something special away from what it means to be human.’
To some extent, we are all familiar with computerised art. The question is: where does the work of the artist stop and the creativity of the computer begin? Consider one of the oldest machine artists, Aaron, a robot that has had paintings exhibited in London’s Tate Modern and the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art. Aaron can pick up a paintbrush and paint on canvas on its own. Impressive perhaps, but it is still little more than a tool to realise the programmer’s own creative ideas.
Simon Colton, the designer of the Painting Fool, is keen to make sure his creation doesn’t attract the same criticism. Unlike earlier ‘artists’ such as Aaron, the Painting Fool only needs minimal direction and can come up with its own concepts by going online for material. The software runs its own web searches and trawls through social media sites. It is now beginning to display a kind of imagination too, creating pictures from scratch. One of its original works is a series of fuzzy landscapes, depicting trees and sky. While some might say they have a mechanical look, Colton argues that such reactions arise from people’s double standards towards software-produced and human-produced art. After all, he says, consider that the Painting Fool painted the landscapes without referring to a photo. ‘If a child painted a new scene from its head, you’d say it has a certain level of imagination,’ he points out. ‘The same should be true of a machine.’ Software bugs can also lead to unexpected results. Some of the Painting Fool’s paintings of a chair came out in black and white, thanks to a technical glitch. This gives the work an eerie, ghostlike quality. Human artists like the renowned Ellsworth Kelly are lauded for limiting their colour palette – so why should computers be any different?
Researchers like Colton don’t believe it is right to measure machine creativity directly to that of humans who ‘have had millennia to develop our skills’. Others, though, are fascinated by the prospect that a computer might create something as original and subtle as our best artists. So far, only one has come close. Composer David Cope invented a program called Experiments in Musical Intelligence, or EMI. Not only did EMI create compositions in Cope’s style, but also that of the most revered classical composers, including Bach, Chopin and Mozart. Audiences were moved to tears, and EMI even fooled classical music experts into thinking they were hearing genuine Bach. Not everyone was impressed however. Some, such as Wiggins, have blasted Cope’s work as pseudoscience, and condemned him for his deliberately vague explanation of how the software worked. Meanwhile, Douglas Hofstadter of Indiana University said EMI created replicas which still rely completely on the original artist’s creative impulses. When audiences found out the truth they were often outraged with Cope, and one music lover even tried to punch him. Amid such controversy, Cope destroyed EMI’s vital databases.
But why did so many people love the music, yet recoil when the discovered how it was composed? A study by computer scientist David Moffat of Glasgow Caledonian University provides a clue. He asked both expert musicians and non-experts to assess six compositions. The participants weren’t told beforehand whether the tunes were composed by humans or computers, but were asked to guess, and then rate how much they liked each one. People who thought the composer was a computer tended to dislike the piece more than those who believed it was human. This was true even among the experts, who might have been expected to be more objective in their analyses.
Where does this prejudice come from? Paul Bloom of Yale University has a suggestion: he reckons part of the pleasure we get from art stems from the creative process behind the work. This can give it an ‘irresistible essence’, says Bloom. Meanwhile, experiments by Justin Kruger of New York University have shown that people’s enjoyment of an artwork increases if they think more time and effort was needed to create it. Similarly, Colton thinks that when people experience art, they wonder what the artist might have been thinking or what the artist is trying to tell them. It seems obvious, therefore, that with computers producing art, this speculation is cut short – there’s nothing to explore. But as technology becomes increasingly complex, finding those greater depths in computer art could become possible. This is precisely why Colton asks the Painting Fool to tap into online social networks for its inspiration: hopefully this way it will choose themes that will already be meaningful to us.
Complete the table below.
Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8. The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
9. It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
10. According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
11. Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture.
12. Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
13. Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
Reading Passage 2 has six paragraphs, A-F
Choose the correct heading for each paragraph from the list of headings below.
Write the correct number, i-viii , in boxes 14-19 on your answer sheet.
List of Headings
i The productive outcomes that may result from boredom
ii What teachers can do to prevent boredom
iii A new explanation and a new cure for boredom
iv Problems with a scientific approach to boredom
v A potential danger arising from boredom
vi Creating a system of classification for feelings of boredom
vii Age groups most affected by boredom
viii Identifying those most affected by boredom
14. Paragraph A
15. Paragraph B
16. Paragraph C
17. Paragraph D
18. Paragraph E
19. Paragraph F
Look at the following people (Questions 20-23 ) and the list of ideas below.
Match each person with the correct idea, A-E .
List of Ideas
A The way we live today may encourage boredom.
B One sort of boredom is worse than all the others.
C Levels of boredom may fall in the future.
D Trying to cope with boredom can increase its negative effects.
E Boredom may encourage us to avoid an unpleasant experience.
Write the correct letter, A-E , in boxes 20-23 on your answer sheet.
20. Peter Toohey
21. Thomas Goetz
22. John Eastwood
23. Francoise Wemelsfelder
Complete the summary below.
Write your answers in boxes 24-26 on your answer sheet.
Responses to boredom
For John Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is that people cannot 24. , due to a failure in what he calls the ‘attention system’, and as a result they become frustrated and irritable. His team suggests that those for whom 25. is an important aim in life may have problems in coping with boredom, whereas those who have the characteristic of 26. can generally cope with it.
Choose the correct letter, A , B , C or D .
Write the correct letter in boxes 27-31 on your answer sheet.
27. What is the writer suggesting about computer-produced works in the first paragraph?
28. According to Geraint Wiggins, why are many people worried by computer art?
29. What is a key difference between Aaron and the Painting Fool?
30. What point does Simon Colton make in the fourth paragraph?
31. The writer refers to the paintings of a chair as an example of computer art which
Complete each sentence with the correct ending, A-G below.
Write the correct letter, A-G , in boxes 32-37 on your answer sheet.
A generating work that was virtually indistinguishable from that of humans.
B knowing whether it was the work of humans or software.
C producing work entirely dependent on the imagination of its creator.
D comparing the artistic achievements of humans and computers.
E revealing the technical details of his program.
F persuading the public to appreciate computer art.
G discovering that it was the product of a computer program
32. Simon Colton says it is important to consider the long-term view then
33. David Cope’s EMI software surprised people by
34. Geraint Wiggins criticized Cope for not
35. Douglas Hofstadter claimed that EMI was
36. Audiences who had listened to EMI’s music became angry after
37. The participants in David Moffat’s study had to assess music without
Do the following statements agree with the claims of the writer in Reading Passage 3?
In boxes 38-40 on your answer sheet, write
YES if the statement agrees with the claims of the writer
NO if the statement contradicts the claims of the writer
NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this
38. Moffat’s research may help explain people’s reactions to EMI.
39. The non-experts in Moffat’s study all responded in a predictable way.
40. Justin Kruger’s findings cast doubt on Paul Bloom’s theory about people’s prejudice towards computer art.

Time’s up
2. environment
6. accommodation
9. NOT GIVEN
12. NOT GIVEN
25. pleasure
26. curiosity
39. NOT GIVEN

27 out of 40
That is now corrected, Thank you!
The box for questions # 20 to 23 and 32 to 37 are missing.
Looks like you are using an ad-blocker. We request you disable the ad-blocker and refresh your browser to view the content.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reading Passage 1: The headline of the passage: Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website Questions 1-7 (Completing table with ONE WORD ONLY):In this type of question, candidates are asked to write only one word to complete a table on the given topic. For this type of question, first, skim the passage to find the keywords in the paragraph concerned with the answer, and then scan to find the ...
The Academic passage, Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website reading answers, appeared in an IELTS Test. Try to find the answers to get an idea of the difficulty level of the passages in the actual reading test. If you want more passages to solve, try taking one of our IELTS reading practice tests. Let's see how easy this passage is for you ...
Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website. New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country's gross domestic product, and is the country's largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make ...
More importantly, perhaps, the growth of tourism in New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
READING PASSAGE 1. You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 1-13 which are based on Reading Passage 1 below.. Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website. New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world.
Tourism New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Answers: Part 1. New Zealand is a small country with a minimum of just four million inhabitants that are spread across the country in a peaceful manner. Currently, the total GDP of the country has the highest percentage of tourism in it. Tourism contributes to making up to 9% of this country's GDP and ...
Answer: False 'Case study: Tourism New Zealand website'- Reading Answer Explanation- CAM- 13. 11 Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture. Location: 6 th paragraph. Explanation: The location of the answer is in the middle line of the paragraph. 'It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities ...
Cambridge IELTS Vocabulary Cambridge IELTS 13 Reading Test 1: Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website. N ew Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist- generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country's gross domestic product, and is the country's ...
READING PASSAGE 1 You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 1-13 which are based on Reading Passage 1 below. Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country's gross domestic product,
Remember that paragraph 3 refers to famous people and places/locations. We find the answer in the middle of paragraph 3: "Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for block buster films which had made use of New Zealand's stunning scenery as a backdrop".
This is an IELTS Cambridge 13 Test 1 Reading test Answers. In this post, you will check the Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website reading answers, driverless cars reading answers, Artificial artist reading answers. The user can check the answers for reading and analyze their mistakes.
Cambridge IELTS 13 - Cambridge 13 reading test 1 answers - case study tourism new zealand website reading answers, artificial artists reading answers
Cambridge IELTS 13 - Test 1 - Reading Passage 1 - Case Study: Tourism New Zealand Website. 5.0 (1 review) Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; ... Cambridge IELTS 13 - Test 1 - Reading Passage 1 - Case Study: Tourism New Zealand Website. 5.0 (1 review) Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; Q-Chat; a case study.
More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
Answer: NO Locate. 7 An analysis of deviance can act as a model for the analysis of tourism. 7. Answer: YES Locate. 8 Tourists usually choose to travel overseas. 8. Answer: NOT GIVEN. 9 Tourists focus more on places they visit than those at home. 9.
READING PASSAGE 1 . Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website. New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country's gross domestic product, and is the country's largest export sector.
More importantly, perhaps, the growth of tourism in New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
JSS? 1 READING PASSAGE 1 Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website READING You snotpc soend about 20 minutes on Questions 1—13, which are based on Reading Passage 1 betow. k key feax-e z: re campa gn was the website www.newzealand.ccm, which provided premia vsrzs zz New Zea and with a single gateway to everything the destination had to crer. The ~ean cr re website was a database of tourism ...
The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004.
पर्यटन New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Answers: Part 1. New Zealand is a small country with a minimum of just four million inhabitants that are spread across the country in a peaceful manner. Currently, the total GDP of the country has the highest percentage of tourism in it. Tourism contributes to making up to 9% of this country ...
More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
You should spend around 20 minutes attempting Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website reading answers to Questions 1-13 based on the passage below. Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website. New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world.
Cambridge 13 IELTS Academic Reading Test 1. View Answers. READING PASSAGE 1. You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 1-13 which are based on Reading Passage 1 below. Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website. New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the ...