
- Online Class
- Ask Doubt on Whatsapp
- Search Doubtnut

A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9km/hr and 10km/hr respectively. If A takes 36 minutes more than B, the distance travelled by each is

The correct Answer is: B
Step by step video, text & image solution for A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9km/hr and 10km/hr respectively. If A takes 36 minutes more than B, the distance travelled by each is by Maths experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 14 exams.
Related Playlists
TIME AND DISTANCE
STATISTICS AND DATA INTERPRETATION
TIME AND WORK
Similar Questions
A and B travel the same distance at 9 km/h and 10 km/h respectively.if A takes 20 minutes longer than B the distance travelled by each is:
A and B start at the same time with speed of 40km/hr and 50 km/hr respectively. If in covering the journey A takes 15 minutes longer than B, the total distance of the journey is
Two cars, X and Y, travel from A to B at average speeds of 50 km/hr and 75 km/hr respectively. If X takes 2 hours more than Y for the journey, then the distance between A and B in km is ______
Two cars A and B travel from one city to another city, at speeds of 60 km/hr and 108 km/hr respectively. If car B takes 2 hours lesser time than car A for the journey, then what is the distance (in km) between the two cities ?
Two cars A and B travel from one city to another, at speeds of 72 km/hr and 90 km/hr respectively. If car B takes 1 hour lessar than car A for the journey, then what is the distance (in km) between the two cities ?
Two horses cover the same distance at the rate of 10 km/hr and 15 km hr, respectively. The distance travelled when one takes 12 minutes longer than the other is:
Two trains start form stations A and B and travel towards each other at a speed of 50 kmph and 60 kmph respectively. A the time of their meeting, the second train had travelled 120 km more than the first. The distance between A and B is 600 k m b. 1440 k m c. 1320 k m d. 1660 k m
Mr. Prasad travelled equal distances at speeds of 2 km/hr., and 6 km/hr., and took a total of 55 minutes to complete. Find the total distance he travelled, in km.
KIRAN PUBLICATION - TIME AND DISTANCE - Type -XI
A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9km/hr and 10km/hr respec...
I walk a certain distance and ride back taking a total time of 37 minu...
A and B start at the same time with speed of 40km/hr and 50 km/hr resp...
A man can reach a certain place in 30 hours. If he reduces his speed b...
A, B and C are start at the same time in the same direction to run aro...
A person, who can walk down a hill a the speed of 4 (1)/(2) km/hr and ...
A walks at a uniform rate of 4 km an hour and 4 hours after his start,...
A car completes a journery in 10 hours. If it covers half of the journ...
A and B run a kilometre and A wins by 25 sec. A and C run a kilometre ...
Two cars start at the same time from one point and move along two road...
In a 1 km race, A beats B by 30 seconds and B beats C by 15 seconds. I...
Two guns are fired from the same place at an interval of 6 minutes. A ...
Ram arrives at a Bank 15 minutes earlier than scheduled time If he dri...
A and B started at the same time from the same place for a certain des...
In covering a distance of 30 km, Abhay takes 2 hours more than Sameer....
A man complete a certain journey by car. If he travels 30% of distance...
The distance of two places A to B is 60 km. At the same time a man sta...
P and Q are 27 km away. Two trains with speed of 24 km/hr and 18 km/ h...
Ravi and Ajay start simultaneously from a place A towards B, 60 km apa...
A man travelled a distance of 61 km in 9 hours, parts on foot at the r...
If a man walks at the rate of 5 km/hour he misses a train by 7 minutes...

Average Speed Formula: Definition, Examples, Facts, FAQs
What is the average speed formula, average speed formula, how to find average speed, solved examples on average speed formula, practice problems for average speed, frequently asked questions on average speed formula.
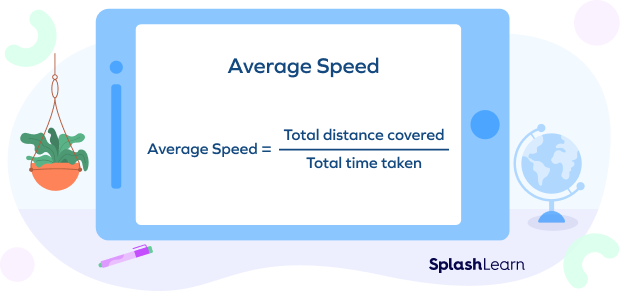
The average speed formula is given by the total distance traveled divided by the time taken to cover that distance.
The formula to find average speed is
Average speed $= \frac{Total \;distance}{Time}$
Observe the car in the given image. The distance it covers in the different time intervals is different. The speed of the car is not constant.
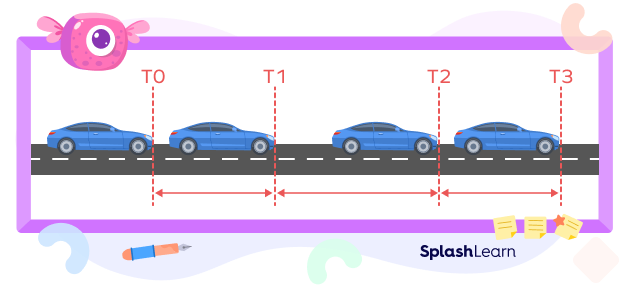
When you travel from one place to another by some vehicle, the speed changes from time to time. You do not travel with the same speed throughout the journey. The average speed, as the name itself suggests, gives us the mean value or the average value of the speed at which you traveled.
It is kind of an estimate to understand the speed by which an object finishes its journey. It provides insights into how fast an object is moving over a given distance and time. Calculating average speed allows us to estimate travel times and make comparisons between different routes or means of transportation.

The average speed formula can be given by
Average Speed $=$ Total distance covered $\div$ Total time taken
Average speed formula for a round trip
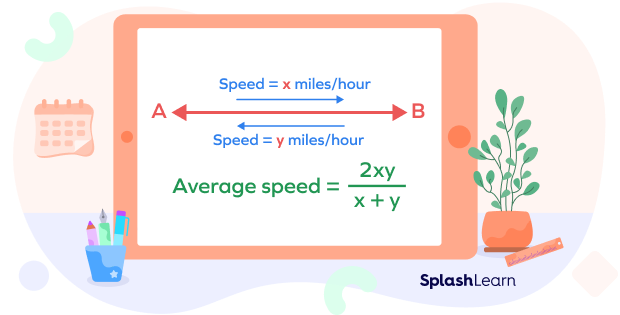
Alt tag: Average speed formula for the round journey
Derivation:
Suppose you travel a distance “d” from A to B with the speed of x miles per hour and the distance from B to A with the speed of y miles per hour. In this case, the same distance is covered (both ways) but with the different speeds. In this case, the average speed is given by
Total distance traveled $= d + d = 2d$
Time taken to go from A to B $= \frac{Distance}{Speed} = dx$
Time taken to go from B to A $= \frac{Distance}{Speed} = dy$
Total time taken $= \frac{d}{x} + \frac{d}{y} = \frac{d(x + y)}{xy}$
Average speed $=$ Total distance covered $÷$ Total time taken
Thus, the average speed equation becomes
Average speed $= \frac{2d}{\frac{d(x + y)}{xy}} = \frac{2xy}{x + y}$
Let’s understand steps to calculate average speed of an object . Let’s examine the procedure in more detail:
Step 1: Calculate the total distance traveled. If the two different speeds of the given journey are given, calculate the two distances separately using the formula: distance = Speed × time.
Step 2: Calculate the time taken to travel the total distance.
Step 3: Divide the total distance by total time taken to find the average speed. Assign the unit depending on the units of distance and time. For example, if the distance is given in miles and the time is in hours, the average speed will be measured in miles per hour (written as miles/hr).
Example 1: Joy travels the distance of 42 miles in 3 hours and 26 miles in 2 hours. Find his average speed.
Total distance traveled $= 42 + 26 = 68$ miles
Total time taken $= 3 + 2 = 5$ hours
Average speed $= \farc{68}{5} = 13.6$ miles/hr
Example 2: A bus travels the first 3 hours of journey with the speed of 20 miles/hour and the next 2 hours of the journey with the speed of 25 miles per hour. Find its average speed.
Distance $=$ Speed $\times$ time
The distance traveled in the first 3 hours with the speed of 20 mph $= 20 \times 3 = 60$ miles
The distance traveled in the next 2 hours with the speed of 25 mph $= 25 \times 2 = 50$ miles
Total distance traveled $= 60 + 50 = 110$ miles
Average speed $= \frac{110}{5} = 22$ miles/hour
Facts about Average Speed Formula
- Average speed is a scalar quantity, which can only be represented by magnitude. It has no direction.
- Average speed is independent of the direction of travel; it only depends on the total distance and time.
- It is essential to differentiate average speed from average velocity. Average velocity is a vector quantity that considers both magnitude and direction.
The average speed formula is calculated by dividing the total distance covered by the total time taken. In this article, we explored the concept of average speed, its formulas with different cases, and examples. Let’s solve a few examples and practice problems based on these concepts.
1. John walks a distance of 5 miles in 2 hours. Calculate his average speed.
Solution:
Using the average speed formula , we get
Average speed $= \frac{Total \;Distance}{Total \;Time}$
Average speed $= \frac{5 \;miles}{2 \;hours}$
Average Speed $= 2.5$ miles/hour
2. A car travels at a speed of 24 miles/hr for 2 hours and then decides to slow down to 18 miles/hr for the next 2 hours. What is the average speed?
The distance traveled in the first 2 hours with the speed of 24 mph $= 24 \times 2 = 48$ miles
The distance traveled in the next 2 hours with the speed of 18 mph $= 18 \times 2 = 36$ miles
Total distance traveled $= 48 + 36 = 84$ miles
Total time taken$ = 2 + 2 = 4$ hours
Average speed $= \frac{84}{4} = 21$ miles/hour
3. Walter drives at a speed of 60 mph from his house to his office every day. He returns from work at the speed of 45 mph. What’s his average speed for the round trip?
Solution:
Walter travels the same distance (both ways) with different speeds. We will use the average speed formula for the round trip.
$x = 60$ mph speed with which Walter travels from home to office
$y = 45$ mph speed with which Walter travels back to home from office
Average speed $= \frac{2xy}{x + y} = \frac{2\times 60 \times45}{60 + 45} = \frac{210}{105} = 51.42$ miles/hour
Average Speed Formula: Definition, Examples, Facts, FAQs
Attend this quiz & Test your knowledge.
A kid walks a distance of 5 miles in 3 hours. What is the average speed?
A runner completes the first 1.5 hours of a race with the speed of 9 miles per hour and the next 1 hour with the speed of 10 miles per hour. what is the runner's average speed, if a car covers distances $d_{1},\; d_{2}$, and $d_{3}$ for time intervals $t_{1},\; t{_2}$, and $t_{3}$ respectively, the average speed is.
What is the average speed calculation formula?
Average Speed $=$ Total Distance / Total Time is the average speed equation .
What distinguishes average speed from average velocity?
While average velocity accounts for both magnitude and direction, average speed solely takes into consideration the amplitude of motion.
Can average speed be negative?
Average speed does not have direction and it can only be positive or zero.
RELATED POSTS
- Quarter Past – Definition with Examples
- Octagon Formula For Area and Perimeter With Derivation
- Half of – Definition with Examples
- 30 60 90 Triangle – Definition with Examples
- Hour Hand On a Clock

Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun., you see real learning outcomes..
Make study-time fun with 14,000+ games & activities, 450+ lesson plans, and more—free forever.
Parents, Try for Free Teachers, Use for Free

A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9...
A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9 km/hr and 10 km/hr respectively. If A takes 36 min more than B, the distance travelled by each is :
Answer: Option B
Solution(By Examveda Team)
This Question Belongs to Arithmetic Ability >> Speed Time And Distance
Join The Discussion
Comments ( 1 ).

Related Questions on Speed Time and Distance
Two buses start from a bus terminal with a speed of 20 km/h at interval of 10 minutes. What is the speed of a man coming from the opposite direction towards the bus terminal if he meets the buses at interval of 8 minutes?
Walking $$\frac{3}{4}$$ of his normal speed, Rabi is 16 minutes late in reaching his office. The usual time taken by him to cover the distance between his home and office:
Two trains for Mumbai leave Delhi at 6 am and 6.45 am and travel at 100 kmph and 136 kmph respectively. How many kilometers from Delhi will the two trains be together:
A. 262.4 km
C. 283.33 km
E. None of these
A man takes 6 hours 15 minutes in walking a distance and riding back to starting place. He could walk both ways in 7 hours 45 minutes. The time taken by him to ride back both ways is:
B. 4 hours 30 min.
C. 4 hours 45 min.
More Related Questions on Speed Time and Distance
Read More: MCQ Type Questions and Answers
- Arithmetic Ability
- Competitive Reasoning
- Competitive English
- Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- State GK
- History
- Geography
- Current Affairs
- Banking Awareness
- Computer Fundamentals
- Networking
- C Program
- Java Program
- Database
- HTML
- Javascript
- Computer Science
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Chemical Engineering
- Automobile Engineering
- Biotechnology Engineering
- Mining Engineering
- Commerce
- Management
- Philosophy
- Agriculture
- Sociology
- Political Science
- Pharmacy
A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9km/hr and 10 km/hr respectively. If A takes 36 minutes more than B, the distance travelled by each is

Model 1 Basic Time & Distance using formula Section-Wise Topic Notes With Detailed Explanation And Example Questions
Most important quantitative aptitude - 5 exercises.
New 499+ Basic Time and Distance MCQ with Solved Solution »
Top 499+ Time and Distance Aptitude MCQs on Usual Speed »
Top 399+ Time and Distance MCQs On Average Speed For SSC »
New 499+ Time and Distance MCQs Based on Ratios For BANK »
Top 389+ Time and Distance MCQs Based on Races For SSC »
Top 10,000+ Aptitude Memory Based Exercises
The following question based on time & distance topic of quantitative aptitude
The correct answers to the above question in:
Answer: (b)
Let the distance between A and B be x km, then
$x/9 - x/10 = 36/60 = 3/5$
$x/90 = 3/5$
$x = 3/5 × 90$ = 54 km.
Using Rule 9,
Here, $S_1 = 9, t_1 = x, S_2 = 10, t_2 = x - 36/60$
$S_1t_ 1 = S_2t_ 2$
$9 × x = 10(x - 36/60)$
9x = 10x - 6 = 6
Distance travelled = 9 × 6 = 54 km
Practice time & distance (Model 1 Basic Time & Distance using formula) Online Quiz
Discuss form, read more basic problems formulas based quantitative aptitude questions and answers.
Question : 1
A man rides at the rate of 18 km/ hr, but stops for 6 mins. to change horses at the end of every 7th km. The time that he will take to cover a distance of 90 km is
a) 6 hrs. 24 min.
b) 6 hrs. 18 min.
c) 6 hrs. 12 min.
90 km = 12 × 7km + 6 km.
To cover 7 km total time taken = $7/18$ hours + 6 min. = $88/3$ min.
So, (12 × 7 km) would be covered in $(12 × 88/3)$ min.
and remaining 6km is $6/18$ hrs or 20 min.
Total time = $1056/3$ + 20
= $1116/{3 × 60}$ hours = 6$1/5$ hours
= 6 hours 12 minutes.
Question : 2
A man travelled a certain distance by train at the rate of 25 kmph. and walked back at the rate of 4 kmph. If the whole journey took 5 hours 48 minutes, the distance was
Answer: (c)
Let the distance be x km.
Total time = 5 hours 48 minutes
= $5 + 48/60 = (5 + 4/5)$ hours
= $29/5$ hours
$x/25 + x/4 = 29/5$
${4x + 25x}/100 = 29/5$
5 × 29x = 29 × 100
$x = {29 × 100}/{5 × 29}$ = 20 km.
Using Rule 5, If a bus travels from A to B with the speed x km/h and returns from B to A with the speed y km/h,then the average speed will be $({2xy}/{x + y})$
Here, x = 25, y = 4
Average speed = ${2xy}/{x + y}$
= ${2 × 25 × 4}/{25 + 4} = 200/29$
Total Distance = $200/29 × 5{4}/5$
= $200/29 × 29/5$ = 40 km
Required distance = 20 km
Question : 3
A man travelled a distance of 80 km in 7 hrs partly on foot at the rate of 8 km per hour and partly on bicycle at 16km per hour. The distance travelled on the foot is
Answer: (d)
Journey on foot=x km
Journey on cycle = (80 –x)km
$x/8 + {80 - x}/16 = 7$
${2x + 80 - x}/16 = 7$
x + 80 = 16 × 7 = 112
x= 112 - 80 = 32 km.
Using Rule 13, Let a man take 't' hours to travel 'x' km. If he travels some distance on foot with the speed u km/h and remaining distance by cycle with the speed v km/h,then time taken to travel on foot. Time = ${(vt - x)}/{(v - u)}$ Distance travelled on foot = Time × u
Here, x = 80, t = 7, u = 8, v = 16
Time = $({vt - x}/{v - u})$
=$({16 × 7 - 80}/{16 - 8})$
=$({112 - 80}/8) = 32/8$ = 4 hrs
Distance travelled
= 4 × 8 = 32 kms
Question : 4
A train is travelling at the rate of 45km/hr. How many seconds it will take to cover a distance of $4/5$ km ?
a) 120 sec.
Using Rule 1, Distance = Speed × Time Speed = $\text"Distance"/\text"Time"$ , Time = $\text"Distance"/\text"Speed"$ 1 m/s = $18/5$ km/h, 1 km/h = $5/18$ m/s
Time taken = $\text"Distance"/ \text"time"$
= ${4/5}/45$ hour
= ${4 × 60 × 60}/{5 × 45}$ sec. = 64 seconds
Question : 5
A person started his journey in the morning. At 11 a.m. he covered $3/8$ of the journey and on the same day at 4.30 p.m. he covered $5/6$ of the journey. He started his journey at
a) 6.30 a.m.
b) 7.00 a.m.
c) 3.30 a.m.
d) 6.00 a.m.
Answer: (a)
Difference of time
= 4.30 p.m - 11.a.m.
= $5{1}/2$ hours $11/2$ hours
Distance covered in $11/2$ hrs
= $5/6 - 3/8 = {20 - 9}/24 = 11/24$ part
Since, $11/24$ part of the journey is covered in $11/2$ hours
$3/8$ part of the journey is covered in
= $11/2 × 24/11 × 3/8$
= $9/2$ hours = 4$1/2$ hours.
Clearly the person started at 6.30 a.m.
Question : 6
A man covers $2/15$ of the total journey by train, $9/20$ by bus and the remaining 10 km on foot. His total journey (in km) is
Let the total journey be of x km, then
${2x}/15 + {9x}/20 + 10 = x$
$x - {2x}/15 - {9x}/20$ = 10
${60x - 8x - 27x}/60$ = 10
${25x}/60$ = 10
$x = {60 × 10}/25$ = 24 km
GET time & distance PRACTICE TEST EXERCISES
Model 1 basic time & distance using formula, model 2 vehicles in x/y of its usual speed, model 3 problems on average speed, model 4 time & distance with ratios, model 5 problems with races, time & distance shortcuts and techniques with examples, verbal reasoning question & answer quiz, non verbal reasoning question & answer quiz, quantitative aptitude question & answer quiz, computer mcq question & answer quiz, general english question & answer quiz, history gk question & answer quiz, polity gk question & answer quiz, geography gk question & answer quiz, economy gk question & answer quiz, general awareness gk question & answer quiz, recently added subject & categories for all competitive exams, ssc steno: time & work questions solved problems with pdf.
Free Time and work Aptitude-based Practice multiple questions with solutions, Quiz series, Mock Test & Downloadable PDF for SSC Steno (Grade C & D) 2024 Exam
Continue Reading »
SSC STENO 2024: Free Reading Comprehension MCQ Test PDF
Top Reading Comprehension English Section-wise multiple choice questions and answers, Full Mock Test Series & Online Quiz for SSC Steno Grade C & D 2024 Exam
Free Percentage Questions Answers for SSC STENO 2024 Exam
Important Top Percentage Aptitude-based multiple choice questions and answers practice quiz series, Online Mock Test PDF for SSC Steno Grade C & D 2024 Exam
Free Antonyms (English) MCQ Test for SSC STENO 2024 Exam
Top Antonyms General English Section-based multiple choice questions and answers, Free Full Test Series & Online Quiz PDF for SSC Steno Grade C & D 2024 Exam
Distance Calculator
What is distance, the distance formula for euclidean distance, distance to any continuous structure, distance to a line and between 2 lines, how to find the distance using our distance calculator, driving distance between cities: a real-world example, distance from earth to moon and sun - astronomical distances, distance beyond length.
Have you ever wanted to calculate the distance from one point to another, or the distance between cities? Have you ever wondered what the distance definition is? We have all these answers and more, including a detailed explanation of how to calculate the distance between any two objects in 2D space. As a bonus, we have a fascinating topic on how we perceive distances (for example as a percentage difference ); we're sure you'll love it!
Prefer watching over reading? Learn all you need in 90 seconds with this video we made for you :
Before we get into how to calculate distances, we should probably clarify what a distance is . The most common meaning is the 1D space between two points. This definition is one way to say what almost all of us think of distance intuitively, but it is not the only way we could talk about distance. You will see in the following sections how the concept of distance can be extended beyond length, in more than one sense that is the breakthrough behind Einstein's theory of relativity.
If we stick with the geometrical definition of distance we still have to define what kind of space we are working in . In most cases, you're probably talking about three dimensions or less, since that's all we can imagine without our brains exploding. For this calculator, we focus only on the 2D distance (with the 1D included as a special case). If you are looking for the 3D distance between 2 points we encourage you to use our 3D distance calculator made specifically for that purpose.
To find the distance between two points, the first thing you need is two points, obviously . These points are described by their coordinates in space. For each point in 2D space, we need two coordinates that are unique to that point. If you wish to find the distance between two points in 1D space you can still use this calculator by simply setting one of the coordinates to be the same for both points . Since this is a very special case, from now on we will talk only about distance in two dimensions.

The next step, if you want to be mathematical, accurate, and precise , is to define the type of space you're working in. No, wait, don't run away! It is easier than you think. If you don't know what space you're working in or if you didn't even know there is more than one type of space, you're most likely working in Euclidean space . Since this is the "default" space in which we do almost every geometrical operation, and it's the one we have set for the calculator to operate on. Let's dive a bit deeper into Euclidean space , what is it, what properties does it have and why is it so important?
The Euclidean space or Euclidean geometry is what we all usually think of 2D space is before we receive any deep mathematical training in any of these aspects. In Euclidean space, the sum of the angles of a triangle equals 180º and squares have all their angles equal to 90º; always. This is something we all take for granted, but this is not true in all spaces . Let's also not confuse Euclidean space with multidimensional spaces. Euclidean space can have as many dimensions as you want, as long as there is a finite number of them, and they still obey Euclidean rules .
We do not want to bore you with mathematical definitions of what is a space and what makes the Euclidean space unique, since that would be too complicated to explain in a simple distance calculator. However, we can try to give you some examples of other spaces that are commonly used and that might help you understand why Euclidean space is not the only space. Also, you will hopefully understand why we are not going to bother calculating distances in other spaces .

The first example we present to you is a bit obscure, but we hope you can excuse us, as we're physicists , for starting with this very important type of space: Minkowski space . The reason we've selected this is because it's very common in physics , in particular it is used in relativity theory, general relativity and even in relativistic quantum field theory. This space is very similar to Euclidean space, but differs from it in a very crucial feature: the addition of the dot product, also called the inner product (not to be confused with the cross product).
Both the Euclidean and Minkowski space are what mathematicians call flat space . This means that space itself has flat properties; for example, the shortest distance between any two points is always a straight line between them (check the linear interpolation calculator). There are, however, other types of mathematical spaces called curved spaces in which space is intrinsically curved and the shortest distance between two points is no a straight line.
This curved space is hard to imagine in 3D, but for 2D we can imagine that instead of having a flat plane area, we have a 2D space, for example, curved in the shape of the surface of a sphere. In this case, very strange things happen . The shortest distance from one point to another is not a straight line, because any line in this space is curved due to the intrinsic curvature of the space. Another very strange feature of this space is that some parallel lines do actually meet at some point . You can try to understand it by thinking of the so-called lines of longitude that divide the Earth into many time zones and cross each other at the poles.

It is important to note that this is conceptually VERY different from a change of coordinates . When we take the standard x , y , z x, y, z x , y , z coordinates and convert into polar, cylindrical, or even spherical coordinates, but we will still be in Euclidean space. When we talk about curved space, we are talking about a very different space in terms of its intrinsic properties . In spherical coordinates, you can still have a straight line and distance is still measured in a straight line, even if that would be very hard to express in numbers.

Coming back to the Euclidean space, we can now present you with the distance formula that we promised at the beginning . The distance formula is
which relates to the Pythagorean Theorem, which states that a 2 + b 2 = c 2 a^2+b^2=c^2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 . Here, a a a and b b b are legs of a right triangle and c c c is the hypotenuse. Suppose that two points, ( x 1 , y 1 ) (x_1, y_1) ( x 1 , y 1 ) and ( x 2 , y 2 ) (x_2, y_2) ( x 2 , y 2 ) , are coordinates of the endpoints of the hypotenuse . Then ( x 2 − x 1 ) 2 (x_2 - x_1)^2 ( x 2 − x 1 ) 2 in the distance equation corresponds to a 2 a^2 a 2 and ( y 2 − y 1 ) 2 (y_2 - y_1)^2 ( y 2 − y 1 ) 2 corresponds to b 2 b^2 b 2 . Since c = a 2 + b 2 c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} c = a 2 + b 2 , you can see why this is just an extension of the Pythagorean theorem .
The distance formula we have just seen is the standard Euclidean distance formula , but if you think about it, it can seem a bit limited. We often don't want to find just the distance between two points. Sometimes we want to calculate the distance from a point to a line or to a circle. In these cases, we first need to define what point on this line or circumference we will use for the distance calculation, and then use the distance formula that we have seen just above.
Here is when the concept of perpendicular line becomes crucial. The distance between a point and a continuous object is defined via perpendicularity. From a geometrical point of view, the first step to measure the distance from one point to another, is to create a straight line between both points, and then measure the length of that segment . When we measure the distance from a point to a line, the question becomes "Which of the many possible lines should I draw?". In this case the answer is: the line from the point that is perpendicular to the first line . This distance will be zero in the case in which the point is a part of the line. For these 1D cases, we can only consider the distance between points, since the line represents the whole 1D space .

This imposes restrictions on how to compute distances in some interesting geometrical instances. For example, we could redefine the concept of height of a triangle to be simply the distance from one vertex to the opposing side of the triangle. In this case, the triangle area is also redefined in terms of distance, since the area is a function of the height of the triangle.
Let's look at couple examples in 2D space. To calculate the distance between a point and a straight line we could go step by step (calculate the segment perpendicular to the line from the line to the point and the compute its length) or we could simply use this 'handy-dandy' equation :
where the line is given by A x + B y + C = 0 Ax+By+C = 0 A x + B y + C = 0 and the point is defined by ( x 1 , y 1 ) (x_1, y_1) ( x 1 , y 1 ) .
The only problem here is that a straight line is generally given as y = m x + b y=mx+b y = m x + b , so we would need to convert this equation to the previously show form:
so we can see that A = m A=m A = m , B = − 1 B=-1 B = − 1 and C = b C=b C = b . This leaves the previous equation with the following values:
For the distance between 2 lines, we just need to compute the length of the segment that goes from one to the other and is perpendicular to both. Once again, there is a simple formula to help us :
if the lines are A 1 x + B 1 y + C 1 = 0 A_1x+B_1y+C_1=0 A 1 x + B 1 y + C 1 = 0 and A 2 x + B 2 y + C 2 = 0 A_2x+B_2y+C_2=0 A 2 x + B 2 y + C 2 = 0 . We can also convert to slope intercept form and obtain:
for lines y = m 1 x + b 1 y=m_1x+b_1 y = m 1 x + b 1 and y = m 2 x + b 2 y=m_2x+b_2 y = m 2 x + b 2 .
Notice that both line needs to be parallel since otherwise the would touch at some point and their distance would then be d = 0 d=0 d = 0 . That's the reason the formulas omit most of the subscripts since for parallel lines: A 1 = A 2 = A A_1=A_2=A A 1 = A 2 = A and B 1 = B 2 = B B_1=B_2=B B 1 = B 2 = B while in slope intercept form parallel lines are those for which m 1 = m 2 = m m_1=m_2=m m 1 = m 2 = m .
As we have mentioned before, distance can mean many things , which is why we have provided a few different options for you in this calculator. You can calculate the distance between a point and a straight line, the distance between two straight lines (they always have to be parallel), or the distance between points in space. When it comes to calculating the distances between two point, you have the option of doing so in 1, 2, 3, or 4 dimensions. We know, we know, 4 dimensions sounds scary , but you don't need to use that option. And you can always learn more about it by reading some nice resources and playing around with the calculator. We promise it won't break the Internet or the universe.
We have also added the possibility for you to define 3 different points in space, from which you will obtain the 3 pairs of distances between them, so, if you have more than two points, this will save you time. The number of dimensions you are working in will determine the number of coordinates that describe a point, which is why, as you increase the number of dimensions, the calculator will ask for more input values.
Even though using the calculator is very straightforward, we still decided to include a step-by-step solution. This way you can get acquainted with the distance formula and how to use it (as if this was the 1950's and the Internet was still not a thing). Now let's take a look at a practical example: How to find the distance between two points in 2-D.
Suppose you have two coordinates, ( 3 , 5 ) (3, 5) ( 3 , 5 ) and ( 9 , 15 ) (9, 15) ( 9 , 15 ) , and you want to calculate the distance between them. To calculate the 2-D distance between these two points, follow these steps:
- Input the values into the formula: ( x 2 − x 1 ) 2 + ( y 2 − y 1 ) 2 \sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2} ( x 2 − x 1 ) 2 + ( y 2 − y 1 ) 2 .
- In the formula, subtract the values in the parentheses.
- Square both quantities in the parentheses.
- Add the results.
- Take the square root.
- Use the distance calculator to check your results.
Working out the example by hand, you get:
which is equal to approximately 11.66 11.66 11.66 . Note, that when you take the square root, you will get a positive and negative result, but since you are dealing with distance, you are only concerned with the positive result . The calculator will go through this calculations step by step to give you the result in exact and approximate formats.
Let's take a look of one of the applications of the distance calculator. Suppose you are traveling between cities A and B, and the only stop is in city C, with a route A to B perpendicular to route B to C. We can determine the distance from A to B, and then, knowing the gas price, determine fuel cost , fuel used and cost per person while traveling. The gas calculator, that you can find on our site, can ease that for you.
The difficulty here is to calculate the distances between cities accurately . A straight line (like what we use in this calculator) can be a good approximation, but it can be quite off if the route you're taking is not direct but takes some detour, maybe to avoid mountains or to pass by another city. In that case, just use Google maps or any other tool that calculates the distance along a path not just the distance from one point to another as the crow flies.

Our calculator can give proper measurements and predictions for distances between objects, not the length of a path . With this in mind, there are still multiple scenarios in which you might actually be interested in the distance between objects, regardless of the path you would have to take. One such example is the distance between astronomical objects .
When we look at a distance within our Earth, it is hard to go far without bumping into some problems , from the intrinsic curvature of this space (due to the Earth curvature being non-zero) to the limited maximum distance between two points on the Earth. It is because of this, and also because there is a whole universe beyond our Earth , that distances in the universe are of big interest for many people. Since we have no proper means of interplanetary traveling, let alone interstellar travels, let's focus for now on the actual Euclidean distance to some celestial objects. For example the distance from the Earth to the Sun, or the distance from the Earth to the Moon.
These distances are beyond imaginable for our ape-like brains. We struggle to comprehend the size of our planet, never mind the vast, infinite universe. This is so difficult that we need to use either scientific notation or light years, as a unit of distance for such long lengths . The longest trips you can do on Earth are barely a couple thousand kilometers, while the distance from Earth to the Moon, the closest astronomical object to us, is 384,000 km . On top of that, the distance to our closest star, that is the distance from Earth to the Sun , is 150,000,000 km or a little over 8 light minutes .

When you compare these distances with the distance to our second nearest star (Alpha Centauri) , which is 4 light years , suddenly they start to look much smaller. If we want to go even more ridiculous in comparison we can always think about a flight from New York to Sydney, which typically takes more than 20 h and it's merely over 16,000 km , and compare it with the size of the observable universe, which is about 46,600,000,000 light years !
Here, we have inadvertently risen a fascinating point , which is that we measure distances not in length but in time. Thus, we extend the notion of distance beyond its geometrical sense. We will explore this possibility in the next section as we speak about the importance and usefulness of distance beyond the purely geometrical sense . This is a very interesting path to take and is mostly inspired by the philosophical need to extend every concept to have a universal meaning, as well as from the obvious physical theory to mention, when talking about permutations of the space and time, or any other variable that can be measured .
Typically, the concept of distance refers to the geometric Euclidean distance and is linked to length. However, you can extend the definition of distance to mean just the difference between two things , and then a world of possibilities opens up. Suddenly one can decide what is the best way to measure the distance between two things and put it in terms of the most useful quantity. A very simple step to take is to think about the distance between two numbers, which is nothing more than the 1D difference between these numbers . To obtain it, we simply subtract one from the other and the result would be the difference, a.k.a. the distance.
We could jump from this numerical distance to, for example, difference or distance in terms of the percentage difference, which in some cases might provide a better way of comparison . This is still just one level of abstraction in which we simply remove the units of measurement. But what if we were to use different units altogether?

By extending the concept of distance to mean something closer to difference , we can calculate the difference between two temperatures, or other related quantity like pressure. But we don't need to get really extreme, let's see how two points can be separated by a different distance, depending on the assumptions made . Coming back to the driving distance example, we could measure the distance of the journey in time, instead of length. In this case, we need an assumption to allow such translation; namely the way of transport.
There is a big difference in the time taken to travel 10 km by plane versus the time it takes by car . Sometimes, however, the assumption is clear and implicitly agreed on, like when we measure the lightning distance in time which we then convert to length. This brings up an interesting point, that the conversion factor between distances in time and length is what we call "speed" or "velocity" (remember they are not exactly the same thing). Truth be told, this speed doesn't have to be constant as exemplified by accelerated motions such as that of a free fall under gravitational force, or the one that links stopping time and stopping distance via the breaking force and drag or, in very extreme cases, via the force of a car crash.

Another place where you can find weird units of distance are in solid state physics, where the distance a particle travels inside of a material is often expressed as an average of interactions or collisions. This distance is linked to length by using the mean free path, which is the mean distance (in length) a particle travels between interactions. If we want to get even more exotic we can think about the distance from the present value to the future value of something like a car.
We don't want to, however, make anyone's brain explode, so please don't think too hard about this . Just take this calculator and use it for length-based distance in 2D space. You can always return to this philosophical view on distances if you ever find yourself bored!
How to find the distance between two points?
To find the distance between two points we will use the distance formula: √[(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]:
- Get the coordinates of both points in space.
- Subtract the x-coordinates of one point from the other, same for the y components.
- Square both results separately.
- Sum the values you got in the previous step.
- Find the square root of the result above.
If you think this is too much effort, you can simply use the Distance Calculator from Omni
Is distance a vector?
Distance is not a vector . The distance between points is a scalar quantity, meaning it is only defined by its value. However, the displacement is a vector with value and direction. So the distance between A and B is the same as the distance from B to A, but the displacement is different depending on their order.
What is a klick in distance?
Click is slang for a kilometer which is 0.62 miles. It is actually written with "k" (Klick) as it is derived from the word kilometer. It is commonly used in the military and motorcyclists.
What is the distance formula?
The distance formula is: √[(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²] . This works for any two points in 2D space with coordinates (x₁, y₁) for the first point and (x₂, y₂) for the second point. You can memorize it easily if you notice that it is Pythagoras theorem and the distance is the hypothenuse, and the lengths of the catheti are the difference between the x and y components of the points.
How to find the distance of a vector?
The distance of a vector is its magnitude . If you know its components:
- Take each of the components of the vector and square them.
- Sum them up.
- Find the square root of the previous result.
- Enjoy the good work!
If you know its polar representation , it will be a number and an angle. That number is the magnitude of the vector, which is its distance.

What is the SI unit of distance?
The SI unit of distance is the meter , abbreviated to "m". A meter is approximately 3.28 feet. Other common units in the International System of units are the centimeter (one one-hundredth of a meter, or 0.39 inches) and the kilometer (one thousand meters or 0.62 miles), among others.
What is the distance from A to B?
The distance from A to B is the length of the straight line going from A to B. The distance from B to A is the same as the distance from A to B because distance is a scalar
What is the dimension of distance?
Distance is a measure of one-dimensional space. The distance between two points is the shortest length of 1D space between them. If you divide distance over time you will get speed, which has dimensions of space over time.
Is light-year time or distance?
A light-year is a measurement of distance. It is 9.461×10 12 kilometers or 5.879×10 12 miles, which is the distance traveled by a ray of light in a perfect vacuum over the span of a year.
How to solve for distance with velocity and time?
The velocity and the moving time of an object you can calculate the distance:
- Make sure the speed and time have compatible units (miles per hour and hours, meter per second, and seconds…).
- If they aren't, convert them to the necessary units.
- Multiply the velocity by the time .
- The result should be the distance traveled in whichever length units your speed was using!
Condense logarithms
Humans vs vampires, round to the nearest thousand.
- Biology (100)
- Chemistry (100)
- Construction (144)
- Conversion (295)
- Ecology (30)
- Everyday life (262)
- Finance (570)
- Health (440)
- Physics (510)
- Sports (105)
- Statistics (182)
- Other (182)
- Discover Omni (40)

Cars A and B: Rate, Distance and Time Problem

2 Answers By Expert Tutors

John M. answered • 01/02/17
Engineering manager professional, proficient in all levels of Math
- Distance (D) = Rate (R) * Time (T)
- For Car A:
- D = 30T {Eqn 1}
- The Distance D and the time T is the same as for Car A
- But, unlike Car A, Car B travels at two different rates. It travels at 20mph for a time T1. Then it passes Car A and travels at a rate of x for a period of time T2.
- D = (20T1) + (x * T2)
- Note that T2 must equal the total time T minus T1, so
- D = (20T1) + (x * (T - T1)) {Eqn2}
- Substitute Eqn 1 into Enq 2 : 30T = 20T1 + xT - xT1
- Rewrite as: 30T = 20T1 + x(T-T1) {Eqn 3}
- At what point do the two cars pass one another?
- Car A travels 30T1 = D1
- Car B is traveling in the opposite direction at 20T1 = D2
- D2 = D - D1 (where D is the total circular length of the track)
- Substituting, 20T1 = D - 30T1. Or 50T1 = D {Eqn 4}
- Now we can establish a relationship between T and T1 by substituting Eqn1 into Eqn4
- D = 30T = 50T1
- (30/50)T = T1
- T1 = (3/5)T {Eqn 5}
- Now substitute Eqn 5 into Eqn 3
- 30T = 20T1 + x (T-T1)
- 30T = 20(3/5)T+ x (T - 3/5 T)
- 30T = 12T + xT(2/5)
- 18T = (2/5)x
- (5/2)18 = x
- Recall that x is the speed that Car B must travel after it passes Car A.

Arthur D. answered • 01/02/17
Forty Year Educator: Classroom, Summer School, Substitute, Tutor
Still looking for help? Get the right answer, fast.
Get a free answer to a quick problem. Most questions answered within 4 hours.
Choose an expert and meet online. No packages or subscriptions, pay only for the time you need.
RELATED TOPICS
Related questions, what are all the common multiples of 12 and 15.
Answers · 9
need to know how to do this problem
Answers · 8
what are methods used to measure ingredients and their units of measure
How do you multiply money.
Answers · 6
spimlify 4x-(2-3x)-5
Answers · 14
RECOMMENDED TUTORS

Elizabeth B.

find an online tutor
- Math tutors
- 7th Grade Math tutors
- SAT Math tutors
- Geometry tutors
- Precalculus tutors
- ACCUPLACER College-Level Math tutors
- Algebra tutors
- Algebra 1 tutors
Solver Title
Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Expanded Form Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- Pre Calculus
- Given Points
- Given Slope & Point
- Slope Intercept Form
- Start Point
- Parallel Lines
- Perpendicular
- Perpendicular Lines
- Perpendicular Slope
- Is a Function
- Domain & Range
- Slope & Intercepts
- Periodicity
- Domain of Inverse
- Critical Points
- Inflection Points
- Monotone Intervals
- Extreme Points
- Global Extreme Points
- Absolute Extreme
- Turning Points
- End Behavior
- Average Rate of Change
- Piecewise Functions
- Discontinuity
- Values Table
- Compositions
- Arithmetics
- Circumference
- Eccentricity
- Conic Inequalities
- Transformation
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Conversions

Most Used Actions
Number line.
- distance\:(-3\sqrt{7},\:6),\:(3\sqrt{7},\:4)
- distance\:(-5,\:8d),\:(0,\:4)
- distance\:(-2,\:-3),\:(-1,\:-2)
- distance\:(p,\:1),\:(0,\:q)
- distance\:(3\sqrt{2},7\sqrt{5})(\sqrt{2},-\sqrt{5})
- distance\:(-2,-3),(-1,-2)
distance-calculator
- High School Math Solutions – Perpendicular & Parallel Lines Calculator Parallel lines have the same slope, to find the parallel line at a given point you should simply calculate the...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.

11 Best Hotels Walking Distance To Disneyland
D isneyland, the original of the Disney theme parks, is truly an original. Built in the center of Anaheim, Disneyland doesn’t have the same amount of space around the parks as Walt Disney World enjoys. As a result, however, there are many different hotels within walking distance of Disneyland, including chain hotels and Disney-owned and operated hotels.
When planning a Disneyland vacation, you may be wondering which of these hotels is best for you. The truth is, it really does depend on your situation. Some of these hotels offer more space for larger families, while some are best for younger kids. So, it’s important to do some research and see what the best hotels in walking distance to Disneyland are best for your family vacation.
Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links. A purchase/click through one of these links may result in a commission paid to us at no additional cost to you. We did receive a complimentary stay at the Howard Johnson Anaheim Hotel and Water Playground but all opinions are my own.
Save money on your Disneyland tickets and your Southern California vacation by booking through Get Away Today . You can also save $10 on your Southern California vacation of 2 days or more with the code FTM10. We booked our most recent two trips to Disneyland through Get Away Today.
Best Hotels Walking Distance To Disneyland
The disneyland hotel.
Arguably the most nostalgic hotel on this list is the Disneyland Hotel, which is one of the three Disney owned and operated hotel at Disneyland. The Disneyland Hotel will be offering Disney Vacation Club villas and studios, as well as traditional hotel rooms. It’s close to Disneyland, near Downtown Disney, and is a very convenient place to stay.
In addition to the location, the Disneyland Hotel offers two themed pools, two monorail themed waterslides, Goofy’s Kitchen restaurant, Tangaroa Terrace Tropical Bar & Grill, and Trader Sam’s Enchanted Tiki Bar.
Guests at the Disneyland Hotel can take advantage of Early Entry. With this program, you’ll be able to enter the parks 30 minutes in advance of the park opening to the general public. It’s a great way to ride some of the attractions with a much lower wait time and fewer crowds.
Why stay here:
- Nostalgia, including retro pools and themed waterslides
- Great restaurants right on property
- Early entry to the theme parks
- Close proximity to Downtown Disney and the Disneyland theme parks
Book: Book the Disneyland Hotel here .
Element by Westin Anaheim Resort Convention Center
The Element by Westin Anaheim Resort Convention Center is a hotel located on Clementine Street within walking distance of Disneyland. It’s a Disney Good Neighbor Hotel, and is great for families looking for a little more space.
The hotel offers studio suites, kids’ suites (with bunk beds), and one bedroom suites. All suites have a full kitchen, which is great if you want to prepare some meals in the room to save money. This is a modern hotel with a business center, outdoor garden area, rental bikes, free breakfast buffet, and more.
- Save money with in-suite kitchens and free breakfast daily
- Rooms with plenty of space including bunk bed rooms
- Outdoor saline pool
- Walking distance to front entrance of Disneyland
- Pet-friendly hotel for additional fee
Book here: Book the Element here .
Cambria Hotel & Suites Anaheim Resort
This new hotel is located about .8 miles from Disneyland, and is about a 15-20 minute walk. While there isn’t a shuttle, you can take public bus transportation if you’d rather not walk. It offers both suites and traditional hotel rooms.
Rooms have two showers, which can definitely be beneficial when getting ready in the morning. There are several family suite configurations, some of which include bunk beds to accommodate more.
In addition, this hotel is located in a complex with quite a few restaurant options, including Starbucks, Jersey Mikes, California Fish Grill, Yogurtland, Habit Burger, Ono Hawaiian BBQ, and Luna Grill. Guests at the Cambria can enjoy a free daily breakfast buffet, as well as a 30,000 square foot water park with pool, kids’ pool, waterslides, splash area, fire pit, movie screen, and outdoor bar.
- Free breakfast buffet
- Two showers in each room
- 30,000 square foot water park, perfect for a day away from the parks
- Proximity of several restaurants, including Starbucks
Book here: You can book the Cambria Hotel and Suites here .
Tropicana Inn & Suites
The Tropicana Inn and Suites is located on Harbor Blvd., about five minutes away from the main entrance of Disneyland. This bright, colorful inn is popular with families looking for the convenience of a hotel within walking distance of Disneyland, but also needing a little more space to spread out.
Room options at the Tropicana Inn and Suites include double rooms, family suites, park view rooms, and double queen rooms with a sleeper chair accommodating a fifth person. Most rooms have a mini fridge and microwave, although the suites have fully-equiped kitchens.
The Tropicana offers an outdoor heated pool, and jacuzzi, as well as the Cove Market with essentials you may need for your vacation.
- Very close proximity to Disneyland
- Wide variety of room types
- Suites with kitchens available
Book here: Click here to book the Tropicana Hotel .
Clementine Hotel & Suites Anaheim
Located on South Clementine Street, the Clementine Hotel and Suites is located a quarter-mile from Disneyland Resort. It’s a condo-style hotel, offering studios, one-bedroom, two-bedroom, and loft-style suites. There is a breakfast available for an additional fee, but it will be included in the resort fee later this year.
Unlike most of the hotels in the area, the Clementine Hotel and Suites offers free parking (for one vehicle for most rooms, and two vehicles for bi-level or 2-bedroom suites). Amenities include a fire pit, outdoor heated pool, lobby mart with essentials, on-site playground, heated outdoor swimming pool, and sports court. Pets are welcome for an additional fee.
- Suites with kitchens
- Pet-friendly
- Complimentary parking
Book here: You can book the Clementine Hotel here .
Disney’s Paradise Pier Hotel
Disneyland’s Paradise Pier Hotel is currently undergoing a transformation into Disney’s Pixar Pier Hotel. It should be completely later this year, and the hotel is remaining open during the renovation.
If you are looking for Disney theming on your Disneyland vacation, this is an excellent option. Like the other Disney owned and operated hotels, it offers early park entry, and is located close to the parks.
The hotel offers standard hotel rooms as well as 1, 2, and 3-bedroom suites. These rooms come in a variety of different configurations, offering both regular beds and sofa beds. This hotel near Disneyland offers some amenities that are currently unavailable due to construction, including pools, fitness center, and a kids’ theater (guests can use amenities at the Disneyland Hotel while these are closed).
- Fun theming (especially once the renovation is complete)
- Great room configuration options
- Early theme park entry
- Quick walk to Disneyland
- Close proximity to Disney Springs
Book here: You can book the Paradise Pier Hotel here .
Disney’s Grand Californian Hotel and Spa
The grandest of the Disneyland hotels is the Grand Californian Hotel, located very close to Disneyland (and closest of the three Disney owned hotels). This is the most luxurious of the Disneyland hotels, and is priced accordingly.
While you’ll be right in the heart of Disneyland, this resort will make you feel completely separated and remote. It’s California themed, with natural elements incorporated.
Amenities at the Grand Californian include the Redwood Pool and the Mariposa Pool, the Tenaya Stone Spa, Storytellers Café, and Napa Rose restaurant. A princess breakfast is hosted daily at Napa Rose (make reservations well in advance), and is great for kids looking to meet the princesses.
The Grand Californian is also a Disney Vacation Club property, with DVC studios and villas on site. Regular hotel rooms are also available.
- There’s no better option if you are looking for a luxury stay in the heart of Disneyland
- Two beautiful pools
- Great restaurants
- Very close proximity to the Disneyland theme parks and Downtown Disney
- On property spa
- Early park entry
Book here: Click here to book the Grand Californian Hotel and Spa .
Howard Johnson by Wyndham Anaheim Hotel and Water Playground
Guests looking for convenient access to the Disneyland Parks with a touch of mid-century nostalgia should definitely check out the Howard Johnson Anaheim Hotel and Water Playground . This hotel is located on South Harbor Drive in Anaheim and is within quick walking distance of the front entrance of the Disneyland parks.
The Howard Johnson offers some newly renovated rooms (these are the 2-queen bedrooms), which are colorfully decorated in a nostalgic mid-century style. There’s also the House of the Retro Future Suite , a one-of-a-kind suite with some fun retro-future touches.
The hotel offers Castaway Cove, a water playground with a drench bucket, small slides, spray fountains, a kiddie pool, and more. There’s also the garden pool, a business center, a gift shop, and more.
- Walking distance to Disneyland
- The water playground is great for families with younger kids
- A fun nostalgic decor
- Some newly renovated rooms
Book here: Click here to book the Howard Johnson Anaheim Hotel and Water Playground .
Courtyard Anaheim Theme Park Entrance & Waterpark Resort
My most recent stay at Disneyland included four nights at the Courtyard Anaheim Theme Park Entrance and Waterpark Resort . This hotel, located on South Harbor Blvd, is one of the best options for larger families because all rooms accommodate six guests.
The Courtyard Anaheim Theme Park Entrance offers an on-site restaurant, called the Bistro, with Starbucks Coffee. There’s also a small gift shop, and a sundries shop.
Parking is valet only (for an additional fee), but you’re easily able to walk to the front entrance of Disneyland in just a few minutes.
The standard rooms at the Courtyard are fantastic for families. They include a mini fridge, microwave, small dinette area, two showers (one stall, one combo shower/tub), and a set of bunk beds. Some of the rooms have water park and theme park views. During my stay, I overlooked the water park and was able to see the Disneyland fireworks a few nights.
The waterpark is a big draw here. It’s currently available exclusively to resort guests but does require a reservation. It offers a dunk bucket, spray area, pool, waterslides, and more.
See our hotel room tour here:
- The fun waterpark
- Rooms that accommodate 6 guests
- Close proximity to the theme parks
- Nice, modern rooms
Book here: Book your stay at the Courtyard Anaheim here .
Westin Anaheim Resort
My son and I stayed at the Westin Anaheim Resort last July, and really loved our stay. It opened recently, and is now one of the best hotels within walking distance of Disneyland. It’s one of my favorite hotels I’ve stayed in recently.
The Westin Anaheim Resort is located behind Pixar Pier in Disney’s California Adventure Park. However, to access the parks, you’ll need to walk down through Disney Springs. It is a bit of a longer walk than the Harbor Blvd hotels but still very doable.
Rooms at the Westin include all their signature elements, including the Heavenly Bed and Shower. While some rooms have theme park views, others do not. We didn’t have a view, but didn’t spend too much time in the room.
The Westin offers some on-site dining options, including RISE Rooftop Lounge, the Tangerine Room, Bar 1030, Bella’s Splash Pool Bar, Fleming’s Prime Steakhouse & Wine Bar, Puesto, and the Blossom Cafe & Market. My son and I loved getting breakfast at the Blossom Cafe each morning (additional fee applies).
Guests staying at the Westin can enjoy a fitness center and outdoor pool, as well as a hot tub. We really loved this resort – it’s very comfortable and the nearby food options are great.
- Signature Westin hotel features that make this a comfortable stay
- Great dining options
- Fantastic service
- More upscale than some of the nearby hotels
- Some rooms with theme park views
- Fireworks view from rooftop lounge
Book here: Book your stay at the Westin Anaheim here .
Fairfield Inn Anaheim Resort
The Fairfield Inn Anaheim Resort, located adjacent to the Courtyard Anaheim on Harbor Blvd, is a short walk to the Disneyland gates. It offers guest rooms with pullout sofa beds, as well as themed rooms and junior suites.
The hotel has a fitness center, outdoor pool, game room, and whirlpool. A Panera Bread is attached to the resort and offers room service to the guest rooms.
- Affordable rates
- Close location to the front entrance of Disneyland
- Pullout sofa to accommodate another guest
Book here: Click here to book .
Frequently Asked Questions
If you are just visiting Disneyland, you really don’t need to rent a car if you are staying at one of these hotels within walking distance. For most hotels, you’ll need to pay for parking, which can be a waste if you aren’t using your car. If you are renting a car, you can compare rates here .
I’d recommend three days, which gives you enough time to visit the popular attractions at both theme parks.
You’ll have several airport options for your Disneyland vacation. LAX is the largest, and you are likely to find the most flights to and from there. But John Wayne Airport (SNA), is the closest, and Long Beach Airport (LGB) and Hollywood Burbank Airport (BUR) are also both options.
The Disneyland Hotel and Disney’s Grand Californian Resort and Spa are probably the two closest hotels to Disneyland. For easy access, these are some of the best options.
The post 11 Best Hotels Walking Distance To Disneyland appeared first on Family Travel Magazine .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A and B travel the same distance at a speed of 9 km/hr. and 10 km/hr respectively. A takes 36 minutes more than B. Concept used : Time = Distance/Speed . Calculations : Let the distance travelled be d km . According to the question . Time taken by A - time taken by B = 36 minutes = 3/5 hours (d/9) - d(10) = 3/5 . ⇒ d = 54 km
A and B travel the same distance at 9 km/h and 10 km/h respectively.if A takes 20 minutes longer than B the distance travelled by each is: View Solution A and B start at the same time with speed of 40km/hr and 50 km/hr respectively.
Quantitative Aptitude:- playlists- https://youtube.com/channel/UCj_7f1sTlOETw_QtzCr8--Q/playlistsMiscellaneous Qu:-"https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLjWvZ9...
Time × Speed = Distance. Calculation: Let the time taken by A be Q hours. According to the question, 8 × Q = 12 × (Q - 1/2) ⇒ Q = 1.5. Hence, distance travelled = 8 × 1.5 = 12 km. ∴ The distance travelled by each one of them is 12 km. Download Solution PDF.
A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9 km/hr and 10 km/hr respectively. If A takes 36 minutes more than ... for more pdf join telegram :- @edu214ram 13. A and B travel the same distance at ...
Solution. Let be the total number of time in hours that Car B took to drive the distance. This means that for have the time Car B traveled miles and for half the time Car B traveled miles. That means the total distance traveled is miles, so Because both cars traveled the same distance, for half the distance Car A took hours and for half the ...
Like, the same distance, from B to A it'll take 100 minutes if the seed is 60 M/hr. It 'll take 250 minutes to travel a total distance of 200 Miles. So, we can figure it out by an equation to get the average like this. 200x60/250 = 48.
A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9 km/hr and 10 km/hr respectively. If A takes 36minutes more than B, the distancetravelled by each is48 km (2) 5...
distance = speed x time. Rate and speed are similar since they both represent some distance per unit time like miles per hour or kilometers per hour. If rate r is the same as speed s, r = s = d/t. You can use the equivalent formula d = rt which means distance equals rate times time. distance = rate x time. To solve for speed or rate use the ...
Step 2: Let the distance travelled by each be x km. Then, we can write the time taken by A and B as follows: Time taken by A = x/9 hours Time taken by B = x/10 hours Step 3/4 Step 3: According to the problem, A takes 1/3 hours more than B. So, we can write the equation: x/9 - x/10 = 1/3 Answer Step 4: Solve the equation for x.
A and B travel the same distance at 9 km/h and 10 km/h respectively. If A takes 36 minutes longer than B, the distance travelled by each is: a) 48 km b) 54 km c) 60 km d) 125 km. Instant Video Answer ...
VIDEO ANSWER: A&B are mostly the same speed of 45 km/h along the same direction. A third car C is moving from the opposite direction with the speed of 36 kilometers per arm reached a car in the interval of five minutes, a few cars and we should be in ... A and b travel the same distance at speeds of 9 km/hr and 10 km/hr respectively. If a takes ...
Suppose you travel a distance "d" from A to B with the speed of x miles per hour and the distance from B to A with the speed of y miles per hour. In this case, the same distance is covered (both ways) but with the different speeds. In this case, the average speed is given by. Total distance traveled $= d + d = 2d$
A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9 km/hr and 10 km/hr respectively. If A takes 36 min more than B, the distance travelled by each is : x x. x 9 − x 10 = 36 60 ⇒ x 90 = 3 5 ⇒ x = 3 5 × 90 ⇒ x = 54km Hence option B is correct x 9 − x 10 = 36 60 ⇒ x 90 = 3 5 ⇒ x = 3 5 × 90 ⇒ x = 54 km Hence option B is correct.
A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9km/hr and 10 km/hr respectively. If A takes 36 minutes more than B, the distance travelled by each is . A) 48 km : B) 54 km : C) 60 km : D) 66 km : Correct Answer: B) 54 km : Description for Correct answer:
A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9 km/hr and 10 km/hr respectively. If A takes 36 minutes more than B, the distance travelled by each is : [A]48 km [B]54 km [C]60 km [D]66 km Show Answer .
Questions : A and B travel the same distance at speed of 9 km/hr and 10 km/ hr respectively. If A takes 36 minutes more than B, the distance travelled by each is (a) 66 km (b) 60 km (c) 54 km (d) 48 km. The correct answers to the above question in: Answer: (b)
To find the distance between two points we will use the distance formula: √ [ (x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]: Get the coordinates of both points in space. Subtract the x-coordinates of one point from the other, same for the y components. Square both results separately. Sum the values you got in the previous step.
Distance (D) = Rate (R) * Time (T) For Car A: D = 30T {Eqn 1} For Car B: The Distance D and the time T is the same as for Car A; But, unlike Car A, Car B travels at two different rates. It travels at 20mph for a time T1. Then it passes Car A and travels at a rate of x for a period of time T2. D = (20T1) + (x * T2)
The boats A and B travel with constant speeds of vA = 14 m/s and UB = 12 m/s when they leave the pier at O at the same time. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the distance between them when t = 3 s Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 11 HA ? dAB = 35 m Figure 1 of 1 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining ...
a and b travel the same distance at the rate 8 kilometer and 10 kilometre and hour respectively. if i take 30 minutes longer b, the distance travelled by b is. Instant Answer. Step 1/7 1. Let's assume that the distance travelled by both a and b is d kilometers. Step 2/7 2. We know that the time taken by a to travel this distance is given by t ...
Free distance calculator - Compute distance between two points step-by-step
You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Question: The boats A and B travel with constant speeds of VA = 15 mls and VB = 10 mls when they leave the pier at O at the same time. Determine the distance between themwhen t = 4 s. The boats A and B travel with constant speeds of VA = 15 mls and ...
The post 11 Best Hotels Walking Distance To Disneyland appeared first on Family Travel Magazine. Disneyland, the original of the Disney theme parks, is truly an original.