

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

What’s Up: April 2024 Skywatching Tips from NASA

NASA VIPER Robotic Moon Rover Team Raises Its Mighty Mast

NASA’s Curiosity Searches for New Clues About Mars’ Ancient Water
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

Veronica T. Pinnick Put NASA’s PACE Mission through Its Paces

That Starry Night Sky? It’s Full of Eclipses

Scientists Use NASA Data to Predict Solar Corona Before Eclipse
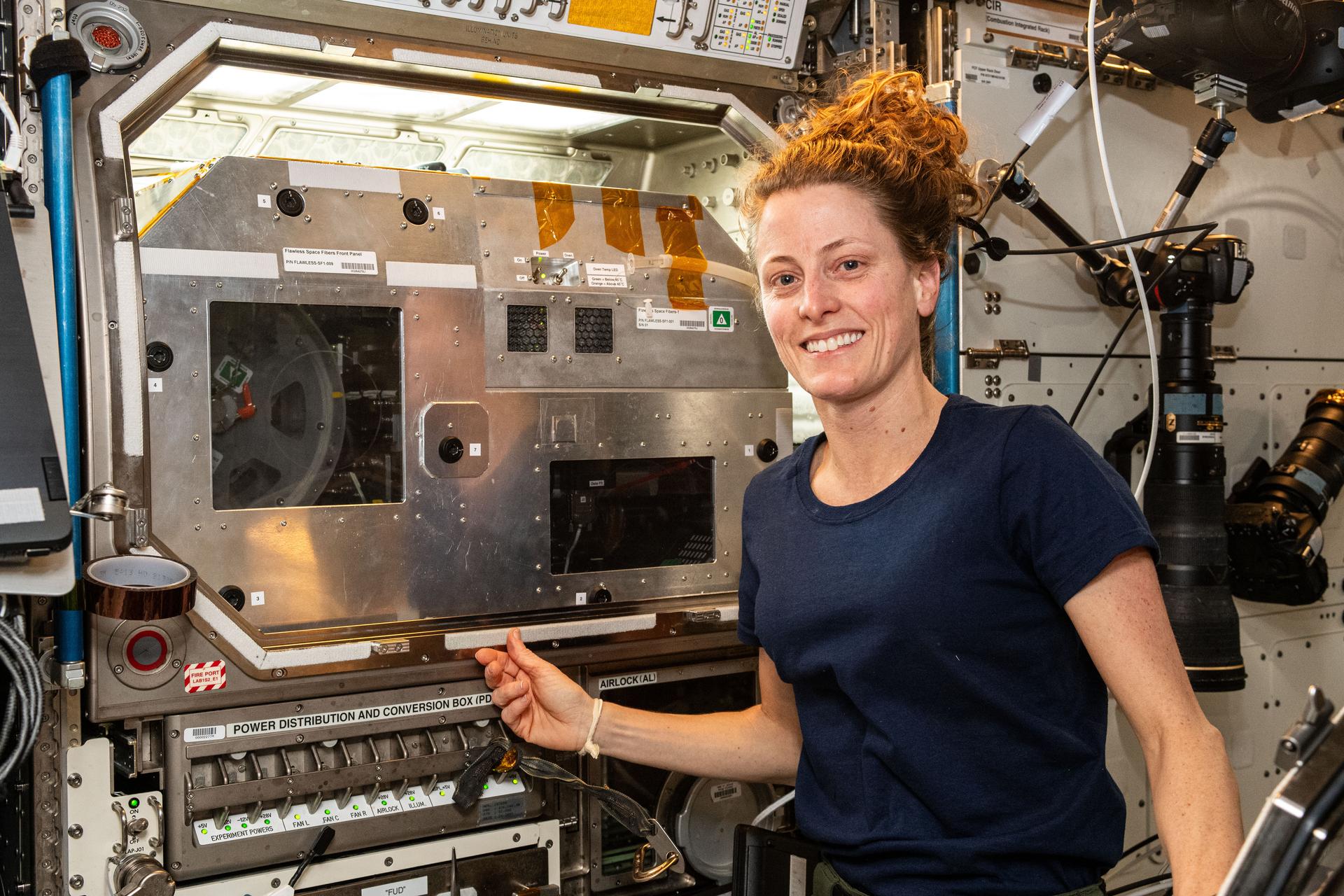

NASA Astronaut Loral O’Hara, Expedition 70 Science Highlights

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas
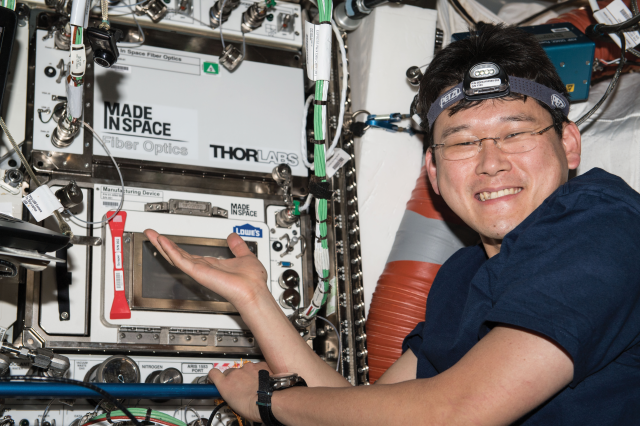

Optical Fiber Production
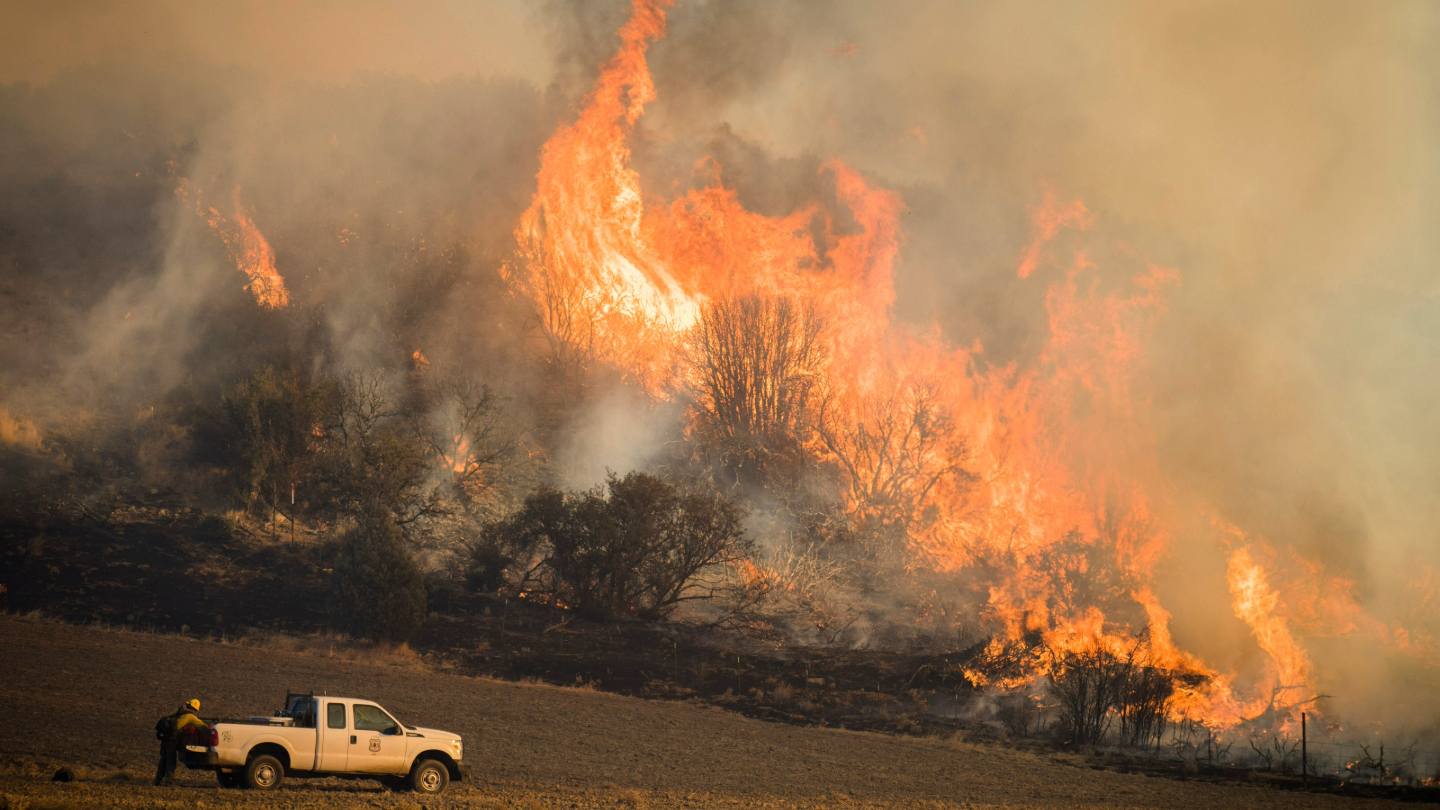

NASA Data Shows How Drought Changes Wildfire Recovery in the West

Antarctic Sea Ice Near Historic Lows; Arctic Ice Continues Decline

NASA Partnerships Bring 2024 Total Solar Eclipse to Everyone

Universe Stories

Hubble Finds a Field of Stars


NASA Awards Astrophysics Postdoctoral Fellowships for 2024

ARMD Solicitations

F-15D Support Aircraft
University Teams Selected as Finalists to Envision New Aviation Responses to Natural Disasters

David Woerner
Tech Today: Cutting the Knee Surgery Cord
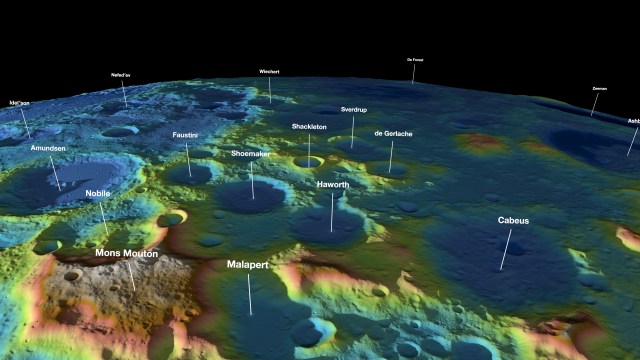
NASA, Industry Improve Lidars for Exploration, Science

NASA, Salisbury U. Enact Agreement for Workforce Development

NASA, Partners Select Universities for CubeSat Summer Program

NASA Engineer Chris Lupo Receives 2024 Federal Engineer Award

NASA’s OSIRIS-REx Earns Neil Armstrong Space Flight Achievement Award
Meet the Two Women Leading Space Station Science

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos

Resultados científicos revolucionarios en la estación espacial de 2023
The voyage to interstellar space.
Susannah Darling

Katy Mersmann
The magnetometer, the cosmic ray subsystem, the plasma instrument.
By all means, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 shouldn’t even be here. Now in interstellar space, they are pushing the limits of spacecraft and exploration, journeying through the cosmic neighborhood, giving us our first direct look into the space beyond our star.
But when they launched in 1977, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 had a different mission: to explore the outer solar system and gather observations directly at the source, from outer planets we had only seen with remote studies. But now, four decades after launch, they’ve journeyed farther than any other spacecraft from Earth; into the cold, quiet world of interstellar space.
Originally designed to measure the properties of the giant planets, the instruments on both spacecraft have spent the past few decades painting a picture of the propagation of solar events from our Sun. And the Voyagers’ new mission focuses not only on effects on space from within our heliosphere — the giant bubble around the Sun filled up by the constant outflow of solar particles called the solar wind — but from outside of it. Though they once helped us look closer at the planets and their relationship to the Sun, they now give us clues about the nature of interstellar space as the spacecraft continue their journey.
The environment they explore is colder, subtler and more tenuous than ever before, and yet the Voyagers continue on, exploring and measuring the interstellar medium, a smorgasbord of gas, plasma and particles from stars and gas regions not originating from our system. Three of the spacecraft’s 10 instruments are the major players that study how space inside the heliosphere differs from interstellar space. Looking at this data together allows scientist to piece together our best-yet picture of the edge of the heliosphere and the interstellar medium. Here are the stories they tell.
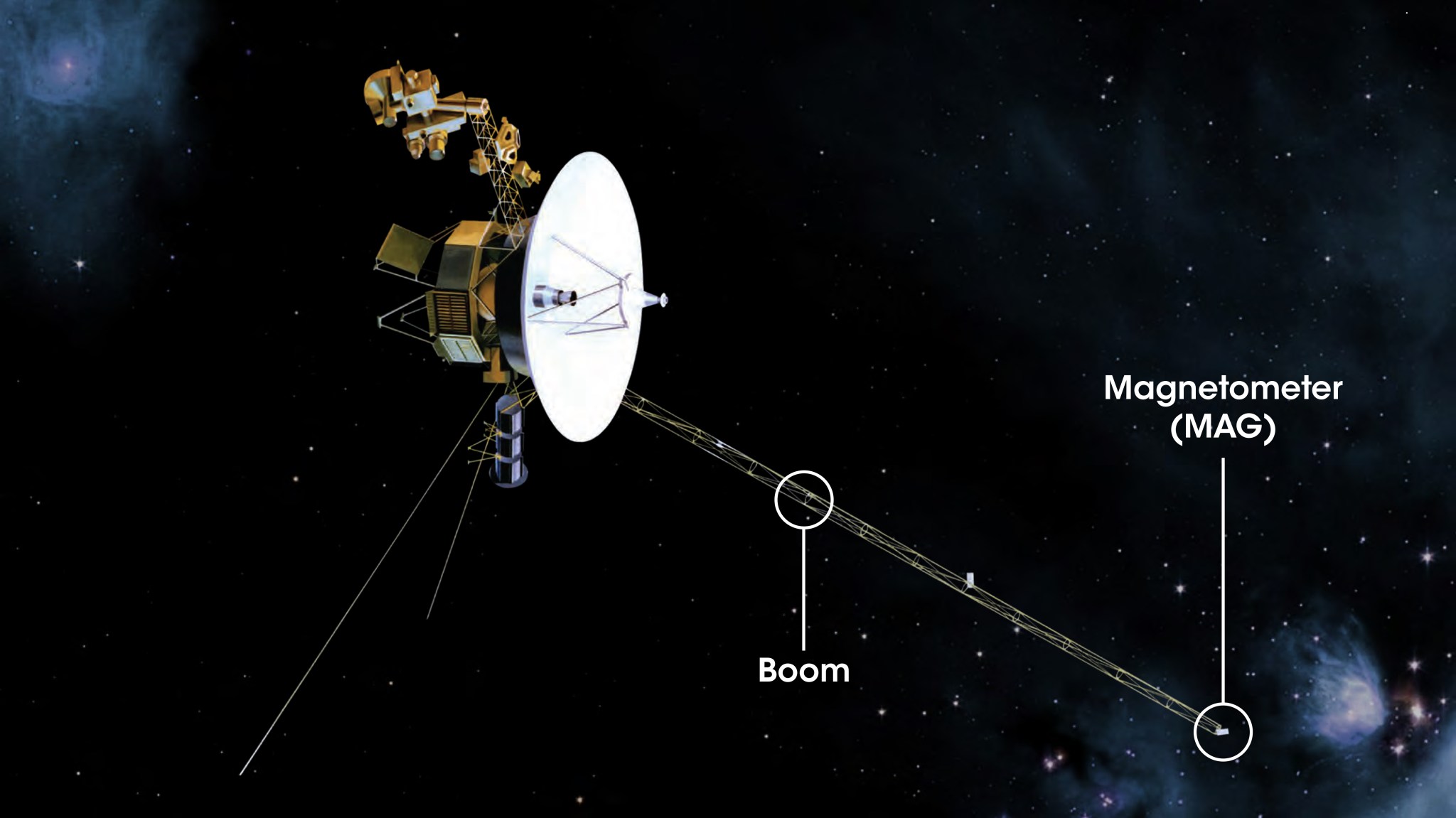

On the Sun Spot , we have been exploring the various instruments on Voyager 2 one at a time, and analyzing how scientists read the individual sets of data sent to Earth from the far-reaching spacecraft. But one instrument we have not yet talked about is Voyager 2’s Magnetometer, or MAG for short.
During the Voyagers’ first planetary mission, the MAG was designed to investigate the magnetospheres of planets and their moons, determining the physical mechanics and processes of the interactions of those magnetic fields and the solar wind. After that mission ended, the Voyager spacecraft studied the magnetic field of the heliosphere and beyond, observing the magnetic reach of the Sun and the changes that occur within that reach during solar activity.
Getting the magnetic data as we travel further into space requires an interesting trick. Voyager spins itself around, in a calibration maneuver that allows Voyager to differentiate between the spacecraft’s own magnetic field — that goes along for the ride as it spins — and the magnetic fields of the space it’s traveling through.
The initial peek into the magnetic field beyond the Sun’s influence happened when Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause in 2012. Scientists saw that within the heliosphere, the strength of the magnetic field was quite variable, changing and jumping as Voyager 1 moved through the heliosphere. These changes are due to solar activity. But once Voyager 1 crossed into interstellar space, that variability was silenced. Although the strength of the field was similar to what it was inside the heliosphere, it no longer had the variability associated with the Sun’s outbursts.
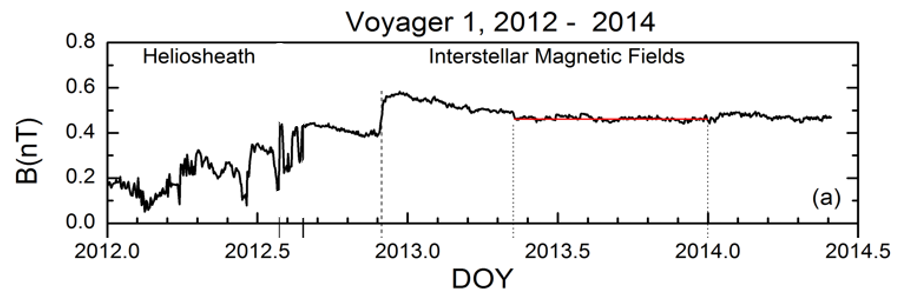
This graph shows the magnitude, or the strength, of the magnetic field around the heliopause from January 2012 out to May 2014. Before encountering the heliopause, marked by the orange line, the magnetic strength fluctuates quite a bit. After a bumpy ride through the heliopause in 2012, the magnetic strength stops fluctuating and begins to stabilize in 2013, once the spacecraft is far enough out into the interstellar medium.
In November 2018, Voyager 2 also crossed the heliopause and similarly experienced quite the bumpy ride out of the heliopause. Scientists are excited to see how its journey differs from its twin spacecraft.
Scientists are still working through the MAG data from Voyager 2, and are excited to see how Voyager 2’s journey differed from Voyager 1.
Much like the MAG, the Cosmic Ray Subsystem — called CRS — was originally designed to measure planetary systems. The CRS focused on the compositions of energetic particles in the magnetospheres of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Scientists used it to study the charged particles within the solar system and their distribution between the planets. Since it passed the planets, however, the CRS has been studying the heliosphere’s charged particles and — now — the particles in the interstellar medium.
The CRS measures the count rate, or how many particles detected per second. It does this by using two telescopes: the High Energy Telescope, which measures high energy particles (70MeV) identifiable as interstellar particles, and the Low Energy Telescope, which measures low-energy particles (5MeV) that originate from our Sun. You can think of these particles like a bowling ball hitting a bowling pin versus a bullet hitting the same pin — both will make a measurable impact on the detector, but they’re moving at vastly different speeds. By measuring the amounts of the two kinds of particles, Voyager can provide a sense of the space environment it’s traveling through.
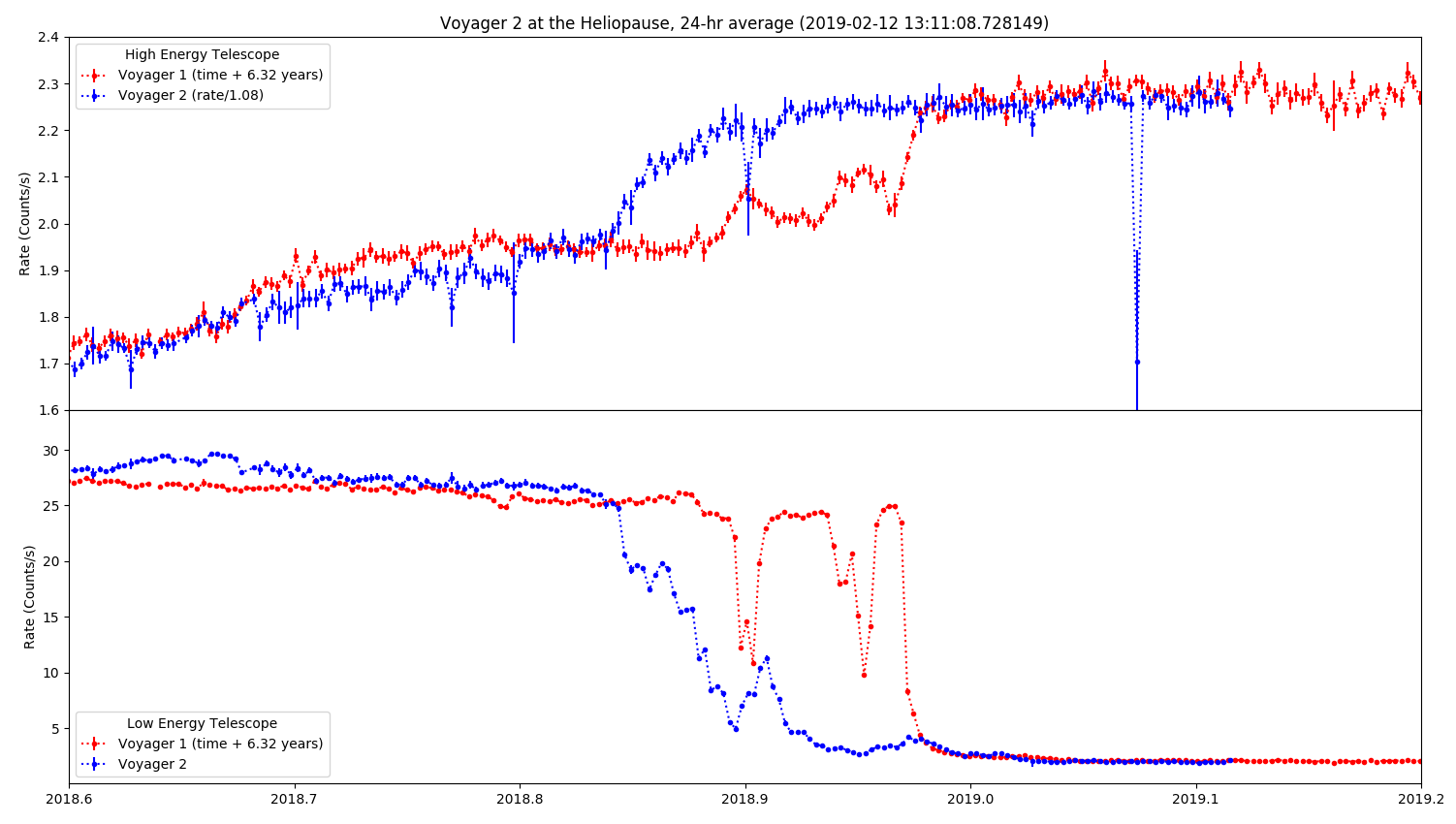
These graphs show the count rate — how many particles per second are interacting with the CRS on average each day — of the galactic ray particles measured by the High Energy Telescope (top graph) and the heliospheric particles measured by the Low Energy Telescope (bottom graph). The line in red shows the data from Voyager 1, time shifted forward 6.32 years from 2012 to match up with the data from Voyager around November 2018, shown in blue.
CRS data from Voyager 2 on Nov. 5, 2018, showed the interstellar particle count rate of the High Energy Telescope increasing to count rates similar to what Voyager 1 saw then leveling out. Similarly, the Low Energy Telescope shows a severe decrease in heliospheric originating particles. This was a key indication that Voyager 2 had moved into interstellar space. Scientists can keep watching these counts to see if the composition of interstellar space particles changes along the journey.
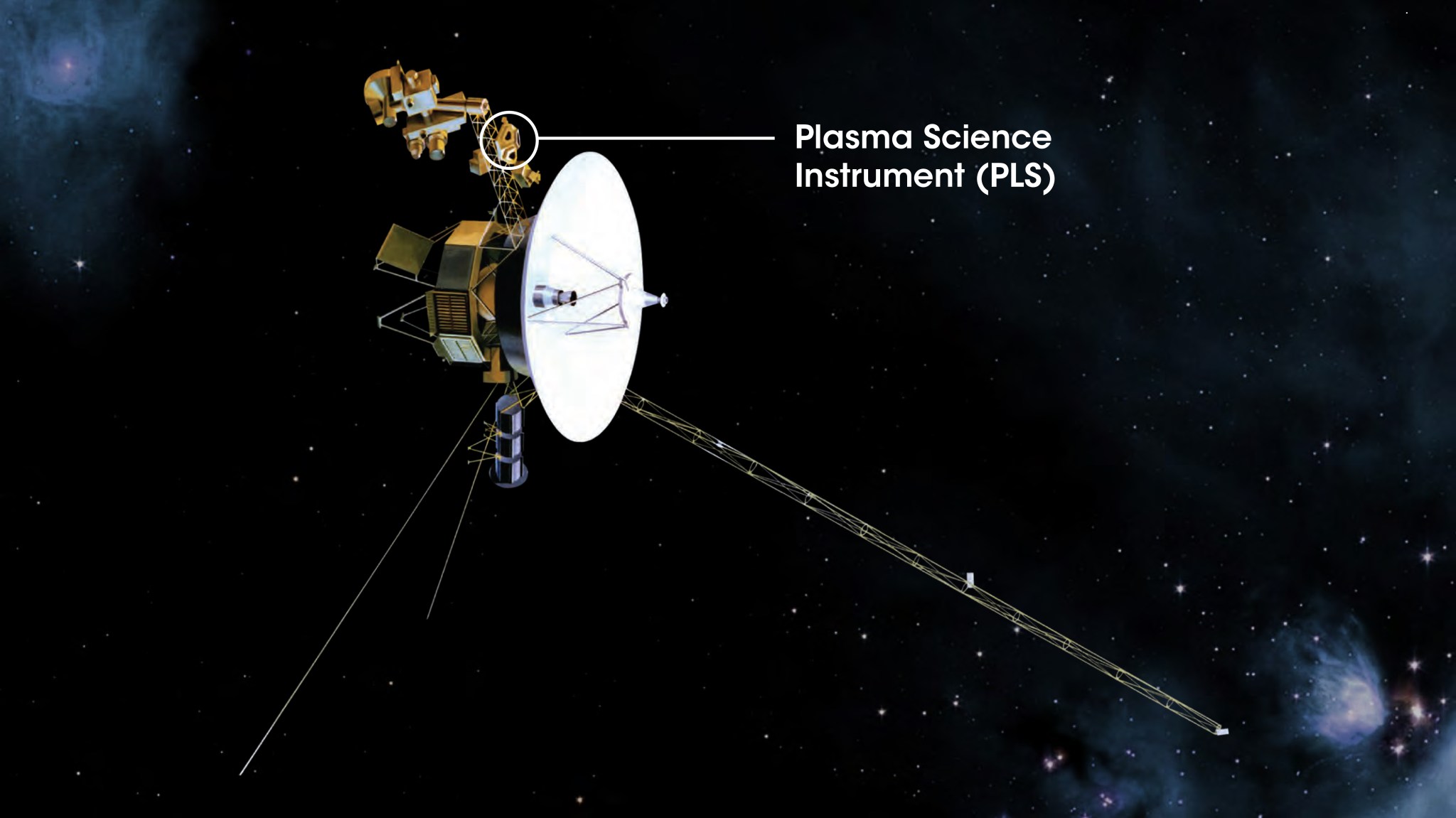

The Plasma Science instrument, or PLS, was made to measure plasma and ionized particles around the outer planets and to measure the solar wind’s influence on those planets. The PLS is made up of four Faraday cups, an instrument that measures the plasma as it passes through the cups and calculates the plasma’s speed, direction and density.
The plasma instrument on Voyager 1 was damaged during a fly-by of Saturn and had to be shut off long before Voyager 1 exited the heliosphere, making it unable to measure the interstellar medium’s plasma properties. With Voyager 2’s crossing, scientists will get the first-ever plasma measurements of the interstellar medium.
Scientists predicted that interstellar plasma measured by Voyager 2 would be higher in density but lower in temperature and speed than plasma inside the heliosphere. And in November 2018, the instrument saw just that for the first time. This suggests that the plasma in this region is getting colder and slower, and, like cars slowing down on a freeway, is beginning to pile up around the heliopause and into the interstellar medium.
And now, thanks to Voyager 2’s PLS, we have a never-before-seen perspective on our heliosphere: The plasma velocity from Earth to the heliopause.
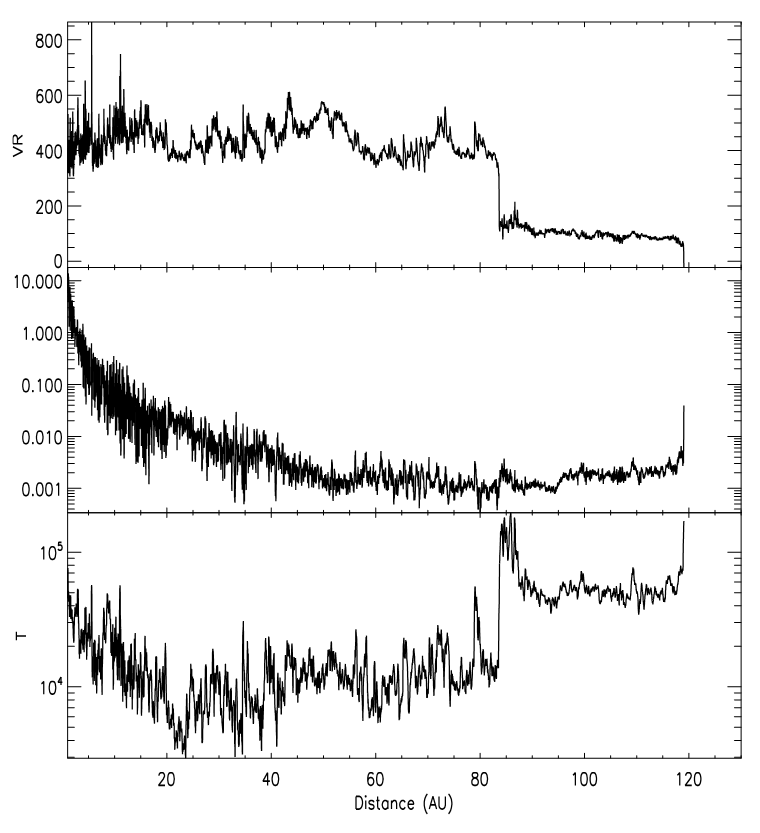
These three graphs tell an amazing story, summarizing a journey of 42 years in one plot. The top section of this graph shows the plasma velocity, how fast the plasma across the heliosphere is moving, against the distance out from Earth. The distance is in astronomical units; one astronomical unit is the average distance between the Sun and Earth, about 93 million miles. For context, Saturn is 10 AU from Earth, while Pluto is about 40 AU away.
The heliopause crossing happened at 120 AU, when the velocity of plasma coming out from the Sun drops to zero (seen on the top graph), and the outward flow of the plasma is diverted — seen in the increase in the two bottom graphs, which show the upwards and downward speeds (the normal velocity, middle graph) and the sideways speed of the solar wind (the tangential velocity, bottom graph) of the solar wind plasma, respectively. This means as the solar wind begins to interact with the interstellar medium, it is pushed out and away, like a wave hitting the side of a cliff.
Looking at each instrument in isolation, however, does not tell the full story of what interstellar space at the heliopause looks like. Together, these instruments tell a story of the transition from the turbulent, active space within our Sun’s influence to the relatively calm waters on the edge of interstellar space.
The MAG shows that the magnetic field strength decreases sharply in the interstellar medium. The CRS data shows an increase in interstellar cosmic rays, and a decrease in heliospheric particles. And finally, the PLS shows that there’s no longer any detectable solar wind.
Now that the Voyagers are outside of the heliosphere, their new perspective will provide new information about the formation and state of our Sun and how it interacts with interstellar space, along with insight into how other stars interact with the interstellar medium.
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 are providing our first look at the space we would have to pass through if humanity ever were to travel beyond our home star — a glimpse of our neighborhood in space.
Related links:
- Video: “NASA Science Live: Going Interstellar”
- Explore Voyager 2 data on “The Sun Spot” blog
By Susannah Darling NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center , Greenbelt, Md.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Voyage to Interstellar Space. By all means, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 shouldn’t even be here. Now in interstellar space, they are pushing the limits of spacecraft and exploration, journeying through the cosmic neighborhood, giving us our first direct look into the space beyond our star. But when they launched in 1977, Voyager 1 and Voyager ...
Veel vertaalde voorbeeldzinnen bevatten "interstellar travel" – Engels-Nederlands woordenboek en zoekmachine voor een miljard Engelse vertalingen.
Deep space exploration (or deep-space exploration) is the branch of astronomy, astronautics and space technology that is involved with exploring the distant regions of outer space. [1] However, there is little consensus on the meaning of "distant" regions. In some contexts, it is used to refer to interstellar space.