You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

Thailand Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
There are no notices currently in effect for Thailand.
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
There is no longer active cholera transmission and vaccine is not recommended.
Cholera - CDC Yellow Book
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Thailand.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Thailand. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Thailand.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
Japanese Encephalitis
Recommended for travelers who
- Are moving to an area with Japanese encephalitis to live
- Spend long periods of time, such as a month or more, in areas with Japanese encephalitis
- Frequently travel to areas with Japanese encephalitis
Consider vaccination for travelers
- Spending less than a month in areas with Japanese encephalitis but will be doing activities that increase risk of infection, such as visiting rural areas, hiking or camping, or staying in places without air conditioning, screens, or bed nets
- Going to areas with Japanese encephalitis who are uncertain of their activities or how long they will be there
Not recommended for travelers planning short-term travel to urban areas or travel to areas with no clear Japanese encephalitis season.
Japanese encephalitis - CDC Yellow Book
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine for US Children
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Thailand take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Thailand.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Rabid dogs are commonly found in Thailand. However, if you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in Thailand, rabies treatment is often available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Thailand.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
Required for travelers ≥9 months old arriving from countries with risk for YF virus transmission; this includes >12-hour airport transits or layovers in countries with risk for YF virus transmission. 1
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Avoid bug bites.
Chikungunya
- Mosquito bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
- Mosquito bite
Leishmaniasis
- Sand fly bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
Airborne & droplet
Avian/bird flu.
- Being around, touching, or working with infected poultry, such as visiting poultry farms or live-animal markets
- Avoid domestic and wild poultry
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Thailand, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Thailand. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Some diseases in Thailand—such as dengue, Zika, and filariasis—are spread by bugs and cannot be prevented with a vaccine. Follow the insect avoidance measures described above to prevent these and other illnesses.
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Thailand include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Leptospirosis, a bacterial infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Thailand. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Thailand’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Thailand. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Thailand may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Thailand, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Thailand, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Thailand .
Traffic flows on the left side of the road in Thailand.
- Always pay close attention to the flow of traffic, especially when crossing the street.
- LOOK RIGHT for approaching traffic.
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
To call for emergency services while in Thailand, dial 1669 for an ambulance, 199 for the fire department, and 191 for the police. Write these numbers down to carry with you on your trip.
Learn as much as you can about Thailand before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Thailand from the US Department of State.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Thailand for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
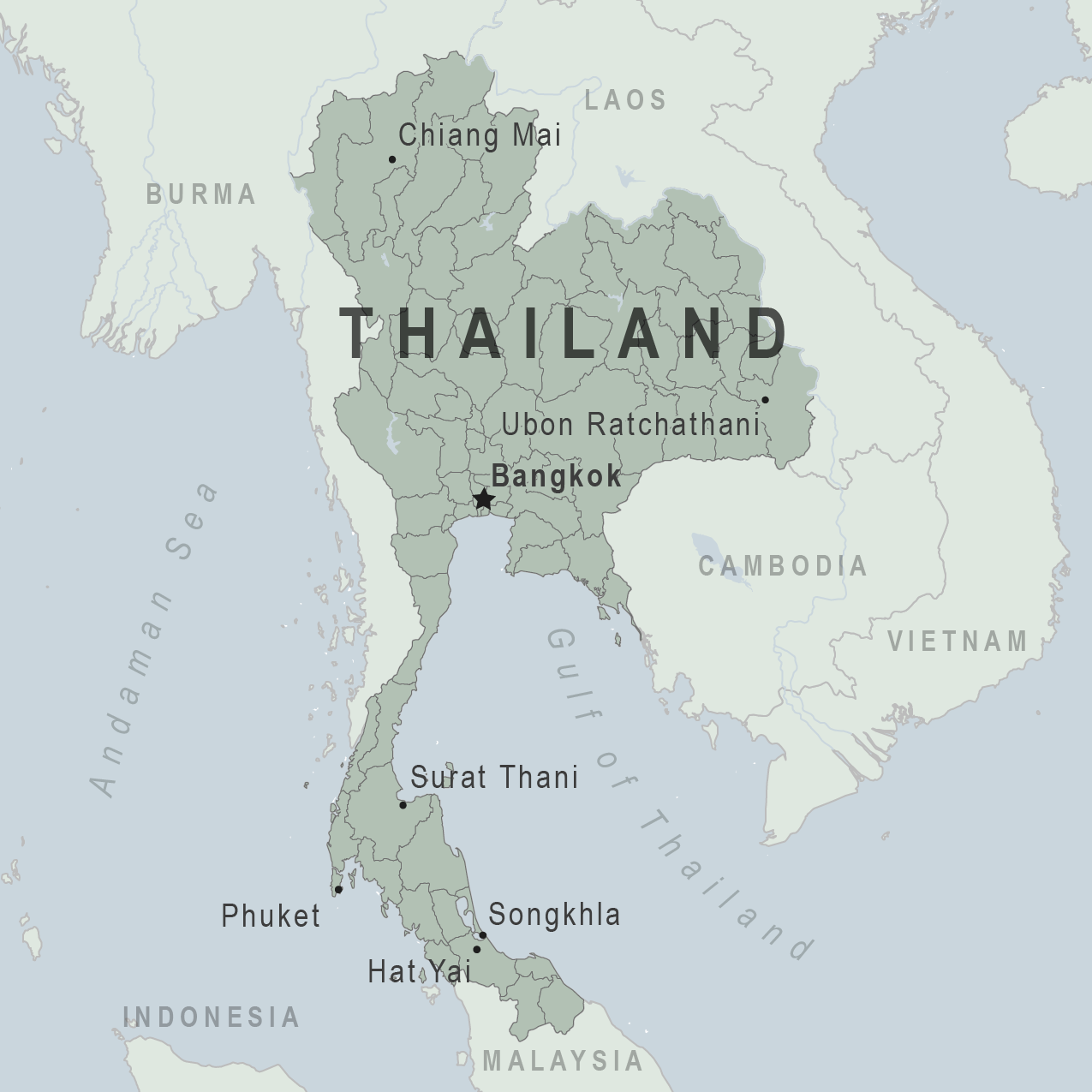
Travel Vaccines and Advice for Thailand

Thailand is a popular destination with its tropical climate, food, culture and beaches.
Thai is the official language of Thailand. But, other smaller languages spoken in rural areas. The primary religion of Thailand is Buddhism and is prevalent in many aspects of culture throughout Thailand. Islam is also practiced in Southern provinces.
Bangkok, Thailand’s capital city, is also the largest city in the country. Bangkok is highly populated with congested streets, modern buildings and temples. It is most known for its nightlife.
Thailand’s other major cities include Ayutthaya, Chiang Mai, and Chiang Rai.
Do I Need Vaccines for Thailand?
Yes, some vaccines are recommended or required for Thailand. The CDC and WHO recommend the following vaccinations for Thailand: typhoid , cholera , hepatitis A , polio , yellow fever , Japanese encephalitis , chikungunya , rabies , hepatitis B , influenza , COVID-19 , pneumonia , chickenpox , shingles , Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis) and measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) .
See the bullets below to learn more about some of these key immunizations:
- Typhoid – Food & Water – Recommended for travelers to most regions.
- Cholera – Food & Water – Cholera is rare, but present in Thailand. Vaccination is recommended for travelers at increased risk or visiting areas with active transmission.
- Hepatitis A – Food & Water – Recommended for most travelers.
- Polio – Food & Water – Generally considered a routine vaccination for most travel itineraries. Single adult booster recommended.
- Yellow Fever – Mosquito – Required if traveling from a country with risk of yellow fever transmission
- Japanese Encephalitis – Mosquito – Recommended depending on itinerary and activities. Recommended for extended travel, recurrent travelers and travel to rural areas. Present throughout country, especially northern regions. Most cases from May to October.
- Chikungunya – Mosquito – Thailand is a higher risk region. Vaccination is recommended.
- Rabies – Saliva of Infected Animals – High risk country. Vaccine recommended for long-term travelers and those who may come in contact with animals.
- Hepatitis B – Blood & Body Fluids – Recommended for travelers to most regions.
- Influenza – Airborne – Vaccine components change annually.
- COVID-19 – Airborne – Recommended for travel to all regions, both foreign and domestic.
- Pneumonia – Airborne – Two vaccines given separately. All 65+ or immunocompromised should receive both.
- Chickenpox – Direct Contact & Airborne – Given to those unvaccinated that did not have chickenpox.
- Shingles – Direct Contact – Vaccine can still be given if you have had shingles.
- TDAP (Tetanus, Diphtheria & Pertussis) – Wounds & Airborne – Only one adult booster of pertussis required.
- Measles Mumps Rubella (MMR) – Various Vectors – Given to anyone unvaccinated and/or born after 1957. One time adult booster recommended.
See the table below for more information:
Specific Vaccine Information
- Typhoid – Typhoid, caused by Salmonella Typhi, spreads via contaminated food and water, especially in areas with poor sanitation. Protect yourself by practicing good hygiene and safe food habits. Vaccination can significantly reduce the risk of typhoid infection, especially when traveling to endemic areas.
- Hepatitis A – Be sure to protect yourself from hepatitis A, a contagious liver infection caused by HAV, through vaccination. The virus spreads through contaminated food, water, and close contact. Along with vaccination, maintaining proper hygiene and avoiding undercooked shellfish are essential for prevention.
- Japanese Encephalitis – Japanese encephalitis is a mosquito-spread viral disease that affects the central nervous system. Prevention is achieved through protective attire and vaccination.
- Chikungunya – Chikungunya, a mosquito-borne virus, can be prevented by avoiding mosquito bites and reducing breeding sites. The chikungunya vaccine provides teh best protection.
- Rabies – Rabies is a deadly viral illness transmitted mainly through animal bites. Vaccination is pivotal, with pre-exposure and post-exposure options available to protect against this potentially fatal disease.
- Hepatitis B – The hepatitis B virus leads to liver infection through contact with infected fluids. The most effective safeguard is the hepatitis B vaccine, administered in a series of shots that stimulate the body to produce antibodies, providing long-term immunity. It is crucial for infants and those at an increased risk of exposure.
- Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) – Measles, mumps, and rubella are viral infections that can spread through close contact and respiratory droplets. Vaccination is the most effective way to halt their transmission. The MMR vaccine, given in two doses, strengthens immunity, reducing the chances of contracting and spreading these diseases.
Malaria In Thailand
Malaria is primarily found the border provinces, near Burma, Cambodia and Malaysia. Some rare cases have been identified in Bangkok, Chiang Mai and Chiang Rai. Parasites in Thailand are resistant to chloroquine and mefloquine. Consult with a travel health specialist on which antimalarial will be best for your trip.
To find out more about these vaccines, see our vaccinations page. Ready to travel safely? Book your appointment either call or book online now.
Other Ways to Stay Healthy In Thailand
Prevent bug bites in thailand.
Safeguard against bug bites by dressing appropriately and using EPA-registered repellents with DEET, picaridin, or OLE. If bitten, cleanse the area, refrain from scratching, and mitigate discomfort with OTC treatments. Seek medical aid for serious reactions.
Food and Water Safety In Thailand
When traveling, ensure food safety by adhering to CDC recommendations, which include eating fully cooked foods, avoiding raw seafood, and selecting reputable dining places. Safely drink bottled beverages, avoiding ice in uncertain water sources, and consume alcohol in moderation. Prevent travelers’ diarrhea through hand hygiene and avoiding street food in unsanitary areas.
Infections To Be Aware Of In Thailand
- Avian/Bird Flu – Avian flu, also known as bird flu, is a contagious virus that affects birds and can spread to humans. Preventing it involves vaccination of poultry, strict biosecurity on farms, safe handling and cooking of poultry, surveillance for outbreaks, and raising public awareness.
- Dengue – Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne illness with symptoms ranging from mild to severe, including high fever and pain. The CDC emphasizes prevention through avoiding mosquito bites by using repellents and removing standing water. Treatment focuses on symptom relief and hydration, avoiding certain pain relievers that can worsen bleeding risks.
- Leishmaniasis – Leishmaniasis is transmitted by sand flies’ bites. To prevent its spread, individuals should use insect repellents, wear long-sleeved clothing and limit outdoor activities during sand fly activity periods. Eliminating breeding sites and early diagnosis are crucial for effective prevention.
- Zika – Zika, a mosquito-borne virus, can cause mild to severe symptoms and poses significant risks during pregnancy. Prevention strategies include using insect repellent, safe sex practices, and avoiding travel to affected areas.
Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Thailand?
U.S. citizens staying in Thailand for 30 days or less do not need a visa. But, their passport must be valid for at least six months from the date of entry.
Sources: Embassy of Thailand and U.S. State Department
Always carry your passport and visa with you to avoid arrest in Thailand.
What is the Climate Like in Thailand?
Thailand is a country with a tropical climate that is hot and humid throughout the year. The temperature ranges from 25 to 35 degrees Celsius during the day. The weather can be different depending on where you are in Thailand. Here are some popular tourist destinations:
- Bangkok : Bangkok is hot and humid all year round. It rains a lot, especially between May and October.
- Phuket : Phuket is a tropical place. It can rain a lot from May to October. The temperature is usually between 75 and 90 degrees.
- Chiang Mai : Chiang Mai has a tropical climate with three different seasons: cool, hot, and rainy. The cool season runs from November to February, the hot season from March to May, and the rainy season from June to October.
- Pattaya : Pattaya is hot and humid all year round. It rains a lot, especially between May and October.
- Koh Samui : Koh Samui is an island that has two different seasons: dry and rainy. The dry season runs from December to April, and the rainy season from May to November.
Remember that weather can change, so always check the forecast before you travel.
How Safe is Thailand?
In the past few years, there have been periodic terrorist attacks at popular tourist attractions in Thailand,. This remains a high-concern today. There is an ongoing risk of terrorist attacks in Thailand.
The National Council for Peace and Order (NCPO) has placed strict restrictions on media and have banned political gatherings. Tourists may be detained by the military for openly criticizing the NCPO.
Pick-pocketing is common in Thailand as is sexual violence in bars and isolated areas.
Do not use your passport as collateral. Many rental places are scams.
In Southern Thailand (Yala, Pattani, Narathiwat, and Songkhla), martial law is still prevalent. Tourists are cautioned against traveling to these areas.
Temples in Thailand
Avoid mosquitoes and other bugs, insect-borne disease are a threat throughout the world., keep the bugs away with passport health’s repellent options .
There are over 40,000 temples in Thailand, making them popular tourist attractions. These temples range in age and architecture and many are still in use today.
Wat Pho, located in Bangkok, is one of the most popular due to its size and attractions within. It is one of the largest complexes in the country, holding many buildings. Wat Pho houses the largest reclining Buddha and largest collection of Buddha images.
The site is also headquarters for the teaching and preservation of Thai medicine. There, tourists can find two massage schools and pavilions.
You must take off your shoes to enter and you purchase coins to put into bowls for good luck. All the money goes towards renovating and up-keeping the site.
What Should I Take To Thailand?
Thailand is a hot and humid country, it’s important to pack lightweight and comfortable clothing. You should bring comfortable shoes for walking, sun protection like sunscreen, hats, and sunglasses to avoid the strong sun rays. Mosquitoes are common in Thailand, so it’s important to bring insect repellent to avoid bites.
Thailand uses different types of electrical outlets, so it’s recommended to bring a universal adapter. It’s also recommended to pack any prescription medication and over-the-counter medications such as pain relievers, anti-diarrhea medication, and motion sickness medication.
Thailand is a cash-based society, so it’s important to bring cash and credit cards. If you plan to visit the beaches or go swimming, don’t forget to pack swimwear and a beach towel. When visiting temples or other religious sites, make sure to dress respectfully, covering your shoulders and knees, and avoid wearing revealing clothing in public places.
Don’t forget to bring your passport, visa (if required), travel insurance, and any other important travel documents.
U.S. Embassy in Thailand
All Americans visiting Tunisia should register online with the U.S. Department of State before departure. This will inform the office of your travel plans within the country and will allow them to reach out in the case of an emergency or evacuation.
Once in Thailand, the information for the U.S. Embassy is:
U.S. Embassy Bangkok 95 Wireless Road Bangkok 10330 Thailand Telephone: + (66) (2) 205-4049, 02-205-4049 (within Thailand) Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(66) (2) 205-4000, 02-205-4000 (within Thailand) Fax: +(66) (2) 205-4103, 02-205-4103 (within Thailand) Email: [email protected]
If you have any questions about traveling to Thailand or are wondering what shots you may need for your trip, schedule an appointment with your local Passport Health travel medicine clinic. Call us at or book online now! and protect yourself today.
Customer Reviews
Passport health – travel vaccines for thailand.
On This Page: Do I Need Vaccines for Thailand? Is Cholera in Thailand? Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Thailand? What is the Climate Like in Thailand? How Safe is Thailand? Temples in Thailand What Should I Take To Thailand? U.S. Embassy in Thailand

- Records Requests
- Passport Health App
- Privacy Center
- Online Store

Update to Covid-19 vaccine guide for travellers to Thailand

The Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT) on Monday provided an update to guide to Covid-19 vaccines for international travellers to Thailand effective from December 16, 2021.
International travellers, including returning Thais and foreign residents, who are above 18 years of age should get fully vaccinated for Covid-19 with a vaccine approved by Thailand’s Ministry of Public Health (MoPH) or the World Health Organisation (WHO) no less than 14 days before their travel date.
Travellers 12-17 years of age, travelling with parents under the Test & Go entry scheme and Sandbox Programme, are not required to be vaccinated but must have a negative RT-PCR test result within 72 hours before travelling. Those unaccompanied must get vaccinated with at least one dose of an approved vaccine and must have a negative RT-PCR test result.
Travellers 6-11 years of age, travelling with parents under the Test & Go entry scheme and Sandbox Programme, must have a negative RT-PCR test result within 72 hours before travelling.
Travellers under 6 years of age, travelling with parents with a negative RT-PCR test result within 72 hours before travelling, are not required to have a pre-arrival negative RT-PCR test result and can have saliva test when entering the Kingdom.
Travellers previously infected within 3 months before travelling must have a medical certificate of recovery or get vaccinated with at least one dose of an approved vaccine for an unspecified period of time before travelling.
List of approved Covid-19 vaccines
Currently, the MoPH has approved the following manufacturers and vaccines:
- CoronaVac by Sinovac Biotech Ltd – 2 doses needed / 2-4-week interval;
- AstraZeneca or Covishield by AstraZeneca and the University of Oxford, SK Bioscience (South Korea), Siam Bioscience, and Serum Institute of India (Covishield) – 2 doses needed / 4-12-week interval;
- Pfizer–BioNTech or Comirnaty by Pfizer Inc. and BioNTech 2 doses needed / 3-week interval;
- Janssen or Janssen/Ad26.COV2.S by Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc. – 1 dose needed;
- Moderna by Moderna Inc. – 2 doses needed / 4-week interval);
- Sinopharm or COVILO by Sinopharm Co., Ltd. – 2 doses needed / 3-4-week interval);
- Sputnik V by the Gamaleya Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology – 2 doses needed – 3-week interval).
Meanwhile, the WHO’s guidance on the Covid-19 vaccines is available here .
Have you been fully vaccinated?
According to the MoPH, travellers are considered fully vaccinated if:
- They get their second dose of a 2-dose vaccine; such as, the AstraZeneca or Pfizer vaccines, no less than 14 days before their travel date to Thailand.
- They get a single-dose vaccine; such as, Janssen vaccine, no less than 14 days before their travel date to Thailand.
- In case of mix-and-match vaccines, travellers should get their second dose of a different vaccine within the recommended interval of the first vaccine no less than 14 days before their travel date to Thailand. For example, if the first vaccine is CoronaVac from Sinovac Biotech and the second vaccine is AstraZeneca, the time between the two doses is 2-4 weeks.
Travellers who do not meet these criteria may be denied entry into Thailand.
Requirements for the ‘Certificate of Covid-19 Vaccination’
The travellers’ Certificate of Covid-19 Vaccination should contain the following details:
- Given name and last name;
- Date of Birth;
- Nationality;
- Passport or Identification No.;
- Name of the Covid-19 vaccine;
- Vaccination dates;
- Vaccine manufacturer and lot/batch number;
- Authorised organisation in the country of origin.
In addition to being fully vaccinated, international travellers should have all of their advance arrangements in good order for arrival and entry. For more information on Thailand’s reopening programmes, see: https://www.tatnews.org/thailand-reopening/ .
Covid-jab rules for travellers confirmed
Aviation regulator says requirement will apply to all passengers on international flights landing from 1am Monday
PUBLISHED : 7 Jan 2023 at 20:50
WRITER: Online Reporters

The requirement that all international travellers show proof of full Covid-19 vaccination before boarding flights to Thailand will take effect from Sunday, the Civil Aviation Authority of Thailand (CAAT) said on Saturday.
The aviation regulator has formally notified all parties about the change to arrival rules for international travellers aged 18 and over. They will take effect for flights landing in Thailand from 1am local time on Monday and will remain in effect at least until the end of the month.
The vaccination requirement was scrapped last October but it has been revived as travel from China is about to resume worldwide on a large scale. Many countries have responded with special measures out of concern that Covid-19 is sweeping through China since the country scrapped its zero-Covid restrictions last month.
Public Health Minister Anutin Charnvirakul has said that any rules adopted in Thailand must not discriminate against any particular country.
According to the CAAT, everyone travelling to the country from Sunday must show proof of full vaccination or a letter certifying that they have recovered from Covid-19 infections no more than six months prior. Unvaccinated travellers must have proof of why they cannot receive a vaccine.
Details of the approved vaccines and required number of doses are available on the CAAT website .
Airlines will be responsible for checking the relevant documents before passengers board and must bar those without the correct paperwork. It is not clear whether passengers will also be required to show the documents again when they land in Thailand.
As well, people who will be travelling from Thailand to a country where a negative RT-PCR test is a condition of entry must show proof of health insurance. This is to ensure that the costs of their care will be covered if they test positive before leaving Thailand.
Thai passport holders or travellers in transit are not required to submit proof of vaccination or hold a Covid-19 insurance policy.
A Xiamen Airlines flight with 200 passengers is scheduled to be the first flight from China to touch down at Suvarnabhumi Airport on Sunday.
- Coronavirus
- International travellers
RECOMMENDED
Court accepts petition for dissolution of move forward, more wage hikes to be mulled: pm, pm downplays reshuffle talk, first thailand road safety forum launches at ait, concerns rise over vaping by young people.

Covid outbreak at Prachuap prison
Flu, dengue fever pose risk, covid-19 detector probes wastewater.

This website is managed by Siam Legal International - a law firm in Thailand

Thailand Travel Restrictions
(Updated on October 10, 2023 Bangkok, Thailand)
UPDATED THAILAND TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS
The Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT) has announced that Thailand continues to welcome all international tourists in 2023.
Thailand’s Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Public Health, said “International travelers arriving in Thailand are not required to show proof of vaccination.”
In addition, foreign tourists are not required to show ATK or RT-PCR test results.
Exercise normal precautions for COVID 19 prevention.
Thailand does recommend COVID insurance for visitors from all countries when visiting Thailand.
After months of strict travel restrictions because of the COVID-19 pandemic, Thailand is restored a return to normalcy by easing all travel restrictions and quarantine requirements to allow tourists to enter the country.
Travelers around the world are now keen to find out when and how they can travel to Thailand in 2023. What important things do travelers need to know about Thailand Travel Restrictions if they are planning to fly to the Land of Smiles? Here is some helpful information for you.

Required Documents for Travel to Thailand in 2023
Please have the following documents ready.
- Passport with at least six month validity
- Visa or visa exemption qualification
- Buy Thailand Travel Insurance
- Boarding pass to be presented at Passport Control
- Hotel booking confirmation if asked by Immigration Officer
- Note: Vaccination record no longer required
Incorrect documents will delay the entry screening by rules from the Thai immigration bureau and its Thai immigration officials.
Buy Your Insurance Now
Latest News as of October 10, 2023
- For up-to-date information and weekly updates regarding current Thailand travel restrictions, please visit the Weekly Updates for Thailand Travel Restrictions .
- As of October 1, 2022, Thailand will no longer have COVID entry requirements. Please exercise normal precautions as necessary when visiting Thailand.
- Buy your COVID Insurance now at AXA Thailand .
- Book your hotel in Thailand at Agoda.com
- Travelers may join our Facebook Group to ask questions, get help, and read the latest developments: https://www.facebook.com/groups/howtoenterthailand
Travel to Thailand
Travelers may enter Thailand with or without vaccination. Vaccination is not required.
No phone app for reporting or tracking is required.
No need to show proof of any vaccination or insurance coverage.

Entry and Exit Requirements
Each country or territory determines its own entry and exit requirements at its borders. If you fail to meet these requirements for your destination, your embassy will not be able to assist you. The following information is provided by Thai authorities and is subject to change without notice.
The entry prerequisites differ based on the passport type you are holding for travel.
Prior to your journey, consult with your travel carrier regarding passport stipulations, as their validity rules might be stricter than those mandated by the destination country.
Ensure that your passport has at least six months of validity upon your arrival in Thailand.
Other Entry Requirements
Immigration officers at the Thai border may request to see a ticket for your return or onward journey, as well as evidence of adequate funds to sustain you throughout your visit. Failure to present these documents may result in denial of entry.

Entry Stamp
Obtain your entry stamp directly from an immigration officer when entering Thailand. Avoid acquiring your visa, visa extension, or entry stamp through visa shops or travel agents within the country.
Passports that have been modified or carry fake visas and entry/exit stamps will be considered invalid. Individuals caught with such passports may face imprisonment, fines, and deportation, and might also be barred from future entry into Thailand.

Do You Need a Visa to Enter Thailand?
Visitors from countries under the Visa Exemption List are not required to obtain a Thai visa in order to travel to Thailand for tourism purposes. The Thai Immigration Bureau will allow foreigners to stay in Thailand for 30 days. Tourists will be able to apply for a 30 days visa extension at any local immigration office in Thailand.
If you wish to stay longer or are traveling for a purpose other than tourism, please know that the normal 60-day Tourist Visa, Thai Elite Visa , and other non-immigrant visas are available at Thai Embassies or Consulates around the world.
Do you want to stay in Thailand for 5, 10, or 20 years? You may consider the Thai Elite Visa program. It is an easy-to-apply and hassle-free visa application for your long-term stay in Thailand. For more information about the Thai Elite Membership and Visa application, you may check this page: https://www.thaiembassy.com/thailand-visa/thai-elite-visa
Thailand Pass is no longer in effect
As of July 1, 2022, Thailand Pass is no longer required for foreign travelers entering Thailand.
Vaccinated travelers do not need to provide proof of vaccination before arriving. Unvaccinated travelers are also under no restrictions and can freely travel to Thailand.
Thailand COVID Insurance for Foreigners

It is recommended for foreigners traveling to Thailand to have a travel insurance policy before departing to Thailand. This is for their protection during the course of their trip to Thailand.
Having a reliable travel insurance policy that covers disruptions beyond Covid protects the investment you’ve made so you can feel secure and covered while enjoying what Thailand has to offer.
Purchasing a protection is affordable than paying the hospital bill out from your pocket. The average travel insurance cost for a trip to Thailand is only around $100 to $150.
Foreigners can get a Thailand travel insurance policy covering COVID-19 easily and conveniently. Visitors can buy the travel insurance online with a credit card and the insurance policy and COVID-19 certificate will be sent to you instantly.
Purchase your COVID Travel Insurance for foreigners HERE .

Flights to Thailand Have Resumed
Regarding flights to Thailand, the normal commercial passenger flights are operating as normal. Before booking flights to Thailand, travelers should ensure that they study the different categories of visas granted to foreign nationals at this time to determine the possibility of travel.
Check within your country’s state department for travel advisories during COVID-19.
No Quarantine Required
Traveling to Thailand has no restrictions at this time.

Travel Advisory for Thailand
Tourism is vital to the economy of Thailand. The Thai government has reopened the Kingdom of Thailand to foreign visitors during the COVID-19 pandemic without restriction.
It is important to review news about fast-changing developments within the country before you make travel plans. Information is available on this website, Tourism Authority of Thailand, and on government sites listed below.
Please research your destination of travel and its travel advisory so you have a pleasant experience for your stay in Thailand.
- Bangkok: No restrictions
- Pattaya: No restrictions
- Phuket: No restrictions
- Koh Samui: No restrictions
- Chiang Mai: No restrictions
- Hua Hin: No restrictions
List of Countries that may allow Travel to Thailand (Check with your Embassy for Travel Advisory):
- United States citizens should check with the US Department of State for any travel advisory, news, and emergency situations on their website for Thailand Travel Advisory .
- United Kingdom citizens can check for travel restrictions and news on the FDCO website for Foreign Travel Advice Thailand .
- Australian citizens still must obtain government approval to travel to Thailand. News, emergency assistance, or other important information can be found on their government site COVID-19 and travel Thailand and the Australian Embassy Thailand website for Australians in Thailand.
There are no travel requirements and restrictions in place at this time for foreigners entering Thailand.
We recommend contacting your local Thai embassy or consulate before making any plans or reservations. You may also leave your questions in the comment section.
Top 20 Questions Asked this Week by our Visitors
What is the visa exemption scheme.
Thailand has a Visa Exemption Scheme that allows nationals from certain countries to enter Thailand for tourism purposes without a visa. Visitors under this scheme will be granted a stay of a specific duration, typically 30 or 45 days, but this may vary based on the traveler’s nationality and the current regulations in place.
Where can I apply for a tourist visa for Thailand?
You can apply for a Thai tourist visa at a Royal Thai Embassy or Consulate in your home country or in a third country.
Below are the general steps involved, but note that processes may vary slightly at different embassies or consulates:
Steps to Apply for a Thai Tourist Visa:
- Find the Nearest Thai Embassy or Consulate: Look for a Royal Thai Embassy or Consulate in your country of residence or a neighboring country. You can usually find this information on the Thai Ministry of Foreign Affairs’ official website or by conducting a simple online search.
- Prepare Required Documents: Typically, you will need your passport (with at least six months’ validity), completed visa application form, passport-sized photographs, proof of travel arrangements (like flight and hotel bookings), and evidence of financial means.
- Submit Application: You may need to submit your visa application and required documents in person, although some embassies or consulates may offer online submission or postal services. Be sure to check the specific submission guidelines for the embassy or consulate where you’re applying.
- Pay Visa Fee: There will usually be a non-refundable visa application fee, which can vary by location and visa type. Payment methods can also differ, so verify this in advance.
- Wait for Processing: Visa processing times can vary. Some applications are processed in a few days, while others may take weeks. Check the estimated processing time and plan accordingly.
- Receive Visa: Once approved, you’ll receive your visa, which will be stamped or affixed to a page in your passport. Carefully review the visa to confirm that all information is accurate and understand the terms of your stay.
Are there any restrictions on tourists coming to Thailand?
Travel restrictions and requirements for entering Thailand can change frequently due to the ongoing global situation with the COVID-19 pandemic, and other factors that might influence travel policies. The information provided here might be outdated, so it is imperative that you check the most current and relevant travel advisories and updates.
Here are some general restrictions and requirements for tourists entering Thailand.
General Entry Requirements:
- Visa Requirements: Depending on your nationality, you may need a visa to enter Thailand. Some nationals can enter under the Visa Exemption Scheme, while others might need to apply for a visa in advance.
- Valid Passport: A passport with at least six months of remaining validity is typically required.
- Proof of Funds: You might need to demonstrate that you have sufficient funds to support yourself during your stay.
- Onward or Return Ticket: Some travelers may need to show a confirmed ticket for return or onward travel.
Additional Restrictions:
- Travel advisories and restrictions can also depend on the ongoing global and local situation, such as public health concerns, security issues, or other emergencies.
How do I buy an ATK test?
You can also purchase an ATK self-test from pharmacies and 7-11’s in Thailand. They cost between 100-150 Thai baht. ATK testing is optional and not required by the Thai government.
Is Thai Airways operating normal flights in and out of Thailand?
Are masks required to be worn in thailand.
No. You will see many Thai people wearing masks for public health protection.
Is COVID 19 treatment and medicine available foreigners?
Yes, you may visit any clinic or hospital in Thailand for treatment of COVID 19. Please exercise normal precautions while traveling to obtain treatment if infected or use telemedicine so you can stay safely in your accommodations.
Visitors insured with AXA Travel Insurance will have full coverage for COVID 19 medical treatment. AXA is the most popular Thailand Travel Insurance for foreign travelers.
What is the best time of year to travel to Thailand?
November to February is the best time of year to visit Thailand as it is during the cool season.
What activities can you to do in Thailand?
- Island hopping
- Scuba diving
- Boat ride in the Andaman sea
- Eat delicious food
- Savory and Tasty Thai foods
What is the best way to find hotels?
You can find listings for hotels in all areas at Agoda .
When is the low season for travel to Thailand?
April to May are the hot season. July to September is a rainy. These months are the low season.
Are there any restrictions for foreign passport holders?
Travel restrictions and requirements for foreign passport holders entering Thailand can vary widely based on a number of factors, including the traveler’s nationality, the purpose of the visit, the duration of the stay, and the current global and local health situation.
General Entry Restrictions:
- Visa Regulations: Visa policies vary, with some passport holders eligible for visa exemption, visa-on-arrival, or e-visas, while others must secure visas in advance.
- Passport Validity: A minimum passport validity, often six months, is a standard requirement.
- Financial Proof: Travelers might need to demonstrate they possess adequate funds for their stay.
- Return or Onward Ticket: A confirmed ticket for onward or return travel may be necessary.
- Travel History: Entry restrictions might apply based on recent travel history, including visits to specific countries or regions.
Specific Passport-Based Restrictions:
- Diplomatic/Official Passports: Holders of diplomatic or official passports may face different entry requirements or procedures.
- Restricted Nationalities: Some countries impose entry limitations or additional requirements on passport holders from specific nations due to diplomatic relations or security concerns.
Additional Checks and Requirements:
- Security and Background Checks: Security considerations can lead to additional screening, requirements, or restrictions for travelers from certain countries.
Can I rent a private car/taxi from the airport to the hotel?
Yes. travelers can find metered taxis available outside of the airport. All request the use of the meter. Private car and car hire is also available at the airport counters.
Does the hotel provide transportation?
Hotels charge an additional fee for transportation to and from the airport. The easiest transportation is the metered taxi.
What is the best way to exchange currency?
If you need money exchanged to use for transportation it is best to do it once outside the Customs area.
The best exchange rates for Thai currency can be found in the tourist areas with popular exchange services such as SuperRich or Dee Money.
What insurance should I get?
The most popular insurance coverage is THB 750,000 coverage for medical expenses due to accidents and illnesses (including COVID-19) and THB 1 million for accidental death and disability. You can find trusted insurance coverage at AXA Thailand .
What happens after I get my AXA Insurance policy?
After applying for your AXA Insurance, you will receive an email with your policy. You can then upload the policy on your phone for easy reference.
City Travel Guide
- How to Travel to Bangkok
- How to Travel to Phuket
- How to Travel to Pattaya
- How to Travel to Chiang Mai
- How to Travel to Samui
- How to Travel to Hua Hin
Other Thai Elite Visa Pages
Related posts.

How to Travel to Thailand in 2024

Best Places to Retire in Thailand for Couples

How to Retire in Thailand for Couples

Thailand Travel Restrictions 2023
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This form collects your name, email and content so that we can keep track of the comments placed on the website. By submitting this form, you accepted and agreed on our privacy policy and terms .
588 Comments
Just to make totally sure, I’m gonna ask this very simply: I have no vaccination papers. I have no negative Covid test. I have no travel insurance. Am I still allowed to enter Thailand?
Hello, Lars Andersen.
Unless you are from one of the countries with yellow fever, you do not need to provide vaccination papers and are allowed to enter Thailand.
How much cash in gbp can I bring into Thailand (phuket) for spending money etc?
I would like to ask if I am holding an Indian passport with valid Australian tourist visa, do I need a tourist visa? or can I enter Thailand on the basis of my valid Australian visa?
Also if Nepalese passport holder has valid Australian student visa, do they need to apply tourist visa?
Hello, Chandar Parkas Dimri.
You cannot enter Thailand with any Australian visa. You will need to apply for a Thailand Tourist Visa to enter Thailand. If you’re coming to Thailand to study, you will need to apply for an Education Visa.
I have got a question regarding the updated guidelines as of January 9, 2023
>Airline passengers 18 years old or older must provide proof of full vaccination
I have full vaccination, but it was done in October 2021, do I need to get a new vaccine?

Yes, that is acceptable. You do not need to get a new vaccine. Thank you.
Hi there, we are looking at coming to Thailand for over 30 days but in 2 stints. We will be doing Bangkok and the north followed by the south a few month later. What kind of VISA do you recommend for this?
You can use the 45 days Visa Exemption stamp on each visit. There is no need to get a visa. Please check this information on this page: https://www.thaiembassy.com/weekly-updates/thailand-travel-restrictions-for-november-2022
We will travel Thailand this Monday..
What are the needed requirements?
Dear Marfele,
You may find the entry requirements here: https://www.thaiembassy.com/weekly-updates/thailand-entry-requirements-for-october-2022 Thank you.
If you are vaccinated and Travel to Thailand without PCR testing before leaving SA do you still need to do PCR when you arrive in Thailand but you are fully vaccinated?
Dear Deidre,
The latest entry requirements are posted here: https://www.thaiembassy.com/weekly-updates/thailand-entry-requirements-for-october-2022
Hi, is there a restriction to travel to Phuket from Malaysia by train? (Travelling from Malaysia to Padang Besar Train Station to Hat Yai Train Station to Phuket train terminal 2). Thanks a lot

Dear Oscar,
For this month, just prepare your vaccination card and passport. On October 1st, restriction will be removed.
For more information about travel to Thailand, please check this link: https://www.siam-legal.com/legal-guide/how-to-enter-thailand-2022-guide.pdf
Hi, I’ve read in some of your news that all corona rules fall away from 1 October, that we can travel into the country without having to show a test or certificate. is that right ? Vikram
Dear Vikram,
Yes. Official statement will be announce by the Gazette on October 1st.
For more information about travel to Thailand, please check this link: https://www.thaiembassy.com/weekly-updates/thailand-entry-requirements-for-october-2022
Hello . It says on some Thai websites that from 1 October no one needs a negative test or to show a corona certificate on arrival in Thailand. Is that right ? We will arrive on 1 October in Phuket. Should I be tested as I am not vaccinated?
Dear Albina,
On October 1st, restriction will be removed.
Hello. Should children aged 2 have a negative test ? Up to what age should children have a test ?
If the parents are unvaccinated, children will require too.
Hello again. Is it okay with an Antigen test taken at the hospital or do we have to take only PCR
Yes, It should be professional RAT.
Yordmanu, I have a current, one year ‘retirement’ visa extension and have just returned to UK after a 90 day Thailand Pass trip. I’ve booked a one-way flight back to Thailand for the 9th. November – Will I have to buy insurance & will I be allowed to travel back to Thailand on this one-way ticket? I have an a Thailand address (30 year lease) and a history of travellng back & forth. Peter
Dear Peter,
Insurance is now an optional. It’s not compulsory but still recommended.
Hello. We will travel to Phuket on 1 October. My husband has a dose of vaccine and has been infected with covid twice. Does he have to prove a negative test or does he have to have proof from the doctor that he has had covid twice and has a vaccine? I am not vaccinated but have undergone covid 2 times the children aged 14 and 11 have not been vaccinated, should they have a test before we arrive? Albina
If fully vaccinated, just vaccination certificate and certificate of recovery since he got infected.
For unvaccinated, you need to have negative RT PCR within 72 hours of your arrival. Same procedure with your kids.
I am a Thailand passport holder and returning to Chiang Mai from Kuala Lumpur. What requirements do I need to enter Thailand?
Passport and proof of vaccination.
Do you know the phone number of the Thai embassy in Thailand?
hi, i have 1 question. how about unvaccinated kids age 8-year-old and 4++-year-old?do they need to do pcr test?
If you are fully vaccinated , No. If unvaccinated, same procedure with parents.
I’m seeing conflicting info. Some websites say yes or no, regarding that before departing to thailand, one must show a negative pcr test. For the most part, it seems like no, you don’t have to.. but then more reputable sites say yes, people need to.
so which is it? planning to depart in october of 2022
Dear Balrto,
Negative RT PCR is for those unvaccinated.
Is a “supervised RAT travel test” signed and witnessed by a pharmacist in Australia permitted for entry to Thailand?
Dear Nathan,
Yes, it should be a professional RAT.
Me and my friends will fly to Phuket. Me and my husband have international certificate of vaccination without QR-code on Covid-19. Vaccine is comirnaty (we have two dose and booster) . On website: https://www.tatnews.org/2022/06/covid-19-vaccine-guide-for-travellers-to-thailand/ The information is that when vaccine comirnaty, the 2nd dose must be after 3 weeks, but in my and husband’s certificate is after 4 weeks (first – 19.05.2022, second – 16.06.2022 and booster is 22.01.2022). Is this a problem? Do we need to take a test? Thx You in advance.
No, it means 3 weeks after your shot, more than 21 days in valid.
Do I need to purchase health insurance if I’m only staying in Bangkok for 1 day since my destination is the following day when I arrived in Bandkok?
Insurance is optional. Not compulsory but still recommended.
do the vaccine certificates require to have a qr code? or is that up to the discretion of the airline?
Not really, any proof that you are fully vaccinated will be accepted. If so, then maybe it’s the airlines requirements.
i will arrive bangkok 17:00, transit to Taipei, Taiwan 12:55 on next day. do i still need to book hotel + insurance and proceed PCR test. I am unvaccinated.
Insurance is not compulsory but still recommended. If you are unvaccinated, you need a 72 hours negative RT PCR.
I have flight 06.10 I’m arrive g to Thailand 07.10. I’m not vaccined is that mean I have to take test 04.10 then is 72h before my arrival or I shuld take tests 05.10 or 06.10?
You can do it on 5.10 , validity should be 72 hours upon arrival.
Hello, I might be coming to Thailand in the next month or so, coming from China (not a Chinese citizen). I have been vaccinated but my vaccination shows on my phone – is this presentable?
Hi Charles,
Any proof that you are fully vaccinated.
How long is the Vaccine considered before expiring if I am vaccinated with 2 shots?
Last shot should be not more than 12 months.
Traditional herbal medicines are based on the use of natural remedies like Herbs and Roots, no special food, no lifestyle change to permanently cure drug resistance diseases. people who use this methods like me will definitely testify. three years ago I was permanently cured from herpes simplex virus by Dr Okosun, an African herbalist who eradicates diseases and viruses which the world believes has no cure today with the use of herbs Dr Okosun herbs are hundred percent natural, no after effect and is guaranteed method of getting rid of herpes and other drug resistance diseases which the doctors made us believe has no cure, im one of the hundreds of people cured by dr okosun and you can get in touch with this dr and get your healing just as i did via drokosun55@gmail .com his mobile or whatsapp +2348124363791
Is a photo copy or a photo of my covid card ok? I left my original at home so I wouldn’t lose it.
Yes, any proof that you are fully vaccinated.
On your website it says that the test should be done with 72 hours before departure. So is it before departure or arrival? A international flight might take More 30 hours. If there is a delay, 72 hours will easily be passed. If the test is invalid upon arrival, what should be done?
Validity should be within 72 hours of arrival.
I receive my PCR test result by email. Do I need to print it out to show upon arrival? If my result is expired upon arrival, can I do a pcr test I the airport? If so, how much is it?
The result should be valid within 72 hours of your arrival, incase you need to repeat again the test.
I was just reading a site through Japan Airlines for Thailand entry from United States, it says as of August 31 1. no test required 2. No quarantine
Is this correct?
Thank you Jim
Yes you’re right, no test required if fully vaccinated. If unvaccinated, 72 hours negative RT PCR.
If I’m unvaccinated I understand that I need to have RT PCR within 72 hours upon arrival, but do I also HAVE to quarantine upon arrival in addition to the test?
No quarantine upon arrival if you have negative result.
I have 2 doses of pfizer is it considered fully vaccinated? I got my 2nd shot last Oct. 2021 and I will be travelling on Aug.3. Do I need to show RT-PCR negative result ?
Yes, 2 doses is fully vaccinated.
I know that for the moment i can enter with test but what are the chances that the thai government will change the rules and make the vaccination obligatory again for 5 octobre? thanks
i am not vaccinated but i will be travelling to thailand on 5 october.
Do I only need a negative covid test to enter thailand?
And what are the chances that the thai government will change the rules and make the vaccination obligatory again? If so, how long before I should be vaccinated in order to travel safely on the 5th of october?
Yes, you can still enter even unvaccinated. You just need to have RT PCR within 72 hours upon arrival.
Hi there, just wondering if transiting in Bangkok (not leaving the airport) on the way to Malaysia if I still need to provide a RT/PCR test? I am not vaccinated. Thanks in advance
The unvaccinated or not fully vaccinated travellers without a negative test result within 72 hours of travel is required to follow the public health instructions and guidelines as deemed appropriate by the Health Control officer at the point of arrival.
A little urgent!
Hi! I am have 2 doses of pfizer vaccine but it has expired 2 months ago, I have read that i am still able to travel in there as thailand do not request for the booster.
Is that correct? Hope someone replies me fast. Thank you ser/madam!
Yes, 2 doses is fully vaccinated . Your last shot should not be longer than 12 months, otherwise, you need to get booster.
We are arriving in BKK on the 29th and are not vaccinated or recovered.
I would like to know if we can get vaccinated this week. Is the vaccine already valid or is it necessary, for example, to be vaccinated since 20 days minimum for the vaccine to be valid in Thailand?
Have a good day
Hi Grandjean,
14 days of your vaccination.
You do not need to be vaccinated to go to Thailand. Just take an official antigen test 72 hours before departure.
Hi, for the insurance policy how many days should I buy if I will be staying in thailand for 5 days?
You can get the period of your stay or even 1 week.
How long do we have to be vaccinated for the Covid certificate to be valid?
Not more than 12 months with your last shot. If so, you can get booster.
Hi, thank you for your work. So unvaccinated travelers who got Covid recently in a month can submit a recovery certificate instead of a negative test result to enter Thailand. Is that right that I understand? or must submit a negative test result even though got Covid recently? Also, what is the acceptable date for a recent recovery? Is it 30 days or 40days?
If you recovered at covid, you need to get certificate of recovery . You still need to get a 72 hours negative RT PCR if you are unvaccinated, that is the requirements for unvaccinated traveler.
Hi!. I’m travelling from the UK to BKK on 30th Aug., 2022. I’m over 60 and had both my vaccination jabs plus a booster shot back in 2021. Is there anything else I need to enter Thailand?. 😀
Just vaccination certificate and passport.
hi iam travelling to Thailand from Kuwait will transit in Bangkok then internal flight to koh samui for 12 days then to Phuket for another 12 days iam not vaccinated please advise with needed documents and when i travel from koh samui to phuket do i need to do PCR?
and it will be undergo quarantine for unvaccinated travellers?
For unvaccinated traveler, you need to have negative 72 hours RT PCR.
Nice, Now you can visit and travel in Thailand with your pocket money. But how? It is possible due to the Discount code or promo code of Travel Accommodation Services Provider, Like Klook, Trip com and so many in the Thailand. So You can get Klook Thailand Discount code from here ส่วนลด Klook and save some amount.
Yes, most hotel had their own discount and promotion, you can stay in any hotel you want. You can also check here https://www.agoda.com/search?cid=1897011&city=9395
Hi We are travelling to Phuket Airport and on to hotel in Khao Lak on 25 November from UK for 15 nights. We have had 3 Vaccinations, the latest one December 21. Do we need another one given it will be a year since the last one. What is the longest time since last vaccination to be considered fully vaccinated.
It should not last more than 12 months.
Hi i am planning to visit in thailand next year with my family for a week, do we need to get a visa? Or what are the requirements? Thank you
You can check with this site if you are eligible for visa exemption which means that you can enter Thailand without visa for 30 days. https://www.thaiembassy.com/thailand-visa/thai-visa-exemption-and-bilateral-agreement
You can check this site if you are eligible for visa exemption which means that you can enter Thailand without visa for 30 days. https://www.thaiembassy.com/thailand-visa/thai-visa-exemption-and-bilateral-agreement
Hi, i am traveling to Bangkok 29th of august. I got world travel insurance her in Danmark, please let me know if need to buy any extra insurance. I am fully vaccinated. thanks
Hi Maqsood,
Insurance is not compulsory but highly suggested.
Hi, I am unvaccinated and got Covid 2 weeks ago and gonna visit Thailand in 14days. In this case, recovery certificate can be submitted instead of negative results from ATK or PCR test? Because dead covid virus can be left in the body and some people got still positive results after they got covid. I will flight from Korea.
Yes, bring your certificate of recovery.
Thank you. So do you mean that I can submit a recovery certificate in recent instead of the negative test result? Is that right that I understand?
You need to bring the certificate of you recovery so the health representative can check the level status of your infection just incase you get positive result again.
hi is a booster covid19 vaccine mandatory to enter Thailand? I’m vaccinated with 1 J&J last Aug 2021 which only needs 1 shot. would this be an issue?
Hello Vans,
If you’re fully vaccinated, you must show proof of vaccination a booster isn’t required for entry at this stage.
thank you mary for this.
I need to transit from BKK to Mumbai in 5 hours gap .Unfortunately,I can’t get thorough check in because I bought different airlines.So,I need to pass the immigration of Thuwaanabumi Air port and collect my luggage and again I need to entry into Department of that airport.Is it ok for me because I will re entry into BKK after 4 days.My trip is tomorrow.
Hi. If i’m travelling with my family from malaysia to thailand and one of my child 12 yr old is not vaccine can my child enter thailand together with us ( already complete vaccine . do she need to perform atk ?
Hello Saiful,
Children under the age of 18 do not need a certificate of vaccination if they are travelling with fully vaccinated parents. If they travel with parents who are not fully vaccinated, they must present an RT-PCR / Professional ATK COVID-19 test result issued within 72 hours before departure.
Im fully vaccinated , do i still need to stay at a SHAplus hotel when i visit thailand?
You can enter in any hotel you want.
I cannot enter into Thailand within 14th days from tested positive. Correct? Thailand Embassy of Japan and Singapore informed me like that.
As long as you are fully recovered and tested negative after your quarantine period, you can able to travel in Thailand.
For those previously infected with COVID-19 are considered fully vaccinated if they have received a single dose of COVID-19 vaccine at any time after their recovery.
Please be advised that your proof or medical record of COVID-19 recovery must be shown alongside your single-dose vaccination certificate.
My daughter got covid last Sunday. I have lived in Singapore, and in SIngapore, can go out from 7th day(1st day is positive day) I have a plan to go to Thailand this Sunday. When I called and asked Thailand embassy in Japan today, embassy officer mentaioned she cannot enter Thailand within14days from positive result tested.. Also it is showing in homepage in Thailand embassy of Japan. If she with negative and doctor record , she can go in Thailand before 14days?
Hello Kato,
My daughter got covid last Sunday. I have lived in Singapore, and in SIngapore, can go out from 7th day(1st day is positive day) I have a plan to go to Thailand this Sunday. When I called and asked Thailand embassy in Japan today, embassy officer mentaioned she cannot enter Thailand within14days from positive result tested.. Also it is showing in homepage in Thailand embassy of Japan.
Hello Do i still need a test 72 hrs before departure if I have 1 of the 2 Covid vaccines and just recovered from Covid? Thank you
Hello Tash,
Hi, I’m from Malaysia. Yesterday on 1 August 2022 I tested positive for covid-19 by using the RTK-Nasal swab self-test kit. According to Ministry of Health of Malaysia, I only need to quarantine for 7 days since I have taken the 3 dos of the covid-19 vaccine. However, I am required to attend a regional meeting in Bangkok on 15 August 2022. Can I enter Bangkok on the 14 of August since we will be traveling to Bangkok 1 day earlier?
Sorry to hear that. Yes, you can still travel to Thailand as long as after you have quarantined you tested negative. And just provide your proof or medical record of COVID-19 recovery alongside of your vaccination certificate.
I am travelling to Bangkok on 10th August to visit a bank on the 11th August and departing Bangkok on 12th August for UK. I am fully vaccinated in Cambodia with 3 vaccinations. I am a British citizen. Do I require a PCR test before I enter Thailand?
Hello Robert,
Since you are fully vaccinated you don’t need a negative RT-PCR test result. Just provide your proof of vaccination upon arrival, that would be enough.
hi im planning to visit phuket and bangkok , is there a minimum days i have to spend at phuket before going to bangkok ?
Hello Bell,
There’s no minimum days you can stay on each area in Thailand, as long as your visa are still valid you are free to travel around.
I have one shot of a two-shot vaccine + a booster (in total 2 shots). The reason I only had one shot the first time is because I had been infected with COVID and therefore according to local regulations one shot was enough. Am I considered fully vaccinated for travel to Thailand?
Thank you for your prompt response. To clear out, I have proof that I was tested positive and then subsequently negative test. The report is in Italian (I live in Italy), but the words “positivo” and “negativo” are pretty clear. The tests were conducted by an accredited private hospital in Milan, Italy. I assume I would be able to use this?
If you can provide the English translation that would be better, but if you only have written in Italian you can still use that.
Hi there, I am from UK. I plan to visit Thailand in mid of August 2022 with my 12 years old son. I had 3 Covid Vaccines but my son hasn’t receive them yet. Does my son need to do Fit to Fly Pro-Antigen Covid test or he doesn’t need to do it? Hope to hear from you soon. Thank you.
Hello Tidaratt,
Will I be able to enter Thailand with the negative result of PCR Test 72 hrs? The lab has the PCR Test. They said the PCR Test and the RT-PCR Test is the same thing.
Hello Usanee,
The RT-PCR test and PCR test are different, however, any of those are accepted as long as it was issued by a certified Clinic or Hospital, containing personal information of the travelers and information of the vaccine (name, batch number, dates).
I have an appointment with Medical facility in Bangkok, for yearly medical checkups at the end of August 2020. I have already took COVID 19 full vaccination (1st, 2nd and booster). My visa will stamped on arrival at the air port since my country is not in the list Thai visa except countries. So what else required from?
Hello Assefa,
The entry measures for Thai and Foreign Nationals are only proof of either a certificate of vaccination or a negative RT-PCR or professional ATK test result within 72 hours of travel. These can be in a print or digital format.
I am from Kuwait, I am a two-dose restaurant and I have health insurance. Do I need anything else to enter Thailand?
Hello Nael,
Hi, may I know what’s the procedure if foreigners get COVID during their stay in Thailand?
Anyone who tests positive, regardless of whether they have recovered from COVID-19 in the last 90 days, are required to quarantine at their own expense for 10-14 days or possibly longer depending on their situation and under the direction of public health officials.
Hi, do you need to be vaccinated to enter Thailand? Or is a PCR test acceptable when taken 3 days before arriving?
Hello Eliana,
Full vaccination is not mandatory to enter Thailand, however, if you provide your proof of vaccination, you won’t need to present a negative PCR test.
A negative RT-PCR or professional ATK test result must be issued within 72 hours before departure.
I need to make a trip to Thailand in early October for business meetings with our local office as well as clients in Bangkok. Since the trip is not for tourism purposes, do I need to get a visa (U.S. passport holder traveling from the U.S.)
Hello Dawn,
If you’ll stay less than 30 days in Thailand, you don’t need to apply for a visa since U.S Passport holders are entitled for 30 days visa exemption.
Hi. I m planning to travel to Thailand in September/October. I have 2 sinovac shots that are confirmed in a local covid19 vaccination card in English incl. Batch numbers etc but I don’t have the yellow WHO vaccination certificate booklet. Is my local certificate valid or do I need the yellow WHO booklet? Thanks a lot and kind regards Thomas
Hello Thomas,
You don’t need a yellow booklet, just provide the proof of your vaccination given by your country.
Hi , I am planning to travel to Thailand in October for 1 week . I have received the Johnson and Johnson single dose covid vaccine. Do I have to get a booster shot to or am I considered vaccinated
Hello Naomi,
Travelers to Thailand, foreign and Thai, are considered fully vaccinated if they get their second dose of a 2-dose vaccine no less than 14 days before their travel date to Thailand also if they get a single-dose vaccine no less than 14 days before their travel date to Thailand.
Hi I am a U.K. citizen I am fully vaccinated plus had a 3 rd booster jab in December 2021 , I am planing to go to thailand in October 2022 , for 2 weeks am I considered fully vaccinated or would I need a 4 th booster vaccination Thanks in advance
Hello Eddie,
Travelers to Thailand are considered fully vaccinated if they have already a 2-dose of vaccine.
May I ask Children under 18 without vaccinated who are traveling with vaccinated parents can enter to Thailand?
Yes they can. Thailand has no COVID restrictions anymore.
Dear, I am French citizen, I plan to come from 08/08 to Thailand: – Do I need visa or there is a 30 days exemption for French citizen ? – In case there is a Visa exemption, do I need to register somewhere or I just need to show up at the customs ? Thank you
Hello Quentin,
France Passport holders not required to obtain a visa when entering Thailand for tourism purposes and will be permitted to stay in Thailand for a period not exceeding 30 days on each visit. The visa will be stamp by the Immigration officer on the day you have arrived in Thailand.
Hi Quentin,
Check here if you are eligible for visa exemption, https://www.thaiembassy.com/thailand-visa/thai-visa-exemption-and-bilateral-agreement
Do you have to book a SHA hotel on first night if your already vaccinated?
Hello Timmy,
If you are fully vaccinated, you don’t need a hotel booking confirmation just provide a proof of your vaccination.
You can stay in any hotel of you choice.
Hi I am fully vaccinated 2 dose with moderna But it is 1 year ago already since I got my second dose. I do not have booster. Do I need booster to enter Thailand now?
Yes, last shot should not more than 12 months.
I am considering booking an airbnb in Phuket but have concerns about legality. I am seeing mix reviews online stating that it is illegal to book villas in Thailand for less than 30 days. Can you please clarify if it will be legal to book a villa in Phuket for 5 days or less. The villa is listed on Airbnb website.
https://www.airbnb.com/rooms/43272871?adults=6&children=0&infants=0&check_in=2023-05-20&check_out=2023-05-23&source_impression_id=p3_1658235414_A4%2B4qyfIvFCIfYDo
Dear Rochelle,
When you come to Thailand, you are allowed to stay in a hotel, hostel, villa or private residence such as house or condo. Thank you.
I live in HK and will have a flight to Australia and transit in Thailand. I am not vaccinated. Do i have to do test? Thank you
Yes, for unvaccinated you need 72 hours RT PCR .
Hi, Do I still have to fill up and get the Thai Pass and purchase USD10,000 covid coverage as of today 19 July 2022? Fyi, I am from Malaysia.
Thailand Pass was no longer required, no need to apply. Insurance is not compulsory but highly recommended, better to get for security.
Is 2time vaccination sinovac aprroved in Thailand ?
COVID-19 vaccine guide for travellers to Thailand
Bangkok, Updated on 28 June, 2022.
List of approved COVID-19 vaccines in Thailand
- CoronaVac (Sinovac) – 2 doses needed / 2nd dose after 2-4 weeks;
- AstraZeneca (Vaxzevria, Covishield) – 2 doses needed / 2nd dose after 4-12 weeks;
- Pfizer-BioNTech (Comirnaty, Tozinameran (INN)) – 2 doses needed / 2nd dose after 3 week;
- Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) – 1 dose needed;
- Moderna (Spikevax) – 2 doses needed / 2nd dose after 4 weeks);
- COVILO (Sinopharm, Hayat-Vax) – 2 doses needed / 2nd dose after 3-4 weeks);
- Sputnik V – 2 doses needed / 2nd dose after 3 weeks);
- Covaxin – 2 doses needed / 2nd dose after 4 weeks;
- Novavax (Nuvaxovid) / Covovax – 2 doses needed / 2nd dose after 3 weeks);
- Medigen – 2 doses needed / 2nd dose after 4 weeks;
- TURKOVAC / ERUCOV-VAC – 2 doses needed / 2nd dose after 4 weeks;
- Sputnik Light – 1 dose needed;
- CansinoBio (Ad5-nCov / Convidecia) – 1 dose needed.
Have you been fully vaccinated?
According to the MoPH, travellers are considered fully vaccinated if:
- They get their second dose of a 2-dose vaccine no less than 14 days before their travel date to Thailand.
- They get a single-dose vaccine no less than 14 days before their travel date to Thailand.
- In case of mix-and-match vaccines, travellers should get their second dose of a different vaccine within the recommended interval of the first vaccine no less than 14 days before their travel date to Thailand.
Requirements for the ‘Certificate of COVID-19 Vaccination’
The travellers’ Certificate of COVID-19 Vaccination should contain the following details:
- Given name and last name;
- Date of Birth;
- Nationality;
- Passport or Identification No.;
- Name of the COVID-19 vaccine;
- Vaccination dates;
- Vaccine manufacturer and lot/batch number;
- Authorised organisation in the country of origin.
Who need to be vaccinated to enter Thailand?
- Everyone 18 years of age and older must be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 with an approved vaccine at least 14 days before travelling to Thailand.
- Travellers 5-17 years of age travelling to Thailand unaccompanied must get vaccinated with at least 1 dose of an approved vaccine at least 14 days before travelling to Thailand. Those travelling with parents are exempt from this requirement.
Guidelines for travellers who have previously been infected with COVID-19
- Those previously infected with COVID-19 are considered fully vaccinated if they have received a single dose of COVID-19 vaccine at any time after their recovery. They are required to submit proof or medical record of COVID-19 recovery alongside the single-dose vaccination certificate.
- Those fully vaccinated before contracting COVID-19 are still considered to be fully vaccinated.
- Those recovered from COVID-19 within 3 months before travelling to Thailand must present a valid medical certificate certifying the full recovery (within 3 months but no less than 14 days before travelling) or that they are asymptomatic in case the COVID-19 RT-PCR – or professional ATK – test shows a positive result.
In addition to being fully vaccinated, international travellers should have all of their advance arrangements in good order for arrival and entry. For more information: https://www.tatnews.org .
TAT Newsroom
Tat welcomes japanese idol group fes☆tive to thailand, ubon ratchathani candle festival 2022 set to wow visitors, related articles.

Thailand expands visa-free access for tourists from China and Kazakhstan

Jellyfish warning for travellers in Thailand

We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Situation in Haiti March 29, 2024
U.s. citizens in haiti, update january 10, 2024, information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Before You Go
Learn About Your Destination
While Abroad
Emergencies
Share this page:
Travel Advisory July 24, 2023
Thailand - level 1: exercise normal precautions.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed.
Exercise normal precautions in Thailand. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Reconsider travel to:
- Yala, Pattani, Narathiwat, and Songkhla provinces due to civil unrest associated with ongoing insurgent activities.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Thailand.
If you decide to travel to Thailand:
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Thailand.
- Have evacuation plans that do not rely on U.S. government assistance.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Yala, Pattani, Narathiwat, and Songkhla Provinces – Level 3: Reconsider Travel
Periodic violence directed mostly at Thai government interests by a domestic insurgency continues to affect security in the southernmost provinces of Yala, Pattani, Narathiwat, and Songkhla. In Songkhla, the insurgency is most active in the districts of Chana, Thepha, Nathawat, and Saba Yoi. U.S. citizens are at risk of death or injury due to the possibility of indiscriminate attacks in public places.
The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in these provinces as U.S government employees must obtain special authorization to travel to these provinces.
Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
Embassy Messages
View Alerts and Messages Archive
Quick Facts
6 months from date of entry required
One page is required per entry stamp; please note endorsement pages are not considered blank passport page
No, if your stay is less than 30 days
Yellow fever may be required if arriving from certain countries with yellow fever
Embassies and Consulates
U.S. Embassy Bangkok 95 Wireless Road Bangkok 10330 Thailand Telephone: + (66) (2) 205-4049, 02-205-4049 (within Thailand) Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(66) (2) 205-4000, 02-205-4000 (within Thailand) Fax: +(66) (2) 205-4103, 02-205-4103 (within Thailand) Email: [email protected]
CONSULATE
U.S. Consulate General Chiang Mai 387 Witchayanond Road Chiang Mai 50300 Thailand Telephone: +(66) (53) 107-777, 053-107-777 (within Thailand) Emergency After-Hours Telephone: +(66) 81-881-1878, 081-881-1878 (within Thailand) Fax: +(66) (53) 252-633, 053-252-633 (within Thailand) Email: [email protected]
Destination Description
Learn about the U.S. relationship to countries around the world.
Entry, Exit and Visa Requirements
Visit the Royal Thai Embassy website for the most current visa information.
- U.S. citizen tourists entering Thailand for fewer than 30 days do not require a visa.
- We strongly recommend that your passport be valid for at least six months beyond the date of your arrival in Thailand to avoid possible denied entry.
- Thai immigration officials or airline staff may ask for your onward/return ticket.
- Business travelers, U.S. government employees travelling on official business, teachers, retirees, and those planning to stay longer than 30 days should check with the Royal Thai Embassy about visa requirements .
- If you overstay your visa, you will be fined. Depending on the length of overstay, you may also be arrested, detained, deported at your own expense, and banned from re-entering Thailand.
We strongly recommend you carry a copy of your U.S. passport identification page and current Thai visa to help avoid detention by the Thai immigration police.
Thailand’s entry/exit information is subject to change without notice. For the most current information, please see The Royal Thai Police Immigration Bureau .
You can find detailed information on vaccinations and other health precautions on the CDC website .
HIV/AIDS Restrictions: Some HIV/AIDS entry restrictions exist for visitors to and foreign residents of Thailand. However, these restrictions are generally not enforced. Please verify this information with the Royal Thai Embassy before you travel.
Find information on dual nationality , prevention of international child abduction and customs regulations on our websites.
COVID-19 Requirements: There are no COVID-related entry requirements for U.S. citizens.
Safety and Security
Terrorism: Terrorist groups and those inspired by such organizations are intent on attacking U.S. citizens abroad. Terrorists are increasingly using less sophisticated methods of attack – including knives, firearms, and vehicles – to more effectively target crowds. Frequently, their aim is unprotected or vulnerable targets, such as:
- High-profile public events (sporting contests, political rallies, demonstrations, holiday events, celebratory gatherings, etc.)
- Hotels, clubs, and restaurants frequented by tourists
- Places of worship
- Shopping malls and markets
- Public transportation systems (including subways, buses, trains, and scheduled commercial flights)
For more information, see our Terrorism page.
Periodic acts of violence in Thailand remain a concern. In August 2019, several small explosions and related arson events occurred in various locations throughout Bangkok resulting in no deaths but some injuries and minor property damage. Several small-scale bombings occurred near some tourist locations in the far Southern provinces in August 2016 and December 2018. In August 2015, an explosion near the Erawan Shrine in downtown Bangkok killed at least 20 people and injured more than 100. The U.S. Department of State assesses there is a continued risk of terrorism in Southeast Asia, including in Thailand.
If a protest or demonstration is expected to pass near the U.S. Embassy or Consulate facilities, Embassy and Consulate entrances and functions may be restricted. The U.S. Embassy in Bangkok’s website , Facebook, and Twitter sites and the U.S. Consulate General in Chiang Mai’s website , Facebook , and Twitter sites post information about local events that may affect Embassy functions. Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive security and safety messages.
Far Southern Thailand: Periodic violence directed mostly at Thai government interests by a domestic insurgency continues to affect security in the southernmost provinces of Yala, Pattani, Narathiwat, and Songkhla. U.S. citizens are at risk of death or injury due to the possibility of indiscriminate attacks in public places. Martial law is in force in this region.
The U.S. government has limited ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in these provinces. Travel to this region by U.S government employees must be reviewed and approved in advance. For more information on terrorist threats against U.S. citizens worldwide and steps to take as a result of these threats, please see the Worldwide Caution .
- Crimes of opportunity, such as pick-pocketing, bag-snatching, and burglary, occur in Thailand.
- Violent crimes against foreigners are relatively rare. However, murders, rapes, and assaults against foreigners do occur.
- Sexually motivated violence, committed by either Thai citizens or foreigners, is most likely to occur after time spent at bars, clubs, and parties, on beaches, or in remote/isolated areas. The Thai police response will differ from an investigation in the United States; investigating officials have publicly discredited people who have reported being the victim of crimes . In addition to making a report at the police jurisdiction in which the crime occurred, we advise contacting the Embassy and engaging a local attorney if you are a victim of an assault.
- When traveling alone, exercise caution, stay near other travelers, and ensure friends or family know how to contact you.
- Taxi and “tuk-tuk” drivers may attempt to charge excessive fares or refuse passengers. You should either request the driver use the meter or agree on the fare beforehand.
- At the airport use only public transportation from the airport’s official pick-up area, cars from the limousine counters, or a car from your hotel.
- Rental scams do occur in Thailand. Many rental motorbike, jet ski, and car companies will hold your passport until you pay for real or fictitious damages. We advise against using your passport as collateral.
- Exorbitant bar tab scams occur in Thailand. Some bars and entertainment venues will charge exorbitant prices for drinks or unadvertised cover charges and threaten violence if you don’t pay.
- Other scams involving gems, city tours, entertainment venues, and credit cards are common, especially in tourist areas.
International Financial Scams: See the Department of State and the FBI pages for information.
Internet romance and financial scams are prevalent in Thailand. Scams are often initiated through Internet postings/profiles or by unsolicited emails and letters. Scammers almost always pose as U.S. citizens who have no one else to turn to for help. Common scams include:
- Romance/Online dating
- Money transfers
- Grandparent/Relative targeting
- Free Trip/Luggage
- Work permits/job offers
Victims of Crime: U.S. citizen victims of crime are encouraged to contact the U.S. Embassy or Consulate for assistance. Report crimes to the local police by calling 191 or the Tourist Police at 1155 and contact the U.S. Embassy at +66 (0) 2-205-4049 or Consulate at +(66) (53) 107-777. Remember that only local officials have the authority to investigate and to prosecute a crime.
Domestic Violence: U.S. citizen victims of domestic violence are encouraged to contact the U.S. Embassy or Consulate for assistance. Report crimes to the local police by calling 191 or the Tourist Police at 1155 and contact the U.S. Embassy at +66 (0) 2-205-4049 or Consulate at +(66) (53) 107-777. Remember that only local officials have the authority to investigate and to prosecute a crime.
See our webpage on help for U.S. victims of crime overseas .
- Help you find appropriate medical care
- Assist you in reporting a crime to the police
- Contact relatives or friends with your written consent
- Explain the local criminal justice process in general terms
- Provide a list of local attorneys
- Provide our information on victim’s compensation programs in the U.S.
- Provide an emergency loan for repatriation to the United States and/or limited medical support in cases of destitution
- Help you find accommodation and arrange flights home
- Replace a stolen or lost passport
Tourism: The tourism industry is unevenly regulated, and safety inspections for equipment and facilities do not commonly occur. Hazardous areas/activities are not always identified with appropriate signage, and staff may not be trained or certified either by the host government or by recognized authorities in the field. In the event of an injury, appropriate medical treatment is typically available only in/near major cities. First responders are generally unable to access areas outside of major cities and to provide urgent medical treatment. U.S. citizens are encouraged to purchase medical evacuation insurance. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage .
Local Laws & Special Circumstances
Criminal Penalties: You are subject to local laws. If you violate local laws, even unknowingly, you may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Individuals establishing a business or practicing a profession that requires additional permits or licensing should seek information from the competent local authorities, prior to practicing or operating a business.
Furthermore, some laws are also prosecutable in the United States, regardless of local law. For examples, see our website on crimes against minors abroad and the Department of Justice website.
Arrest Notification: If you are arrested or detained, ask police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy immediately. See our webpage for further information.
Conditions at the Bangkok Immigration Detention Center (IDC): Conditions in immigration detention centers (IDCs) where authorities detain foreign nationals who violate immigration laws remain poor and most are overcrowded. IDCs, administered by the Immigration Police Bureau, which reports to the Royal Thai Police (RTP), are not subject to many of the regulations that govern the regular prison system. U.S. citizen detainees often complain of stark, austere living conditions, overcrowding, and unhealthy conditions. Personal security is poor. In addition, the main IDC in Bangkok does not dependably provide adequate medical or mental health care. In 2019, two U.S. citizens died while in custody at the Bangkok IDC. Deportations are self-funded and it may take up to two weeks for Thai authorities to process a case before deportation. Detainees must have funds to purchase a phone card and do not have access to the internet. Prior approval and a security escort are required to visit a Western Union or an ATM machine.
- Please see the Immigration Act B.E. 1979 for more information about Thai Immigration violations.
- Please see the Department of State’s Report on Human Rights Practices for Thailand for further information.
Lèse majesté (Royal Insult): Thais hold the monarchy in the highest regard. Making a critical or defamatory comment about the royal family is punishable by a prison sentence of up to 15 years per offense. As an example, purposely tearing Thai bank notes, which carry an image of the King, may be considered a lèse majesté offense.
- Prostitution is illegal in Thailand. Serious consequences include criminal conviction and imprisonment, particularly in the case of child prostitution.
- Commercial surrogacy is banned.
- Personal use of even non-lethal military equipment, such as protective vests and night vision scopes, is prohibited.
- Illegal drugs carry severe penalties. Expect long jail sentences under harsh conditions, heavy fines, or even execution for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs.
- Shoplifting can result in large fines and lengthy detention followed by deportation.
- Domestic Issues: Local police are reluctant to become involved in domestic issues. You may call the Family Services Emergency hotline by dialing 1300 from any Thai phone.
- Possessing counterfeit or pirated goods is a crime in Thailand. For more information see the intellectual property section of the U.S. Department of Justice website .
Customs may enforce strict regulations on Buddha images, firearms, bullets and/or bullet casings, bullet-proof vests, night vision devices and other para-military type equipment, explosives, drugs, radios, books, and recordings, which might be cultural property and/or considered harmful to the public interest.
Faith-Based Travelers: See the following webpages for details:
- Faith-Based Travel Information
- International Religious Freedom Report – see country reports
- Human Rights Report – see country reports
- Hajj Fact Sheet for Travelers
- Best Practices for Volunteering Abroad
LGBTI Travelers: There are no known legal restrictions on same-sex sexual relations or the organization of LGBTI events in Thailand. However, LGBTI groups report that in the case of sexual crimes, police tend to downplay sexual abuse claims from LGBTI victims.
See our LGBTI Travel Information page and section 6 of our Human Rights report for further details.
Travelers Who Require Accessibility Assistance. Sidewalks and street crossings are not suitable for travelers with mobility issues. Newly constructed buildings, facilities, and transportation equipment should be accessible by law for persons with mobility issues. However, enforcement of these provisions is not uniform.
Students: See our Students Abroad page and FBI travel tips .
Women Travelers: Some victims of sexual assault or domestic violence find that Thai authorities do not handle such cases with as much sensitivity or consideration for privacy as they would expect in the United States. See our travel tips for Women Travelers .
Ambulance services are:
- not present throughout the country or are unreliable in most areas except for Bangkok and other major cities.
- Injured or seriously ill travelers may prefer to take a taxi or private vehicle to the nearest major hospital rather than wait for an ambulance.
Medical treatment is generally adequate in Thailand’s urban areas. In Bangkok, Chiang Mai, Phuket, and Pattaya, good facilities exist for routine, long-term, and emergency health care. Basic medical care is available in rural areas, but English-speaking providers are rare.
Medical tourism is an established and rapidly growing industry. You should consult with your local physician before traveling and also refer to information on medical tourism from CDC.
We do not pay medical bills. Be aware that U.S. Medicare/Medicaid does not apply overseas. Most hospitals and doctors overseas do not accept U.S. health insurance.
Medical Insurance: Make sure your health insurance plan provides coverage overseas. Most care providers overseas only accept cash payments. See our webpage for more information on insurance providers for overseas coverage. Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for more information on type of insurance you should consider before you travel overseas.
We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation.
Medicine for personal use is allowed as long as the amount does not exceed a 30-day supply and you bring the medicine with you. Do not mail medicine to Thailand without first confirming it will be allowed into the country.
If traveling with prescription medication, check with Thailand Customs and the Thailand Food and Drug Administration to ensure the medication is legal in Thailand. Always, carry your prescription medication in original packaging with your doctor’s prescription.
The following diseases are present:
- Chikungunya
- Japanese encephalitis
- Tuberculosis:
- Hepatitis A and B
- Melioidosis
Vaccinations: Be up-to-date on all vaccinations recommended by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Further health information:
- World Health Organization
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Air Quality: The air quality in Thailand varies considerably and fluctuates with the seasons, but seasonal smog is a problem. In recent years the air quality in Bangkok, Chiang Mai, Khon Kaen, Lampang, Nan, and Samut Sakhon have exceeded Thai and U.S. government daily standards for fine particulate matter (PM 2.5) for a portion of the year. In Chiang Mai and other northern provinces, annual agricultural burning, approximately February through late April, and forest fires cause days with unhealthy to hazardous air quality based on the U.S. index. In Bangkok environs, airborne dust and auto pollutants are prevalent in the cooler, dry period (December-February). Anyone who travels where pollution levels are high is at risk. People at the greatest risk from air pollution exposure include:
- Infants, children, and teens
- People over 65 years of age
- People with lung disease such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema;
- People with heart disease
- People who work or are active outdoors
For Bangkok and Chiang Mai, U.S. Mission Thailand is reporting the U.S. EPA’s Air Quality Index (AQI) calculated from PM2.5 data captured by monitors owned and maintained by the Royal Thai Government. The information and advice on health protection measures to take is available
Visit AirNow Department of State for information on air quality at U.S. Embassies and Consulates.
The U.S. Embassy maintains a list of doctors and hospitals . We do not endorse or recommend any specific medical provider or clinic.
Health facilities in general:
- Adequate health facilities are available in Bangkok and other major cities but health care in rural areas may be below U.S. standards.
- Hospitals and doctors require payment “up front” prior to service or admission. Credit card payment is not always available.
- Medical staff at public hospitals may speak little or no English.
- Patients bear all costs for transfer to or between hospitals.
- Psychological and psychiatric services are limited, even in the larger cities, with hospital-based care only available through government institutions.
Medical Tourism and Elective Surgery:
- Medical tourism is a rapidly growing industry. People seeking health care overseas should understand that medical systems operate differently from those in the United States and are not subject to the same rules and regulations. Anyone interested in traveling for medical purposes should consult with their local physician before traveling and visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information on Medical Tourism.
- We strongly recommend supplemental insurance to cover medical evacuation in the event of unforeseen medical complications.
- Your legal options in case of malpractice are very limited in Thailand.
- Although Thailand has many elective/cosmetic surgery facilities that are on par with those found in the United States, the quality of care varies widely. If you plan to undergo surgery in Thailand, make sure that emergency medical facilities are available and professionals are accredited and qualified.
Pharmaceuticals:
- Exercise caution when purchasing medication overseas. Pharmaceuticals, both over the counter and requiring prescription in the United States, are often readily available for purchase with little controls. Counterfeit medication is common and may prove to be ineffective, the wrong strength, or contain dangerous ingredients. Medication should be purchased in consultation with a medical professional and from reputable establishments.
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration are responsible for rules governing the transport of medication back to the United States. Medication purchased abroad must meet their requirements to be legally brought back into the United States. Medication should be for personal use and must be approved for usage in the United States. Please visit the U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Food and Drug Administration websites for more information.
Assisted Reproductive Technology and Surrogacy:
- If you are considering traveling to Thailand to have a child through use of assisted reproductive technology (ART) or surrogacy, please see our ART and Surrogacy Abroad page .
- Surrogacy is illegal for foreigners in Thailand, subject to complex local regulation. For additional information, visit the Government of Thailand’s website for information on foreigner surrogacy.
- If you decide to pursue parenthood in Thailand via assisted reproductive technology (ART) with a gestational mother, be prepared for long and unexpected delays in documenting your child’s citizenship. Be aware that individuals who attempt to circumvent local law risk criminal prosecution.
Water Quality:
- In many areas, tap water is not potable. Bottled water and beverages are generally safe, although you should be aware that many restaurants and hotels serve tap water unless bottled water is specifically requested. Be aware that ice for drinks may be made using tap water.
Adventure Travel:
- Visit the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website for more information about Adventure Travel .
COVID-19 Testing: For the most current list of COVID-19 testing locations in Thailand approved by the Ministry of Public Health, please visit: http://service.dmsc.moph.go.th/labscovid19 . Testing is paid for by U.S. citizens.
The Ministry of Public Health provides a list of 44 laboratories approved to conduct COVID-19 testing found here .
Please Note : Same-day Covid-19 testing is available at most private hospitals throughout Thailand. Please reference this list of testing locations and contact the provider directly to inquire about COVID-19 testing options, scheduling, cost, and other information.
COVID-19 Vaccines: The COVID-19 vaccine is available for U.S. citizens to receive in Thailand. According to Thai authorities, both private and public hospitals are providing COVID-19 vaccines. More information on a list of hospitals in Thailand is available here .
The Bang Rak Vaccination and Health Center, the Institute of Dermatology, and the Bamrasnaradura Infectious Diseases Institute are currently providing free bivalent vaccines to non-Thai citizens on a walk-in basis.
Visit the FDA's website to learn more about FDA-approved vaccines in the United States.
Travel and Transportation
Road Conditions and Safety:
- Traffic accidents are common in Thailand. According to the World Health Organization , in 2018, Thailand had one of the world’s highest traffic-related fatality rates. Bangkok and some parts of Chiang Mai have heavy traffic.
- Reckless driving: Speeding, reckless passing, and failure to obey other traffic laws are common in all regions of Thailand. Traffic moves on the left. Some drivers move illegally against the traffic. Scooters and motorbikes commonly drive on the sidewalks during rush hour and other periods of heavy traffic. Commercial drivers commonly consume alcohol, amphetamines, and other stimulants.
- Accidents involving motorcycles can be deadly . Riders may incur serious injuries when they are not wearing helmets or proper clothing and footwear. According to the World Health Organization, in 2016, 74 percent of traffic fatalities involved riders of 2-and 3-wheeled vehicles. Use of motorcycle helmets is mandatory, but this law is sporadically enforced.
- Use a pedestrian bridge to cross the road where one is available, including in front of the U.S. Embassy on Wireless Road and on Sukhumvit Road, where many pedestrians have been killed and several U.S. citizens seriously injured. Look carefully in both directions before crossing streets, even when using a marked crosswalk.
- If you have a traffic accident, you should contact your insurance company for guidance in dealing with the other party and the police.
- Emergency vehicles: Congested roads and a scarcity of ambulances can make it difficult for accident victims to receive timely medical attention
Traffic Laws:
- Driving under influence is punishable by law . If you are found to be intoxicated, you could be jailed for a minimum of two years and subject to a fine.
- Bribes are illegal. If you are found guilty, you could be imprisoned up to five years, face severe fines, or both.
- Lack of ID.
- Not obeying traffic laws and traffic signals.
- Driving slowly in regular lanes of traffic.
- If you are involved in a traffic accident, you should contact your auto insurance company for guidance .
Public Transportation:
- Mass transit: In Bangkok, the BTS elevated "Skytrain," “Airport Rail Link” mass transit, and the underground MRT systems are reliable, inexpensive, air conditioned, and often faster than Bangkok traffic.
- Bus system: Bangkok also has an extensive bus system, but buses can be overcrowded and are often driven with little or no regard for passenger safety.
- For hire vehicles: Cities outside of Bangkok typically have only rudimentary public transportation and usually do not have metered taxis. In many cases, motorcycle taxis, tuk-tuks, bicycle-powered rickshaws, and pick-up trucks will be the only options available for travelers without their own transport.
- Smartphone-based for-hire vehicle service exist in Bangkok and other large cities. Those affiliated with registered taxis, such as Grab Taxi, Line Taxi, and All Thai Taxi are legal, but their affiliated car services are under legal review.
See our Road Safety page for more information.
Aviation Safety Oversight: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has assessed the government of Thailand’s Civil Aviation Authority as not being in compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards for oversight of Thailand’s air carrier operations. Further information may be found on the FAA’s safety assessment page .
Maritime Travel: Mariners planning travel to Thailand should also check for U.S. maritime advisories and alerts . Information may also be posted to the U.S. Coast Guard homeport website , and the NGA broadcast warnings .
For additional travel information
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive security messages and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
- See the State Department’s travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories .
- Follow us on Twitter and Facebook .
- See traveling safely abroad for useful travel tips.
Review information about International Parental Child Abduction in Thailand . For additional IPCA-related information, please see the International Child Abduction Prevention and Return Act ( ICAPRA ) report.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, thailand map, learn about your destination, enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
Make two copies of all of your travel documents in case of emergency, and leave one with a trusted friend or relative.
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba
Bosnia and Herzegovina
British Virgin Islands
Burkina Faso
Burma (Myanmar)
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Cote d Ivoire
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eswatini (Swaziland)
Falkland Islands
France (includes Monaco)
French Guiana
French Polynesia
French West Indies
Guadeloupe, Martinique, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélemy (French West Indies)
Guinea-Bissau
Isle of Man
Israel, The West Bank and Gaza
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Republic of North Macedonia
Republic of the Congo
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
The Bahamas
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Vatican City (Holy See)

External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Before you travel check that:
- your destination can provide the healthcare you may need
- you have appropriate travel insurance for local treatment or unexpected medical evacuation
This is particularly important if you have a health condition or are pregnant.
Emergency medical number
Dial 1669 and ask for an ambulance.
Contact your insurance or medical assistance company promptly if you’re referred to a medical facility for treatment.
Vaccinations and health risks
At least 8 weeks before your trip check:
- the latest information on vaccinations and health risks in TravelHealthPro’s Thailand guide
- where to get vaccines and whether you have to pay on the NHS travel vaccinations page
Health risks in Thailand include:
- dengue fever
See the ‘Other risks’ section of the TravelHealthPro Thailand guide for more on health risks .
To avoid mosquito-borne viruses, such as dengue fever and Zika virus, take steps to avoid being bitten by mosquitoes.
Air quality
There can be high levels of air pollution in large cities. This includes Bangkok and Chiang Mai, which are also affected by seasonal regional smoke haze from the burning of trees. The high pollution and particulate count sometimes reach dangerous levels. This may worsen bronchial, sinus or asthma conditions.
Check air quality levels for many cities on the World Air Quality Index website .
The legal status and regulation of some medicines prescribed or bought in the UK can be different in other countries.
Hospitals and pharmacies across Thailand will usually accept UK prescriptions. Brand name medication can often be more expensive than locally produced medication.
Medication sold on the street may not be genuine or may have been stolen. Taking medication without medical advice or a prescription can have serious health consequences.
Read best practice when travelling with medicines on TravelHealthPro . The NHS has information on whether you can take your medicine abroad .
Healthcare facilities in Thailand
FCDO has a list of English-speaking doctors in Thailand . All hospitals require guarantee of payment before treating patients. Make sure you have adequate health insurance.
Private hospitals in Thailand are of a high standard but can be expensive. Public hospitals and clinics do not always meet UK standards, particularly outside Bangkok.
COVID-19 healthcare in Thailand
Check the latest information on risk from COVID-19 risk for Thailand on TravelHealthPro .If you have severe symptoms, or any questions related to COVID-19, while in Thailand, call the Thai COVID-19 Hotline on 1422. There is more information on the PR Thai Government Facebook page .
Travel and mental health
Read FCDO guidance on travel and mental health . There is also mental health guidance on TravelHealthPro .
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.

- Vaccinations for Mexico
- Vaccinations for Brazil
- Vaccinations for Argentina
- Vaccinations for Peru
- Vaccinations for Ecuador
- Vaccinations for Panama
- Vaccinations for South Africa
- Vaccinations for Kenya
- Vaccinations for Tanzania
- Vaccinations for Botswana
- Vaccinations for Uganda
- Vaccinations for Bali and Indonesia
Vaccinations for Thailand
- Vaccinations for Myanmar (Burma)
- Vaccinations for Vietnam
- Vaccinations for Cambodia
- Vaccinations for Laos
- Vaccinations for Philippines
- Vaccinations for China
- Vaccinations for Hong Kong
- Vaccinations for India
- Vaccinations for Sri Lanka
- Vaccinations for Nepal
- Vaccinations for Fiji
- Vaccinations for Vanuatu
- Vaccinations for Papua New Guinea
- Yellow Fever
- Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
- Corporate Vaccinations

When it comes to travelling in Thailand and South East Asia in general, there are a few precautions that should be taken to protect against diseases and other incidents.
Thailand and medical tourism
Increasing numbers of Australians also travel to Thailand as medical tourists, and medical procedures in any foreign country carry their own set of risks. If you are planning on travelling to Thailand as a medical tourist you should speak to the Travel Vaccination Clinic about what you intend to have done and associated risks as well as any relevant vaccination advice provided below. Any medical or dental procedures you have done should occur in a sterile environment where all equipment is properly sanitised.
This website provides general advice on vaccinations for Thailand and is not a substitute for adequate medical advice from a Travel Vaccination Clinic doctor or your own doctor. You should consult a doctor about your own travel plans, including:
- How up to date you are with the childhood immunization schedule
- Your travel itinerary while in Thailand and elsewhere on your trip
- Intended activities and style of accommodation
- Your general health and well being ahead of travelling
Vaccinations required for Thailand
Travellers to Thailand should consider getting vaccinated against the following diseases, and should ensure they are fully up to date with the Australian childhood immunization schedule, which will protect against some common preventable diseases, including hepatitis A, occurring throughout Thailand.
Hepatitis A and Typhoid
Hepatitis A can be passed on through contaminated food or water in all parts of Thailand and it is recommended travellers get vaccinated against Hepatitis A before leaving Australia.
Typhoid is also present in Thailand and can be passed on through contaminated food or water. It is recommended to vaccinate against Typhoid in particular if you are travelling to rural areas, visiting friends or relatives in Thailand or if you are an adventurous eater.
Both Hepatitis A and Typhoid vaccinations can be administered in one shot, and this lasts for a number of years once administered. You should speak to the Travel Vaccination Clinic about getting vaccinated against Hepatitis A and Typhoid, as well as taking food safety precautions and avoiding water that has not been boiled or treated (unless bottled).
Taking these precautions will also help protect you against other food and water borne illnesses such as Cholera.
Hepatitis B might be contracted if you meet a new partner in Thailand, get a tattoo or piercing or undergo cosmetic medical procedures. The disease can be contracted through sexual contact, or exposure to needles or bodily fluids so the vaccine is highly recommended for anyone who might undertake activities that put them at risk of contracting Hepatitis B.
Japanese Encephalitis in Thailand – should you get vaccinated?
Travellers to Thailand may be exposed to Japanese Encephalitis, and cases can be asymptomatic or cause severe vomiting or febrile illness with symptoms similar to those of meningitis. Cases are rare, but do occur occasionally.
Japanese Encephalitis takes up to two weeks to incubate in humans, and most reported cases occur in children. Vaccination is mainly necessary for longer stays in Thailand (of more than one month) but those doing a lot of outdoor activities, and visiting rural or remote areas even on shorter trips should also consider vaccination against Japanese Encephalitis.
Malaria and other mosquito borne illnesses in Thailand
Malaria is present in Thailand , however risk level depends on where you are going and what you are doing. There are precautions to take against mosquito bites such as using repellent, wearing long, loose clothing, using a mosquito net where appropriate and avoiding contact with insects and mosquitos. You should discuss these with the doctor during your appointment as other mosquito borne illnesses such as dengue fever and including Chikungunya Fever, Japanese Encephalitis and Filariasis are also present in Thailand.
The main area recommended for anti-malarial drugs is forested land that borders Myanmar, Cambodia and Laos. There is little to no risk of Malaria recorded in Bangkok, Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai or Koh Phangan, Koh Samui, Pattaya, Phang Nga, and Phuket.
Rabies risk in Thailand is low but still present, so avoiding contact with dogs and other mammals is essential. In certain cases travellers should still take precautions as avoiding contact may not be enough where an animal initiates contact with a human, and especially a child, for example. Increased risk of exposure to rabies occurs with:
- Those who intend doing outdoor/adventure activities such as caving or adventure travel where the risk of animal bites is increased
- Those working with animals during their time in Thailand
- Those travelling to remote areas for an extended period of time
- Children who may not be as likely to report animal bites or contact with mammals
If you might fit into any of these categories you need to speak with the doctor about your situation and consider getting vaccinated. Australia remains one of only a few rabies-free countries in the world, so it is important to consider the risk before returning home.
Other precautions for travellers to Thailand
Generally it is advised not to get any temporary black henna tattoos while in Thailand, as the dye in them can severely irritate the skin.
There is also a high rate of HIV/Aids infections in Thailand, so those who may meet a new partner should use precautions.
Some areas of Thailand can experience smoke haze or increased pollution, especially during March and April each year. This can aggravate conditions such as asthma, sinus conditions or bronchial problems. Those experiencing any issues or symptoms should stay up to date with local meteorological warnings and take precautions when pollution is reported as high. Help can also be sought from local medical authorities.
Is Yellow Fever present in Thailand?
There is no risk of contracting Yellow Fever in Thailand, and you may be required to produce proof of Yellow Fever vaccination if you are arriving from a country with risk of Yellow Fever infection (but this does not often include short transits through the airport, for example). If you have any concerns about the destination you will be arriving from, speak to the doctor about them during your appointment.
Book your appointment now at our Sydney CBD clinic, get instant confirmation.
- Skip navigation
- Find a branch
- Help and support
Popular searches
- Track a parcel
- Travel money
- Travel insurance
- Drop and Go
Log into your account
- Credit cards
- International money transfer
- Junior ISAs
Travel and Insurance
- Car and van insurance
- Gadget insurance
- Home insurance
- Pet insurance
- Travel Money Card
- Parcels Online
For further information about the Horizon IT Scandal, please visit our corporate website
- Vaccinations needed for Thailand
Some vaccinations for Thailand are recommended and some are mandatory in certain circumstances. It’s important to know which vaccinations or injections for Thailand you need to get before you leave home.
Posted: 22/1/2022 | By Amanda Duffy

Thailand is a hugely popular destination for British holidaymakers, with over a million people travelling there annually. It has a tropical monsoon climate and a hugely diverse geography, including a long coastline, dense rainforest, paddy fields and high mountain ranges. Unfortunately, it also has a few health risks that we don’t have in Britain, and that means it’s vital that you take sensible medical precautions before you travel .
Some vaccinations for Thailand are recommended, and some are mandatory in certain circumstances, so it’s important to know what vaccinations or injections for Thailand you need to get before you leave home.
If you're planning a trip to Thailand, consider a Post Office travel insurance policy.
What vaccinations do i need for thailand.
Check the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO) travel advice for Thailand, which includes entry requirements such as vaccinations. It’s recommended that travellers to Thailand have jabs for tetanus and hepatitis A, possibly for yellow fever too, and they should also take additional precautions depending on which regions they’re visiting and the activities they plan to do.
Contracted through the contamination of cuts, burns and wounds, is a potential issue across the region, and in places where medical care is limited. An infection can be an unpleasant experience causing a tightening of the muscles in the body, which can than affect swallowing and breathing. A total of five injection doses of the tetanus vaccine are recommended for life in the UK and boosters are recommended if you haven’t had one for ten years.
Hepatitis A
A liver infection spread through contaminated water and food that causes high temperatures, joint pain, nausea, jaundice and itchy skin among other symptoms. It is prevalent anywhere sanitation is poor and has no specific treatment. Jabs for hepatitis A can be given in one dose.
Yellow fever
Vaccination against yellow fever is mandatory for all travellers over nine months of age arriving from any countries with a risk of yellow fever – even if they’ve only transited (for more than 12 hours) through the airport. Remember to double-check your full travel itinerary before you leave and carry your certificate to prove you’ve been vaccinated.
Is there a risk of malaria in Thailand?
Mosquitoes are an ongoing problem in Thailand, especially for anyone spending any time in rural areas and lowland paddy fields where they breed. Malaria is the most well known and serious condition spread by mosquitoes, causing severe fever and sometimes even proving fatal – with some symptoms developing as long as a year after exposure.
In areas where malaria is a risk you should avoid mosquito bites by covering up with clothing such as long sleeves and long trousers, especially after sunset, use insect repellents on exposed skin and, when necessary, sleep under a mosquito net. A course of antimalarial tablets such as Atovaquone, Proguanil or Doxycycline is also advised for anyone spending significant time in any affected regions.
What about other diseases?
Other mosquito borne viruses present in Thailand include Dengue Fever , which causes fever, headache, severe joint and muscular pain, and the Zika virus , which is relatively mild but can have serious side effects for pregnant women. Both diseases are more common in urban areas than rural, and there is no effective vaccination or jab for either – with the best method of prevention to try and avoid being bitten.
Mosquitoes also spread the brain disease Japanese encephalitis and, though unlikely, vaccination should be considered for anyone spending a long period in any of Thailand’s mosquito hotspots. Cholera may also be an issue, and this can be vaccinated against too if you’re planning on spending any serious amount of time in the rural areas.

How do I get vaccinations for Thailand?
Anyone requiring injections for Thailand should visit their GP six to eight weeks before they leave. They should also check for any medical updates on the official government website .
Many travel vaccinations are free on the NHS , including those for tetanus, diphtheria, polio, typhoid, hepatitis A and cholera so be sure to take advantage of this and get your free travel jabs.
High street chains like Boots and Superdrug also offer vaccination services but the costs can vary greatly. The International Society of Travel Medicine has clinics in 90 countries and provides pre-travel immunisation and counseling.
It’s important to be aware that not having the required inoculations could invalidate a travel insurance policy
Stay #TravelAware
Thailand is one of the UK's favourite travel destinations but which of these items can you not take into the country?
Did you correctly guess which item isn't allowed into Thailand?
Want to learn about more local laws for any country across the world? Visit www.gov.uk/foreign-travel-advice to stay in the loop with travel advice.
Interested in travel insurance?
Other travel products.
Order foreign currency online or in selected branches. Pick up in any branch or get it delivered to your home.
One prepaid Mastercard™ that stores up to 22 currencies.
Get your passport application right the first time. We can even complete and submit it for you digitally.
This might interest you

It's a proud feeling when children turn eighteen and start holidaying on their ...

If you're travelling abroad as a family, it makes sense to take out insurance ...

Fancy trekking in a remote Asian rainforest? A wild time in New York? Flying ...

With festivals overseas becoming the new norm, festivalgoers need to do a bit ...

Learn about the different types of travel insurance available from Post Office, ...

There’s no better feeling than planning an amazing trip to an exotic ...

The opportunities to combine business and leisure have never been greater. You ...
Travelling with high blood pressure is fine – but it’s important to make sure ...

If you're travelling to an EU country from the UK, make sure you take a Global ...

If you're living with cancer but love to travel, can you get travel insurance ...

Going backpacking is one of life’s great adventures. But before you set off ...

You should be able to get the right cover to travel abroad if you’re diabetic, ...

Exploring the globe can be scary, but there’s so much to find at the edge of ...

Do you need travel insurance for your trip? Is travel insurance worth it? And, ...

So, you’ve booked your flights, accommodation and activities. What next?

Travel insurance for a holiday in the UK isn't something you must have, but it ...

As you get older, being able to go where you want when you want is all part of ...

Adventurous holidays can take many forms, from action-packed itineraries in ...

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise a high degree of caution to Thailand overall due to the risk of civil unrest and the threat of terrorism, including in Bangkok and Phuket.
Higher levels apply in some areas.
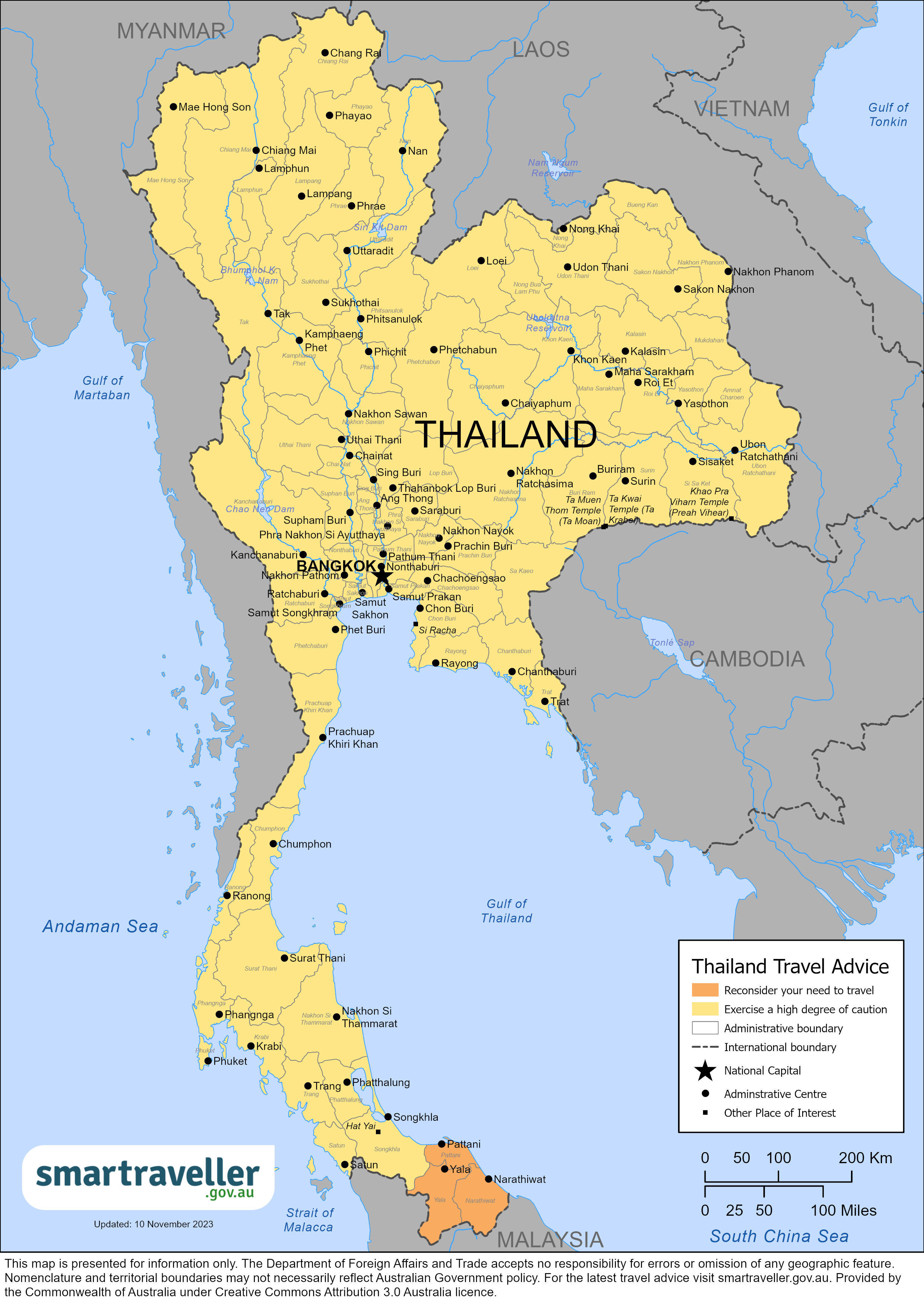
Thailand (PDF 998.61 KB)
Asia (PDF 2.21 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 1669 for medical emergencies and rescue services.
Call 1724 for an ambulance in Bangkok. 1669 Nationwide.
Call 191 for police.
Call 1155 for the tourist police.
Advice levels
Exercise a high degree of caution to Thailand overall due to the risk of civil unrest and the threat of terrorism, including in Bangkok and Phuket.
Exercise a high degree of caution to Thailand overall due to the possibility of civil unrest and the threat of terrorism, including in Bangkok and Phuket.
Reconsider your need to travel to Yala, Pattani and Narathiwat provinces.
Reconsider your need to travel to:
- Yala province,
- Pattani province, and
- Narathiwat province
due to ongoing risks of low-level insurgent activity.
See Safety .
- Anti-government protests have previously occurred in Bangkok and other areas of Thailand. The security environment can be unpredictable and turn violent. Those attending protests can face arrest or other legal consequences. Monitor local media for information on protest locations and avoid public gatherings. Take official warnings seriously and follow the advice of local authorities.
- Popular tourist areas in Thailand may be the target of terrorist attacks. Thai authorities have warned of possible bombings on symbolic dates or holidays. Be alert to possible threats. Take official warnings seriously and follow the advice of local authorities.
- Border areas near Cambodia, Myanmar and Malaysia are dangerous due to violence, armed conflict and landmines. Pay close attention to your personal security.
- Reconsider your need to travel to the 3 most southern provinces of the Thailand-Malaysia border: Yala, Pattani and Narathiwat. Low-level insurgent activity continues to occur in these areas.
- Sexual assault, assault, robbery and drink spiking can happen to tourists. Never leave your drink unattended. Stick with people you trust at parties, in bars, nightclubs and taxis.
Full travel advice: Safety
- If you're visiting Thailand and then travelling to a country that requires COVID-19 testing (RAT or PCR test) for entry, you'll need to purchase medical insurance prior to your arrival in Thailand. The insurance will need to provide cover for COVID-19 treatment.
- Travellers have been arrested for carrying medicine they bought at a Thai pharmacy without a prescription. Get medical advice before buying medicine.
- Insect-borne diseases include malaria, Zika virus, dengue, chikungunya, Japanese encephalitis and filariasis. Use insect repellent. Ensure your accommodation is insect-proof as possible.
- Animals in parts of Thailand can carry rabies. Don't ever feed, pat or tease monkeys. If you're bitten or scratched by a dog, monkey or other animal, get treatment immediately.
- Thailand has high levels of air pollution. Air pollution can make bronchial, sinus or asthma conditions worse. Check air quality levels on the World Air Quality Index .
- Medical tourism is common. Avoid discount and uncertified medical establishments. Their standards can be poor. Research medical service providers and choose with care.
Full travel advice: Health
- Penalties for drug offences are severe. They include the death penalty.
- Commercial surrogacy is illegal. E-cigarettes, e-baraku, vaporisers and refills are illegal. Smoking on some beaches is illegal. Travel without carrying identification is illegal.
- Penalties for breaking the law can apply to anyone aged under 18 years. Penalties for children can include detention in a juvenile or adult prison.
- Thailand has the death penalty for serious crimes, including murder, attempted murder and rape. Crimes against the state and offences against the monarchy can also attract the death penalty. Take care not to cause offence about the monarchy, including on social media.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- You can get a visa exemption for up to 30 days if you arrive through one of the international airports or for up to 15 days if you enter through a land border (restricted to 2 entries per calendar year). Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. You should contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Thailand or see the Thai government's Facebook page for the latest details.
- You may be subject to biometric screening at points of entry, and restrictions may change at short notice. Check with your airline, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) or the nearest Thai Embassy for the latest information.
- You can transit between international flights in Bangkok's Suvarnabhumi Airport . Ensure that your connecting flight is booked on the same itinerary and ticket. You must remain in the transiting area in the airport.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter tells you what the Australian Government can and can't do to help when you're overseas.
- For consular help, contact the Australian Embassy, Bangkok , the Australian Consulate-General, Phuket or the Passport and Notarial Services, Chiang Mai .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy's social media accounts.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Civil unrest and political tension, security situation .
The security situation can be unpredictable in Thailand. Large protests have occurred in Bangkok and other areas. In previous years, large political protests and government crowd control operations have resulted in violence.
More incidents are possible.
To stay safe during periods of unrest:
- avoid demonstrations, processions and public gatherings
- follow media and other sources
- take official warnings seriously
- follow the advice of local authorities
- If you see a suspicious package, stay clear and report it to Police
More information:
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Thailand-Cambodia border
Thailand and Cambodia have an ongoing border dispute. There's a risk of landmines and unexploded weapons near the Thai-Cambodian border area.
Be extra careful at tourist areas, including:
- the Preah Vihear temple - Khao Pra Viharn in Thailand
- the Ta Kwai temple - Ta Krabei in Cambodia
- the Ta Muen Thom temple - Ta Moan in Cambodia
Tourist attractions and border crossings in this area may close with little or no notice.
Thailand-Myanmar border
Fighting and armed theft can occur along the Thai-Myanmar border. This includes:
- fighting between the Burmese military and armed ethnic opposition groups
- clashes between Thai security forces and armed criminal groups, such as drug traffickers
Armed clashes between the military and opposition groups inside Myanmar may lead to border closures.
If you try to cross the border illegally, you may be detained and deported.
Bandits may target you if you travel through national parks in this border region.
If you travel to this region:
- monitor the news
- watch out for other signs of unrest
- pay close attention to your personal security
Thailand-Malaysia border
Reconsider your need to travel to or from the three most southern provinces:
Violence includes attacks and bombings, with deaths and injuries. Since 2004, over 6500 people have been killed and many more injured in these provinces.
Bombings are often coordinated to target people who respond to the first explosion.
Over the past few years, multiple coordinated explosions have occurred in the southern border provinces, and low-level insurgent activity continues.
If you travel to or stay in these provinces, you could get caught up in violence directed at others.
Attacks can happen at any time.
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
Attacks, including bombings, are possible anytime. They can happen anywhere, including Bangkok and Phuket.
Popular tourist areas may be the target of terrorist attacks.
Thai authorities have warned of possible bombings on symbolic dates or holidays.
In August 2016, around 24 incidents with improvised explosive devices (IEDs), arson and other suspicious events killed 4 people and injured over 30.
Some IEDs were detonated in popular tourist spots, including:
- Hua Hin, Patong Beach and Loma Park in Phuket
- Surat Thani
On 10 March 2019, several IEDs exploded in Phatthalung and Satun provinces. No people were killed or injured.
IED incidents have occurred in Bangkok and other tourist areas in recent years. On 2 August 2019, a series of explosions occurred in public places throughout Bangkok, including near Chong Nonsi BTS Station and outside several Thai Government buildings.
In May 2017, attacks at a Bangkok Military Hospital and the National Theatre injured 26 people.
Possible targets for future attacks include:
- shopping malls, markets and banks
- hotels and beach resorts
- restaurants, bars and nightclubs
- schools and places of worship
- outdoor recreation events
Other targets include public buildings, public transport, airports and sea ports.
To reduce your risk of being involved in a terrorist attack:
- have a clear exit plan in case there's a security incident
- be alert to possible threats
- report suspicious activity or items to police
- monitor the media for threats
If there is an attack, leave the area as soon as it's safe. Avoid the affected area in case of secondary attacks.
Sexual assault and violent crime
Travellers may experience sexual assault , other assault and robbery .
Be extra careful in tourist spots such as Khao San Road in Bangkok and the night-time entertainment zones in Bangkok, Pattaya and Phuket.
Be aware of drink-spiking. Don't drink homemade or local cocktails. They can contain narcotics or poison. You're at higher risk of sexual assault and theft if you get drugged.
Never leave your drink unattended.
Stick with people you trust at parties, in bars, nightclubs and taxis.
Get urgent medical attention if you think you or someone else has been drugged.
If you're a victim of violent crime, including rape, get immediate medical attention.
Under Thai law, courts will only accept the results of a medical examination from some government hospitals. After you've been examined by a government hospital, you can receive medical attention at a private hospital. Please contact the Australian Embassy Bangkok, Consulate-General Phuket, Consulate Chang Mai or Consular Emergency Centre in Canberra for assistance.
- Partying safely
Petty crime
Money and passports have been stolen from budget hotel and hostel rooms, and from bags on public transport. Thieves also target luggage stored on trains and below buses.
Bags have been snatched by thieves on motorcycles, or sliced open with razor blades.
To reduce your risk of theft:
- don't leave valuables in luggage stowed under buses or away from you on trains
- be wary of motorcycles approaching from behind as you walk on the footpath
- hold bags and backpacks in front of you
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
More information:
Cyber security when travelling overseas
Tours and adventure activities
Transport and tour operators don't always follow safety and maintenance standards. This includes for:
- scuba diving
- elephant safaris
- bungee jumping
If you plan to do an adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
If proper safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Climate and natural disasters
Thailand experiences natural disasters and severe weather , including:
- earthquakes
Severe weather events are likely to disrupt transport, electricity and communications.
To stay safe during severe weather:
- check media and weather reports
- check in with your tour operator
- don't enter areas affected by flooding or landslides
If there is a natural disaster:
- secure your passport in a safe, waterproof place
- keep in contact with friends and family
- monitor the media and other local sources of information
- Register with the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System to receive alerts on major disasters.
Storms and floods
Severe storms and widespread seasonal flooding can occur without warning. This includes flash floods.
The wet season in north and central Thailand is from May to October.
In Koh Samui and the south-east of the peninsula, the wet season is from November to March.
- Thai Meteorological Department
- Mekong River Commission — flood levels for the Mekong River
Earthquakes and tsunamis
Earthquakes occur in Thailand.
Tsunamis are more likely in Thailand because of the risk of earthquakes.
Check with the US Tsunami Warning Centre for updates on seismic activity and tsunamis.
If you're near the coast, move to high ground straight away if advised, or if you:
- feel a strong earthquake that makes it hard to stand up
- feel a weak, rolling earthquake that lasts a minute or more
- see a sudden rise or fall in sea level
- hear loud and unusual noises from the sea
Don't wait for official warnings such as alarms or sirens. Once on high ground, monitor local media.
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
If you're visiting Thailand and then travelling to a country that requires COVID-19 testing (RAT or PCR test) for entry, you'll need to purchase medical insurance prior to your arrival in Thailand. The insurance will need to provide cover for COVID-19 treatment.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers, including in terms of health and travel disruptions
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in Thailand. Take enough legal medicine for your trip.
Get medical advice before buying medicine in Thailand. Travellers have been arrested for carrying medicine they bought at a Thai pharmacy without a prescription.
Carry a copy of your prescription or a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
- Medications
Health risks
Insect-borne illnesses.
Zika virus is a risk in Thailand. If you are pregnant, defer non-essential travel to affected areas. Speak to your doctor before you travel. Several cases have been reported, including in Bangkok.
The Department of Health's Zika virus bulletin has advice for all travellers on how to reduce Zika virus risks. There's no vaccine for Zika virus.
Malaria is a risk throughout the year in rural areas. The worst affected areas are near the borders with Cambodia, Laos and Myanmar.
Dengue occurs in Thailand. It's common during the rainy season:
- November to March in Koh Samui and the south-east of Thailand
- May to October in the rest of Thailand, including Phuket
Dengue peaks in July and August although it is prevalent throughout the year . There's no vaccine or specific treatment for dengue.
Other insect-borne diseases include:
- chikungunya
- Japanese encephalitis
To protect yourself from disease:
- make sure your accommodation is insect-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
- consider taking medicine to prevent malaria
- get vaccinated against Japanese encephalitis
- Infectious diseases
Animals in parts of Thailand can carry rabies .
Rabies is deadly. Humans can get rabies from mammals, such as:
- other animals
Don't ever feed, pat or tease monkeys, even if you're encouraged to.
If you're bitten or scratched by a dog, monkey or other animal, get treatment as soon as possible.
Smoke haze and air pollution
Thailand has high levels of air pollution. It can reach hazardous levels. Bangkok and Chiang Mai can be particularly bad.
Air pollution can make bronchial, sinus or asthma conditions worse.
Smoke haze is an issue across the north and north-east of Thailand from March to April.
Check air quality levels on the World Air Quality Index .
Get advice from your doctor before you travel.
Medical care
Medical facilities.
The standard of medical facilities varies .
In an emergency, we recommend you contact an ambulance on 1669.
Private hospitals in major cities have high standards of medical care. Services can be limited in other areas.
Hospitals and doctors often need to confirm your insurance before they'll treat you, even in an emergency. Otherwise you may need to pay cash up-front. Costs can be very high.
Hospitals in Bangkok and other large cities can treat serious illnesses and accidents. In other areas, you may need to be moved to a place with better facilities. Medical evacuation can be very expensive.
Decompression chambers are located near popular dive sites in:
Medical tourism
Medical tourism , including for cosmetic and sex-change operations, is common.
Standards at discount and uncertified medical establishments can be poor. Serious and life-threatening complications can result.
Some hospitals and clinics have refused to compensate patients:
- who aren't satisfied with the results of cosmetic surgery
- who are harmed during surgery
- who die during surgery
Do your research. Choose your medical service providers with care.
Don't use discount or uncertified medical service providers.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed , the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Penalties for drug offences are severe. They include the death penalty.
Possession of even small quantities of drugs for recreational purposes can lead to long jail sentences and deportation.
Thai authorities may conduct spot-checks for illegal drugs in tourist areas.
Travellers have been targeted for narcotic tests. Under Thai law, authorities have the right to demand urine samples from people suspected of taking illegal drugs.
If you're asked to submit a urine sample, ask to do it at a police station. You can also ask to contact the Tourist Police. Call 1155 for English-speaking officers.
Private recreational use of cannabis is legal if the THC content is below 0.2% in weight. Cannabis use in public places remains illegal, and smoking outside is considered a public nuisance, and offenders risk fines and arrest. It is still illegal to sell or supply any extracts of cannabis containing more than 0.2% of THC.
Follow directions from local authorities.
- Carrying or using drugs
Surrogacy laws
Commercial surrogacy is illegal.
- Going overseas for international surrogacy
- Going overseas to adopt a child
E-cigarettes
E-cigarettes, e-baraku, and other related vaporisers, including refills, are prohibited. You can't import or transfer them through Thailand, even for personal use.
Producing or selling these items is illegal. You face either 10 years of imprisonment or a fine up to THB1 million, or both.
Penalties for breaking the law can be severe.
These penalties can also apply to anyone aged under 18 years who is subject to Thai juvenile judicial processes. Penalties can include detention in a juvenile or adult prison.
The death penalty can apply to:
- attempted murder
- crimes against the state, including treason
- some offences against the monarchy
Insulting the monarchy, or defacing images of the monarchy - including on a bank note bearing the King's image - can lead to prison terms of up to 15 years.
Take care not to cause offence when posting, commenting or liking items about the monarchy, including on social media.
In Thailand, it's illegal to:
- travel without carrying identification
- gamble - other than at a few major race tracks
- make a false statement to police, including about an insurance claim
It is also illegal to smoke on beaches in tourist areas, including:
- Prachuap Khiri Khan
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law and respecting customs
Dual citizenship
Thai-Australian dual nationals may be liable to complete military conscription.
If you're a dual national, contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Thailand before you travel.
- Dual nationals
Local customs
Respect local customs and take care to not offend. Deliberately ignoring local customs can cause grave offence.
Do not show the soles of your feet or touch the top of a person's head. These are insulting in Thai culture.
If in doubt, ask for local advice.
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Australian tourists can get a visa exemption for:
- up to 30 days, if you arrive through one of the international airports
- up to 15 days, if you enter through a land border (restricted to 2 entries per calendar year)
For longer stays, or if you're travelling for reasons other than tourism, you'll need to apply for a visa before you travel.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest Embassy or consulate of Thailand, the Royal Thai Embassy Canberra or Royal Thai Consulate-General Sydney . See the official website of the Tourism Authority of Thailand for the latest details about visas, currency, customs and quarantine rules.
Visas overstays
If you overstay your visa, you'll need to pay a fine before you can leave. You can also be:
- banned from re-entering Thailand
Thai authorities can blacklist you, which means you can never return to Thailand.
Penalties for not paying the fine include long prison sentences. Conditions at Immigration Detention Centres are harsh.
- Thai Immigration Bureau
Border measures
International passengers can transit Suvarnabhumi Airport , Bangkok.
You may be subject to biometric screening at points of entry. Clarify entry requirements with your airline, International Air Transport Association (IATA) or your nearest Thai Embassy.
Travellers are responsible for all COVID-19 treatment expenses if their medical insurance does not provide adequate coverage for COVID-19 illness.
Departure from Thailand
Travellers should refer to the relevant airline or travel provider for information about departing Thailand.
- Royal Thai Embassy , Canberra
- Thai government's Facebook page
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
Don't give your passport to third parties - like a jet ski or motorcycle rental businesses - as a guarantee. Companies may hold on to the passport and ask for payment for damages.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can't guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTI travellers
The currency of Thailand is the Thai Baht (THB).
You can convert Australian dollars for THB in tourist areas, major cities and towns.
ATMs are available in cities and regional centres.
Most hotels, restaurants and higher-end shops accept international credit cards.
Card skimming occurs. See Safety
Local travel
Driver's permit.
To drive a car or motorcycle in Thailand, you'll need a valid Australian driver's licence for the type of vehicle you're using.
To drive a motorbike, you'll need a valid motorcycle licence. Some rental companies will tell you otherwise.
You are required to have an International Driving Permit (IDP).
Don't drive any vehicles not covered by your Australian licence.
The Department of Land Transport issues Thai driver’s licences. Contact them to confirm:
- your eligibility
- what documents you need to apply
The legal driving age in Thailand is 18.
Road travel
You're more likely to die in a motor vehicle accident in Thailand than in Australia.
Thailand has one of the highest traffic-related fatality rates in the world. Motorcyclists are most at risk.
Road accidents are common, including in resort areas such as Phuket, Pattaya and Koh Samui.
Driving in Thailand is dangerous due to:
- reckless passing
- ignoring traffic laws
Be extra careful during holidays, such as Songkran (Thai New Year). Alcohol use and congestion are worse during these times.
Don't drink and drive.
If you're walking, use overhead walkways. Look in both directions before crossing streets, even at marked crossways.
- Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Under Thai law, motorcycle riders and passengers must wear a helmet. However, hire companies or motorcycle taxis rarely provide helmets. You may need to shop around to hire a helmet.
Australians are regularly injured or die in motorbike accidents in Thailand. Alcohol is often involved.
If you're in an accident, police may detain or arrest you until compensation is agreed. This can often cost 1000s of dollars.
Many vehicle hire companies don't have insurance.
If you have a motorcycle accident, you could be responsible for any damages, loss or costs associated with injury to others. The embassy can't help you negotiate on compensation demands.
Lawyers who can represent you are available from:
- Australian Embassy and Consulates-General in Thailand
- the Consular Emergency Centre in Canberra
If you plan to hire a motorbike, make sure:
- your insurance policy covers it
- you have a valid motorcycle licence
- the hiring company has comprehensive and third-party insurance
- you know the excess you would need to pay if you have an accident
- you always wear a helmet
Don't drink and drive, or drink and ride.
Never give your passport as a deposit or guarantee.
Taxis, tuktuks and motorcycle taxis
Official, metered taxis are generally safe and convenient. Be alert to possible scams and safety risks.
Be aware of apparently friendly taxi or tuktuk drivers who offer you cheap tours. They will take you to shops where they receive a commission. You may be overcharged or sold worthless goods or gems.
Before you get in an unmetered taxi, tuktuk or motorcycle taxi, agree on the fare and the route.
Make sure your bags are secure when you're travelling in a tuktuk or motorcycle taxi.
Never put yourself in danger by confronting a taxi, tuktuk or motorcycle taxi driver. Call the Tourist Police on 1155 if you need help.
Be careful when opening taxi doors. Look out for other vehicles, pedestrians and cyclists.
Ferry and speedboat travel can be dangerous. Serious incidents involving tourists have occurred and people have died.
If you plan on travelling by boat or ferry:
- check safety standards are in place
- check there is enough safety equipment for everyone
- wear your life jacket at all times
- avoid travelling after dark
- don't get on overcrowded boats
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Thailand's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Call 1724 for an ambulance in Bangkok.
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
Australian Embassy, Bangkok
181 Wireless Road Lumphini, Pathumwan Bangkok, Thailand. 10330 Phone: (+66 2) 344 6300 Fax: (+66 2) 344 6593 Website: thailand.embassy.gov.au Email: [email protected] Facebook: Australia in Thailand Twitter: @AusAmbBKK
Check the Embassy website for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
Australian Consulate-General, Phuket
6th Floor CCM Complex 77/77 Chalermprakiat Rama 9 Road (Bypass Road) Muang Phuket, Thailand, 83000 Phone: (+66 76) 317 700 Fax: (+66 76) 317 743 Website: phuket.consulate.gov.au E-mail: [email protected]
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Thailand?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
- Company History
- Mission Statement
- Philippines
- South Africa
- Afghanistan
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- British Virgin Islands
- Burkina Faso
- Canary Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Cote d'Ivoire
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Dominican Republic
- Easter Island
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- Guinea-Bissau
- Liechtenstein
- Madeira Islands
- Marshall Islands
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- North Korea
- North Macedonia
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Palestinian Territories
- Papua New Guinea
- Pitcairn Islands
- Puerto Rico
- Republic of the Congo
- Saint Barthelemy
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre-et-Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Sierra Leone
- Sint Eustatius
- Solomon Islands
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- South Korea
- South Sudan
- Switzerland
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- U.S. Virgin Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Wake Island
- Western Sahara
- Travel Vaccines
- Travel Health Consultations
- Travellers’ Diarrhea Kits
- Dengue Fever Prevention
- Malaria Prevention
- Chikungunya Prevention
- Zika Prevention
- Ebola Virus
- Yellow Fever
- Hepatitis A
- Japanese Encephalitis
- Hepatitis B
- Tickborne Encephalitis (TBE)
- Tetanus-Diphtheria-Pertussis
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella
- Influenza (Flu)
- Blood Tests
- Vitamin Injections
- Physician Referral Program
- London – Euston Travel Clinic

Travel Vaccines and Advice for Thailand

Thailand is a popular destination with its tropical climate, food, culture and seasides.
Thai is the official language of Thailand. But, other smaller languages spoken in rural areas. The primary religion of Thailand is Buddhism and is prevalent in many aspects of culture throughout Thailand. Islam is also practiced in Southern provinces.
Bangkok, Thailand’s capital city, is also the largest city in the country. Bangkok is highly populated with congested streets, modern buildings and temples. It is most known for its nightlife.
Thailand’s other major cities include Ayutthaya, Chiang Mai, and Chiang Rai.
Do I Need Vaccines for Thailand?
See the bullets below to learn more about some of these key immunisations:
- Hepatitis A – Food & Water – Recommended for most travellers to the region, especially if unvaccinated.
- Hepatitis B – Blood & Body Fluids – Recommended for travellers to most regions.
- Tetanus – Wounds or Breaks in Skin – Recommended for travellers to most regions, especially if not previously vaccinated.
- Typhoid – Food & Water – Jab lasts 3 years. Oral vaccine lasts 5 years, must be able to swallow pills. Oral doses must be kept in refrigerator.
- Yellow Fever – Mosquito – Required if travelling from a country with risk of yellow fever transmission
- Japanese Encephalitis – Mosquito – Recommended depending on itinerary and activities. Recommended for extended travel, recurrent travellers and travel to rural areas. Present throughout country, especially northern regions. Most cases from May to October.
- Rabies – Saliva of Infected Animals – High risk country. Vaccine recommended for long-stay travellers and those who may come in contact with animals.
See the tables below for more information:
Various mosquito-borne diseases are present in Thailand. Malaria poses a threat to travellers to some regions of the country. Ensure you are protected with antimalarials.
Dengue , Zika and chikungunya can also be found in Thailand. While there are no vaccines available for these diseases, there are steps you can take to prevent them. Be sure to use mosquito repellents, netting and wear proper clothing.
Medical treatment is adequate and common in urban areas. Healthcare is also available in rural areas, though the health care providers may not speak English.
To find out more about these vaccines, see our vaccinations page . Ready to travel safely? Book your appointment either ring or start booking online now .
Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Thailand?
No visa is required for stays under 30 days in Thailand if arriving by air for tourism purposes. Other types of travellers may require a visa. Passports must be valid for at least six months beyond the date of entry. Proof of yellow fever vaccination may be required if you are travelling from a region where yellow fever is present.
Sources: Embassy of Thailand and GOV.UK
What is the Climate Like in Thailand?
Thailand has a tropical climate, warm and humid with temperatures are around 30.
There are three seasons in Thailand: the cool season (November-February); the hot season (March-May); and the rainy season (June-October).
The most popular tourist times are between November and March, when weather is mild and enjoyable.
How Safe is Thailand?
In the past few years, there have been periodic terrorist attacks at popular tourist attractions in Thailand,. This remains a high-concern today. There is an ongoing risk of terrorist attacks in Thailand.
The National Council for Peace and Order (NCPO) has placed strict restrictions on media and have banned political gatherings. Tourists may be detained by the military for openly criticising the NCPO.
Pick-pocketing is common in Thailand as is sexual violence in bars and isolated areas.
Do not use your passport as collateral. Many rental places are scams.
In Southern Thailand (Yala, Pattani, Narathiwat, and Songkhla), martial law is still prevalent. Tourists are cautioned against travelling to these areas.
Temples in Thailand
There are over 40,000 temples in Thailand, making them popular tourist attractions. These temples range in age and architecture and many are still in use today.
Wat Pho, located in Bangkok, is one of the most popular due to its size and attractions within. It is one of the largest complexes in the country, holding many buildings. Wat Pho houses the largest reclining Buddha and largest collection of Buddha images.
The site is also headquarters for the teaching and preservation of Thai medicine. There, tourists can find two massage schools and pavilions.
You must take off your shoes to enter and you purchase coins to put into bowls for good luck. All the money goes towards renovating and upkeeping the site.
What Should I Take To Thailand?
Here are some essential items to consider for your trip to Thailand:
- Slip-on Shoes are best, especially if you’re planning to travel to many temples. You will need to take your shoes off quite frequently.
- Insect spray to ward off mosquitoes that could be carrying disease.
- Shops in Thailand have sun cream, but your options are limited.
- If you’re planning on visiting temples, buy clothing items that cover your shoulders, knees and ankles.
Embassy of the United Kingdom in Thailand
If you are in Thailand and have an emergency (for example, been attacked, arrested or someone has died) contact the nearest consular services. Contact the embassy before arrival if you have additional questions on entry requirements, safety concerns or are in need of assistance.
British Embassy Bangkok AIA Sathorn Tower, Floor 12A 11/1 South Sathorn Road, Sathorn Bangkok 10120 Thailand Telephone: +66 (0) 2 305 8333 Emergency Phone: +66(0)2 305 8333 Fax: +66 (0) 2 255 9278 Contact Form: Click Here
If you have any questions about travelling to Thailand or are wondering which jabs you may need for your trip, schedule an appointment with your local Passport Health travel medicine clinic. Ring us up at or book online now and protect yourself today.
On This Page: Do I Need Vaccines for Thailand? Do I Need a Visa or Passport for Thailand? What is the Climate Like in Thailand? How Safe is Thailand? Temples in Thailand What Should I Take To Thailand? Embassy of the United Kingdom in Thailand

- Privacy Policy
- Automatic Data Collection Statement
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn more

Information on how to stay safe and healthy abroad. About us.
- Destinations
- Asia (East)
- Asia (Central)
- Australasia & Pacific
- Central America
- Europe & Russia
- Middle East
- North America
- South America & Antarctica
Thailand (Asia)
Advice for all destinations.
Read the information on the COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel page for advice on travelling during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Vaccinations and malaria risk
Review both the Vaccination and Malaria sections on this page to find out if you may need vaccines and/or a malaria risk assessment before you travel to this country.
If you think you require vaccines and/or malaria risk assessment, you should make an appointment with a travel health professional:
- How to make an appointment with a travel health professional
A travel health risk assessment is also advisable for some people, even when vaccines or malaria tablets are not required.
- Do I need a travel health risk assessment?
Risk prevention advice
Many of the health risks experienced by travellers cannot be prevented by vaccines and other measures need to be taken.
Always make sure you understand the wider risks at your destination and take precautions, including:
- food and water safety
- accident prevention
- avoiding insect bites
- preventing and treating animal bites
- respiratory hygiene
- hand hygiene
Our advice section gives detailed information on minimising specific health risks abroad:
- Travel Health Advice A-Z
Other health considerations
Make sure you have travel insurance before travel to cover healthcare abroad.
Find out if there are any restrictions you need to consider if you are travelling with medicines .
Know how to access healthcare at your destination: see the GOV.UK English speaking doctors and medical facilities: worldwide list
If you feel unwell on your return home from travelling abroad, always seek advice from a healthcare professional and let them know your travel history.
Vaccinations
- Confirm primary courses and boosters are up to date as recommended for life in Britain - including for example, seasonal flu vaccine (if indicated), MMR , vaccines required for occupational risk of exposure, lifestyle risks and underlying medical conditions.
- Courses or boosters usually advised: none.
- Other vaccines to consider: Diphtheria; Hepatitis A; Hepatitis B; Rabies; Tetanus; Typhoid.
- Selectively advised vaccines - only for those individuals at highest risk: Japanese Encephalitis.
Yellow fever vaccination certificate required for travellers aged 9 months or over arriving from countries with risk of yellow fever transmission and for travellers having transited more than 12 hours through an airport of a country with risk of yellow fever transmission.
Notes on the diseases mentioned above
- Diphtheria : spread person to person through respiratory droplets. Risk is higher if mixing with locals in poor, overcrowded living conditions.
Risk is higher where personal hygiene and sanitation is poor.
Risk is higher for long stays, frequent travel and for children (exposed through cuts and scratches), those who may require medical treatment during travel.
- Japanese Encephalitis : spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. This mosquito breeds in rice paddies and mainly bites between dusk and dawn. Risk is highest for long stay travellers to rural areas, particularly if unable to avoid mosquito bites.
- Tetanus : spread through contamination of cuts, burns and wounds with tetanus spores. Spores are found in soil worldwide. A total of 5 doses of tetanus vaccine are recommended for life in the UK. Boosters are usually recommended in a country or situation where the correct treatment of an injury may not be readily available.
- Typhoid : spread mainly through consumption of contaminated food and drink. Risk is higher where access to adequate sanitation and safe water is limited.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease transmitted by mosquitoes.You cannot be vaccinated against malaria.
Malaria precautions
- Malaria risk exists in the forested and hilly areas mainly towards the international borders, all year round. There is also a risk in inland areas of Surat Thani province and parts of the southern border with Malaysia. There is low to no risk in the cities of Bangkok, Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Mae Sot, Pattay and Phuket, the islands of Ko Samui and Ko Chang and the River Quai bridge area.
- Malaria precautions are essential. Avoid mosquito bites by covering up with clothing such as long sleeves and long trousers especially after sunset, using insect repellents on exposed skin and, when necessary, sleeping under a mosquito net.
- Check with your doctor or nurse about suitable antimalarial tablets.
- See malaria map – additional information can be found by clicking on the Regional Information icon below the map.
- High risk areas: atovaquone/proguanil OR doxycycline is advised throughout the year.
- Low to no risk areas: antimalarials are not usually advised.
- If you have been travelling in a malarious area and develop a fever seek medical attention promptly. Remember malaria can develop even up to one year after exposure.
- If travelling to an area remote from medical facilities, carrying standby emergency treatment for malaria may be considered.
Other Health Risks
Altitude and travel, dengue fever.
There is a risk of exposure to coronavirus (COVID-19) in this country.
Please be aware that the risk of COVID-19 in this country may change at short notice and also consider your risk of exposure in any transit countries and from travelling itself.
- The 'News' section on this page will advise if significant case increases or outbreaks have occurred in this country.
Prior to travel, you should:
- Check the latest government guidance on the FCDO Foreign travel advice and country specific pages for travel to this country and the rules for entering the UK on return.
- Ensure you are up to date with UK recommendations on COVID-19 vaccination.
- You can check this in the FAQ's.
- If you are at increased risk of severe COVID-19 you should carefully consider your travel plans and consider seeking medical advice prior to making any decisions.
For further information, see Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel pages.
Zika Virus Infection
This country has been categorised as having a risk of Zika (ZIKV) virus transmission.
ZIKV is mainly spread through mosquito bites. The mosquito responsible most commonly bites during daylight hours and is common in towns and cities.
The illness is usually mild but infection during pregnancy may lead to babies being born with birth defects. There is no vaccine currently available against ZIKV.
Advice for All Travellers
You should practice strict mosquito bite avoidance at all times. Do not travel without adequate travel insurance . Seek pre-travel health advice from a travel health professional 6 to 8 weeks in advance of travel.
Additional recommendations for pregnant travellers or those planning pregnancy
If you are planning pregnancy in the very near future you should consider whether you should avoid travel to this country.
- contact your GP, obstetrician or midwife for further advice, even if you have not been unwell or had any symptoms of ZIKV infection
- use barrier methods of contraception during and after travel and for the duration of your pregnancy, even in you have not been unwell or had any symptoms of ZIKV infection
- If you develop symptoms of ZIKV infection, it is recommended that you avoid becoming pregnant for a further 2 months following your recovery
- 2 months afterwards if you are female
- 3 months afterwards if you are male or if both partners travelled
These measures reduce the chance of sexual transmission of ZIKV and/or the risk of ZIKV infection in pregnancy.
For further information, see Zika virus infection page.
- 89 additional items in the news archive for this country
back to top

Passing Thru Travel
10 Visa and Passport Tips for Hassle-Free Travel 2024
Posted: March 12, 2024 | Last updated: March 12, 2024

Embarking on international travel demands meticulous planning, particularly in navigating the often complex landscape of visas and passports. This guide is your essential compendium, offering in-depth insights and strategic tips to streamline your travel documentation process. Tailored for novice and seasoned travelers, it ensures that your focus remains on the excitement of your journey rather than the nuances of bureaucracy.

1. Understanding Visa Types and Their Specific Requirements
Each visa type demands a unique set of documents and prerequisites. Tourist visas, generally the most straightforward, still require proof of return tickets, accommodation, and sometimes a detailed itinerary. Business visas may need an invitation from a host company, while student and work visas often have more stringent requirements, including proof of enrollment or employment.
Transit visas, overlooked yet crucial for certain layovers, must be considered to avoid unexpected detours. Begin your application process early, as embassies and consulates can take weeks, if not months, to process requests.
Insider’s Tip: Familiarize yourself with the different types of visas—tourist, business, transit, student, and work visas—and understand the specific requirements for each. This knowledge can significantly influence the success of your application and the smoothness of your travel plans.

2. Navigating Passport Validity and Blank Page Requirements
The overlooked detail of passport expiration can derail your travel plans. Regularly check your passport’s expiry date and renew it well in advance if necessary. Countries requiring a certain number of blank pages in your passport do so for immigration stamps. Falling short on this requirement can result in denied boarding or entry.
Keep in mind that renewal times can vary, and expedited services, while available, come with additional costs. This is a critical step in your travel preparation, so make it a priority in your planning stages.
Insider’s Tip: Ensure your passport has sufficient validity — many countries require it to be valid for at least six months beyond your travel date. Also, check for blank pages; some countries require a specific number for entry and exit stamps.

3. Visa Application: Timing and Documentation
Timing is everything in visa applications. Start gathering required documents—such as photographs, travel insurance, financial statements, and any necessary letters or invitations—as early as possible. Be aware of holidays and peak periods, as these can affect processing times.
Online visa applications have simplified the process for many countries, but always have hard copies of essential documents when traveling. A common pitfall is underestimating the time it takes for visa processing; each country has its own timeline, and it’s prudent to allow extra time for any unforeseen complications.
Insider’s Tip: Apply for your visa as soon as your travel dates are confirmed. Late applications can lead to stressful delays or, worse, trip cancellations.

4. Health and Vaccination Documentation
Health documentation is increasingly becoming a staple in international travel. Countries in Africa and South America, for instance, may require proof of Yellow Fever vaccination. COVID-19-related health documentation has also become a norm. Always carry a physical copy of your vaccination records and any other required health documents.
The World Health Organization (WHO) offers a standardized ‘Yellow Card’ that shows vaccination history and is recognized worldwide. Not adhering to these requirements can result in being denied entry, so it’s critical to understand and comply with these health mandates.
Insider’s Tip: Some countries require proof of vaccination against specific diseases. Keep a record of your vaccinations and check the health requirements of your destination country.

5. Understanding Visa Waiver Programs and e-Visas
Many countries have agreements allowing certain nation citizens to enter without a traditional visa. For instance, the Schengen Area in Europe allows travelers from certain countries to enter visa-free for short stays.
Similarly, e-Visas, available through online applications, offer a streamlined process for obtaining travel authorization. These digital visas save time and reduce paperwork but always confirm the specific entry requirements, as they can vary even within visa waiver programs.
Insider’s Tip: Check if the country you visit has a visa waiver program or offers e-Visas, as these can significantly simplify the travel process.

6. Dealing with Visa Denials and Appeals
A visa denial can be disheartening, but it’s not always the end of the road. Embassies usually provide reasons for denial, which you should address in subsequent applications. Some countries offer an appeal process, while others require you to wait a certain period before reapplying.
Understanding the specific protocol of the country you’re applying to is crucial. Ensure your reapplication or appeal addresses all the concerns raised initially. Sometimes, seeking the assistance of a visa consultant or an immigration lawyer can provide clarity and improve your chances in complex cases.
Insider’s Tip: In case of a visa denial, understand the reasons provided and the process for an appeal or reapplication, if applicable.

7. Passport Safety and Copies
Your passport is your most valuable document when traveling abroad. Keep it secure in a hotel safe or a secure, hidden compartment in your luggage. Having copies of your passport (the page with your personal information and any relevant visa pages) is crucial in emergencies.
Store a digital copy in a secure cloud service and email a copy to yourself and a trusted contact back home. In the unfortunate event of losing your passport, these copies will be instrumental in proving your identity and facilitating the replacement process at your embassy or consulate.
Insider’s Tip: Keep your passport safe at all times and carry physical and digital copies in case of loss or theft.

8. Cultural Sensitivity and Local Laws
Cultural awareness is a sign of respect and can affect your entry into a country. Some nations have strict dress codes or norms that, if not adhered to, can lead to issues at immigration. Familiarize yourself with these aspects to avoid unintentional offenses. Additionally, understanding local laws is crucial.
For example, countries in the Middle East have stringent drug laws, and carrying certain prescription medications without proper documentation can lead to serious legal troubles.
Insider’s Tip: Research your destination’s cultural norms and local laws, as these can sometimes impact visa and entry policies.

9. Travel Insurance and Visa Requirements
Travel insurance is often a visa requirement, especially for countries in the Schengen Area. This insurance should cover medical expenses, trip cancellations, lost luggage, and repatriation. Check the specific coverage requirements of your destination country and keep a copy of your insurance policy with your travel documents. Not only is it necessary for some visa applications, but it’s also a prudent safeguard against unforeseen events during your travels.
Insider’s Tip: Some countries require proof of travel insurance for visa issuance. Ensure your policy meets the minimum coverage requirements.

10. Consulate and Embassy Assistance
Embassies and consulates can assist with a range of issues — from lost passports to legal troubles. Before traveling, note the address and contact details of your country’s diplomatic missions in the destination country.
In case of an emergency, such as a lost or stolen passport, political unrest, or natural disasters, they can provide crucial support and guidance. It’s also wise to inform them of your travel plans, particularly if traveling to regions with heightened security risks.
Insider’s Tip: Know the location and contact details of your country’s embassy or consulate in your destination country. They can be invaluable in emergencies.

The Bottom Line
Successful and hassle-free travel hinges on your preparedness, especially regarding visas and passports. By following these tips, you’re paving the way for a journey of ease and enjoyment. Equip yourself with this knowledge, and step confidently into your next journey, knowing you’ve covered every essential detail.
More Articles Like This…
Barcelona: Discover the Top 10 Beach Clubs
2024 Global City Travel Guide – Your Passport to the World’s Top Destination Cities
Exploring Khao Yai 2024 – A Hidden Gem of Thailand
The post 10 Visa and Passport Tips for Hassle-Free Travel 2024 republished on Passing Thru with permission from The Green Voyage .
Featured Image Credit: Shutterstock / Eviart.
For transparency, this content was partly developed with AI assistance and carefully curated by an experienced editor to be informative and ensure accuracy.
More for You
Cicada Map Shows States Where Trillions of Bugs Will Emerge
Forgotten 1990s Blockbusters Everyone Should Rewatch
Say Goodbye To Popcorn Ceilings Without Removing Them Thanks To This DIY
Pilot reveals what happened moments before Boeing 737 Max slid off taxiway
Teen ends up with stoma after period pain worry
Opinion: The problem with Beyoncé’s ‘Jolene’
Fani Willis Gets a Win Against Donald Trump
Popular Fast Food Chain Files Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
30 slang words you may not realize came from TV and movies
ESPN's Molly Qerim Sparks Outrage With Caitlin Clark Jab
Get Rid Of Pesky Wasps Using Two Ingredients You Already Own
Here's Everything Carrie Underwood Eats In A Day At 41—Including The Healthy Hacks From Her Own Backyard
Judge denies New York county executive request to block AG order to rescind transgender athlete ban
Russian Nuclear Submarine Fires Missiles
Amid racist insults, ‘Bachelor’ contestant Rachel Nance won’t apologize for her culture
12 Rude Things You Probably Shouldn’t Be Doing at the Grocery Store
34 movies to watch before they leave Netflix this month
Early signs of dementia can be spotted while a person is shopping
20 facts you might not know about 'Beetlejuice'
Taco Bell makes an unpopular menu move
Thailand records 9.4 mln tourists in first 3 months, $12.4 billion in spending, government says

The Reuters Daily Briefing newsletter provides all the news you need to start your day. Sign up here.
Reporting by Panarat Thepgumpant; Writing by Martin Petty
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

Reaction to Israeli inquiry into killing of Gaza aid workers
Reaction from around the world to an Israeli inquiry into the killing of seven World Central Kitchen aid workers in an air strike in Gaza. The report found serious errors and breaches of procedure by the Israeli military, and two officers were dismissed.

Ukrainian military drones attacked the Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant but caused no damage to its critical infrastructure, Russian state-run RIA news agency quoted the press service of the Russian-controlled facility as saying.

- Program Finder
- Admissions Services
- Course Directory
- Academic Calendar
- Hybrid Campus
- Lecture Series
- Convocation
- Strategy and Development
- Implementation and Impact
- Integrity and Oversight
- In the School
- In the Field
- In Baltimore
- Resources for Practitioners
- Articles & News Releases
- In The News
- Statements & Announcements
- At a Glance
- Student Life
- Strategic Priorities
- Inclusion, Diversity, Anti-Racism, and Equity (IDARE)
- What is Public Health?
How Dangerous is Dengue?
With global warming and world travel, the disease is spreading around the world.
Morgan Coulson
On March 25, Puerto Rico’s health secretary declared an epidemic after cases of dengue began to surge dramatically across the island. The U.S. territory, home to 3.2 million people, has reported at least 549 cases of the mosquito-borne infection so far this year, compared with a total of 1,293 cases for all of 2023.
Anna Durbin , MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Center for Immunization Research and professor in International Health , says she wasn’t surprised. “We're seeing outbreaks in all regions of the world. Dengue is very cyclical. Depending on where you are, we see a bad outbreak every three to four years.”
Dengue is endemic in over 127 countries, and almost half of the world’s population, about 4 billion people , live in areas with a risk of infection. Last year, more than 5 million cases were reported worldwide, according to the WHO.
In this Q&A, Durbin explains the dynamics of dengue infection, who is at greatest risk, and whether it might reach the continental U.S.
What are the symptoms of dengue?
About 75% of people who are infected with dengue have what we call subclinical symptoms, meaning they may have a fever for a day or so and feel achy, but not sick enough to seek medical care. But about 25% of people have much more severe symptoms. They have a high fever, no appetite, severe achiness, and a very low platelet count, which can result in bleeding. Around 5% of people infected with dengue have very severe illness that results in what we call plasma leakage, meaning they can't maintain their blood pressure, and can go into shock. Those are the cases we really worry about.
Who is at the greatest risk of severe infection?
The reason we see health care systems overrun during a dengue outbreak is that we can't predict who's going to develop that very severe form of dengue. We tend to hospitalize a lot of people, mostly to monitor them, and try to prevent them from going on to that stage.
We know that you're more likely to have a severe infection with your second dengue infection, but we also know that doesn't happen to everybody. It's still only a small percentage of those second infections that cause more severe disease.
How many times can a person become infected with dengue?
There are four different kinds of dengue, and we think that when you've been infected with one type of dengue, you have very long-lived if not lifelong immunity to symptomatic or severe disease with that serotype. You can be infected with each of the four serotypes, but your chances of having more severe dengue with your third or fourth infection is quite low.
Can it be deadly?
It can be, although physicians in dengue-endemic areas will tell you that with proper management, nobody should die from dengue if they present [for clinical care] in time.
Fluid resuscitation—replacing lost bodily fluids—is what's key to preventing death, but it has to be done in a careful way. Your blood pressure starts to go down because the plasma in your veins has leaked out. We give fluids to help keep that blood pressure up. But just as fast as that plasma leakage happens, it can reverse. You need really experienced people who know how to treat dengue properly. And if treated properly, the mortality rate is very low, about 0.2%.
I always say that if I got dengue, I wouldn't want to be in a U.S. hospital. I would want to be in Ho Chi Minh City or Bangkok. Because we don't see dengue the way people in Vietnam and Thailand do.
Is there a vaccine?
There are two vaccines, Dengvaxia and Qdenga, but they aren't available to everyone.
Dengvaxia is only approved in the U.S. for kids ages 6 to 16 who have already had dengue. It requires three injections to be given over the course of a year. You also must have a blood test to show that you already had dengue, which can increase the cost.
The second vaccine, Qdenga, requires two doses, three months apart. Right now, the WHO is recommending that Qdenga be used in people ages 6 and older in places where there's a lot of dengue circulating. It won’t be available in the U.S. or Puerto Rico for the foreseeable future, because the company that developed the vaccine, Takeda, withdrew its application to the FDA.
There is another vaccine—a single-dose vaccine—that was developed by the NIH and that we tested at Hopkins. The NIH licensed that vaccine technology to many different manufacturers, including the Instituto Butantan in Brazil. They just published their efficacy results, which look very good. But again, it's not available in the U.S.
Where is dengue most prevalent?
All tropical and subtropical regions of the world. With global warming and world travel we're seeing it spread all over the world. We're now seeing cases in areas where we hadn't seen them before, such as Southern France.
Are you anticipating any dengue outbreaks in the continental U.S.? If so, where would that happen?
I would expect to see it in Florida and Texas, predominantly. We regularly see cases along the Texas-Mexico border. But an outbreak is possible in any of the tropical areas of the U.S. I don't think we'll see huge outbreaks in the continental U.S. the way we've seen in other parts of the world. But we'll certainly see locally acquired cases every year.
We don't see dengue spread quite so much in the continental U.S. because we have so much air conditioning—people don't have windows open. If they do, they generally have screens on those windows which prevent the mosquitoes from entering the house.
What are some misconceptions about dengue?
One big misconception is that it can spread from person to person. It can't—you need a mosquito. If you're with someone who has dengue, that person can’t give it to you directly.
Number two is, if you've had dengue, you won't get it again. You can get it again, and it can be worse depending on how many infections you've had.
Three is that you can only get it in underdeveloped countries. You can get it anywhere the mosquito lives and dengue is circulating. You should be aware—especially if you're traveling—that it's present in all the tropical and subtropical regions of the world.
The other thing to note is that it can take about two weeks to become symptomatic.
What are the treatments for dengue?
Generally, it's rest and fluids. You can also take Tylenol, but you want to be careful about how much you take, because dengue can sometimes have an effect on the liver, as can acetaminophen. We recommend that you do not take non-steroidal anti-inflammatories like ibuprofen or aspirin as they can affect platelet count.
How do I avoid contracting dengue?
It's hard to think about mosquito protection every time you go outside, but you should be protecting yourself using mosquito repellents containing DEET and wearing long sleeves and pants.
Morgan Coulson is an editorial associate in the Office of External Affairs at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Could We Genetically Modify Mosquitos to Die From the Diseases They Carry? (podcast)
The Chemistry of Mosquito Attraction
How Human Challenge Trials Accelerate Vaccine Development
Related Content

New Grant Enables Johns Hopkins Researchers to Implement Community Health Worker-Led Health Interventions for Noncommunicable Diseases in Nepal

New Johns Hopkins Institute Aims to Safeguard Human Health on a Rapidly Changing Planet

Health Policy Analysis Webinar Series Brings Together Global Health Policy Scholars

Five Reasons Why the Global Health Community Should Help Save Forests

The U.S. Syphilis Spike Has Been Brewing for Decades

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Thailand. Rabies - CDC Yellow Book. Typhoid: Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas. Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book. Dosing ...
Customer Reviews. Passport Health - Travel Vaccines for Thailand. Overall rating: 5 stars - 15 reviews. ★★★★★. "Great experience". "The nurse was very professional and knowledgeable about what we needed to safely travel to Thailand.
International travellers, including returning Thais and foreign residents, who are above 18 years of age should get fully vaccinated for Covid-19 with a vaccine approved by Thailand's Ministry of Public Health (MoPH) or the World Health Organisation (WHO) no less than 14 days before their travel date. Travellers 12-17 years of age, travelling ...
The COVID-19 pandemic wreaked havoc on the world. International travel ground to a halt and countries were forced to implement strict processes and entry requirements to halt the spread of the virus. Thailand introduced quarantine measures and Thailand Pass. Thailand Pass required visitors to register details like vaccination status, flight, and hotel bookings, and confirmation
• Get a single-dose vaccine no less than 14 days before the travel date to Thailand • In case of mix-and-match vaccines, get a second dose of a different vaccine within the recommended interval of the first vaccine no less than 14 days before the travel date to Thailand. Guidelines to be considered as fully vaccinated when having been ...
The requirement that all international travellers show proof of full Covid-19 vaccination before boarding flights to Thailand will take effect from Sunday, the Civil Aviation Authority of Thailand ...
After months of strict travel restrictions due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Thailand is gearing up for a return to normalcy by easing some travel restrictions and quarantine requirements and allowing normal tourists to enter the country. Vaccinated travelers are allowed to travel to Thailand without quarantine under the Phuket Sandbox and the Samui Plus Sandbox programs.
For more information: https://www.tatnews.org. Thailand currently approves 13 COVID-19 vaccines, and everyone 18 years of age and older should get fully vaccinated for COVID-19 before travelling to the Kingdom, while rules differ for those under 18 years. Here's an update to our guide to COVID-19 vaccines for international travellers to Thailand.
Last updated: May 17, 2023. The CDC's Order requiring proof of vaccination for non-U.S. citizen nonimmigrants to travel to the United States is no longer in effect. For more information see Requirement for Proof of COVID-19 Vaccination for Air Passengers. Check the CDC website for additional information and Frequently Asked Questions.
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
The basics. Thailand has recorded more than 32,000 deaths and over 4.67 million cases of Covid-19 as of September 26, 2022. Ad Feedback. On average, around 700 Covid-19 cases are reported per day ...
Advice. Travellers'. Diarrhea Kits. Available. Thailand is a popular destination with its tropical climate, food, culture and beaches. Thai is the official language of Thailand. But, other smaller languages spoken in rural areas. The primary religion of Thailand is Buddhism and is prevalent in many aspects of culture throughout Thailand.
FCDO travel advice for Thailand. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences. ... Vaccination requirements (other than COVID-19)
Vaccinations and health risks. At least 8 weeks before your trip check: Health risks in Thailand include: See the 'Other risks' section of the TravelHealthPro Thailand guide for more on health ...
Typhoid is also present in Thailand and can be passed on through contaminated food or water. It is recommended to vaccinate against Typhoid in particular if you are travelling to rural areas, visiting friends or relatives in Thailand or if you are an adventurous eater. Both Hepatitis A and Typhoid vaccinations can be administered in one shot ...
Anyone requiring injections for Thailand should visit their GP six to eight weeks before they leave. They should also check for any medical updates on the official government website. Many travel vaccinations are free on the NHS, including those for tetanus, diphtheria, polio, typhoid, hepatitis A and cholera so be sure to take advantage of ...
Reconsider your need to travel to the 3 most southern provinces of the Thailand-Malaysia border: Yala, Pattani and Narathiwat. Low-level insurgent activity continues to occur in these areas. Sexual assault, assault, robbery and drink spiking can happen to tourists. Never leave your drink unattended.
Advice. Travellers'. Diarrhea Kits. Available. Thailand is a popular destination with its tropical climate, food, culture and seasides. Thai is the official language of Thailand. But, other smaller languages spoken in rural areas. The primary religion of Thailand is Buddhism and is prevalent in many aspects of culture throughout Thailand.
Advice for All Destinations COVID-19. Read the information on the COVID-19: Health Considerations for Travel page for advice on travelling during the COVID-19 pandemic.. Vaccinations and malaria risk. Review both the Vaccination and Malaria sections on this page to find out if you may need vaccines and/or a malaria risk assessment before you travel to this country.
Exploring Khao Yai 2024 - A Hidden Gem of Thailand The post 10 Visa and Passport Tips for Hassle-Free Travel 2024 republished on Passing Thru with permission from The Green Voyage . Featured ...
Thailand recorded 9.4 million foreign tourists in the first three months of this year, who contributed an estimated 454.6 billion baht ($12.4 billion) to the economy in spending, the tourism ...
About 75% of people who are infected with dengue have what we call subclinical symptoms, meaning they may have a fever for a day or so and feel achy, but not sick enough to seek medical care. But about 25% of people have much more severe symptoms. They have a high fever, no appetite, severe achiness, and a very low platelet count, which can ...